- 1Unity2D教程:单例模式、SceneManager.LoadSceneAsync场景切换、Loading界面进度条
- 2mysql undo表空间_MySQL UNDO表空间独立和截断
- 3Chatgpt这么智能,以后会不会取代掉人类?_chatgpt是否会代替人类的大脑
- 4计算机设计大赛 深度学习人体语义分割在弹幕防遮挡上的实现 - python
- 5windows7装python哪个版本好,win7安装哪个版本的python_pycharm win7适配版本
- 6UE4蓝图基础入门(一)变量与蓝图_ue setmenbersin
- 7ChatGPT-4和ChatGPT-3.5知识库截止日期竟然一样?_gpt4数据库截止日期
- 8Unity——InputSystem入门及部分问题讲解_unity inputsystem
- 9python库turtle的双画笔并发绘制兔兔 表白神器_pythonturtle画小白兔
- 10Rabbitmq学习之路3-cluster_rabbitmqctl join_cluster --ram
大模型提效105篇必读论文和代码汇总,涵盖预训练、注意力、微调等7个方向_h2o: heavy-hitter oracle for efficient generative
赞
踩
大型语言模型(LLMs)在NLP领域中具有显著的优势,它们在语言理解和生成方面表现出了强大的能力,甚至可以进行复杂的推理任务。这些能力能让大模型在许多领域都有广泛的应用前景,比如文本生成、对话系统、机器翻译、情感分析等。然而,随着模型规模的增大,所需的计算资源和存储空间也急剧增加...压力于是给到了模型的训练、部署和运行。
因此,我们对于大模型效率的追求越来越高,更多人专注于开发有效技术以提高LLMs的效率。为帮助同学们在这个领域做出自己的创新,我这次就整理了对高效LLMs研究的一些成果来和各位分享,爆肝了105篇,主要从模型和数据两个方面入手,并且细分了7个方向。
全部论文和代码看文末
以模型为中心的方法
模型压缩
SparseGPT: Massive Language models can be accurate pruned in one-shot
大规模语言模型可以在一次操作中精确剪枝
「方法简述:」论文首次展示了一种名为SparseGPT的新方法,可以在一次操作中将大规模语言模型剪枝到至少50%的稀疏度,而无需重新训练,同时保持较小的精度损失。这种方法可以在不到4.5小时内在最大的开源模型OPT-175B和BLOOM-176B上执行,并且可以达到60%的非结构化稀疏度,同时困惑度几乎没有增加。SparseGPT可以应用于半结构化模式,并与权重量化方法兼容。

OPTQ: Accurate Quantization for Generative Pre-trained Transformers
生成式预训练 Transformer 的精确量化
「方法简述:」论文提出了一种名为OPTQ的新方法,可以在一个GPU上对大型语言模型进行高效的压缩。该方法基于近似二阶信息进行一次性权重量化,可以将1750亿个参数的GPT模型压缩到每个权重只有3或4位,同时保持了较高的精度。相对于先前的方法,该压缩方法可以提高2倍以上的压缩增益,并且可以在高端和成本效益更高的GPU上实现端到端推理速度的提高。

Towards the Law of Capacity Gap in Distilling Language Models
迈向蒸馏语言模型能力差距的规律
「方法简述:」Language model distillation是一种将大型教师模型的知识蒸馏到小型学生模型的方法。但是,当教师和学生模型之间的容量差距较大时,这种方法很困难。这是因为较大的教师模型并不总是能产生比从较小的教师模型蒸馏出来的更好的学生模型。本文发现,在不同的学生规模和架构中,最佳的容量差距几乎是一致的,这被称为容量差距定律。该定律指导我们从7B教师模型蒸馏出一个3B的学生模型(MiniMA),并在基准测试中表现出色。

-
LLM-Pruner: On the Structural Pruning of Large Language Models
-
QuIP: 2-bit quantization of large language models with guarantees
-
AWQ: Activation-aware Weight Quantization for LLM Compression and Acceleration
-
OWQ: Lessons Learned from Activation Outliers for Weight Quantization in Large Language Models
-
SpQR: A Sparse-Quantized Representation for Near-Lossless LLM Weight Compression
-
FineQuant: Unlocking Efficiency with Fine-Grained Weight-Only Quantization for LLMs
-
ZeroQuant-V2: Exploring Post-training Quantization in LLMs from Comprehensive Study to Low Rank Compensation
-
ZeroQuant-FP: A Leap Forward in LLMs Post-Training W4A8 Quantization Using Floating-Point Formats
-
OliVe: Accelerating Large Language Models via Hardware-friendly Outlier-Victim Pair Quantization
-
RPTQ: Reorder-based Post-training Quantization for Large Language Models
-
Outlier Suppression+: Accurate Quantization of Large Language Models by Equivalent and Optimal Shift and Scaling
-
QLLM: Accurate and Efficient Low-Bitwidth Quantization for Large Language Models
-
SmoothQuant: Accurate and Efficient Post-Training Quantization for Large Language Models
-
LLM-QAT: Data-Free Quantization Aware Training for Large Language Models
-
LoRAShear: Efficient Large Language Model Structured Pruning and Knowledge Recovery
-
Sheared LLaMA: Accelerating Language Model Pre-training via Structured Pruning
-
LoRAPrune: Pruning meets Low-Rank Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
-
A Simple and Effective Pruning Approach for Large Language Models
-
One-Shot Sensitivity-Aware Mixed Sparsity Pruning for Large Language Models
-
TensorGPT: Efficient Compression of the Embedding Layer in LLMs based on the Tensor-Train Decomposition
-
LoSparse: Structured Compression of Large Language Models based on Low-Rank and Sparse Approximation
-
Baby Llama: Knowledge Distillation from an Ensemble of Teachers Trained on a Small Dataset with no Performance Asset
-
GKD: Generalized Knowledge Distillation for Auto-regressive Sequence Models
-
Token-Scaled Logit Distillation for Ternary Weight Generative Language Models
-
Lion: Adversarial Distillation of Closed-Source Large Language Model
-
Specializing Smaller Language Models towards Multi-Step Reasoning
-
SCOTT: Self-Consistent Chain-of-Thought Distillation
-
Distilling Reasoning Capabilities into Smaller Language Models
高效预训练
Learning to Grow Pretrained Models for Efficient Transformer Training
学习为高效的 transformer 训练预训练模型
「方法简述:」论文提出了一种加速Transformer训练的方法,通过学习如何生长预训练的Transformer模型。具体来说,作者将小模型的参数线性映射到大模型中进行初始化。为了易于学习,作者将线性变换分解为宽度和深度增长操作符的组合,并进一步使用这些增长操作符的克罗内克分解来编码架构知识。在语言和视觉Transformers上的大量实验表明,作者学习的线性增长操作符(LiGO)可以节省高达50%从零开始训练的计算成本,同时始终优于强基线,这些基线也重用较小的预训练模型来初始化更大的模型。
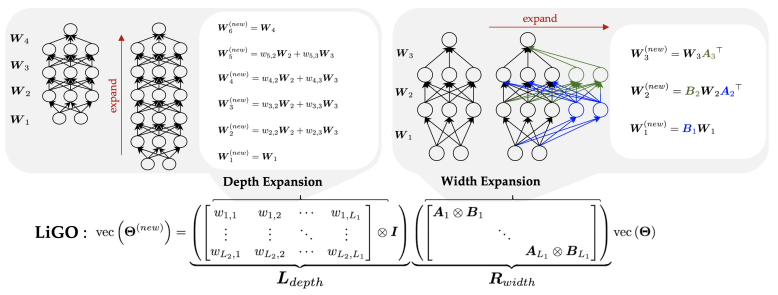
-
Reusing Pretrained Models by Multi-linear Operators for Efficient Training
-
FLM-101B: An Open LLM and How to Train It with $100 K Budget
-
Symbolic Discovery of Optimization Algorithms
-
Sophia: A Scalable Stochastic Second-order Optimizer for Language Model Pre-training
高效微调
OpenDelta: A Plug-and-play Library for Parameter-efficient Adaptation of Pre-trained Models
用于预训练模型参数高效自适应的即插即用库
「方法简述:」论文介绍了一种名为OpenDelta的开源库,用于解决大型预训练模型(PTMs)适应下游任务的挑战。OpenDelta是一个即插即用的库,提供了各种delta tuning方法的实现。该创新技术消除了修改骨干PTM代码的需求,使OpenDelta能够与不同的甚至新的PTM兼容。OpenDelta旨在简单、模块化和可扩展,为研究人员和从业者提供了一个高效的平台来适应大型PTMs。
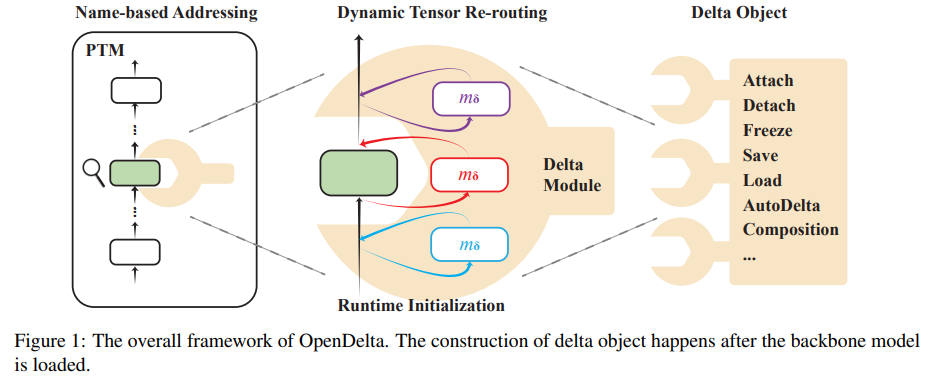
-
LLM-Adapters: An Adapter Family for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
-
Compacter: Efficient Low-Rank Hypercomplex Adapter Layers
-
LoRA-FA: Memory-efficient Low-rank Adaptation for Large Language Models Fine-tuning
-
LoraHub: Efficient Cross-Task Generalization via Dynamic LoRA Composition
-
LongLoRA: Efficient Fine-tuning of Long-Context Large Language Models
-
Multi-Head Adapter Routing for Cross-Task Generalization
-
Adaptive Budget Allocation for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
-
DyLoRA: Parameter-Efficient Tuning of Pretrained Models using Dynamic Search-Free Low Rank Adaptation
-
Tied-Lora: Enhacing Parameter Efficiency of LoRA with Weight Tying
-
LLaMA-Adapter: Efficient Fine-tuning of Language Models with Zero-init Attention
-
Compress, Then Prompt: Improving Accuracy-Efficiency Trade-off of LLM Inference with Transferable Prompt
-
Multi-Task Pre-Training of Modular Prompt for Few-Shot Learning
-
Multitask Prompt Tuning Enables Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning
-
Winner-Take-All Column Row Sampling for Memory Efficient Adaptation of Language Model
-
Memory-Efficient Selective Fine-Tuning
-
Full Parameter Fine-tuning for Large Language Models with Limited Resources
-
Fine-Tuning Language Models with Just Forward Passes
-
Memory-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Compressed Large Language Models via sub-4-bit Integer Quantization
-
LoftQ: LoRA-Fine-Tuning-Aware Quantization for Large Language Models
-
QA-LoRA: Quantization-Aware Low-Rank Adaptation of Large Language Models
-
QLoRA: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs
有效推理
Accelerating Transformer Inference for Translation via Parallel Decoding
通过并行解码加速Transformer翻译推理
「方法简述:」论文提出了一种加速Transformer翻译推理的方法,通过并行解码来解决自回归解码限制了Transformer在机器翻译(MT)中效率的问题。作者提出了三种并行解码算法,并在不同的语言和模型上进行了测试,结果表明并行化可以将速度提高多达38%相对于标准的自回归解码,并且在并行资源上扩展该方法时几乎提高了2倍。最后,作者引入了一个解码依赖图可视化工具(DDGviz),可以让我们了解模型如何学习标记之间的条件依赖性并检查解码过程。

-
PaSS: Parallel Speculative Sampling
-
Medusa: Simple Framework for Accelerating LLM Generation with Multiple Decoding Heads
-
Fast Inference from Transformers via Speculative Decoding
-
Accelerating LLM Inference with Staged Speculative Decoding
-
Accelerating Large Language Model Decoding with Speculative Sampling
-
Speculative Decoding with Big Little Decoder
-
SpecInfer: Accelerating Generative LLM Serving with Speculative Inference and Token Tree Verification
-
Inference with Reference: Lossless Acceleration of Large Language Models
-
Model Tells You What to Discard: Adaptive KV Cache Compression for LLMs
-
SkipDecode: Autoregressive Skip Decoding with Batching and Caching for Efficient LLM Inference
-
H2O: Heavy-Hitter Oracle for Efficient Generative Inference of Large Language Models
-
Scissorhands: Exploiting the Persistence of Importance Hypothesis for LLM KV Cache Compression at Test Time
-
Dynamic Context Pruning for Efficient and Interpretable Autoregressive Transformers
体系结构
「高效注意力」
GQA: Training Generalized Multi-Query Transformer Models from Multi-Head Checkpoints
从多头检查点训练通用多查询Transformer模型
「方法简述:」本文提出了一种名为grouped-query attention(GQA)的方法,是对多查询注意力(MQA)的一种泛化。与仅使用单个键值头的MQA相比,GQA使用中间数量的键值头(多于一个,少于查询头的数量),可以在不降低翻译质量的情况下大大提高解码器的推理速度。作者还提出了一种将现有的多头语言模型检查点上训练为具有MQA的模型的方法,并展示了经过上训练的GQA在速度上与MQA相当,在质量上接近多头注意力。

-
Sumformer: Universal Approximation for Efficient Transformers
-
FLuRKA: Fast fused Low-Rank & Kernel Attention
-
Faster Causal Attention Over Large Sequences Through Sparse Flash Attention
-
HyperAttention: Long-context Attention in Near-Linear Time
「混合专家」
-
PanGu-Σ: Towards Trillion Parameter Language Model with Sparse Heterogeneous Computing
-
Mixture-of-Experts Meets Instruction Tuning:A Winning Combination for Large Language Models
以数据为中心的方法
数据选择
Data-Efficient Finetuning Using Cross-Task Nearest Neighbors
使用跨任务最近邻进行数据高效微调
「方法简述:」论文提出了一种名为cross-task nearest neighbors的方法,用于从大量多任务数据中检索与目标任务最相似的已标记示例,以进行高效的微调。该方法使用少量未标记的目标任务示例来检索最相似的已标记示例,从而避免了在统一采样的提示多任务数据上微调模型的做法。实验结果表明,使用这种方法微调的模型比使用其他方法微调的模型表现更好,并且可以提供更好的初始化,以便在目标任务数据上进行少样本微调。
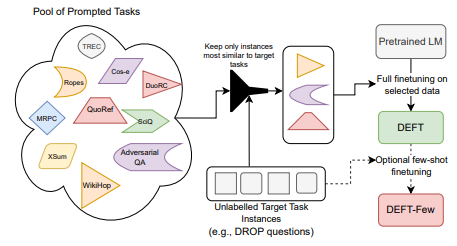
-
Data Selection for Language Models via Importance Resampling
-
MoDS: Model-oriented Data Selection for Instruction Tuning
-
Instruction Mining: When Data Mining Meets Large Language Model Finetuning
-
Data Selection for Fine-tuning Large Language Models Using Transferred Shapley Values
-
Maybe Only 0.5% Data is Needed: A Preliminary Exploration of Low Training Data Instruction Tuning
-
AlpaGasus: Training A Better Alpaca with Fewer Data
-
LIMA: Less Is More for Alignment
提示工程
Unified Demonstration Retriever for In-Context Learning
上下文学习的统一演示检索器
「方法简述:」论文提出了一种名为Unified Demonstration Retriever(UDR)的方法,用于检索各种任务的演示。该方法将不同任务的训练信号转换为语言模型反馈的统一列表级排名形式,并使用多任务列表级排名训练框架进行训练。实验结果表明,UDR在不同场景下表现出色,包括不同的语言模型、未见过的数据集合、不同的演示数量等。
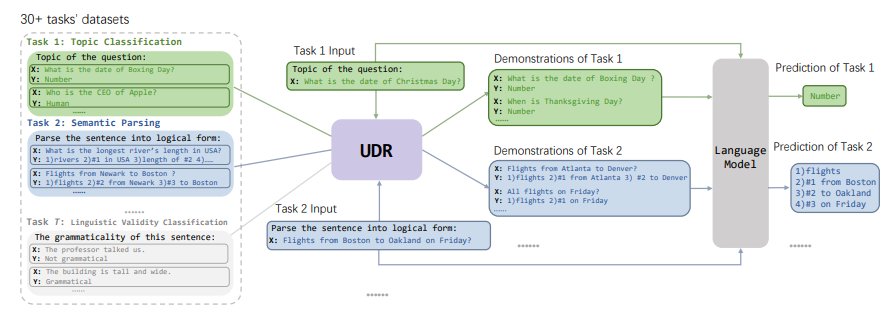
Adapting Language Models to Compress Contexts
调整语言模型以压缩上下文
「方法简述:」论文提出了AutoCompressors方法,用于将预训练的语言模型适应为能够压缩长上下文的模型。这些语言模型可以将长上下文压缩成简洁的摘要向量,然后作为软提示提供给模型使用。作者通过微调OPT和Llama-2模型,展示了AutoCompressors可以利用长上下文来提高困惑度的能力。在上下文学习中,作者发现摘要向量是纯文本演示文稿的良好替代品,可以提高准确性并降低推理成本。最后,作者探索了预先计算大型语料库摘要向量的好处,并将其应用于检索增强的语言建模和段落重排任务。
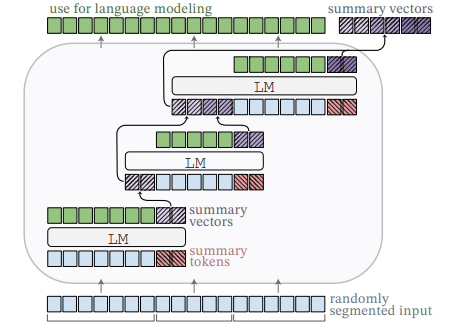
-
Large Language Models Are Latent Variable Models: Explaining and Finding Good Demonstrations for In-Context Learning
-
Self-Adaptive In-Context Learning: An Information Compression Perspective for In-Context Example Selection and Ordering
-
Selective Annotation Makes Language Models Better Few-Shot Learners
-
Instruction Induction: From Few Examples to Natural Language Task Descriptions
-
TeGit: Generating High-Quality Instruction-Tuning Data with Text-Grounded Task Design
-
Self-Instruct: Aligning Language Model with Self Generated Instructions
-
Measuring and Narrowing the Compositionality Gap in Language Models
-
ReAct: Synergizing Reasoning and Acting in Language Models
-
Least-to-Most Prompting enables complex reasoning in large language models
-
Graph of Thoughts: Solving Elaborate Problems with Large Language Models
-
Self-Consistency Improves Chain of Thinking Reasoning in Language Models
-
Graph of Thoughts: Solving Elaborate Problems with Large Language Models
-
Contrastive Chain-of-Thought Prompting
-
LongLLMLingua: Accelerating and Enhancing LLMs in Long Context Scenarios via Prompt Compression
-
Discrete Prompt Compression with Reinforcement Learning
-
Nugget 2D: Dynamic Contextual Compression for Scaling Decoder-only Language Models
关注下方《学姐带你玩AI》 本文内容由网友自发贡献,转载请注明出处:【wpsshop博客】
Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。


