- 1python编写一个简单的课时记录系统
- 2大数据导论(1)——“大数据”相关概念、5V特征、数据类型
- 3JAVA与C++的区别详解_c++和java
- 4Git tag 命令简明教程
- 5软件测试选择题
- 6github学生认证成功,使用苹果的Safari浏览器!!!_github学生认证第一步点击continue没反应的解决方案
- 7CPS1848国产替代芯片 国产SRIO交换芯片_srio 交换模块
- 8基于FPGA的VGA显示彩条、字符、图片_基于fpga的vga显示设计
- 9自然语言处理:大语言模型综述与ChatGPT入门_大型语言模型chatgpt
- 10第1关:HBase Shell 操作:分区压缩_头歌第1关:hbase shell 操作:分区压缩
十大排序算法 JAVA代码_csdn guanhang89
赞
踩
参考了 这篇博客
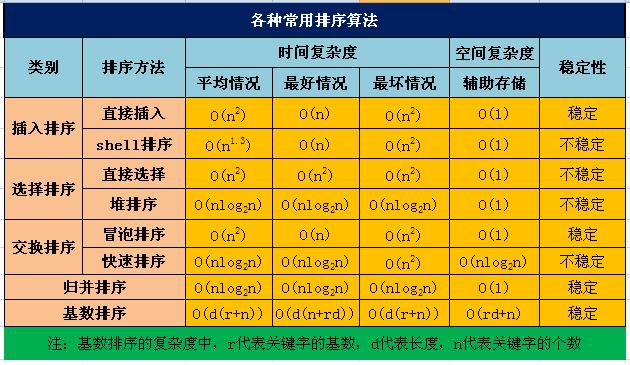
总体总结表:这个有个错误就是归并排序需要一个o(n)的辅助数组
冒泡排序
主要思想:外层循环控制轮数,内循环从0开始,依次和相邻的元素对比,出现逆序就交换。
特点:stable sort(稳定性排序)、In-place sort(不占用额外的空间,只是交换元素)
最优复杂度:当输入数组就是排好序的时候,复杂度为O(n),而快速排序在这种情况下会产生O(n^2)的复杂度。
最差复杂度:当输入数组为倒序时,复杂度为O(n^2)
插入排序比较适合用于“少量元素的数组”。
其实插入排序的复杂度和逆序对的个数一样,当数组倒序时,逆序对的个数为n(n-1)/2,因此插入排序复杂度为O(n^2)。
public class BubbleSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 4, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7}; sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static int[] sort(int[] arr) { boolean swap; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { swap = false; for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (arr[j + 1] < arr[j]) { int tmp = arr[j]; arr[j] = arr[j + 1]; arr[j + 1] = tmp; swap = true; } } if (!swap) { break; } } return arr; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
在算法导论思考题2-2中又问了”冒泡排序和插入排序哪个更快“呢?
插入排序的速度直接是逆序对的个数,而冒泡排序中执行“交换“的次数是逆序对的个数,因此冒泡排序执行的时间至少是逆序对的个数,因此插入排序的执行时间至少比冒泡排序快。
插入排序
主要思想:
特点:stable sort(稳定性排序)、In-place sort(不占用额外空间)
最优复杂度:当输入数组就是排好序的时候,复杂度为O(n),而快速排序在这种情况下会产生O(n^2)的复杂度。
最差复杂度:当输入数组为倒序时,复杂度为O(n^2)
插入排序比较适合用于“少量元素的数组”。
其实插入排序的复杂度和逆序对的个数一样,当数组倒序时,逆序对的个数为n(n-1)/2,因此插入排序复杂度为O(n^2)。
public class InsertSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 4, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7}; sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void sort(int[] array) { int n = array.length; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i ; j >0 ; j--) { if (array[j] < array[j - 1]) { int temp = array[j]; array[j] = array[j - 1]; array[j-1] = temp; } } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
插入排序的改进:内循环发现逆序不交换,采用整体右移,直到没有逆序的时候把元素放在该位置
public class InsertSort2 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 7, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7}; sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void sort(int[] array) { int n = array.length; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { int key = array[i]; int j = i -1; while (j >= 0 && array[j]>key) { array[j + 1] = array[j]; j--; } array[j+1] = key; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
问题:快速排序(不使用随机化)是否一定比插入排序快?
答:不一定,当输入数组已经排好序时,插入排序需要O(n)时间,而快速排序需要O(n^2)时间。
选择排序
特性:In-place sort,unstable sort。
思想:每次找一个最小值。
最好情况时间:O(n^2)。
最坏情况时间:O(n^2)。
public class SelectSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 7, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7}; sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void sort(int[] array) { int n = array.length; for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) { int min = i; for (int j = i+1; j < n; j++) { if (array[j] < array[min]) min = j; } int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[min]; array[min] = temp; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
希尔排序
思想:基于插入排序,交换不相邻的元素已对数组的局部进行排序,并最终用插入排序将局部有序的数组排序。思想是使数组中任意间隔为h的元素都是有序的,这样的数组称为h有序数组.
特性:In-place sort,unstable sort。
思想:每次找一个最小值。
最好情况时间:O(n)。
最坏情况时间:O(n^2)。
public class ShellSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 7, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7, 15}; sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void sort(int[] array) { int n = array.length; int h = 1; while (h<n/3) h = 3*h +1; while (h >= 1) { for (int i = h; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i; j >= h && (array[j] < array[j - h]); j -= h) { int temp = array[j]; array[j] = array[j - h]; array[j-h]= temp; } } h /=3; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
归并排序
特点:stable sort、Out-place sort
思想:运用分治法思想解决排序问题。
最坏情况运行时间:O(nlgn)
最佳运行时间:O(nlgn)
程序中merge的精髓(也就是排序):左半边用尽,则取右半边元素;右半边用尽,则取左半边元素;右半边的当前元素小于左半边的当前元素,则取右半边元素;右半边的当前元素大于左半边的当前元素,则取左半边的元素。实际上大部分发生的都是后面两句话,前面两句只是特殊情况而已。
自顶向下:
public class MergeSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 7, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7}; mergeSort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void mergeSort(int[] array) { int[] aux = new int[array.length]; sort(array, aux, 0, array.length - 1); } private static void sort(int[] array, int[] aux, int lo, int hi) { if (hi<=lo) return; int mid = lo + (hi - lo)/2; sort(array, aux, lo, mid); sort(array, aux, mid + 1, hi); merge(array, aux, lo, mid, hi); } private static void merge(int[] array, int[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) { System.arraycopy(array,0,aux,0,array.length); int i = lo, j = mid + 1; for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { if (i>mid) array[k] = aux[j++]; else if (j > hi) array[k] = aux[i++]; else if (aux[j]<aux[i]) array[k] = aux[j++]; else array[k] = aux[i++]; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
自底向上:
public class MergeSort2 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 7, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7}; sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } public static void sort(int[] array) { int N = a.length; int[] aux = new int[N]; for (int n = 1; n < N; n = n+n) { for (int i = 0; i < N-n; i += n+n) { int lo = i; int m = i+n-1; int hi = Math.min(i+n+n-1, N-1); merge(array, aux, lo, m, hi); } } } private static void merge(int[] array, int[] aux, int lo, int mid, int hi) { for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { aux[k] = array[k]; } // merge back to a[] int i = lo, j = mid+1; for (int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) { if (i > mid) array[k] = aux[j++]; // this copying is unneccessary else if (j > hi) array[k] = aux[i++]; else if (aux[j]<aux[i]) array[k] = aux[j++]; else array[k] = aux[i++]; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
注意:当数组长度为2的幂时,自顶向下和自底向上的归并排序所用的次数和数组访问的次数正好相同,只是顺序不同。其他时候,两种方法的比较和数组的访问次数会有所不同
问:归并排序的缺点是什么?
答:他是Out-place sort,因此相比快排,需要很多额外的空间。
问:为什么归并排序比快速排序慢?
答:虽然渐近复杂度一样,但是归并排序的系数比快排大。
问:对于归并排序有什么改进?
答:就是在数组长度为k时,用插入排序,因为插入排序适合对小数组排序。在算法导论思考题2-1中介绍了。复杂度为O(nk+nlg(n/k)) ,当k=O(lgn)时,复杂度为O(nlgn)
改进:
对小规模子数组采用插入排序:
因为递归会使小规模问题中方法的调用过于频繁,所以改进对它们的处理方法就能改进整个算法。使用插入排序处理小规模的子数组,一般可以将归并排序的运行时间虽短10%~15%。无代码
测试数组是否已经有序:可以添加一个判断条件,如果a[mid]小于a[mid+1],我们就任务数组已经是有序的并跳过merge方法(指的是两个sort后面的merge)。这个改动不影响排序的递归调用,但是任意有序的子数组算法的运行时间就变成线性的了。
不将元素复制到辅助数组:我们可以节省将数组复制到用于归并的辅助数组所用的时间。要做到这一点我们要调用两种排序方法,一种将数据从输入数组排序到辅助数组,一种将数据从辅助数组排序到输入数组,这种方法需要一些技巧,我们要在递归调用的每个层次交换输入数组和输出数组的角色。无代码
快速排序
特性:unstable sort、In-place sort。
最坏运行时间:当输入数组已排序时,时间为O(n^2),当然可以通过随机化来改进(shuffle array 或者 randomized select pivot),使得期望运行时间为O(nlgn)。
最佳运行时间:O(nlgn)
快速排序的思想也是分治法。
当输入数组的所有元素都一样时,不管是快速排序还是随机化快速排序的复杂度都为O(n^2),而在算法导论第三版的思考题7-2中通过改变Partition函数,从而改进复杂度为O(n)。
public class QuickSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 7, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7}; sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void sort(int[] array) { shuffle(array); sort(array, 0, array.length - 1); } private static void sort(int[] array, int lo, int hi) { if (hi<=lo) return; int j = partition(array, lo, hi); sort(array, lo, j - 1); sort(array, j+1, hi); } private static int partition(int[] array, int lo, int hi) { int i = lo; int j = hi + 1; int v = array[lo]; while (true) { while (array[++i] < v) if (i == hi) break; while (v < array[--j]) if (j == lo) break; if (i>=j) break; int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; } int temp = array[lo]; array[lo] = array[j]; array[j] = temp; return j; } /** *打乱数组 */ private static void shuffle(int[] array) { Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); if (array == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument array is null"); int n = array.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int r = i + random.nextInt(n-i); // between i and n-1 int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[r]; array[r] = temp; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
算法改进:
- 切换到插入排序
和大多数排序算法一样,改进快速排序的一个简单办法基于以下两点:
对于小数组,快速排序比插入排序慢;
因为递归,快速排序的sort()方法在小数组中也会调用自己
简单的改动:将sort中的:
if(hi<=lo) return;
- 1
改成
if(hi<=lo+M) {
Insert.sort(a,lo,hi);
return;}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 三取样切分
- 三向切分(将数组分成小于切分元素,等于切分元素和大于切分元素三组数组),代码如下:
public class Quick3way { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 7, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7}; sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void sort(int[] array) { shuffle(array); sort(array, 0, array.length - 1); } private static void sort(int[] array, int lo, int hi) { if (hi <= lo) return; int lt = lo, gt = hi; int v = array[lo]; int i = lo; while (i <= gt) { if (array[i]<v) exch(array, lt++, i++); else if (array[i]>v) exch(array, i, gt--); else i++; } // a[lo..lt-1] < v = a[lt..gt] < a[gt+1..hi]. sort(array, lo, lt-1); sort(array, gt+1, hi); } private static void exch(int[] a, int i, int j) { int swap = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = swap; } /** *打乱数组 */ private static void shuffle(int[] array) { Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); if (array == null) throw new NullPointerException("argument array is null"); int n = array.length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int r = i + random.nextInt(n-i); // between i and n-1 int temp = array[i]; array[i] = array[r]; array[r] = temp; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
堆排序
特性:unstable sort、In-place sort。
最优时间:O(nlgn)
最差时间:O(nlgn)
public class HeapSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = new int[]{2, 3, 5, 8, 9, 0, 7, 5, 1, 6, 8, 7}; sort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } public static void sort(int[] a){ int N = a.length; int[] keys = new int[N+1]; //注意,堆的数据结构是从1开始的,0不用 for (int i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) { keys[i] = a[i-1]; } // //构造堆,使得堆是有序的 for(int k = N/2;k>=1;k--) sink(keys,k,N); //排序,相当于毁掉堆 while(N>1){ exch(keys,1,N--); sink(keys,1,N); } //重新写回数组 for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { a[i] = keys[i+1]; } } private static void sink(int[] a, int k, int N) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub while(2*k<=N){ int j = 2*k; if (j < N && less(a[j], a[j+1])) j++; if (less(a[j], a[k])) break; exch(a, k, j); k = j; } } private static boolean less(int k, int j) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return k < j; } private static void exch(int[] a, int i, int n) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[n]; a[n] = temp; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
计数排序
特性:stable sort、out-place sort。
最坏情况运行时间:O(n+k)
最好情况运行时间:O(n+k)
public class CountingSort { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { int[] array = { 9, 9, 8, 8, 7, 5, 3, 2, 6, 0, 5 }; int[] sort = sort(array, 9); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort)); } /** * 输入数组的元素都是介于0..k之间的 * @param data 待排序数组 * @param k 最大元素 * @return 排序结果 */ public static int[] sort(int[] data, int k) { // 存放临时数据的数组tmp,初始元素都是0;k为数组中最大元素 int[] tmp = new int[k + 1]; // 计算数组中每个元素i出现的次数,存入数组tmp中的第i项,即原数组中的元素值为tmp数组中的下标 for (int i = 0; i <= data.length - 1; i++) { tmp[data[i]]++; } // 计算数组中小于等于每个元素的个数,即从tmp中的第一个元素开始,每一项和前一项相加 for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) { tmp[j] = tmp[j] + tmp[j - 1]; } // result数组用来来存放排序结果 int[] result = new int[data.length]; for (int i = data.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { result[tmp[data[i]] - 1] = data[i]; tmp[data[i]]--; } return result; } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
基数排序
本文假定每位的排序是计数排序。
特性:stable sort、Out-place sort。
最坏情况运行时间:O((n+k)d)
最好情况运行时间:O((n+k)d)
public class RadixSort { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] array = {3,2,3,2,5,333,45566,2345678,78,990,12,432,56}; radixSort(array,10,7); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } private static void radixSort(int[] array,int radix, int distance) { int length = array.length; int[] temp = new int[length]; int[] count = new int[radix]; int divide = 1; for (int i = 0; i < distance; i++) { System.arraycopy(array, 0,temp, 0, length); Arrays.fill(count, 0); for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) { int tempKey = (temp[j]/divide)%radix; count[tempKey]++; } for (int j = 1; j < radix; j++) { count [j] = count[j] + count[j-1]; } for (int j = length - 1; j >= 0; j--) { int tempKey = (temp[j]/divide)%radix; count[tempKey]--; array[count[tempKey]] = temp[j]; } divide = divide * radix; } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
桶排序
假设输入数组的元素都在[0,1)之间。
特性:out-place sort、stable sort。
最坏情况运行时间:当分布不均匀时,全部元素都分到一个桶中,则O(n^2),当然[算法导论8.4-2]也可以将插入排序换成堆排序、快速排序等,这样最坏情况就是O(nlgn)。
最好情况运行时间:O(n)
public class BucketSort { public static void main(String[] args) { double array[] = { 0.78, 0.17, 0.39, 0.26, 0.72, 0.94, 0.26, 0.12, 0.23, 0.68 }; bucketSort(array); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); } public static void bucketSort(double array[]) { int length = array.length; ArrayList arrList[] = new ArrayList[length]; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { //0.7到0.79放在第8个桶里,编号7;第一个桶放0到0.09 int temp = (int) Math.floor(10 * array[i]); if (null == arrList[temp]) arrList[temp] = new ArrayList(); arrList[temp].add(array[i]); } // 对每个桶中的数进行插入排序 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (null != arrList[i]) { Collections.sort(arrList[i]); } } int count = 0; for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { if (null != arrList[i]) { Iterator iter = arrList[i].iterator(); while (iter.hasNext()) { Double d = (Double) iter.next(); array[count] = d; count++; } } } } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37



