热门标签
热门文章
- 1长度最小的子数组——滑动窗口法_长度最小的子数组滑动窗口
- 2WinSCP 以预设密码进行验证 拒绝访问_以预置密码进行验证 拒绝访问
- 3【学习心得】Python中CSV文件存储_csv保存到csv
- 4【Verilog设计—Verilog基础语法】学好就看它了_verilog銝要and
- 5动态规划(DP)之入门学习-数字三角形_1. 每一步可沿左斜线向下或右斜线向下走; 2. 1<=三角形行数<=100 3.…
- 6基于Spring Boot的体质测试数据分析及可视化系统设计与实现
- 7R包的安装以及安装失败的解决_r包arrow安装失败
- 8python获取对象信息和实例属性和类属性_python获取实例所有属性
- 9Python的安装_python 阿里源
- 10python有趣小程序-Python全栈开发-有趣的小程序
当前位置: article > 正文
MS COCO数据集介绍以及pycocotools使用
作者:知新_RL | 2024-05-07 19:47:25
赞
踩
ms coco
MS COCO数据集介绍以及pycocotools使用
1、MS COCO数据集简介

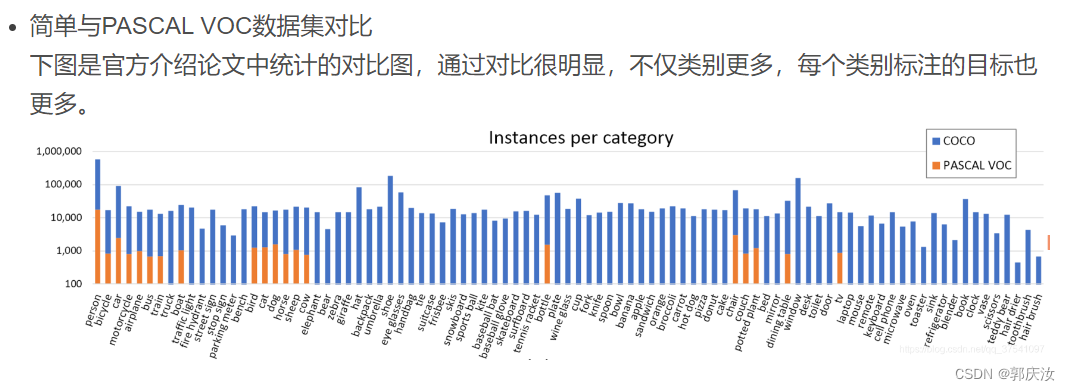
2、MS COCO数据集目录结构

├── coco2017: 数据集根目录
├── train2017: 所有训练图像文件夹(118287张)
├── val2017: 所有验证图像文件夹(5000张)
└── annotations: 对应标注文件夹
├── instances_train2017.json: 对应目标检测、分割任务的训练集标注文件
├── instances_val2017.json: 对应目标检测、分割任务的验证集标注文件
├── captions_train2017.json: 对应图像描述的训练集标注文件
├── captions_val2017.json: 对应图像描述的验证集标注文件
├── person_keypoints_train2017.json: 对应人体关键点检测的训练集标注文件
└── person_keypoints_val2017.json: 对应人体关键点检测的验证集标注文件夹
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
3、 MS COCO标注文件格式
3.1 使用Python的json库查看

import json
json_path = "/data/coco2017/annotations/instances_val2017.json"
json_labels = json.load(open(json_path, "r"))
print(json_labels["info"])
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
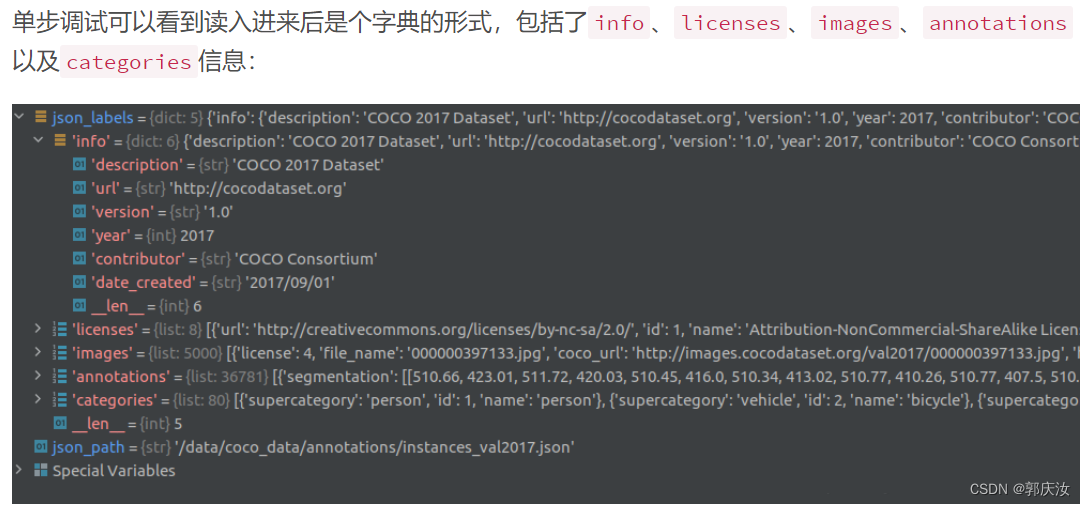
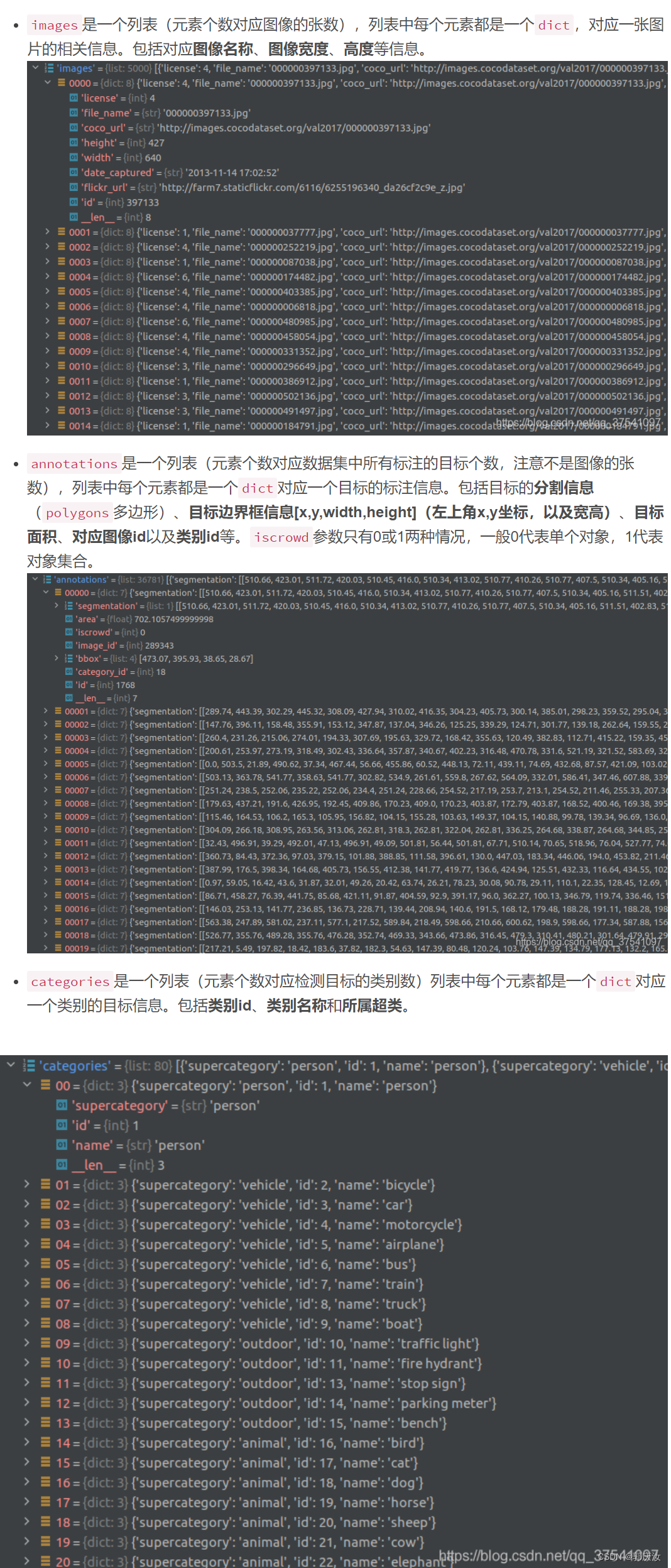
3.2 使用官方cocoAPI查看
安装:
# ubuntu
pip install pycocotools
# Windows
pip install pycocotools-windows
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
读取每张图片的bbox信息
下面是使用pycocotools读取图像以及对应bbox信息的简单示例:
import os
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
json_path = "/data/coco2017/annotations/instances_val2017.json"
img_path = "/data/coco2017/val2017"
# load coco data
coco = COCO(annotation_file=json_path)
# get all image index info
ids = list(sorted(coco.imgs.keys()))
print("number of images: {}".format(len(ids)))
# get all coco class labels
coco_classes = dict([(v["id"], v["name"]) for k, v in coco.cats.items()])
# 遍历前三张图像
for img_id in ids[:3]:
# 获取对应图像id的所有annotations idx信息
ann_ids = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img_id)
# 根据annotations idx信息获取所有标注信息
targets = coco.loadAnns(ann_ids)
# get image file name
path = coco.loadImgs(img_id)[0]['file_name']
# read image
img = Image.open(os.path.join(img_path, path)).convert('RGB')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# draw box to image
for target in targets:
x, y, w, h = target["bbox"]
x1, y1, x2, y2 = x, y, int(x + w), int(y + h)
draw.rectangle((x1, y1, x2, y2))
draw.text((x1, y1), coco_classes[target["category_id"]])
# show image
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
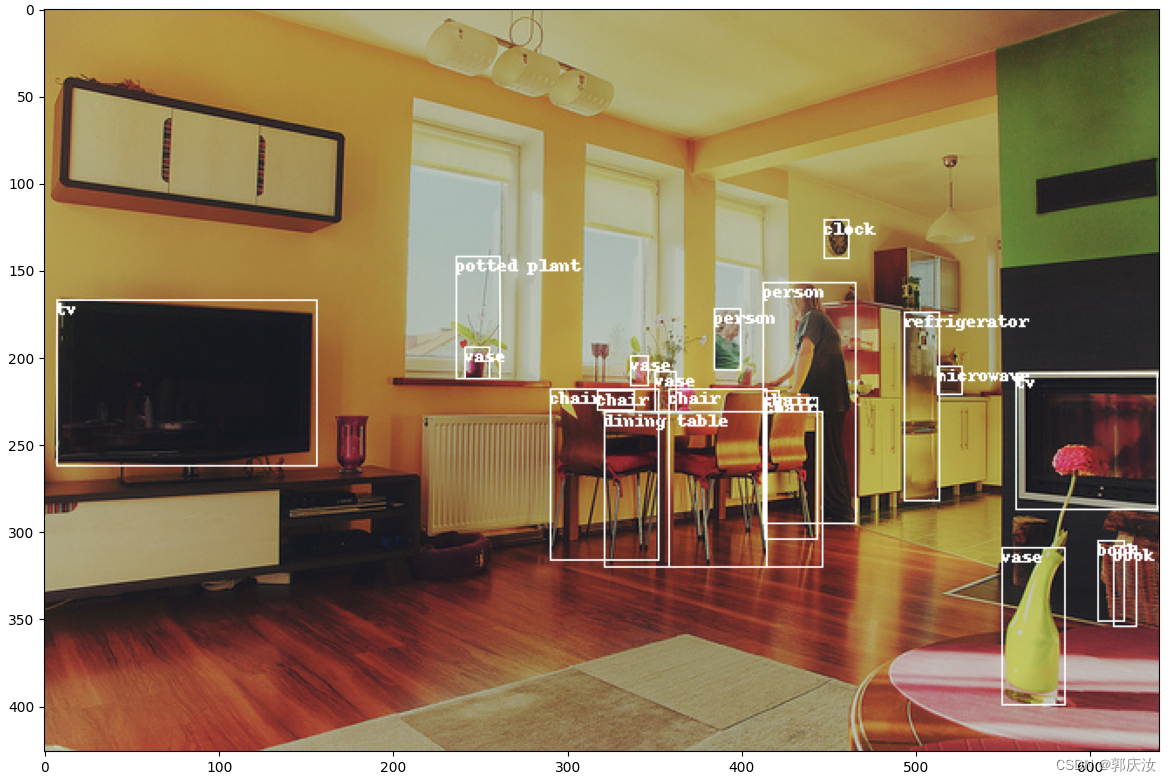
通过pycocotools读取的图像以及对应的targets信息,配合matplotlib库绘制标注图像如下:
读取每张图像的segmentation信息
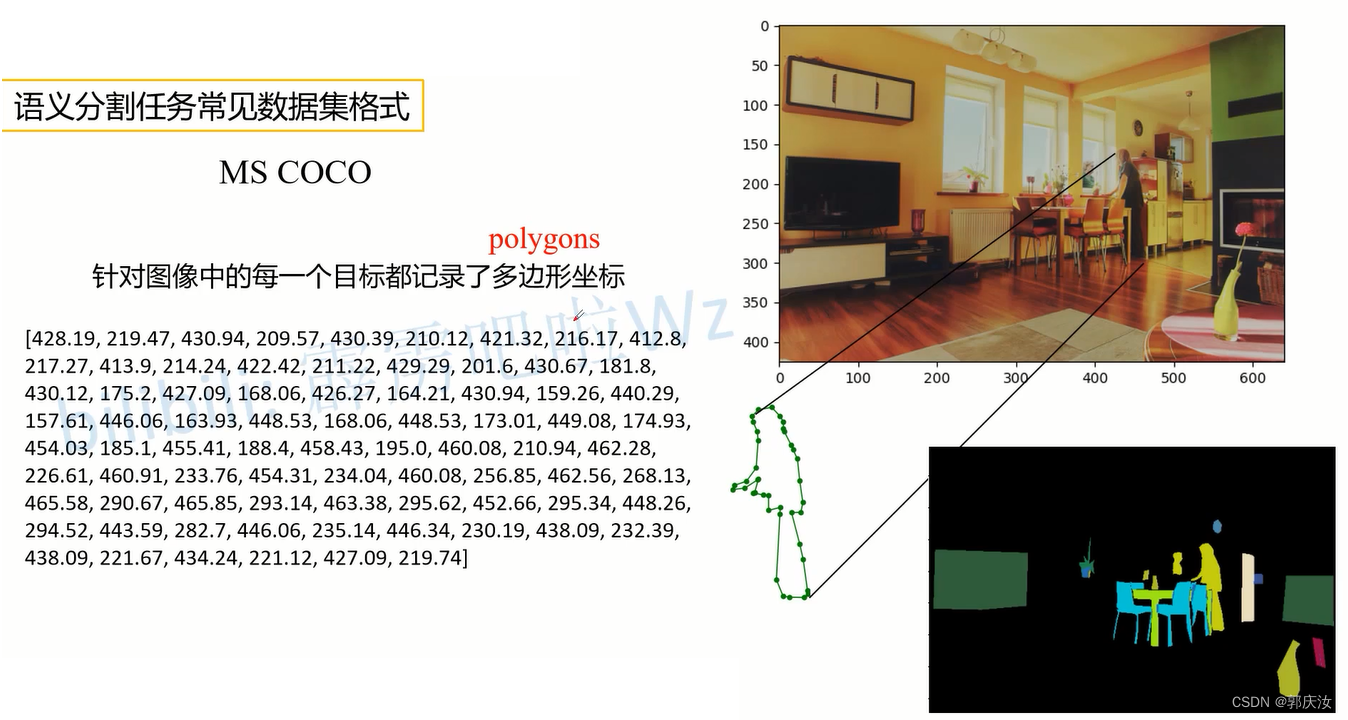
下面是使用pycocotools读取图像segmentation信息的简单示例:
import os
import random
import numpy as np
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from pycocotools import mask as coco_mask
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
random.seed(0)
json_path = "/data/coco2017/annotations/instances_val2017.json"
img_path = "/data/coco2017/val2017"
# random pallette
pallette = [0, 0, 0] + [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(255*3)]
# load coco data
coco = COCO(annotation_file=json_path)
# get all image index info
ids = list(sorted(coco.imgs.keys()))
print("number of images: {}".format(len(ids)))
# get all coco class labels
coco_classes = dict([(v["id"], v["name"]) for k, v in coco.cats.items()])
# 遍历前三张图像
for img_id in ids[:3]:
# 获取对应图像id的所有annotations idx信息
ann_ids = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img_id)
# 根据annotations idx信息获取所有标注信息
targets = coco.loadAnns(ann_ids)
# get image file name
path = coco.loadImgs(img_id)[0]['file_name']
# read image
img = Image.open(os.path.join(img_path, path)).convert('RGB')
img_w, img_h = img.size
masks = []
cats = []
for target in targets:
cats.append(target["category_id"]) # get object class id
polygons = target["segmentation"] # get object polygons
rles = coco_mask.frPyObjects(polygons, img_h, img_w)
mask = coco_mask.decode(rles)
if len(mask.shape) < 3:
mask = mask[..., None]
mask = mask.any(axis=2)
masks.append(mask)
cats = np.array(cats, dtype=np.int32)
if masks:
masks = np.stack(masks, axis=0)
else:
masks = np.zeros((0, height, width), dtype=np.uint8)
# merge all instance masks into a single segmentation map
# with its corresponding categories
target = (masks * cats[:, None, None]).max(axis=0)
# discard overlapping instances
target[masks.sum(0) > 1] = 255
target = Image.fromarray(target.astype(np.uint8))
# 使用putpalette()函数,而且我们可以自定义各个类别区域的颜色。
# putpalette给对象加上调色板,相当于上色:R,G,B
# 三个数一组,对应于RGB通道,可以自己定义标签颜色
target.putpalette(pallette)
plt.imshow(target)
plt.show()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
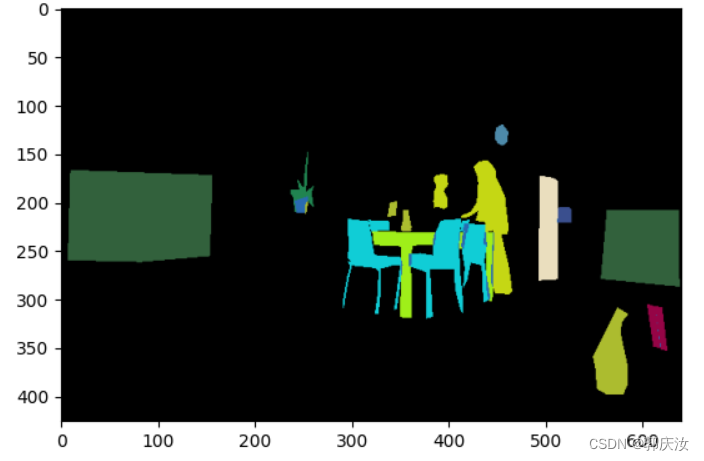
通过pycocotools读取的图像segmentation信息,配合matplotlib库绘制标注图像如下:
读取人体关键点信息
在MS COCO任务中,对每个人体都标注了17的关键点,这17个关键点的部位分别如下:
["nose","left_eye","right_eye","left_ear","right_ear","left_shoulder","right_shoulder","left_elbow","right_elbow","left_wrist","right_wrist","left_hip","right_hip","left_knee","right_knee","left_ankle","right_ankle"]
- 1

[427, 170, 1, 429, 169, 2, 0, 0, 0, 434, 168, 2, 0, 0, 0, 441, 177, 2, 446, 177, 2, 437, 200, 2, 430, 206, 2, 430, 220, 2, 420, 215, 2, 445, 226, 2, 452, 223, 2, 447, 260, 2, 454, 257, 2, 455, 290, 2, 459, 286, 2]
- 1
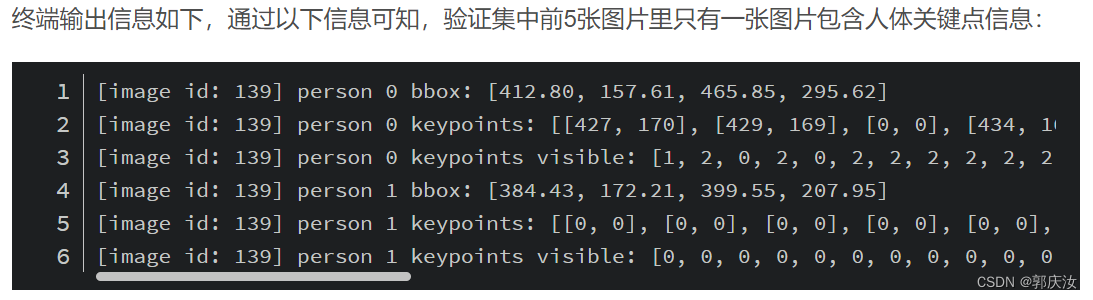
下面是使用pycocotools读取图像keypoints信息的简单示例:
import numpy as np
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
json_path = "/data/coco2017/annotations/person_keypoints_val2017.json"
coco = COCO(json_path)
img_ids = list(sorted(coco.imgs.keys()))
# 遍历前5张图片中的人体关键点信息(注意,并不是每张图片里都有人体信息)
for img_id in img_ids[:5]:
idx = 0
img_info = coco.loadImgs(img_id)[0]
ann_ids = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img_id)
anns = coco.loadAnns(ann_ids)
for ann in anns:
xmin, ymin, w, h = ann['bbox']
# 打印人体bbox信息
print(f"[image id: {img_id}] person {idx} bbox: [{xmin:.2f}, {ymin:.2f}, {xmin + w:.2f}, {ymin + h:.2f}]")
keypoints_info = np.array(ann["keypoints"]).reshape([-1, 3])
visible = keypoints_info[:, 2]
keypoints = keypoints_info[:, :2]
# 打印关键点信息以及可见度信息
print(f"[image id: {img_id}] person {idx} keypoints: {keypoints.tolist()}")
print(f"[image id: {img_id}] person {idx} keypoints visible: {visible.tolist()}")
idx += 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
4、目标检测验证任务mAP

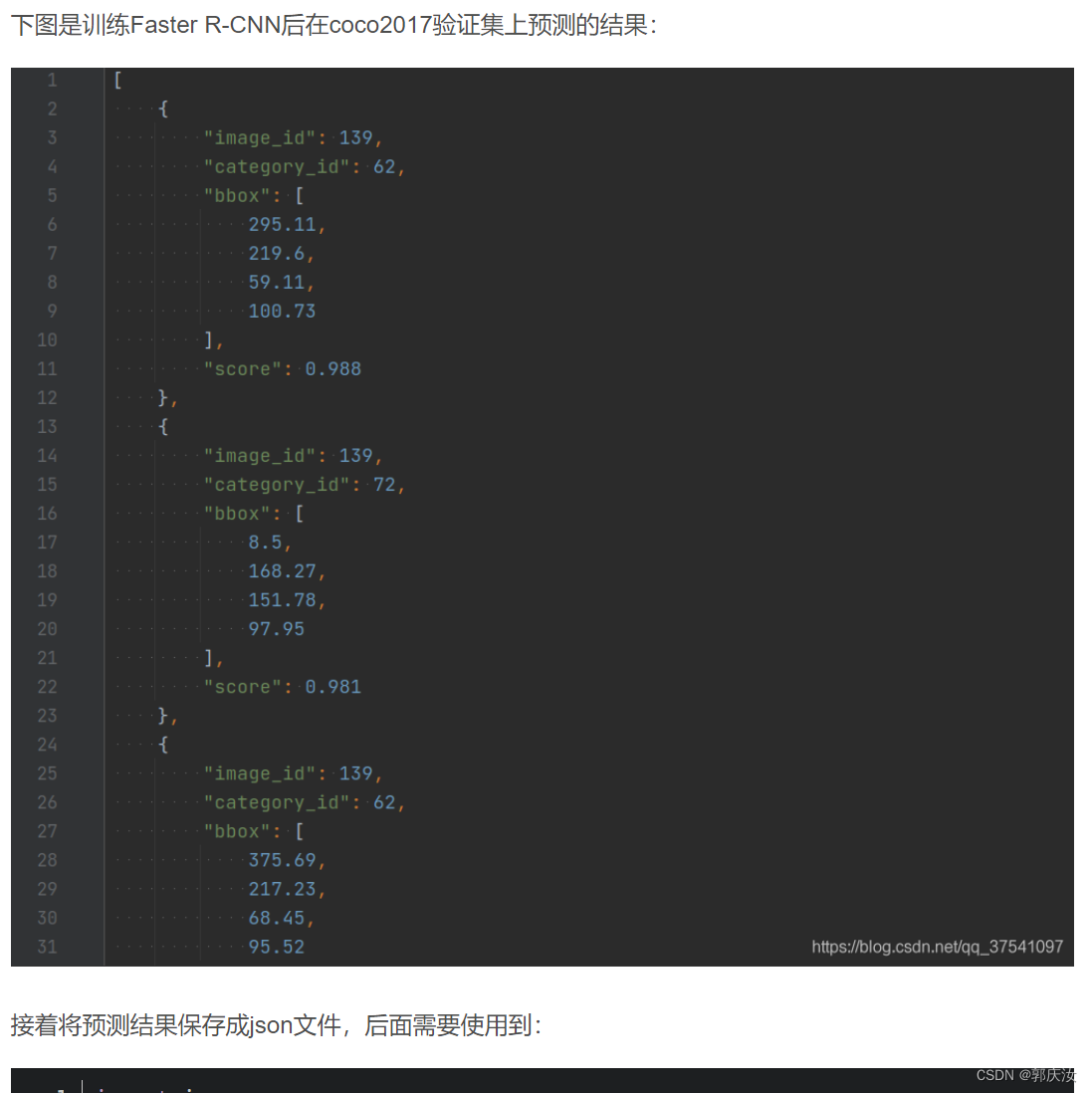
import json
results = [] # 所有预测的结果都保存在该list中
# write predict results into json file
json_str = json.dumps(results, indent=4)
with open('predict_results.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
数据准备:
COCO2017验证集json文件instances_val2017.json
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1ArWe8Igt_q0iJG6FCcH8mg 密码: sa0j
自己训练的Faster R-CNN(VGG16)在验证集上预测的结果predict_results.json(刚刚上面生成的)
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1h5RksfkPFTvH82N2qN95TA 密码: 8alm
示例代码:
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOeval
# accumulate predictions from all images
# 载入coco2017验证集标注文件
coco_true = COCO(annotation_file="/data/coco2017/annotations/instances_val2017.json")
# 载入网络在coco2017验证集上预测的结果
coco_pre = coco_true.loadRes('predict_results.json')
coco_evaluator = COCOeval(cocoGt=coco_true, cocoDt=coco_pre, iouType="bbox")
coco_evaluator.evaluate()
coco_evaluator.accumulate()
coco_evaluator.summarize()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
结果:
loading annotations into memory...
Done (t=0.43s)
creating index...
index created!
Loading and preparing results...
DONE (t=0.65s)
creating index...
index created!
Running per image evaluation...
Evaluate annotation type *bbox*
DONE (t=21.15s).
Accumulating evaluation results...
DONE (t=2.88s).
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.233
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.415
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.75 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.233
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.104
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.262
Average Precision (AP) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.323
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 1 ] = 0.216
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets= 10 ] = 0.319
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= all | maxDets=100 ] = 0.327
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= small | maxDets=100 ] = 0.145
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area=medium | maxDets=100 ] = 0.361
Average Recall (AR) @[ IoU=0.50:0.95 | area= large | maxDets=100 ] = 0.463
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/知新_RL/article/detail/550925
推荐阅读
相关标签


