- 1Spring Boot | Spring Boot “整合JPA“
- 2java面试100题(应届生必备)_java应届生面试题
- 3ubuntu/centos vim配置golang开发环境_ubuntu安装vim-go插件
- 4支持中文的Rasa NLU训练服务部署---Rasa_NLU_Chi_rasa训练中文模型
- 5为什么人工智能和Python要一起学?两者有何联系?_人工智能的底层是python吗
- 6CHATGLM3应用指南——本地部署_chatglm3-ggml-q4_0.bin 部署
- 7毕业设计:基于深度学习的电影推荐算法 -- 以豆瓣为例 大数据
- 8Elasticsearch:使用向量搜索来搜索图片及文字_elasticsearch 向量检索
- 9libsvm java 情感分类_自然语言处理系列篇——情感分类
- 10pytorch实战---IMDB情感分析_pytorch imdb
【pytorch损失函数(3)】nn.L1Loss()和nn.SmoothL1Loss()
赞
踩
今天讨论下:对称损失函数:symmetric regression function such as L1 or L2 norm,注意说说L1
【回归损失函数】L1(MAE)、L2(MSE)、Smooth L1 Loss详解
1. L1 Loss(Mean Absolute Error,MAE)
1.1 数学定义
平均绝对误差(MAE)是一种用于回归模型的损失函数。MAE 是目标变量和预测变量之间绝对差值之和,因此它衡量的是一组预测值中的平均误差大小,而不考虑它们的方向,范围为 0~∞。
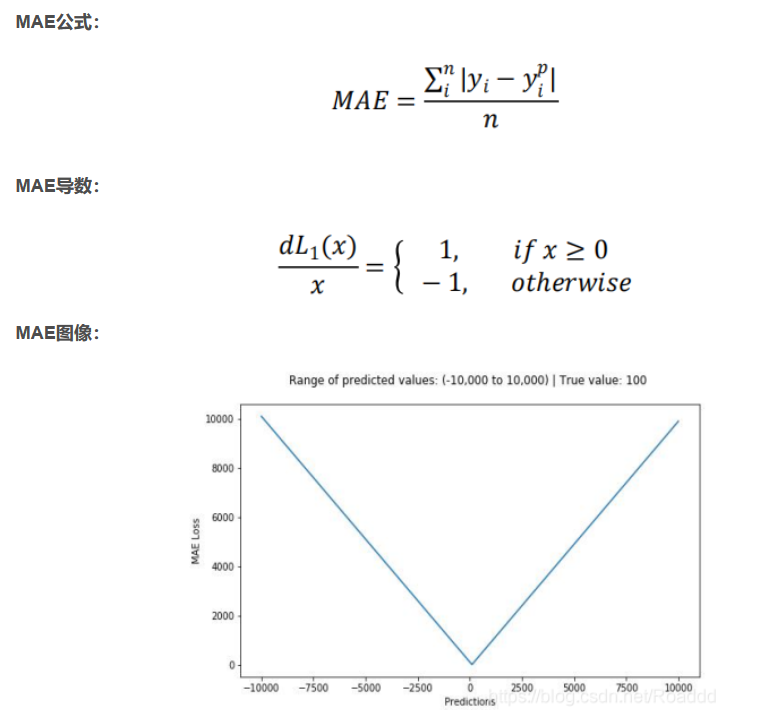
上图为平均绝对误差函数图,其中目标真值为 100,预测范围在-10000 到 10000 之间,均方 误差损失(Y 轴)在预测值(X 轴)=100 处有最小值,范围为 0~∞。
主要问题:
导数为常数,在 Loss 函数最小值处容易震荡,导致难以收敛到最优值。
1.2 、使用场景与问题
https://atcold.github.io/pytorch-Deep-Learning/en/week11/11-1/
Use Case: L1 loss is more robust against outliers and noise compared to L2 loss. In L2, the errors of those outlier/noisy points are squared, so the cost function gets very sensitive to outliers.
Problem: The L1 loss is not differentiable at the bottom (0). We need to be careful when handling its gradients (namely Softshrink). This motivates the following SmoothL1Loss.
1.3 、如何使用
L1范数损失 L1Loss,计算 output 和 target 之差的绝对值。
torch.nn.L1Loss(reduction='mean')
- 1
参数:
reduction-三个值,none: 不使用约简;mean:返回loss和的平均值;sum:返回loss的和。默认:mean。
- 1
2. L2 Loss(Mean Squared Error,MSE)
均方误差(MSE)是最常用的回归损失函数,它是目标变量和预测值的差值平方和。查看这篇文章pytorch——损失函数之nn.MSELoss,(Mean Squared Error,MSE) 均方误差(MSE)(squared L2 norm,平方L2范数)。它也被称为L2 Loss。
3. Smooth L1 Loss
从损失函数对 x 的导数可知,L1 损失函数对 x 的导数为常数,在训练后期,x 很小时, 如果学习率不变,损失函数会在最优值附近波动,很难收敛到最高的精度。L2 损失对 x 的 导数在 x 值很大时,其导数也非常大,在训练初期不稳定。Smooth L1 Loss 结合了 L1 和 L2 的优点:早期使用 L1,梯度稳定,快速收敛,后期使用 L2,逐渐收敛到最优解。
函数的临界点:absolute element-wise error falls below 1。
This function uses L2 loss if the absolute element-wise error falls below 1 and L1 loss otherwise.
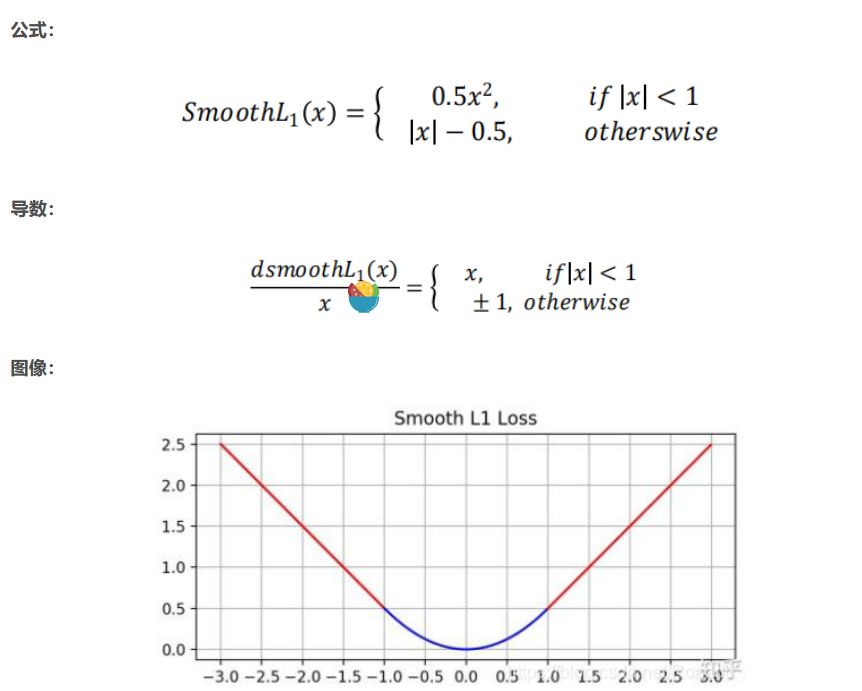
Smooth L1 Loss 结合了 L1 和 L2 的优点:早期使用 L1,梯度稳定,快速收敛,后期使用 L2,逐渐收敛到最优解。
3.2 使用场景与问题
This is advertised by Ross Girshick (Fast R-CNN). The Smooth L1 Loss is also known as the Huber Loss or the Elastic Network when used as an objective function,.
Use Case: It is less sensitive to outliers than the MSELoss and is smooth at the bottom. This function is often used in computer vision for protecting against outliers.
Problem: This function has a scale (0.50.5 in the function above).


