- 1易景空间地图建筑CAD自动识图转换为室内三维地图技术2021年突破_cad自动识别算法
- 2【Go黑帽子】使用Golang编写一个TCP扫描器(基础篇)_golang nmap
- 3PostgreSQL源码分析——INSERT
- 4vue加载vuetify模板UI_vuetifyjs模板
- 5使用 BeeWare 构建 Python GUI 应用程序
- 6论文阅读-一个用于云计算中自我优化的通用工作负载预测框架_虚拟机负载预测
- 7强化学习:AI如何通过反馈提高自身能力_强化学习反馈条件
- 8【进阶篇】2.16 Redis 消息传递发布订阅模式详解_redis发布订阅模式
- 9idea拉取项目及上传项目到Gitee仓库及解除_idea拉取gitee
- 10LSTM 详解及 LSTM 解决时间序列预测问题(附代码)_lstm预测
十大经典排序算法与算法复杂度_十大排序算法时间复杂度
赞
踩
本系列算法整理自:https://github.com/hustcc/JS-Sorting-Algorithm
动图演示:https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/ten-sorting-algorithm.html
排序算法是《数据结构与算法》中最基本的算法之一。
排序算法可以分为内部排序和外部排序,内部排序是数据记录在内存中进行排序,而外部排序是因排序的数据很大,一次不能容纳全部的排序记录,在排序过程中需要访问外存。
常见的内部排序算法有:插入排序、希尔排序、选择排序、冒泡排序、归并排序、快速排序、堆排序、基数排序等。用一张图概括:
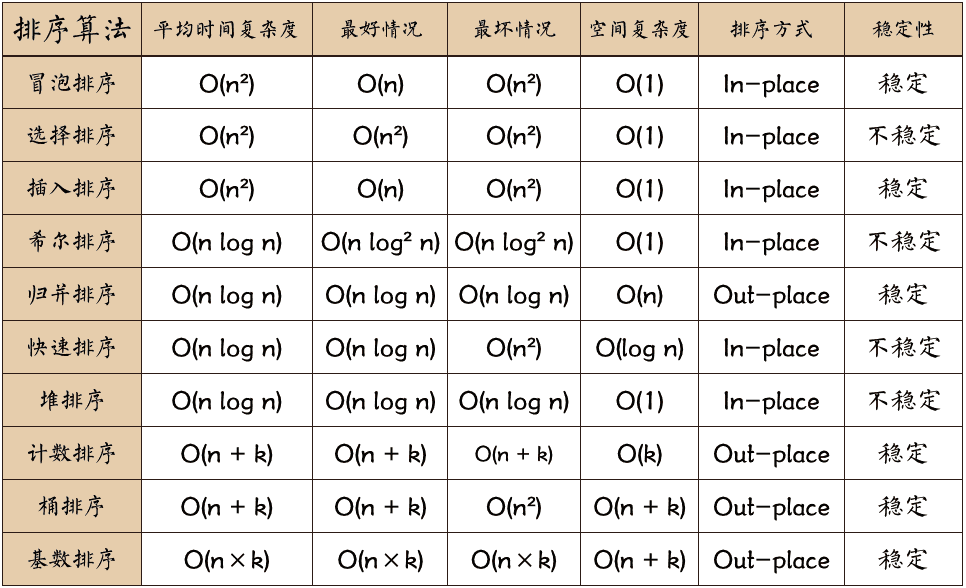
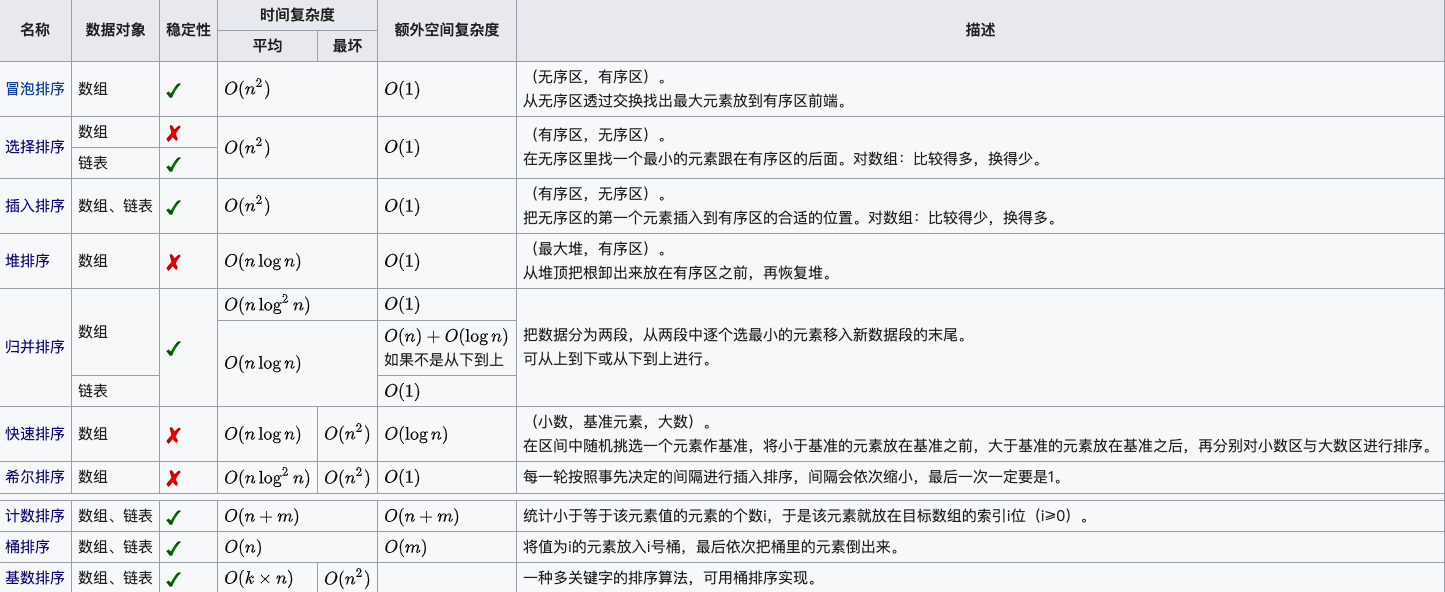
复杂度
主要还是从算法所占用的「时间」和「空间」两个维度去考量。
时间维度:是指执行当前算法所消耗的时间,我们通常用「时间复杂度」来描述。
空间维度:是指执行当前算法需要占用多少内存空间,我们通常用「空间复杂度」来描述。
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/50479555
关于时间复杂度
平方阶 (O(n2)) 排序 各类简单排序:直接插入、直接选择和冒泡排序。
线性对数阶 (O(nlog2n)) 排序 快速排序、堆排序和归并排序;
O(n1+§)) 排序,§ 是介于 0 和 1 之间的常数。 希尔排序
线性阶 (O(n)) 排序 基数排序,此外还有桶、箱排序。
关于稳定性
稳定性的定义
假定在待排序的记录序列中,存在多个具有相同的关键字的记录,若经过排序,这些记录的相对次序保持不变,即在原序列中,ri=rj,且ri在rj之前,而在排序后的序列中,ri仍在rj之前,则称这种排序算法是稳定的;否则称为不稳定的。
稳定的排序算法:冒泡排序、插入排序、归并排序和基数排序。
不是稳定的排序算法:选择排序、快速排序、希尔排序、堆排序。
名词解释:
n:数据规模
k:"桶"的个数
In-place:占用常数内存,不占用额外内存
Out-place:占用额外内存
稳定性:排序后 2 个相等键值的顺序和排序之前它们的顺序相同
python
''' # Create by LokiSharp(loki.sharp#gmail) at 2017-1-22 ''' TOTAL = 5000 def sortTest(func, total=1000): import random, copy, operator, math, time arrList = [i for i in range(-math.floor(total / 2), math.ceil(total / 2))] arrListR = copy.deepcopy(arrList) while operator.eq(arrList, arrListR): random.shuffle(arrListR) # print("--- [Origin List]", arrList, "Use", func.__name__,"with Total:", len(arrList)) # print("--> [Random List]", arrListR, "Use", func.__name__,"with Total:", len(arrList)) start = time.clock() arrListR = func(arrListR) end = time.clock() runtime = end - start # print("--> [Sorted List]", arrListR, "Use", func.__name__,"with Total:", len(arrList)) if operator.eq(arrList, arrListR): print("[Success]", func.__name__, "with Total:", len(arrList), "in %.5fs" % runtime) return True else: print("[Fail]", func.__name__, "with Total:", len(arrList), "in %.5fs" % runtime) return False def bubbleSort(arr): for i in range(1, len(arr)): for j in range(0, len(arr) - i): if arr[j] > arr[j + 1]: arr[j], arr[j + 1] = arr[j + 1], arr[j] return arr def selectionSort(arr): for i in range(len(arr) - 1): # 记录最小数的索引 minIndex = i for j in range(i + 1, len(arr)): if arr[j] < arr[minIndex]: minIndex = j # i 不是最小数时,将 i 和最小数进行交换 if i != minIndex: arr[i], arr[minIndex] = arr[minIndex], arr[i] return arr def insertionSort(arr): for i in range(len(arr)): preIndex = i - 1 current = arr[i] while preIndex >= 0 and arr[preIndex] > current: arr[preIndex + 1] = arr[preIndex] preIndex -= 1 arr[preIndex + 1] = current return arr def shellSort(arr): import math gap = 1 while (gap < len(arr) / 3): gap = gap * 3 + 1 while gap > 0: for i in range(gap, len(arr)): temp = arr[i] j = i - gap while j >= 0 and arr[j] > temp: arr[j + gap] = arr[j] j -= gap arr[j + gap] = temp gap = math.floor(gap / 3) return arr def mergeSort(arr): import math if (len(arr) < 2): return arr middle = math.floor(len(arr) / 2) left, right = arr[0:middle], arr[middle:] return merge(mergeSort(left), mergeSort(right)) def merge(left, right): result = [] while left and right: if left[0] <= right[0]: result.append(left.pop(0)); else: result.append(right.pop(0)); while left: result.append(left.pop(0)); while right: result.append(right.pop(0)); return result def quickSort(arr, left=None, right=None): left = 0 if not isinstance(left, (int, float)) else left right = len(arr) - 1 if not isinstance(right, (int, float)) else right if left < right: partitionIndex = partition(arr, left, right) quickSort(arr, left, partitionIndex - 1) quickSort(arr, partitionIndex + 1, right) return arr def partition(arr, left, right): pivot = left index = pivot + 1 i = index while i <= right: if arr[i] < arr[pivot]: swap(arr, i, index) index += 1 i += 1 swap(arr, pivot, index - 1) return index - 1 def swap(arr, i, j): arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i] def buildMaxHeap(arr): import math for i in range(math.floor(len(arr) / 2), -1, -1): heapify(arr, i) def heapify(arr, i): left = 2 * i + 1 right = 2 * i + 2 largest = i if left < arrLen and arr[left] > arr[largest]: largest = left if right < arrLen and arr[right] > arr[largest]: largest = right if largest != i: swap(arr, i, largest) heapify(arr, largest) def swap(arr, i, j): arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i] def heapSort(arr): global arrLen arrLen = len(arr) buildMaxHeap(arr) for i in range(len(arr) - 1, 0, -1): swap(arr, 0, i) arrLen -= 1 heapify(arr, 0) return arr def countingSort(arr, maxValue=None): bucketLen = maxValue + 1 bucket = [0] * bucketLen sortedIndex = 0 arrLen = len(arr) for i in range(arrLen): if not bucket[arr[i]]: bucket[arr[i]] = 0 bucket[arr[i]] += 1 for j in range(bucketLen): while bucket[j] > 0: arr[sortedIndex] = j sortedIndex += 1 bucket[j] -= 1 return arr def radix_count(exp1): global list n = len(list) output = [0] * (n) count = [0] * (10) for i in range(0, n): index = (list[i] / exp1) count[(index) % 10] += 1 for i in range(1,10): count[i] += count[i - 1] i = n - 1 while i >= 0: index = (list[i]/exp1) output[count[(index) % 10] - 1] = list[i] count[(index) % 10] -= 1 i -= 1 i = 0 for i in range(0,len(list)): list[i] = output[i] def radixSort(): global list max1 = max(list) exp = 1 while max1 / exp > 0: radix_count(exp) exp *= 10 if __name__ == '__main__': sortTest(bubbleSort, TOTAL) sortTest(selectionSort, TOTAL) sortTest(insertionSort, TOTAL) sortTest(shellSort, TOTAL) sortTest(mergeSort, TOTAL) sortTest(quickSort, TOTAL) sortTest(heapSort, TOTAL) sortTest(radixSort, TOTAL)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216



