- 1STM32--基于STM32F103的MAX30102心率血氧测量_stm32与max30102链接图
- 2fastllm移植到Windows加快LLM推理_fastllm windows部署
- 3substance designer制作全景图_substance designe教程
- 4android中设置默认语言、默认时区 1_android 默认时区
- 5ubuntu实战001:将ISO文件挂载配置成apt本地源_ubuntu18配置iso本地apt源
- 6HIDL 原理及使用详解
- 7《PyTorch机器学习从入门到实战》 例程(PyTorch1.2版本可用)_pytorch例程
- 8AIDL打造双进程通讯 模拟跳转三方APK登录Demo_android aidl 跳转到activity
- 9pytest不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序 或批处理文件【已解决】
- 10linux运行bat文件命令_让Linux终端同时运行多个Linux命令
NLP的核心:十大最流行的NLP技术深度解析。_nlp前沿技术
赞
踩
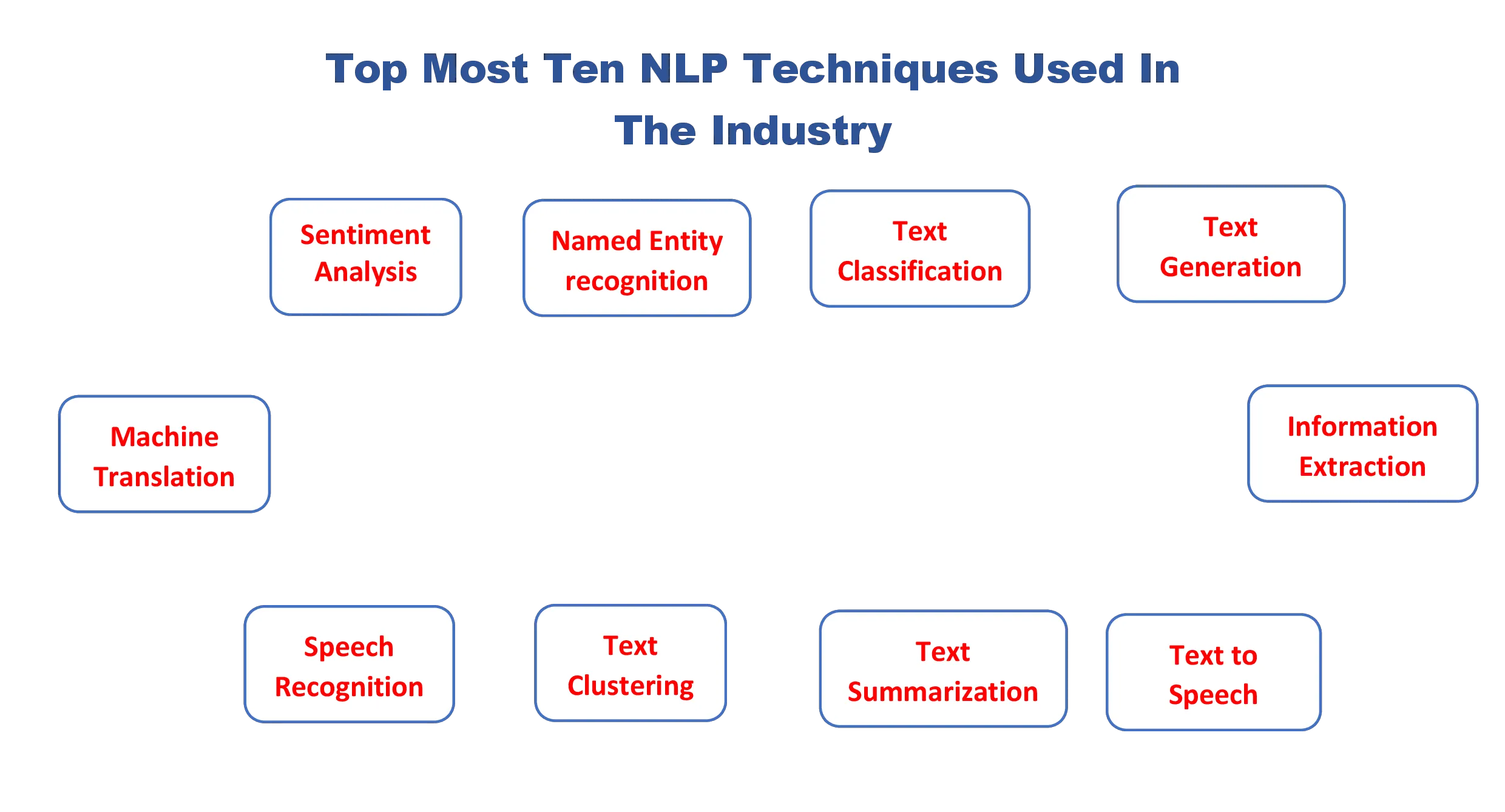
一、情感分析
情感分析是一种判断文本背后情绪色彩的过程,例如推特、产品评论或客户反馈。
情感分析的目标是将文本分类为正面、负面或中性。例如,如果客户写了一篇产品评论,说“非常棒,小孩子很喜欢”,情感分析算法会将文本分类为正面。情感分析广泛应用于电子商务、社交媒体和客户服务等行业,以深入了解客户的意见和偏好。
执行情感分析的一种方式是使用预训练模型,比如Python的nltk库提供的模型。以下是如何使用nltk库将一段文本的情感分类为正面、负面或中性的例子:
import nltk from nltk.sentiment import SentimentIntensityAnalyzer # 初始化情感分析器 sia = SentimentIntensityAnalyzer() # 定义要分析的文本 text = "非常棒,小孩子很喜欢" # 获取情感分数 sentiment_score = sia.polarity_scores(text) # 打印情感得分 print (sentiment_score) # 将情绪分类为正面、负面或中性 ifentiment_score [ 'compound' ] > 0.5 : print ( "Positiveentiment" ) elif情感_score[ 'compound'] < - 0.5 : print ( "Negative sentiment" ) else : print ( "Neutral sentiment" )
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
此例子使用了nltk.sentiment模块中的SentimentIntensityAnalyzer类来分析文本 "我喜欢这个产品,它太棒了"的情绪。polarity_scores()方法返回一个包含文本情绪分数的字典,其中’compound’分数是一个介于-1和1之间的值,-1表示负面,1表示正面,0表示中性。基于compound分数,我们可以将情感分类为正面、负面或中性。
需要注意,这只是一个简单的例子,实际上,情感分析是一个需要大量调整和微调才能获得良好结果的领域。一个预训练的模型可能无法很好地处理某些类型的文本(例如,讽刺),可能需要微调或预处理步骤来提高其性能。
二、命名实体识别 (NER)
命名实体识别(NER)是一种用于从非结构化文本中提取实体,如人名、组织和地点的技术。执行NER的一种方式是使用预训练模型,比如Python的spacy库提供的模型。以下是如何使用spacy库从一段文本中提取命名实体的例子:
import spacy
# Load the pre-trained model
nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm")
# Define text to be analyzed
text = "Barack Obama visited the White House today"
# Process the text with the model
doc = nlp(text)
# Extract named entities
for ent in doc.ents:
print(ent.text, ent.label_)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
这个例子使用了spacy的en_core_web_sm模型来分析文本 Barack Obama visited the White House today。处理过的文本的ents属性返回一个命名实体的迭代器,每个实体都有text和label_这两个属性,分别代表实体的文本和标签。在这个例子中,输出将会是:
Barack Obama PERSON
White House FAC
- 1
- 2
它显示“Barack Obama”是一个人,而“White House”是一个设施。
在spacy中,有多个适用于不同语言的预训练模型,其中一些比其他模型更准确。此外,命名实体识别是一个需要大量调整和微调才能取得良好结果的领域。一个预训练的模型可能无法很好地处理某些类型的文本(例如,技术性文本),可能需要额外的微调或预处理步骤来提高其性能。
三、文本分类
文本分类是一种将文本自动分类到预定义的类别或类中的过程。例如,文本分类算法可能用于将电子邮件分类为垃圾邮件或非垃圾邮件,或者按主题对新闻文章进行分类。文本分类在各种应用中都有使用,包括自然语言处理、信息检索和机器学习。
以下是使用Python库scikit-learn进行文本分类的一个例子。此例子使用了20个新闻组的数据集,其中包含来自20个不同新闻组的文本。目标是训练一个分类器,根据内容预测文本属于哪个新闻组。
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_20newsgroups from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer from sklearn.naive_bayes import MultinomialNB from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score # Load the 20 Newsgroups dataset newsgroups_train = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='train') newsgroups_test = fetch_20newsgroups(subset='test') # Transform the texts into TF-IDF vectors vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer() X_train = vectorizer.fit_transform(newsgroups_train.data) X_test = vectorizer.transform(newsgroups_test.data) y_train = newsgroups_train.target y_test = newsgroups_test.target # Train a Multinomial Naive Bayes classifier clf = MultinomialNB() clf.fit(X_train, y_train) # Predict the newsgroup of the test texts y_pred = clf.predict(X_test) # Evaluate the classifier's accuracy accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) print("Accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(accuracy * 100))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
这段代码将加载20个新闻组的数据集,并将其划分为训练集和测试集。然后,它会使用TfidfVectorizer将文本转换为数值表示,并使用训练集训练一个多项式朴素贝叶斯分类器。最后,它会使用训练好的分类器预测测试文本的新闻组,并评估分类器的准确性。
四、机器翻译
机器翻译是自动将文本从一种语言翻译成另一种语言的过程。例如,机器翻译算法可能将一篇西班牙语的新闻文章翻译成英语。机器翻译在各种行业中都有使用,包括电子商务、国际商务和政府。
以下是一个使用OpenNMT库将英文翻译成法文的例子:
from opennmt import tokenizers from opennmt import models import torch # Tokenize the source and target text. source_tokenizer = tokenizers.new("text", "en") source_text = "Hello, how are you?" source_tokens = source_tokenizer.tokenize(source_text) target_tokenizer = tokenizers.new("text", "fr") target_text = "Bonjour, comment vas-tu?" target_tokens = target_tokenizer.tokenize(target_text) # Build the translation model. model = models.Transformer( source_vocab_size=len(source_tokenizer.vocab), target_vocab_size=len(target_tokenizer.vocab), num_layers=6, hidden_size=512, dropout=0.1, attention_dropout=0.1, relu_dropout=0.1) model.eval() # Convert the tokens to a tensor. source_tokens = torch.tensor(source_tokenizer.encode(source_text)).unsqueeze(0) # Generate a translation. with torch.no_grad(): log_probs, _, _ = model(source_tokens, None, None) tokens = log_probs.argmax(-1) # Decode the translation. translation = target_tokenizer.decode(tokens[0]) print(translation)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
这段代码将输出:“Bonjour, comment vas-tu?”(中文:你好,你好吗?)
请注意,这是一个非常简单的例子,并不能直接运行,因为它需要加载一个预训练的模型。此外,此例子使用的是小数据集作为输入,而针对特定情况可能并没有可用的预训练模型。如果想要了解更多关于机器学习的信息,请点击这里。
五、文本摘要
文本摘要是自动生成较长文本缩减版的过程。例如,文本摘要算法可能会针对一篇长篇新闻文章,生成一个简短的、概括主要要点的摘要。文本摘要在各种应用中都有使用,包括自然语言处理、信息检索和机器学习。
请注意,这是一个非常简单的例子,并不能直接运行,因为它需要加载一个预训练的模型。此外,此例子使用的是小数据集作为输入,而针对特定情况可能并没有可用的预训练模型。
from gensim.summarization import summarize
text = "In computing, stop words are words which are filtered out before or after processing of text. Though stop words usually refer to the most common words in a language, there is no single universal list of stop words used by all natural language processing tools, and indeed not all tools even use such a list. Some tools specifically avoid removing these stop words to support phrase search."
print(summarize(text, ratio=0.2))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
这段代码将输出文本的摘要版,仅保留最重要的20%的句子:“Some tools specifically avoid removing these stop words to support phrase search.”(中文:有些工具特别避免删除这些停用词,以支持短语搜索。)
您可以调整比例参数来改变摘要的文本量,或者使用word_count参数来指定摘要中包含的词数。
六、信息提取
信息提取是从非结构化文本中提取结构化数据的过程。例如,信息提取算法可能会从电商网站中提取产品信息,如价格和库存情况。信息提取在各种行业中都有使用,包括电子商务、金融和医疗保健,以从非结构化文本中提取结构化数据。
以下是一个使用Python和Natural Language Toolkit(NLTK)库进行信息提取的例子:
import nltk
from nltk import word_tokenize, pos_tag, ne_chunk
# 示例文本
text = "Barack Obama 是美国第 44 任总统,任期从 2009 年到 2017 年。"
# 对文本进行分词
tokens = word_tokenize(text)
# POS 标记
tagged_tokens = pos_tag(tokens)
# 命名实体识别
Entity = ne_chunk(tagged_tokens)
print(entities)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
上述代码首先将文本分词成单个词汇,然后进行词性标注,识别每个词的词性,最后进行命名实体识别,识别出人名、组织名和地名等实体。
ne_chunk函数的输出是一个可以进一步处理以提取感兴趣实体的树状结构。
(S (PERSON Barack/NNP) Obama/NNP was/VBD the/DT 44th/JJ (ORGANIZATION President/NNP) of/IN the/DT (GPE United/NNP States/NNPS) ,/, serving/VBG from/IN 2009/CD to/TO 2017/CD ./.)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
请注意,上述例子非常简单,在现实中的应用中,您需要做大量的预处理和模型微调。
七、文本生成
文本生成是自动生成文本的过程,比如编写产品描述或编写新闻文章。例如,文本生成算法可能会将产品图像作为输入,然后生成产品描述。文本生成在各种行业中都有使用,包括电子商务、市场营销和内容创作。
以下是一个使用Python库Hugging Face的transformers中的GPT-2模型进行文本生成的例子:
from transformers import GPT2Tokenizer, GPT2LMHeadModel
# Load the GPT-2 model and tokenizer
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained("gpt2")
# Define the prompt and generate text
prompt = "Once upon a time in a land far, far away"
generated_text = model.generate(input_ids=tokenizer.encode(prompt))
# Decode the generated text
generated_text = tokenizer.decode(generated_text)
print(generated_text)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
这段代码将使用GPT-2模型根据提供的提示“Once upon a time in a land far, far away”(译文:很久很久以前,在一个遥远的地方)生成文本。生成的文本将在控制台上打印出来。
请注意,您可能需要互联网连接来下载预训练模型,同时也需要强大的GPU来生成文本。
八、文本聚类
文本聚类是将相似的文本文档分组的过程。例如,文本聚类算法可能会对新闻文章集合进行处理,并将其分为“体育”、“政治”和“娱乐”等类别。文本聚类在各种应用中都有使用,包括自然语言处理、信息检索和机器学习。
import nltk
from nltk import word_tokenize, pos_tag, ne_chunk
# Sample text
text = "Barack Obama was the 44th President of the United States, serving from 2009 to 2017."
# Tokenize the text
tokens = word_tokenize(text)
# POS tagging
tagged_tokens = pos_tag(tokens)
# Named entity recognition
entities = ne_chunk(tagged_tokens)
print(entities)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
上述代码首先将文本分词成单个词汇,然后进行词性标注,识别每个词的词性,最后进行命名实体识别,识别出人名、组织名和地名等实体。
ne_chunk函数的输出是一个可以进一步处理以提取感兴趣实体的树状结构。
九、语音识别
语音识别是将口语转化为书面文字的过程。例如,语音识别算法可能会在语音控制系统中使用,如虚拟助手,将口头指令转录为计算机可以理解的文字。语音识别在各种行业中都有使用,包括医疗保健、金融和客户服务。
有许多库和框架可以用于各种编程语言的语音识别。以下是如何使用Python中的Speech Recognition库从麦克风转录语音的例子:
import speech_recognition as sr
# create a recognizer object
r = sr.Recognizer()
# create a microphone object
mic = sr.Microphone()
# listen for speech and transcribe it
with mic as source:
r.adjust_for_ambient_noise(source)
audio = r.listen(source)
transcribed_text = r.recognize_google(audio)
print(transcribed_text)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
这个例子使用了recognize_google()函数,该函数利用Google Web语音API进行语音转录。其他的转录选项包括使用recognize_sphinx()函数(它使用CMU Sphinx引擎)或recognize_wit()函数(它使用Wit.ai API)。
你也可以使用这个库来识别文件中的语音:
with sr.AudioFile('audio_file.wav') as source:
audio = r.record(source)
transcribed_text = r.recognize_google(audio)
print(transcribed_text)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
请注意,使用Google Web语音API需要网络连接,而且你可能需要设置凭证并根据你选择的转录引擎安装一些额外的包。
十、文本转语音 (TTS)
文本到语音(TTS)是一种将书面文本转化为口语的技术。它常用于为视觉障碍者进行语音合成、语音助手以及自动客户服务系统等应用。
TTS系统使用多种技术的组合,如自然语言处理和机器学习,来产生逼真的语音。一些TTS软件的例子包括Google的文本到语音、Amazon Polly以及Apple的Siri。
以下是一个使用Python中的gTTS(Google文本到语音)库来将文本转化为语音的例子:
from gtts import gTTS import os text = "Hello, this is an example of text to speech using the gTTS library in Python." # Language in which you want to convert language = 'en' # Passing the text and language to the engine, # here we have marked slow=False. Which tells # the module that the converted audio should # have a high speed myobj = gTTS(text=text, lang=language, slow=False) # Saving the converted audio in a mp3 file named # welcome myobj.save("welcome.mp3") # Playing the converted file os.system("mpg321 welcome.mp3")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
这段代码使用gTTS库将文本“Hello, this is an example of text to speech using the gTTS library in Python.”(译文:“你好,这是一个使用Python中的gTTS库将文本转化为语音的例子。”)转化为语音,并将其保存到一个名为“welcome.mp3”的mp3文件中。
最后一行os.system(“mpg321 welcome.mp3”)使用命令行工具mpg321播放mp3文件。如果你的系统中没有安装mpg321,你可以使用其他播放器来播放mp3文件。
关于高级自然语言处理的进一步学习,可以参考这个链接:microstone123/Natural-Language-processing (github.com)。



