热门标签
热门文章
- 1vscode中使用git_vscode中的git
- 2用 LLama-Factory 训练和微调 LLama3,打造你的专属 AI 模型!_llama factory微调
- 3python处理excel_python3选择excel多列
- 4[永恒之蓝]实战-漏洞复现_永恒之蓝漏洞复现实验
- 5Idea下载github代码失败,如何使用git直接下载代码到本地目录_idea下载代码
- 62023最新青龙面板对接新版傻妞SillyGirl及go-cqhttp+短信登录(ark)全套详细教程_青龙面板傻妞机器人
- 7最新opencv-c++安装及配置教程(VS2019 C++ & opencv4.8)_opencv c++安装
- 8网络安全数据集和开源工具_软件安全数据集
- 9高效获取网站数据,网站爬虫技巧大揭秘!电商平台爬虫API列表!
- 10UE5 使用Postman测试WebsocketServer_ue5 websocket serve
当前位置: article > 正文
Java和MySQL的连接和操作(JDBC)_java连接mysql数据库
作者:秋刀鱼在做梦 | 2024-07-19 17:41:37
赞
踩
java连接mysql数据库
一、数据库的连接
1. 引入JDBC驱动程序
1.1 如何获取驱动程序
驱动程序由数据库提供商提供下载。
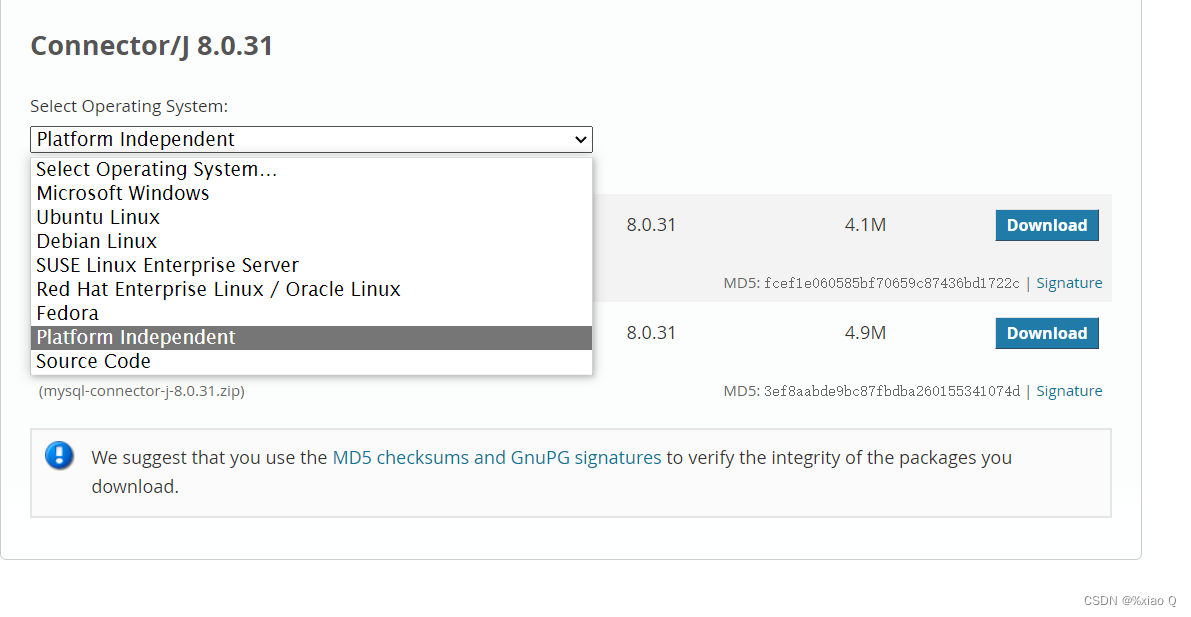
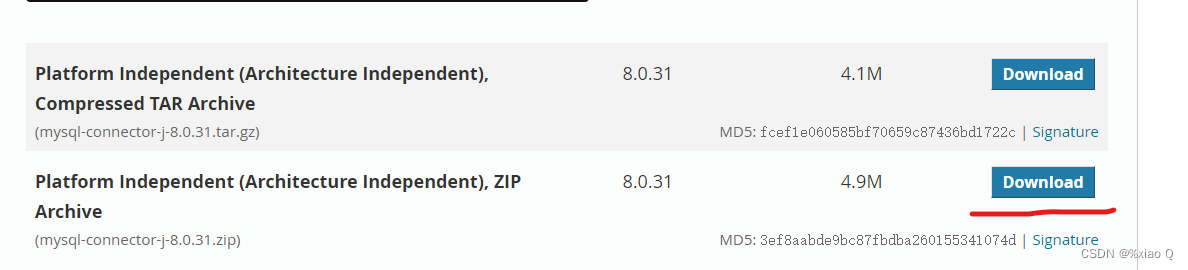
MySQL 的驱动下载地址:http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/
依次点击 Connector/J -> Platform Independent ,如然后下载下面那个

1.2 如何在Java project 项目应用中添加数据库驱动 jar
① 把下载好的mysql-connector-j-8.0.31.jar拷贝到该项目中
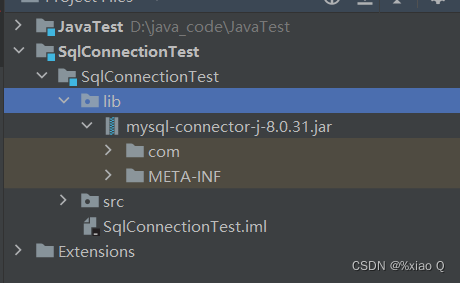
ps:这里的lib文件夹是自己创建的(也可不创建)
② 然后点击Add as Library -> OK,把其添加到项目类路径下
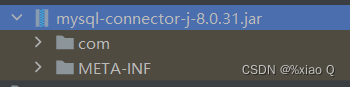
这样就表示成功了
2. 连接操作
2.1 方式一:
@Test public void testConnection1() throws SQLException { //获取Driver实现类对象 Driver driver = new com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver(); //jdbc:mysql协议 //localhost:ip地址 //3306: 默认端口 //student_attendance_system: 数据库名称 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student_attendance_system"; Properties info = new Properties(); //将用户名和密码封装在Property info.setProperty("user", "root"); info.setProperty("password", "0915"); Connection conn = driver.connect(url, info); System.out.println(conn); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
2.2 方式二:队方式一的迭代(目的:为了使程序不出现第三方的API,使得程序有更好的移植性)
@Test public void testConnection2() throws Exception { //1.获取Driver实现类对象 Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance(); //2. 提供数据库连接 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student_attendance_system"; //3. 提供连接需要的用户名和密码 Properties info = new Properties(); info.setProperty("user", "root"); info.setProperty("password", "0915"); //4. 获取连接 Connection conn = driver.connect(url, info); System.out.println(conn); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
2.3 方式三:使用DriverManager替换Driver
@Test public void testConnection3() throws Exception { //1. 获取Driver实现类对象 Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance(); //2. 提供3个类的基本信息 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student_attendance_system"; String user = "root"; String password = "0915"; //注册驱动 DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); //获取连接 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); System.out.println(conn); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
2.4 方式4:可以只加载,不用显示的注册驱动(Driver)
@Test public void testConnection4() throws Exception { //1. 提供3个类的基本信息 String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student_attendance_system"; String user = "root"; String password = "0915"; //2. 加载Driver Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); //也可以省略,因为META-INF/service的java.sql.Driver已经做过了 //相较于方式三,可以省略如下操作: // Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance(); //注册驱动 // DriverManager.registerDriver(driver); //获取连接 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); System.out.println(conn); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
2.5 方式五:将数据库连接需要的4个基本信息声明在配置文件中,通过读取配置文件的方式,获取连接
这里要在src文件夹下建立一个文件(jdbc.properties),可以其他名字,然后在该文件下输入数据库连接需要的属性
ps:一般连数据库用这种方式
文件内容:
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
user=root
password=0915
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
连接代码:
@Test public void testConnection5() throws Exception { // 1. 读取配置文件的4个信息 InputStream is = SqlConnectionTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("src/jdbc.properties"); Properties pros = new Properties(); pros.load(is); String user = pros.getProperty("user"); String password = pros.getProperty("password"); String url = pros.getProperty("url"); String driver = pros.getProperty("driver"); //2. 加载驱动 Class.forName(driver); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); System.out.println(conn); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
3. 拓展
一般在项目中,数据库连接用一个工具类来会更好,这样只要在用的时候,直接调用就好了。
工具类:
package src.Util; import src.SqlConnectionTest.SqlConnectionTest; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.sql.*; import java.util.Properties; /** * @author XiaoQ * @create 2022-12-11 19:26 */ public class JDBCUtils { /** * @Description 获取数据库的连接 * @return Connection * @author XiaoQ * @date 2022/12/11 20:22 */ public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception { // 1. 读取配置文件的4个消息 InputStream is = SqlConnectionTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("src/jdbc.properties"); Properties pros = new Properties(); pros.load(is); String user = pros.getProperty("user"); String password = pros.getProperty("password"); String url = pros.getProperty("url"); String driver = pros.getProperty("driver"); //2. 加载驱动 Class.forName(driver); //3. 获取连接 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); return conn; } /** * @Description 关闭连接和Statement * @return * @author XiaoQ * @date 2022/12/11 20:25 */ static public void closeResource(Connection conn, Statement ps){ try { if(ps != null) ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } try { if(conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } /** * @Description 关闭连接、Statement、ResultSet * @return * @author XiaoQ * @date 2022/12/12 1:51 */ static public void closeResource(Connection conn, Statement ps, ResultSet res){ try { if(ps != null) ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { if(res != null) res.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
二、数据库的操作
1. 数据库的增、删、改操作
1.1 普通的增加操作
@Test public void insertTest(){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { // 1. 读取配置文件的4个消息 InputStream is = SqlConnectionTest.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("src/jdbc.properties"); Properties pros = new Properties(); pros.load(is); String user = pros.getProperty("user"); String password = pros.getProperty("password"); String url = pros.getProperty("url"); String driver = pros.getProperty("driver"); //2. 加载驱动 Class.forName(driver); //3. 获取连接 conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); // System.out.println(conn); //4. 预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement的实例 String sql = "insert into stu values(?, ?, ?)"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //5. 填充占位符 ps.setString(1, "2001"); ps.setString(2, "小黑"); ps.setString(3, "89"); //6. 执行sql语句 ps.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } finally { //7. 资源关闭 try { if(ps != null) ps.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } try { if(ps != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
1.2 使用工具类后普通的修改操作
工具类JDBCUtils具体细节上面有
@Test public void updateTest(){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { //获取数据库连接 conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement String sql = "update stu set name = ? where id = ?"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //填充占位符 ps.setString(1, "小小"); ps.setObject(2, "1003"); //执行操作 ps.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭资源 JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn,ps); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
1.3 通用操作(增、删、改)
操作
public static void update(String sql, Object ...args){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { //获取数据库连接 conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //填充占位符 for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){ ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); } //执行操作 ps.execute(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭资源 JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn,ps); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
测试
@Test
public void commonUpdateTest(){
//增加操作
String sql = "insert into stu values(?, ?, ?)";
update(sql, "1005", "小达", 89);
//修改操作
sql = "update stu set name = ? where id = ?";
update(sql, "小朱", "1005");
//删除操作
sql = "delete from stu where id = ?";
update(sql, "1005");
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
2. 数据库的查询操作
2.1 对一个表的普通查询操作(基础不好或初学者用这个就够了,这个比较简单且比较好理解)
public void test1() { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { //获取数据库的连接 conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //预编译sql语句 String sql = "select * from stu where id = ?"; ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //填充占位符 ps.setObject(1, "2066"); //执行,并返回结果集 resultSet = ps.executeQuery(); if(resultSet.next()){ //获取列值 String id = resultSet.getString(1); //获取第一个字段 String name = resultSet.getString(2); //获取第二个字段 int score = resultSet.getInt(3); //获取第三个字段 //把列值封装到Student对象中 Student stu = new Student(id, name, score); System.out.println(stu); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { //关闭连接 JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, resultSet); } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
2.2 对一个表的通用查询操作
注意:针对于表的字段于类的属性名不相同的情况:
- 必须在声明sql语句时,使用类的属性名来给字段起别名
- 使用ResultSetMetaData时,需要用getColumnLabel()来替换getCoulmnName(),获取列的别名
说明:如果sql语句没有给字段起别名,那么gewtColumnLabel()得到就是列名
操作
public Student queryForStu(String sql, Object ...args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //获取数据库连接 conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //sql语句的预处理 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //占位符填充 for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){ ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); } //执行,并返回结果集 rs = ps.executeQuery(); //获取结果集的元数据 ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); //通过ResultSetMetaData获取结果集的列数 int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); if(rs.next()){ Student stu = new Student(); for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++){ //获取列值 Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i + 1); //getColumnName: 获取列的列名 //getColumnLabel: 获取列的别名(推荐用这个,因为如果没查询起别名的,那么别名就是字段名) String columnName = rsmd.getColumnName(i + 1); //给stu对象指定的columnName属性,赋值为columnValue,通过反射 //注意:如果该表的字段(这里指stu表)不和该类(这里指Student类)的属性对应相同,那么sql查询语句就要给 // 查询的字段起别名,防止反射后报错 Field field = Student.class.getDeclaredField(columnName); //void setAccessible(boolean flag) //为反射对象设置可访问标志。flag为true表明屏蔽java语言的访问检查,使得对象的私有属性也可以被查询和设置 field.setAccessible(true); //访问不符合访问权限对象的成员属性 field.set(stu, columnValue); } return stu; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, rs); } return null; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
测试
@Test
public void testQueryForStu(){
String sql = "select * from stu where id = ?";
Student student = queryForStu(sql, "2066");
System.out.println(student);
sql = "select name from stu where id = ?";
student = queryForStu(sql, "2001");
System.out.println(student);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
2.3 针对不同表的查询,返回一条纪录(泛型)
操作:
/** * @Description 针对不同表的通用查询,返回一条记录 * @return T * @author XiaoQ * @date 2022/12/12 0:50 */ public <T> T getInstance(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object ...args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //获取数据库连接 conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //sql语句的预处理 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //占位符填充 for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){ ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); } //执行,并返回结果集 rs = ps.executeQuery(); //获取结果集的元数据 ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); //通过ResultSetMetaData获取结果集的列数 int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); if(rs.next()){ T t = clazz.newInstance(); for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++){ //获取列值 Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i + 1); //getColumnName: 获取列的列名 //getColumnLabel: 获取列的别名(推荐用这个,因为如果没查询起别名的,那么别名就是字段名) String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1); //给stu对象指定的columnName属性,赋值为columnValue,通过反射 //注意:如果该表的字段(这里指stu表)不和该类(这里指Student类)的属性对应相同,那么sql查询语句就要给 // 查询的字段起别名,防止反射后报错 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); //void setAccessible(boolean flag) //为反射对象设置可访问标志。flag为true表明屏蔽java语言的访问检查,使得对象的私有属性也可以被查询和设置 field.setAccessible(true); //访问不符合访问权限对象的成员属性 field.set(t, columnValue); } return t; } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, rs); } return null; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
测试
@Test
public void test(){
String sql = "select * from stu where id = ?";
Student student = getInstance(Student.class, sql, "1001");
System.out.println(student);
sql = "select t_id id, t_name name, salary from teacher where t_id = ?";
Teacher teacher = getInstance(Teacher.class, sql, "4563");
System.out.println(teacher);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
2.4 针对不同表的通用查询,返回多条记录(泛型)
操作
/** * @Description 对不同表的通用查询,返回多条记录 * @return List<T> * @author XiaoQ * @date 2022/12/12 1:00 */ public <T>List<T> getForList(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object ...args){ Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { //获取数据库连接 conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); //sql语句的预处理 ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); //占位符填充 for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){ ps.setObject(i + 1, args[i]); } //执行,并返回结果集 rs = ps.executeQuery(); //获取结果集的元数据 ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData(); //通过ResultSetMetaData获取结果集的列数 int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount(); //创建集合对象 ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>(); while (rs.next()){ T t = clazz.newInstance(); //处理结果集一行数据中的每一列:给t对象指定的属性赋值 for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++){ //获取列值 Object columnValue = rs.getObject(i + 1); //getColumnName: 获取列的列名 //getColumnLabel: 获取列的别名(推荐用这个,因为如果没查询起别名的,那么别名就是字段名) String columnName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i + 1); //给stu对象指定的columnName属性,赋值为columnValue,通过反射 //注意:如果该表的字段(这里指stu表)不和该类(这里指Student类)的属性对应相同,那么sql查询语句就要给 // 查询的字段起别名,防止反射后报错 Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnName); //void setAccessible(boolean flag) //为反射对象设置可访问标志。flag为true表明屏蔽java语言的访问检查,使得对象的私有属性也可以被查询和设置 field.setAccessible(true); //访问不符合访问权限对象的成员属性 field.set(t, columnValue); } list.add(t); } return list; } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JDBCUtils.closeResource(conn, ps, rs); } return null; }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
测试
@Test
public void test1(){
String sql = "select * from stu";
List<Student> list = getForList(Student.class, sql);
list.forEach(System.out::println);
sql = "select t_id id, t_name name, salary from teacher where salary < ?";
List<Teacher> list1 = getForList(Teacher.class, sql, 1000);
list1.forEach(System.out::println);
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
本文内容由网友自发贡献,转载请注明出处:【wpsshop博客】
推荐阅读
相关标签



