- 1详细剖析Oracle、SOA、OSB结构原理_oracle-osb 视频
- 2芒果植户种植决策系统:基于python爬虫苹果电商销售数据可视化分析(django框架)_基于python数据分析web可视化国内外研究现状
- 3SpringBoot集成开源IM框架MobileIMSDK,实现即时通讯IM聊天功能_im聊天开源框架
- 4【JDK】Mac版安装JDK并配置环境_mac 安装jdk
- 5基于Android的综合社交APP设计与实现_基于android的app的设计与开发
- 6spring cloud 配置中心客户端启动问题_located property source卡住
- 7【C++】2023年数学建模国赛C题87万条数据处理(附源码)_2023数学建模c题代码
- 8YOLOv8检测、分割和分类训练自己数据集_yolov8下载
- 9大数据可视化项目—基于Python豆瓣电影数据可视化分析系统的设计与实现(完整系统源码+数据库+详细文档+论文+部署教程)_基于python的电影数据分析
- 10手把手教你用Python实现2048小游戏_python2048所有添加步骤
yolov8实战第三天——yolov8TensorRT部署(python推理)(保姆教学)_yolov8 tensorrt python
赞
踩
在上一篇中我们使用自己的数据集训练了一个yolov8检测模型,best.py。
yolov8实战第一天——yolov8部署并训练自己的数据集(保姆式教程)-CSDN博客
yolov8实战第二天——yolov8训练结果分析(保姆式解读)-CSDN博客
接下要对best.py进行TensorRT优化并部署。
TensorRT是一种高性能深度学习推理优化器和运行时加速库,可以为深度学习应用提供低延迟、高吞吐率的部署推理。
TensorRT可用于对超大规模数据中心、嵌入式平台或自动驾驶平台进行推理加速。
TensorRT现已能支持TensorFlow、Caffe、Mxnet、Pytorch等几乎所有的深度学习框架,将TensorRT和NVIDIA的GPU结合起来,能在几乎所有的框架中进行快速和高效的部署推理。
一般的深度学习项目,训练时为了加快速度,会使用多GPU分布式训练。但在部署推理时,为了降低成本,往往使用单个GPU机器甚至嵌入式平台(比如 NVIDIA Jetson)进行部署,部署端也要有与训练时相同的深度学习环境,如caffe,TensorFlow等。
由于训练的网络模型可能会很大(比如,inception,resnet等),参数很多,而且部署端的机器性能存在差异,就会导致推理速度慢,延迟高。这对于那些高实时性的应用场合是致命的,比如自动驾驶要求实时目标检测,目标追踪等。
为了提高部署推理的速度,出现了很多模型优化的方法,如:模型压缩、剪枝、量化、知识蒸馏等,这些一般都是在训练阶段实现优化。
而TensorRT 则是对训练好的模型进行优化,通过优化网络计算图提高模型效率。
一、安装TensorRT
下载TensorRT 。
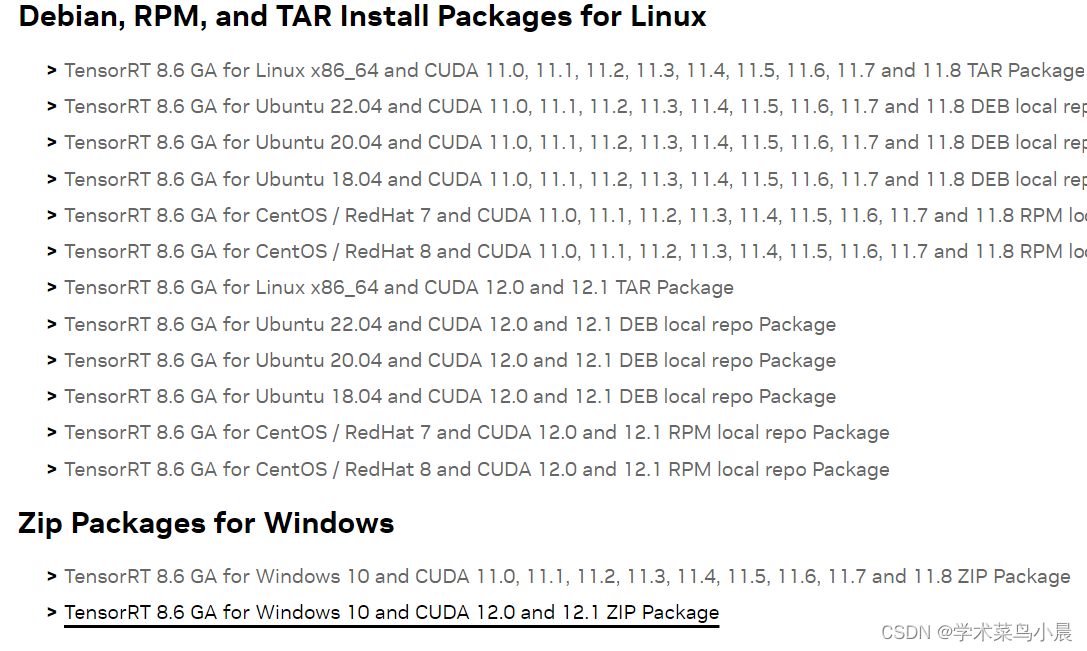
我下载的是8.6里画黑线的那个。
将 TensorRT-8.6.1.6\include中头文件 copy 到C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.7\include
将TensorRT-8.6.1.6\lib 中所有lib文件 copy 到C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.7\lib\x64
将TensorRT-8.6.1.6\lib 中所有dll文件copy 到C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v11.7\bin
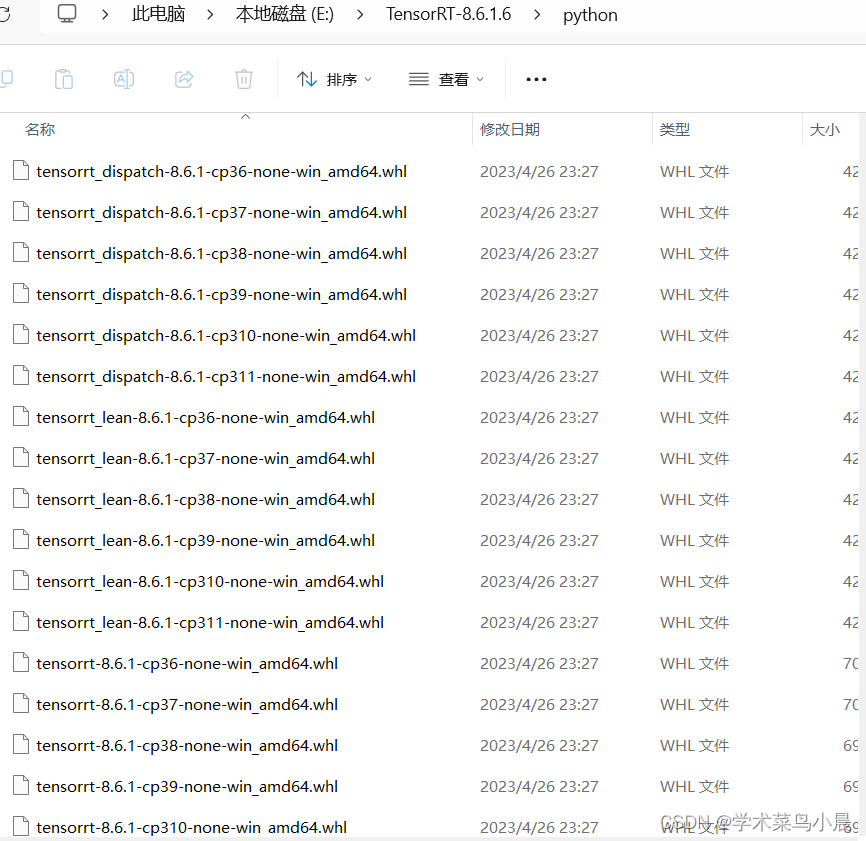
在python文件夹中找到适合自己的。
pip install tensorrt-8.6.1-cp310-none-win_amd64.whl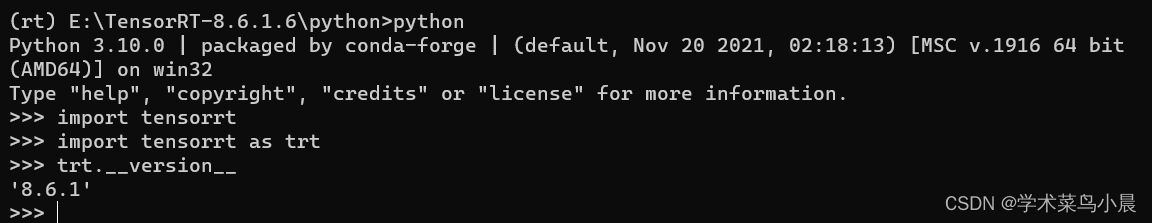 至此TensorRT安装完成。
至此TensorRT安装完成。
二、pt转onnx:
GitHub - triple-Mu/YOLOv8-TensorRT: YOLOv8 using TensorRT accelerate !
参考着这个,下载,安装环境后。
安装onnx:
- pip install onnx -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
- pip install onnxsim -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
- pip install onnxruntime -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
生成onnx:
python export-det.py --weights yolov8n.pt --iou-thres 0.65 --conf-thres 0.25 --topk 100 --opset 11 --sim --input-shape 1 3 640 640 --device cuda:0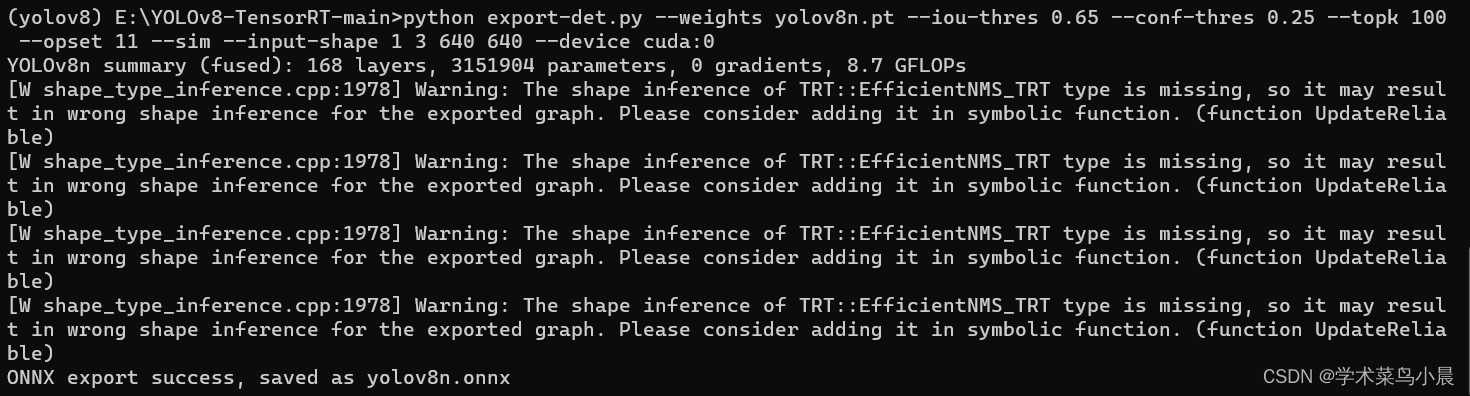
使用上篇文章中的老鼠模型做了测试:
onnx的测试代码:
- import onnxruntime as rt
- import numpy as np
- import cv2
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-
- def nms(pred, conf_thres, iou_thres):
- conf = pred[..., 4] > conf_thres
- box = pred[conf == True]
- cls_conf = box[..., 5:]
- cls = []
- for i in range(len(cls_conf)):
- cls.append(int(np.argmax(cls_conf[i])))
- total_cls = list(set(cls))
- output_box = []
- for i in range(len(total_cls)):
- clss = total_cls[i]
- cls_box = []
- for j in range(len(cls)):
- if cls[j] == clss:
- box[j][5] = clss
- cls_box.append(box[j][:6])
- cls_box = np.array(cls_box)
- box_conf = cls_box[..., 4]
- box_conf_sort = np.argsort(box_conf)
- max_conf_box = cls_box[box_conf_sort[len(box_conf) - 1]]
- output_box.append(max_conf_box)
- cls_box = np.delete(cls_box, 0, 0)
- while len(cls_box) > 0:
- max_conf_box = output_box[len(output_box) - 1]
- del_index = []
- for j in range(len(cls_box)):
- current_box = cls_box[j]
- interArea = getInter(max_conf_box, current_box)
- iou = getIou(max_conf_box, current_box, interArea)
- if iou > iou_thres:
- del_index.append(j)
- cls_box = np.delete(cls_box, del_index, 0)
- if len(cls_box) > 0:
- output_box.append(cls_box[0])
- cls_box = np.delete(cls_box, 0, 0)
- return output_box
-
-
- def getIou(box1, box2, inter_area):
- box1_area = box1[2] * box1[3]
- box2_area = box2[2] * box2[3]
- union = box1_area + box2_area - inter_area
- iou = inter_area / union
- return iou
-
-
- def getInter(box1, box2):
- box1_x1, box1_y1, box1_x2, box1_y2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, \
- box1[0] + box1[2] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
- box2_x1, box2_y1, box2_x2, box2_y2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[1] - box1[3] / 2, \
- box2[0] + box2[2] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
- if box1_x1 > box2_x2 or box1_x2 < box2_x1:
- return 0
- if box1_y1 > box2_y2 or box1_y2 < box2_y1:
- return 0
- x_list = [box1_x1, box1_x2, box2_x1, box2_x2]
- x_list = np.sort(x_list)
- x_inter = x_list[2] - x_list[1]
- y_list = [box1_y1, box1_y2, box2_y1, box2_y2]
- y_list = np.sort(y_list)
- y_inter = y_list[2] - y_list[1]
- inter = x_inter * y_inter
- return inter
-
-
- def draw(img, xscale, yscale, pred):
- img_ = img.copy()
- if len(pred):
- for detect in pred:
- detect = [int((detect[0] - detect[2] / 2) * xscale), int((detect[1] - detect[3] / 2) * yscale),
- int((detect[0]+detect[2] / 2) * xscale), int((detect[1]+detect[3] / 2) * yscale)]
- img_ = cv2.rectangle(img, (detect[0], detect[1]), (detect[2], detect[3]), (0, 255, 0), 1)
- return img_
-
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- height, width = 640, 640
- img0 = cv2.imread('mouse-4-6-0004.jpg')
- x_scale = img0.shape[1] / width
- y_scale = img0.shape[0] / height
- img = img0 / 255.
- img = cv2.resize(img, (width, height))
- img = np.transpose(img, (2, 0, 1))
- data = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
- sess = rt.InferenceSession('best.onnx')
- input_name = sess.get_inputs()[0].name
- label_name = sess.get_outputs()[0].name
- pred = sess.run([label_name], {input_name: data.astype(np.float32)})[0]
- pred = np.squeeze(pred)
- pred = np.transpose(pred, (1, 0))
- pred_class = pred[..., 4:]
- pred_conf = np.max(pred_class, axis=-1)
- pred = np.insert(pred, 4, pred_conf, axis=-1)
- result = nms(pred, 0.3, 0.45)
- ret_img = draw(img0, x_scale, y_scale, result)
- ret_img = ret_img[:, :, ::-1]
- plt.imshow(ret_img)
- plt.show()
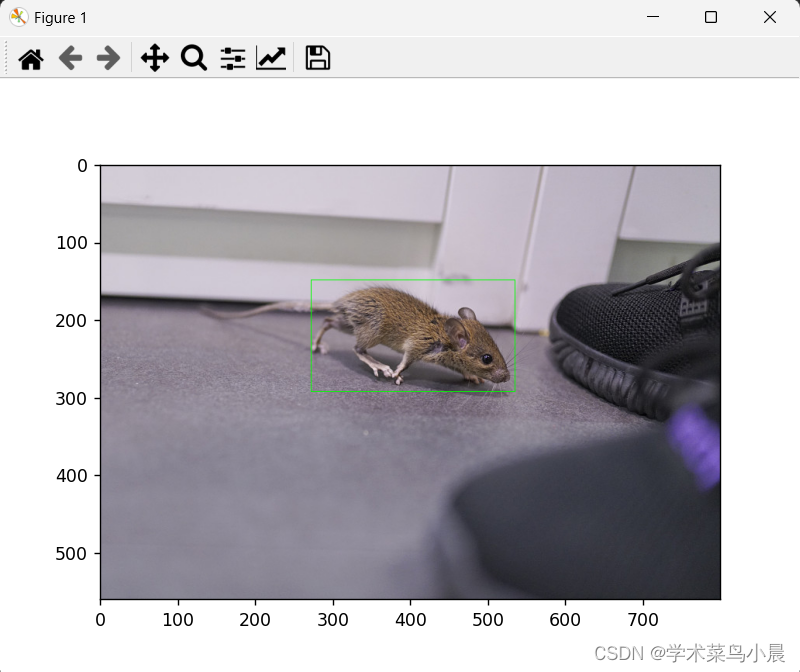
三、TensorRT部署
导出engine模型:
python build.py --weights yolov8n.onnx --iou-thres 0.65 --conf-thres 0.25 --topk 100 --fp16 --device cuda:0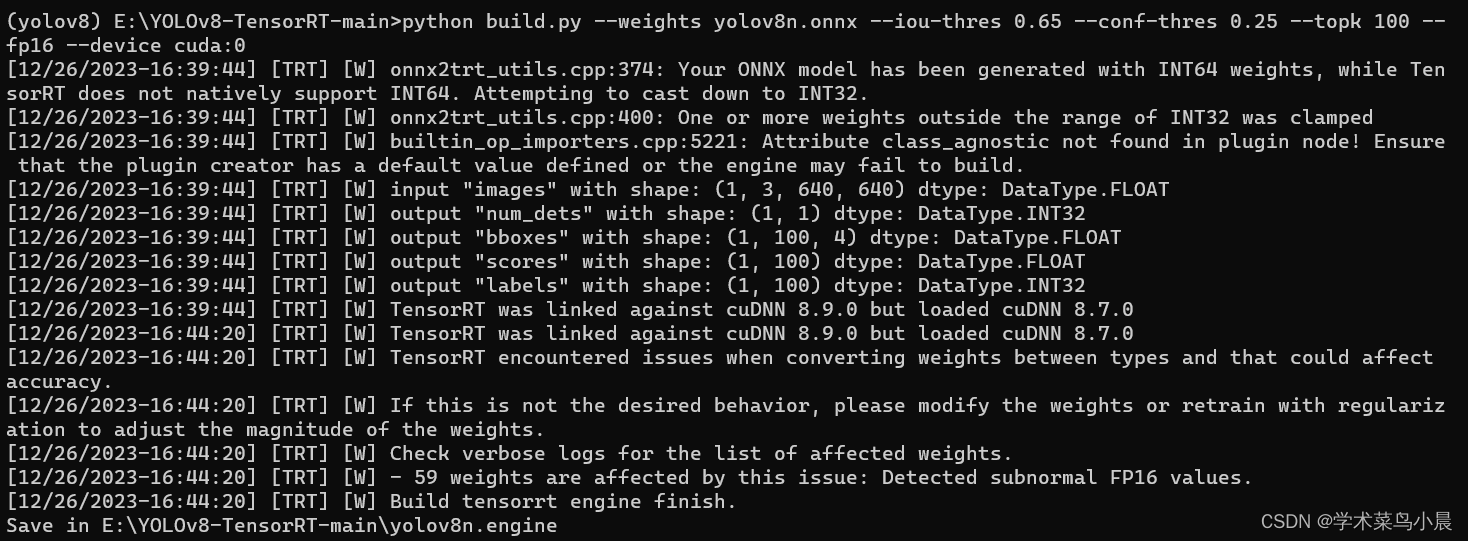
等待一会,engine成功导出。
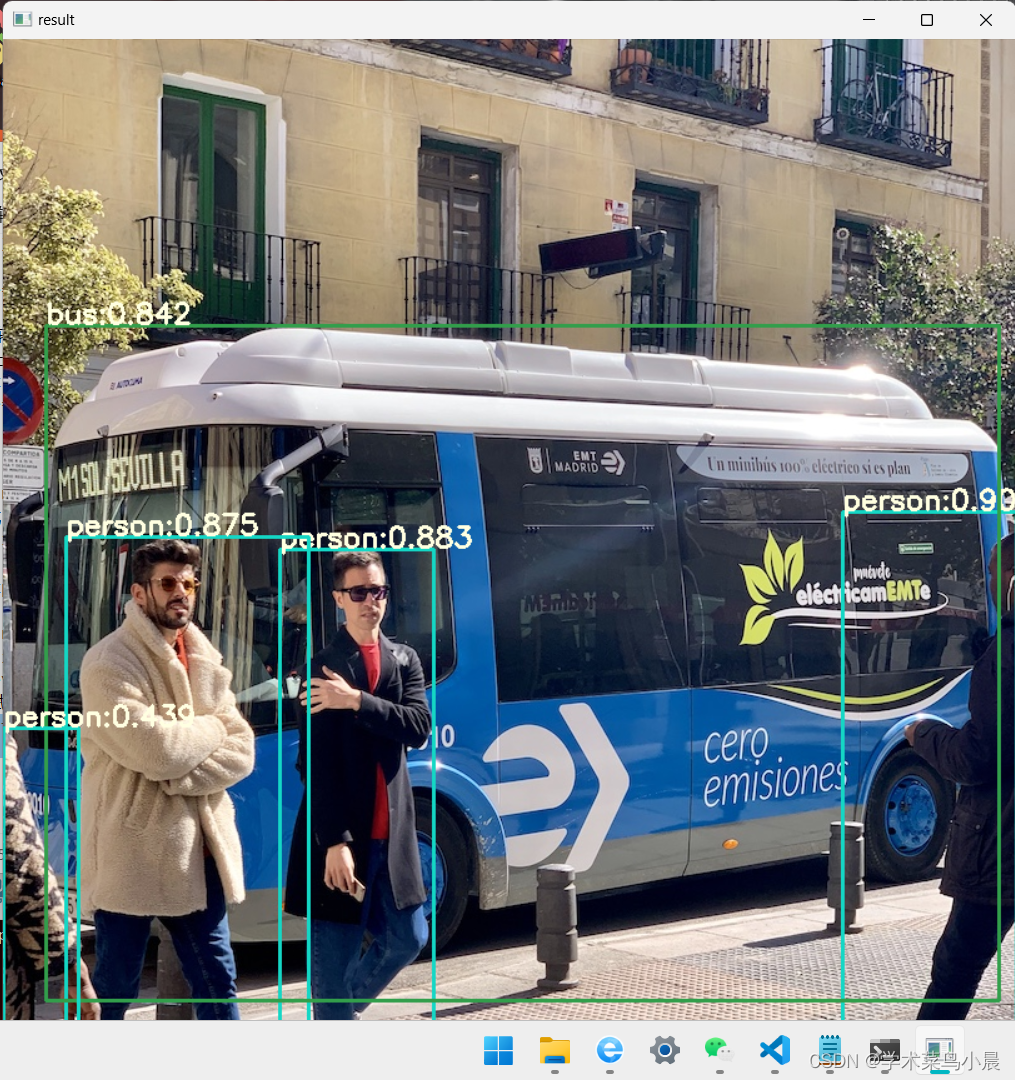
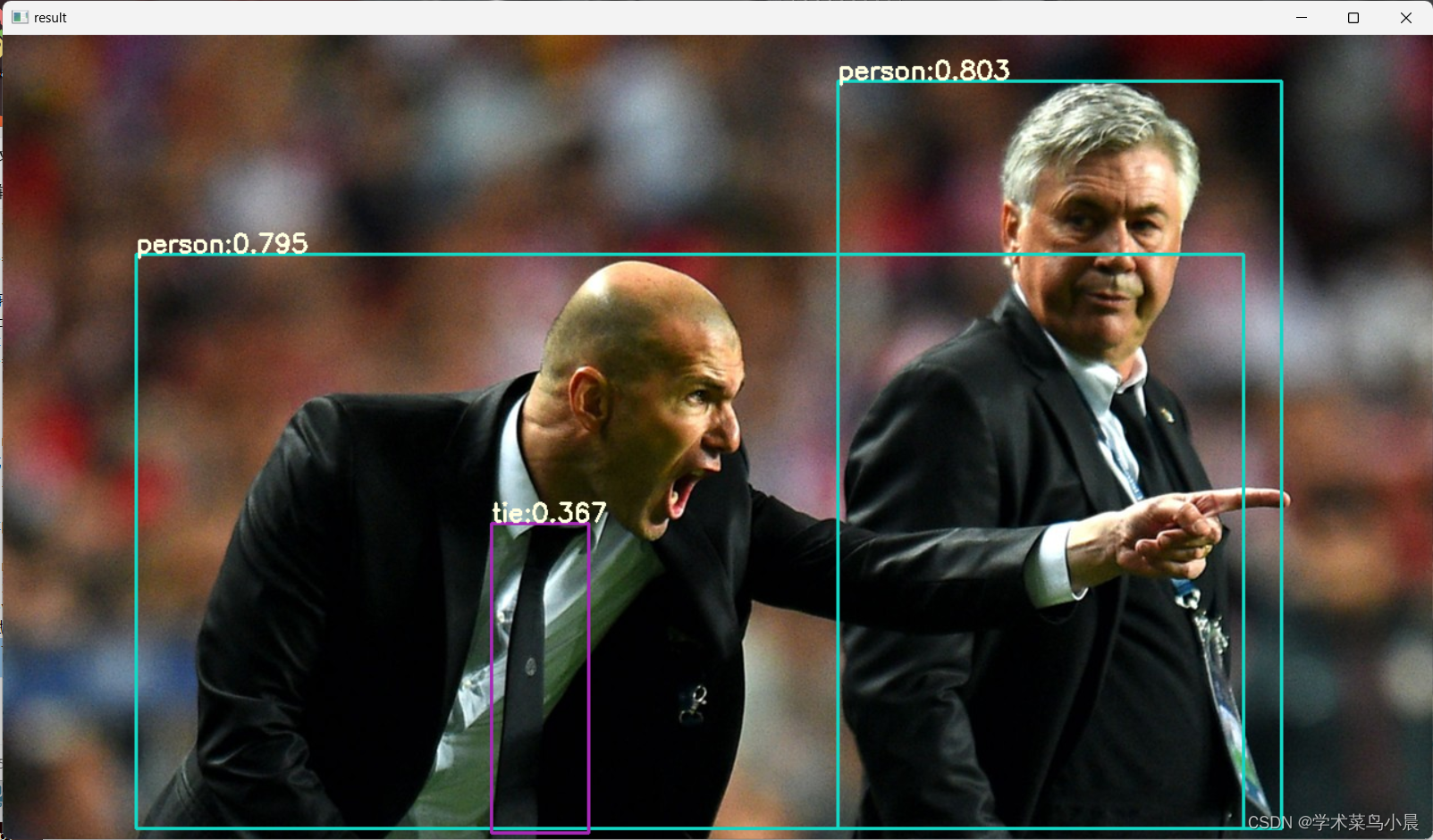
使用python脚本进行推理:
python infer-det.py --engine yolov8n.engine --imgs data --show --out-dir outputs --out-dir outputs --device cuda:0infer-det.py:
- from models import TRTModule # isort:skip
- import argparse
- from pathlib import Path
-
- import cv2
- import torch
-
- from config import CLASSES, COLORS
- from models.torch_utils import det_postprocess
- from models.utils import blob, letterbox, path_to_list
-
-
- def main(args: argparse.Namespace) -> None:
- device = torch.device(args.device)
- Engine = TRTModule(args.engine, device)
- H, W = Engine.inp_info[0].shape[-2:]
-
- # set desired output names order
- Engine.set_desired(['num_dets', 'bboxes', 'scores', 'labels'])
-
- images = path_to_list(args.imgs)
- save_path = Path(args.out_dir)
-
- if not args.show and not save_path.exists():
- save_path.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
-
- for image in images:
- save_image = save_path / image.name
- bgr = cv2.imread(str(image))
- draw = bgr.copy()
- bgr, ratio, dwdh = letterbox(bgr, (W, H))
- rgb = cv2.cvtColor(bgr, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
- tensor = blob(rgb, return_seg=False)
- dwdh = torch.asarray(dwdh * 2, dtype=torch.float32, device=device)
- tensor = torch.asarray(tensor, device=device)
- # inference
- data = Engine(tensor)
-
- bboxes, scores, labels = det_postprocess(data)
- if bboxes.numel() == 0:
- # if no bounding box
- print(f'{image}: no object!')
- continue
- bboxes -= dwdh
- bboxes /= ratio
-
- for (bbox, score, label) in zip(bboxes, scores, labels):
- bbox = bbox.round().int().tolist()
- cls_id = int(label)
- cls = CLASSES[cls_id]
- color = COLORS[cls]
- cv2.rectangle(draw, bbox[:2], bbox[2:], color, 2)
- cv2.putText(draw,
- f'{cls}:{score:.3f}', (bbox[0], bbox[1] - 2),
- cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
- 0.75, [225, 255, 255],
- thickness=2)
- if args.show:
- cv2.imshow('result', draw)
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- else:
- cv2.imwrite(str(save_image), draw)
-
-
- def parse_args() -> argparse.Namespace:
- parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
- parser.add_argument('--engine', type=str, help='Engine file')
- parser.add_argument('--imgs', type=str, help='Images file')
- parser.add_argument('--show',
- action='store_true',
- help='Show the detection results')
- parser.add_argument('--out-dir',
- type=str,
- default='./output',
- help='Path to output file')
- parser.add_argument('--device',
- type=str,
- default='cuda:0',
- help='TensorRT infer device')
- args = parser.parse_args()
- return args
-
-
- if __name__ == '__main__':
- args = parse_args()
- main(args)