- 1大型语言模型(LLM)技术精要_首创将大语言模型(llm)技术引入静态白盒检测场景,进一步降低了白盒测试的误报率,
- 2Harmony OS 父子组件传参_鸿蒙 组件传参
- 3AKShare 快速入门
- 4Spring Boot 与 Spring Security_springboot springsecurity
- 5python--素数求和_python判断素数相加
- 6IP如何异地共享文件?
- 7Java System#exit 无法退出程序的问题探索_system.exit(-1)进程未退出
- 8鸿蒙入门开发教程:一文带你详解工具箱元服务的开发流程_鸿蒙元服务预加载
- 9Java面试八股文整理
- 10详细教程 - 进阶版 鸿蒙harmonyOS应用 第十七节——鸿蒙OS多线程编程指南_鸿蒙 多线程
【Tensorflow+自然语言处理+RNN】实现中文译英文的智能聊天机器人实战(附源码和数据集 超详细)_基于自然语言处理的闲聊机器人
赞
踩
需要源码和数据集请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言私信~~~
一、序列-序列机制概述
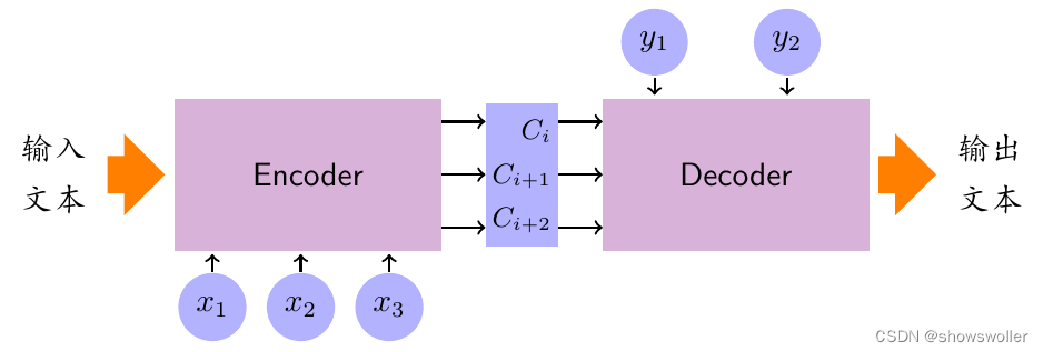
Seq2Seq 是一个 Encoder-Decoder 结构的神经网络,它的输入是一个序列(Sequence),输出也是一个序列(Sequence)。在 Encoder 中,将可变长度的序列转变为固定长度的向量表达,Decoder 将这个固定长度的向量转换为可变长度的目标的信号序列。
序列-序列的基本模型包括三个部分,即编码器、解码器以及连接两者的中间状态向量语义编码,编码器通过学习输入,将其编码成固定大小的状态向量,继而将语义编码传给解码器,解码器再通过对状态向量语义编码的学习输出对应的序列 下图是基本工作流程
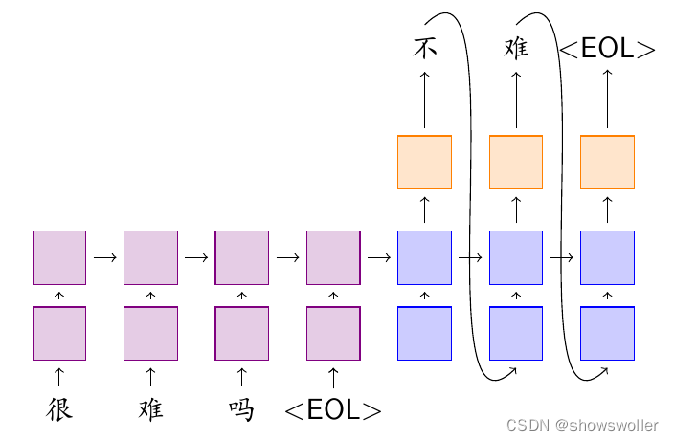

二、注意力机制
注意力机制与编码器-解码器模型的区别在于不再要求编码器将所有输入信息都编码成固定长度的向量,而是编码成向量的序列。
三、集束搜索概述
Beam Search(集束搜索)是基于Seq2Seq的一种搜索算法,通常用在解空间比较大的情况下,为了减少搜索所占用的空间和时间,在每一步深度扩展的时候,剪掉一些质量比较差的结点,保留下一些质量较高的结点,这样就减少了空间消耗,并提高了时间效率,其缺点是潜在的最佳方案可能被丢弃
四、张量流智能机器人实战
智能客服系统的主要功能根据应用场景不同而变化,通常包括会话管理、任务管理、模型管理和权限管理等功能。
(1)会话管理:包含会话分类、问题查询以及问题更新等功能。
(2)任务管理:包括任务配置、任务更新、模型配置等。
(3)模型管理:包括模型更新、数据更新以及访问接口等。
(4)权限管理:包括权限控制、角色匹配以及业务对接等。
1:语料预处理
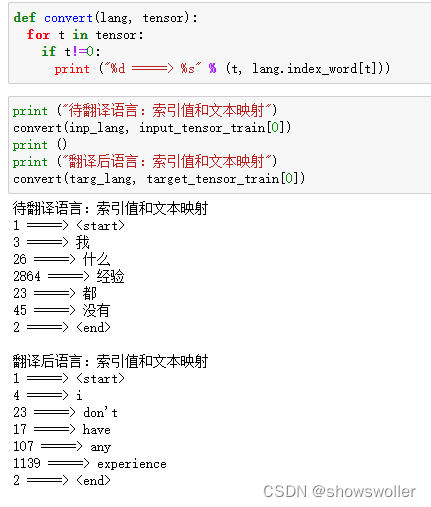
中英文本语料,首先按照行将文本信息切分,如果是英文,则将文本变为小写,然后去掉开始和结尾的空白符并各自加上起始标识符和结束标识符,如果是中文文本,则去掉开始和结尾的空白符直接添加起始和结束标识符
通过将文本映射为索引张量信息,输出部分样本,对比中英文词嵌入处理结果如下
2:训练模型
基于参数配置 训练模型 设置训练轮数为10轮,随着训练轮数增加,损失值逐渐降低

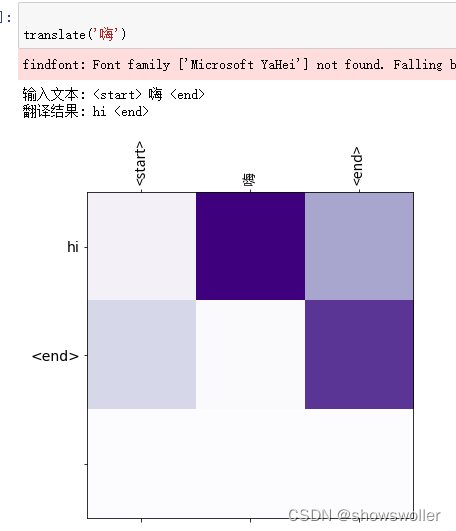
3:测试结果
模型训练结束后 输入中文获得英文翻译结果 部分结果如下图 翻译结果可能会随着训练轮数和训练样本数量发生一定变化
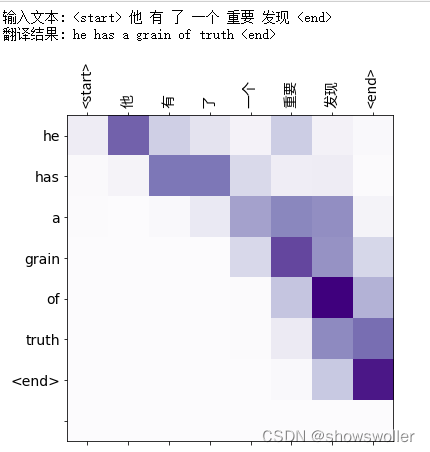
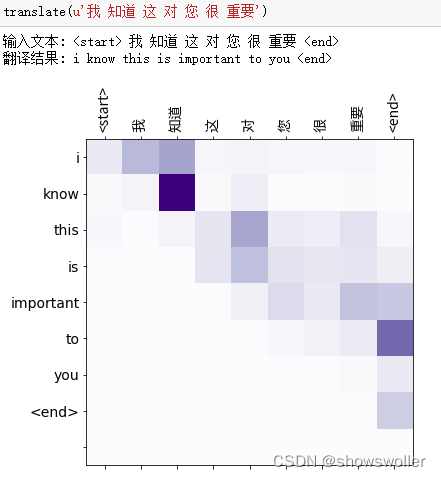
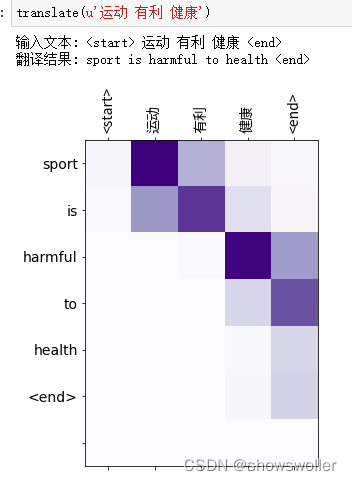
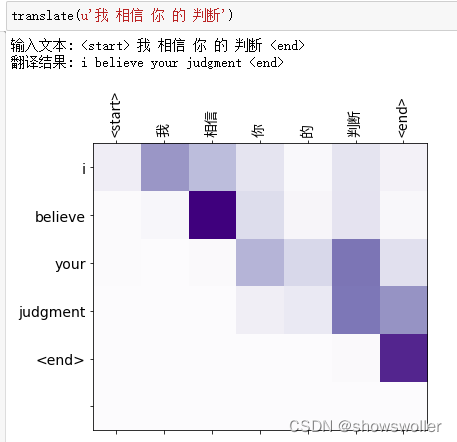
五、代码
部分代码如下 全部代码和数据集请点赞关注收藏后评论区留言私信~~~
-
-
-
- import tensorflow as tf
-
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
- from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
-
- import unicodedata
- import re
- import numpy as np
- import os
- import io
- import time
- import pathlib
- from matplotlib import rcParams
- rcParams['font.family'] = ['Microsoft YaHei']
-
-
-
-
- # 下载文件
- path_to_zip = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
- 'cmn-eng.txt', origin='https://firebasestorage.googleapis.com/v0/b/marine-order-311008.appspot.com/o/cmn-eng.txt?alt=media&token=4d856d2f-ea8b-4ba4-9ba2-9e9dfb8d4080',
- cache_subdir='datasets',extract=False)
- path_to_file = pathlib.Path(path_to_zip).parent/'cmn-eng.txt'
- #path_to_file = "cmn-eng/cmn.txt"
- get_ipython().system('ls /root/.keras/datasets/')
-
- print(pathlib.Path(path_to_zip).parent)
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- # 将 unicode 文件转换为 ascii
- def unicode_to_ascii(s):
- return ''.join(c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
- if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn')
-
-
- def preprocess(text):
- reg = re.compile(r'[a-zA-Z,.?]')
- if reg.match(text):
- text = unicode_to_ascii(text.lower().strip())
- text = re.sub(r"([.!:;,])", r" \1 ", text)
- text = re.sub(r'[" "]+', " ", text)
- text = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z?.!,:;]+", " ", text)
- text = text.rstrip().strip()
- text = '<start> ' + text +' <end>'
- return text
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- en_sentence = u"Information Technology has achieved great advancement"
- sp_sentence = u"信息技术获得巨大进步"
- print(preprocess(en_sentence))
- print(preprocess(sp_sentence))
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- # 1. 去除重音符号
- # 2. 清理句子
- # 3. 返回这样格式的单词对:[ENGLISH, SPANISH]
- get_ipython().system('pip install jieba')
- import jieba
-
- def corpus(path, no):
- lines = io.open(path, encoding='UTF-8').read().strip().split('\n')
- english=[]
- chinese=[]
- out
- print(sp[100:120])
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- def max_length(tensor):
- return max(len(t) for t in tensor)
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- def tokenize(lang):
- lang_tokenizer = tf.keras.preprocessing.text.Tokenizer(
- filters='')
- lang_tokenizer.fit_on_texts(lang)
-
- tensor = lang_tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(lang)
-
- tensor = tf.keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(tensor,
- padding='post')
-
- return tensor, lang_tokenizer
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- def load_dataset(path, num_examples=None):
- # 创建清理过的输入输出对
- targ_lang, inp_lang = corpus(path, num_examples)
-
- input_tensor, inp_lang_tokenizer = tokenize(inp_lang)
- target_tensor, targ_lang_tokenizer = tokenize(targ_lang)
-
- return input_tensor, target_tensor, inp_lang_tokenizer, targ_lang_tokenizer
-
-
- # ### 限制数据集的大小以加快实验速度(可选)
- #
- #
- # 计算目标张量的最大长度 (max_length)
- max_length_targ, max_length_inp = max_length(target_tensor), max_length(input_tensor)
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- # 采用 80 - 20 的比例切分训练集和验证集
- input_tensor_train, input_tensor_val, target_tensor_train, target_tensor_val = train_test_split(input_tensor, target_tensor, test_size=0.2)
-
- # 显示长度
- print(len(input_tensor_train), len(target_tensor_train), len(input_tensor_val), len(target_tensor_val))
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- def convert(lang, tensor):
- for t in tensor:
- if t!=0:
- print ("%d =====> %s" % (t, lang.index_word[t]))
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- print ("待翻译语言:索引值和文本映射")
- convert(inp_lang, input_tensor_train[0])
- print ()
- pri
-
- BUFFER_SIZE = len(input_tensor_train)
- BATCH_SIZE = 64
- steps_per_epoch = len(input_tensor_train)//BATCH_SIZE
- embedding_dim = 256
- units = 1024
- vocab_inp_size = len(inp_lang.word_index)+1
- vocab_tar_size = len(targ_lang.word_index)+1
-
- dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((input_tensor_train, target_tensor_train)).shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE)
- dataset = dataset.batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=True)
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- example_input_batch, example_target_batch = next(iter(dataset))
- example_input_batch.shape, example_target_batch.shape
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- class Encoder(tf.keras.Model):
- def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, enc_units, batch_sz):
- super(Encoder, self).__init__()
- self.batch_sz = batch_sz
- self.enc_raint=None, mask_zero=False, input_length=None,)
- #self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.enc_units,
- # return_sequences=True,
- # return_state=True,
- # recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform')
-
- self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.enc_units,
- return_state=True,
- activation='tanh', recurrent_activation='sigmoid',
- use_bias=True, kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform',
- recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
- bias_initializer='zeros', kernel_regularizer=None,
- recurrent_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
- kernel_constraint=None, recurrent_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None,
- dropout=0.1, recurrent_dropout=0.1, return_sequences=True,
- go_backwards=False, stateful=False, unroll=False, time_major=False,
- reset_after=True,)
-
- def call(self, x, hidden):
- x = self.embedding(x)
- output, state = self.gru(x, initial_state = hidden)
- return output, state
-
- def initialize_hidden_state(self):
- return tf.zeros((self.batch_sz, self.enc_units))
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- encoder = Encoder(vocab_inp_size, embedding_dim, units, BATCH_SIZE)
-
- # 样本输入
- sample_hidden = encoder.initialize_hidden_state()
- sample_output, sample_hidden = encoder(example_input_batch, sample_hidden)
- print ('Encoder output shape: (batch size, sequence length, units) {}'.format(sample_output.shape))
- print ('Encoder Hidden state shape: (batch size, units) {}'.format(sample_hidden.shape))
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- class BahdanauAttention(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
- def __init__(self, units):
- super(BahdanauAttention, self).__init__()
- self.W1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units)
- self.W2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units)
- self.V = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
-
- def call(self, query, values):
- # 隐藏层的形状 == (批大小,隐藏层大小)
- # hidden_with_time_axis 的形状 == (批大小,1,隐藏层大小)
- # 这样做是为了执行加法以计算分数
- hidden_with_time_axis = tf.expand_dims(query, 1)
-
- # 分数的形状 == (批大小,最大长度,1)
- # 我们在最后一个轴上得到 1, 因为我们把分数应用于 self.V
- # 在应用 self.V 之前,张量的形状是(批大小,最大长度,单位)
- score = self.V(tf.nn.tanh(
- self.W1(values) + self.W2(hidden_with_time_axis)))
-
- # 注意力权重 (attention_weights) 的形状 == (批大小,最大长度,1)
- attention_weights = tf.nn.softmax(score, axis=1)
-
- # 上下文向量 (context_vector) 求和之后的形状 == (批大小,隐藏层大小)
- context_vector = attention_weights * values
- context_vector = tf.reduce_sum(context_vector, axis=1)
-
- return context_vector, attention_weights
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- attention_layer = BahdanauAttention(10)
- attention_result, attention_weights = attention_layer(sample_hidden, sample_output)
-
- print("Attention result shape: (batch size, units) {}".format(attention_result.shape))
- print("Attention weights shape: (batch_size, sequence_length, 1) {}".format(attention_weights.shape))
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- class Decoder(tf.keras.Model):
- def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, dec_units, batch_sz):
- super(Decoder, self).__init__()
- self.batch_sz = batch_sz
- self.dec_units = dec_units
- self.embedding = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
- #self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.dec_units,
- # return_sequences=True,
- # return_state=True,
- # recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform')
- self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.dec_units,
- return_state=True,
- activation='tanh', recurrent_activation='sigmoid',
- use_bias=True, kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform',
- recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
- bias_initializer='zeros', kernel_regularizer=None,
- recurrent_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
- kernel_constraint=None, recurrent_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None,
- dropout=0.1, recurrent_dropout=0.1, return_sequences=True,
- go_backwards=False, stateful=False, unroll=False, time_major=False,
- reset_after=True,)
-
- self.fc = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units=vocab_size, activation=None, use_bias=True,
- kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform',
- bias_initializer='zeros', kernel_regularizer=None,
- bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
- bias_constraint=None,)
-
- # 用于注意力
- self.attention = BahdanauAttention(self.dec_units)
-
- def call(self, x, hidden, enc_output):
- # 编码器输出 (enc_output) 的形状 == (批大小,最大长度,隐藏层大小)
- context_vector, attention_weights = self.attention(hidden, enc_output)
-
- # x 在通过嵌入层后的形状 == (批大小,1,嵌入维度)
- x = self.embedding(x)
-
- # x 在拼接 (concatenation) 后的形状 == (批大小,1,嵌入维度 + 隐藏层大小)
- x = tf.concat([tf.expand_dims(context_vector, 1), x], axis=-1)
-
- # 将合并后的向量传送到 GRU
- output, state = self.gru(x)
-
- # 输出的形状 == (批大小 * 1,隐藏层大小)
- output = tf.reshape(output, (-1, output.shape[2]))
-
- # 输出的形状 == (批大小,vocab)
- x = self.fc(output)
-
- return x, state, attention_weights
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- decoder = Decoder(vocab_tar_size, embedding_dim, units, BATCH_SIZE)
-
- sample_decoder_output, _, _ = decoder(tf.random.uniform((64, 1)),
- sample_hidden, sample_output)
-
- print ('Decoder output shape: (batch_size, vocab size) {}'.format(sample_decoder_output.shape))
-
-
- # ## 定义优化器和损失函数
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
- loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(
- from_logits=True, reduction='none')
-
- def loss_function(real, pred):
- mask = tf.math.logical_not(tf.math.equal(real, 0))
- loss_ = loss_object(real, pred)
-
- mask = tf.cast(mask, dtype=loss_.dtype)
- loss_ *= mask
-
- return tf.reduce_mean(loss_)
-
-
- # ## 检查点(基于对象保存)
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- checkpoint_dir = './training_checkpoints'
- checkpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_dir, "ckpt")
- checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(optimizer=optimizer,
- encoder=encoder,
- decoder=decoder)
-
-
- # ## 训练
- #
- # 1. 将 *输入* 传送至 *编码器*,编码器返回 *编码器输出* 和 *编码器隐藏层状态*。
- # 2. 将编码器输出、编码器隐藏层状态和解码器输入(即 *开始标记*)传送至解码器。
- # 3. 解码器返回 *预测* 和 *解码器隐藏层状态*。
- # 4. 解码器隐藏层状态被传送回模型,预测被用于计算损失。
- # 5. 使用 *教师强制 (teacher forcing)* 决定解码器的下一个输入。
- # 6. *教师强制* 是将 *目标词* 作为 *下一个输入* 传送至解码器的技术。
- # 7. 最后一步是计算梯度,并将其应用于优化器和反向传播。
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- @tf.function
- def train_step(inp, targ, enc_hidden):
- loss = 0
-
- with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
- enc_output, enc_hidden = encoder(inp, enc_hidden)
-
- dec_hidden = enc_hidden
-
- dec_input = tf.expand_dims([targ_lang.word_index['<start>']] * BATCH_SIZE, 1)
-
- # 教师强制 - 将目标词作为下一个输入
- for t in range(1, targ.shape[1]):
- # 将编码器输出 (enc_output) 传送至解码器
- predictions, dec_hidden, _ = decoder(dec_input, dec_hidden, enc_output)
-
- loss += loss_function(targ[:, t], predictions)
-
- # 使用教师强制
- dec_input = tf.expand_dims(targ[:, t], 1)
-
- batch_loss = (loss / int(targ.shape[1]))
-
- variables = encoder.trainable_variables + decoder.trainable_variables
-
- gradients = tape.gradient(loss, variables)
-
- optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, variables))
-
- return batch_loss
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- EPOCHS = 10
-
- for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
- start = time.time()
-
- enc_hidden = encoder.initialize_hidden_state()
- total_loss = 0
-
- for (batch, (inp, targ)) in enumerate(dataset.take(steps_per_epoch)):
- batch_loss = train_step(inp, targ, enc_hidden)
- total_loss += batch_loss
-
- if batch % 100 == 0:
- print('第 {}轮 第 {} 批 损失值 {:.3}'.format(epoch + 1,
- batch,
- batch_loss.numpy()))
- # 每 2 个周期(epoch),保存(检查点)一次模型
- if (epoch + 1) % 2 == 0:
- checkpoint.save(file_prefix = checkpoint_prefix)
-
- print('第 {} 轮 损失值 {:.3f}'.format(epoch + 1,
- total_loss / steps_per_epoch))
- print('本轮训练时间为 {} 秒 \n'.format(time.time() - start))
-
-
- # ## 翻译
- #
- # * 评估函数类似于训练循环,不同之处在于在这里我们不使用 *教师强制*。每个时间步的解码器输入是其先前的预测、隐藏层状态和编码器输出。
- # * 当模型预测 *结束标记* 时停止预测。
- # * 存储 *每个时间步的注意力权重*。
- #
- # 请注意:对于一个输入,编码器输出仅计算一次。
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- def evaluate(sentence):
- attention_plot = np.zeros((max_length_targ, max_length_inp))
-
- sentence = preprocess(sentence)
-
- inputs = [inp_lang.word_index[i] for i in sentence.split(' ')]
- inputs = tf.keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences([inputs],
- maxlen=max_length_inp,
- padding='post')
- inputs = tf.convert_to_tensor(inputs)
-
- result = ''
-
- hidden = [tf.zeros((1, units))]
- enc_out, enc_hidden = encoder(inputs, hidden)
-
- dec_hidden = enc_hidden
- dec_input = tf.expand_dims([targ_lang.word_index['<start>']], 0)
-
- for t in range(max_length_targ):
- predictions, dec_hidden, attention_weights = decoder(dec_input,
- dec_hidden,
- enc_out)
-
- # 存储注意力权重以便后面制图
- attention_weights = tf.reshape(attention_weights, (-1, ))
- attention_plot[t] = attention_weights.numpy()
-
- predicted_id = tf.argmax(predictions[0]).numpy()
-
- result += targ_lang.index_word[predicted_id] + ' '
-
- if targ_lang.index_word[predicted_id] == '<end>':
- return result, sentence, attention_plot
-
- # 预测的 ID 被输送回模型
- dec_input = tf.expand_dims([predicted_id], 0)
-
- return result, sentence, attention_plot
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- # 注意力权重制图函数
-
- from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
- get_ipython().system('wget -O taipei_sans_tc_beta.ttf https://drive.google.com/uc?id=1eGAsTN1HBpJAkeVM57_C7ccp7hbgSz3_&export=download')
- get_ipython().system('mv taipei_sans_tc_beta.ttf /usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/matplotlib//mpl-data/fonts/ttf')
-
-
-
- # 自定義字體變數
- font = FontProperties(fname=r'/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/matplotlib/mpl-data/fonts/ttf/taipei_sans_tc_beta.ttf')
-
-
- def plot_attention(attention, sentence, predicted_sentence):
- fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6,6))
- ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
- ax.matshow(attention, cmap=plt.get_cmap('Purples'))
-
- fontdict = {'fontsize': 14}
-
- ax.set_xticklabels([''] + sentence, fontdict=fontdict, rotation=90, fontproperties=font)
- ax.set_yticklabels([''] + predicted_sentence, fontdict=fontdict)
-
- ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))
- ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1))
-
-
- plt.show()
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- def translate(sentence):
- result, sentence, attention_plot = evaluate(sentence)
-
- print('输入文本: %s' % (sentence))
- print('翻译结果: {}'.format(result))
-
- attention_plot = attention_plot[:len(result.split(' ')), :len(sentence.split(' '))]
- plot_attention(attention_plot, sentence.split(' '), result.split(' '))
-
-
- # ## 恢复最新的检查点并验证
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- # 恢复检查点目录 (checkpoint_dir) 中最新的检查点
- checkpoint.restore(tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_dir))
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- translate('嗨')
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- translate(u'他 不幸 找 不到 工作')
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- translate(u'我 想 打 电话')
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
-
-
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- translate(u'运动 有利 健康')
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- translate(u'我 相信 你 的 判断')
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- translate(u'应该 了解 相应 的 规则')
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
- translate(u'我们 终于 达到 了 目标')
-
-
- # In[ ]:
-
-
-
-

创作不易 觉得有帮助请点赞关注收藏~~~


