热门标签
热门文章
- 1HarmonyOS/OpenHarmony应用开发-ArkTS语言渲染控制ForEach循环渲染_arkts foreach
- 2MySQL数据库入门学习 #CSDN博文精选# #IT技术# #数据库# #MySQL#_mysql数据库修改按顺序排序
- 3VB6 错误383 text属性只读_vb6.0提示实时错误383
- 4产品经理必备的五款办公软件
- 5L1-064 估值一亿的AI核心代码(C++)
- 6C++ 离散与组合数学之多重集合
- 7git merge 和 git rebase 的区别_git rebase和git merge的区别
- 8为什么oracle分页第二页会少,浅析Oracle和Mysql分页的区别
- 9Parameter **** is not registered as an output parameter_parameter exec_result is not registered as an outp
- 10《已解决 Kotlin Error: Unresolved reference: name BUG 》_unresolved reference 'name
当前位置: article > 正文
NLP之TF之LSTM:基于Tensorflow框架采用PTB数据集建立LSTM网络的自然语言建模
作者:AllinToyou | 2024-03-16 12:08:35
赞
踩
ptb数据集
NLP之TF之LSTM:基于Tensorflow框架采用PTB数据集建立LSTM网络的自然语言建模
目录
关于PTB数据集
PTB (Penn Treebank Dataset)文本数据集是语言模型学习中目前最被广泛使用数据集。
ptb.test.txt #测试集数据文件
ptb.train.txt #训练集数据文件
ptb.valid.txt #验证集数据文件
这三个数据文件中的数据已经经过了预处理,包含了10000 个不同的词语和语句结束标记符(在文本中就是换行符)以及标记稀有词语的特殊符号。
为了让使用PTB数据集更加方便,TensorFlow提供了两个函数来帮助实现数据的预处理。首先,TensorFlow提供了ptb_raw_data函数来读取PTB的原始数据,并将原始数据中的单词转化为单词ID。
训练数据中总共包含了929589 个单词,而这些单词被组成了一个非常长的序列。这个序列通过特殊的标识符给出了每句话结束的位置。在这个数据集中,句子结束的标识符ID为2。
数据集的下载地址:TF的PTB数据集 (别的数据集不匹配的话会出现错误)
代码实现
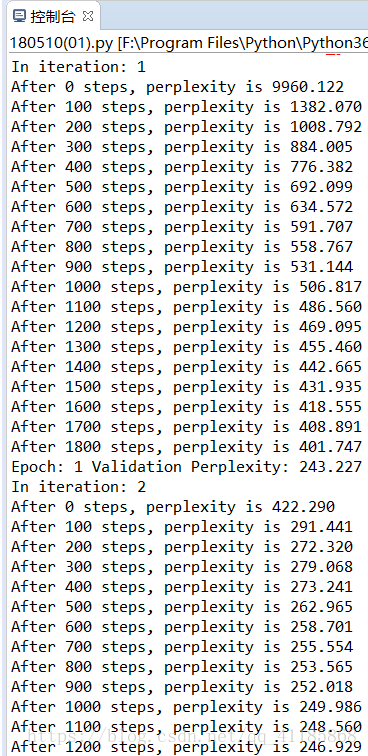
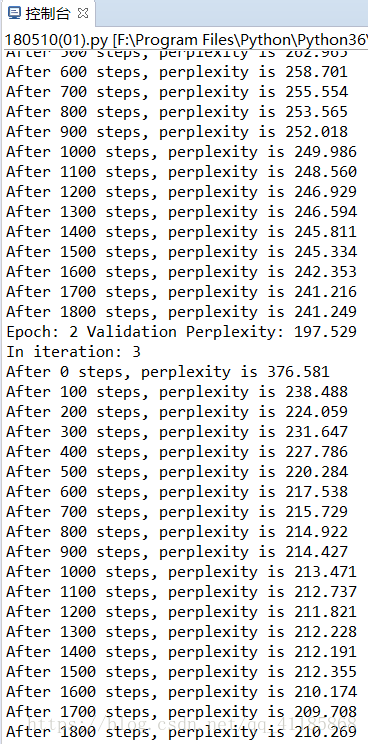
本代码使用2层 LSTM 网络,且每层有 200 个隐藏单元。在训练中截断的输入序列长度为 32,且使用 Dropout 和梯度截断等方法控制模型的过拟合与梯度爆炸等问题。当简单地训练 3 个 Epoch 后,测试复杂度(Perplexity)降低到了 210,如果多轮训练会更低。
- # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
- from __future__ import absolute_import
- from __future__ import division
- from __future__ import print_function
-
- import collections
- import os
- import sys
-
- import tensorflow as tf
-
- Py3 = sys.version_info[0] == 3
-
- def _read_words(filename):
- with tf.gfile.GFile(filename, "r") as f:
- if Py3:
- return f.read().replace("\n", "<eos>").split()
- else:
- return f.read().decode("utf-8").replace("\n", "<eos>").split()
-
-
- def _build_vocab(filename):
- data = _read_words(filename)
-
- counter = collections.Counter(data)
- count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: (-x[1], x[0]))
-
- words, _ = list(zip(*count_pairs))
- word_to_id = dict(zip(words, range(len(words))))
-
- return word_to_id
-
-
- def _file_to_word_ids(filename, word_to_id):
- data = _read_words(filename)
- return [word_to_id[word] for word in data if word in word_to_id]
-
-
- def ptb_raw_data(data_path=None):
- """Load PTB raw data from data directory "data_path".
- Reads PTB text files, converts strings to integer ids,
- and performs mini-batching of the inputs.
- The PTB dataset comes from Tomas Mikolov's webpage:
- http://www.fit.vutbr.cz/~imikolov/rnnlm/simple-examples.tgz
- Args:
- data_path: string path to the directory where simple-examples.tgz has
- been extracted.
- Returns:
- tuple (train_data, valid_data, test_data, vocabulary)
- where each of the data objects can be passed to PTBIterator.
- """
-
- train_path = os.path.join(data_path, "ptb.train.txt")
- valid_path = os.path.join(data_path, "ptb.valid.txt")
- test_path = os.path.join(data_path, "ptb.test.txt")
-
- word_to_id = _build_vocab(train_path)
- train_data = _file_to_word_ids(train_path, word_to_id)
- valid_data = _file_to_word_ids(valid_path, word_to_id)
- test_data = _file_to_word_ids(test_path, word_to_id)
- vocabulary = len(word_to_id)
- return train_data, valid_data, test_data, vocabulary
-
-
- def ptb_producer(raw_data, batch_size, num_steps, name=None):
- """Iterate on the raw PTB data.
- This chunks up raw_data into batches of examples and returns Tensors that
- are drawn from these batches.
- Args:
- raw_data: one of the raw data outputs from ptb_raw_data.
- batch_size: int, the batch size.
- num_steps: int, the number of unrolls.
- name: the name of this operation (optional).
- Returns:
- A pair of Tensors, each shaped [batch_size, num_steps]. The second element
- of the tuple is the same data time-shifted to the right by one.
- Raises:
- tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError: if batch_size or num_steps are too high.
- """
- with tf.name_scope(name, "PTBProducer", [raw_data, batch_size, num_steps]):
- raw_data = tf.convert_to_tensor(raw_data, name="raw_data", dtype=tf.int32)
-
- data_len = tf.size(raw_data)
- batch_len = data_len // batch_size
- data = tf.reshape(raw_data[0 : batch_size * batch_len],
- [batch_size, batch_len])
-
- epoch_size = (batch_len - 1) // num_steps
- assertion = tf.assert_positive(
- epoch_size,
- message="epoch_size == 0, decrease batch_size or num_steps")
- with tf.control_dependencies([assertion]):
- epoch_size = tf.identity(epoch_size, name="epoch_size")
-
- i = tf.train.range_input_producer(epoch_size, shuffle=False).dequeue()
- x = tf.strided_slice(data, [0, i * num_steps],
- [batch_size, (i + 1) * num_steps])
- x.set_shape([batch_size, num_steps])
- y = tf.strided_slice(data, [0, i * num_steps + 1],
- [batch_size, (i + 1) * num_steps + 1])
- y.set_shape([batch_size, num_steps])
- return x, y
- from reader import *
- import tensorflow as tf
- import numpy as np
-
- data_path = 'F:/File_Python/Python_daydayup/data/simple-examples/data' #F:/File_Python/Python_daydayup/data/simple-examples/data
- # 隐藏层单元数与LSTM层级数
- hidden_size = 200
- num_layers = 2
- #词典规模
- vocab_size = 10000
-
- learning_rate = 1.0
- train_batch_size = 16
- # 训练数据截断长度
- train_num_step = 32
-
- # 在测试时不需要使用截断,测试数据为一个超长序列
- eval_batch_size = 1
- eval_num_step = 1
- num_epoch = 3
- #结点不被Dropout的概率
- keep_prob = 0.5
-
- # 用于控制梯度爆炸的参数
- max_grad_norm = 5
- # 通过ptbmodel 的类描述模型
- class PTBModel(object):
- def __init__(self, is_training, batch_size, num_steps):
- # 记录使用的Batch大小和截断长度
- self.batch_size = batch_size
- self.num_steps = num_steps
-
- # 定义输入层,维度为批量大小×截断长度
- self.input_data = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, num_steps])
- # 定义预期输出
- self.targets = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, num_steps])
-
- # 定义使用LSTM结构为循环体,带Dropout的深度RNN
- lstm_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(hidden_size)
- if is_training:
- lstm_cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(lstm_cell, output_keep_prob=keep_prob)
- cell = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([lstm_cell] * num_layers)
-
- # 初始化状态为0
- self.initial_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32)
-
- # 将单词ID转换为单词向量,embedding的维度为vocab_size*hidden_size
- embedding = tf.get_variable('embedding', [vocab_size, hidden_size])
- # 将一个批量内的单词ID转化为词向量,转化后的输入维度为批量大小×截断长度×隐藏单元数
- inputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, self.input_data)
-
- # 只在训练时使用Dropout
- if is_training: inputs = tf.nn.dropout(inputs, keep_prob)
-
- # 定义输出列表,这里先将不同时刻LSTM的输出收集起来,再通过全连接层得到最终输出
- outputs = []
- # state 储存不同批量中LSTM的状态,初始为0
- state = self.initial_state
- with tf.variable_scope('RNN'):
- for time_step in range(num_steps):
- if time_step > 0: tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
- # 从输入数据获取当前时间步的输入与前一时间步的状态,并传入LSTM结构
- cell_output, state = cell(inputs[:, time_step, :], state)
- # 将当前输出加入输出队列
- outputs.append(cell_output)
-
- # 将输出队列展开成[batch,hidden*num_step]的形状,再reshape为[batch*num_step, hidden]
- output = tf.reshape(tf.concat(outputs, 1), [-1, hidden_size])
-
- # 将LSTM的输出传入全连接层以生成最后的预测结果。最后结果在每时刻上都是长度为vocab_size的张量
- # 且经过softmax层后表示下一个位置不同词的概率
- weight = tf.get_variable('weight', [hidden_size, vocab_size])
- bias = tf.get_variable('bias', [vocab_size])
- logits = tf.matmul(output, weight) + bias
-
- # 定义交叉熵损失函数,一个序列的交叉熵之和
- loss = tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example(
- [logits], # 预测的结果
- [tf.reshape(self.targets, [-1])], # 期望正确的结果,这里将[batch_size, num_steps]压缩为一维张量
- [tf.ones([batch_size * num_steps], dtype=tf.float32)]) # 损失的权重,所有为1表明不同批量和时刻的重要程度一样
-
- # 计算每个批量的平均损失
- self.cost = tf.reduce_sum(loss) / batch_size
- self.final_state = state
-
- # 只在训练模型时定义反向传播操作
- if not is_training: return
- trainable_variable = tf.trainable_variables()
-
- # 控制梯度爆炸问题
- grads, _ = tf.clip_by_global_norm(tf.gradients(self.cost, trainable_variable), max_grad_norm)
- # 如果需要使用Adam作为优化器,可以改为tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate),学习率需要降低至0.001左右
- optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
- # 定义训练步骤
- self.train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, trainable_variable))
- def run_epoch(session, model, data, train_op, output_log, epoch_size):
- total_costs = 0.0
- iters = 0
- state = session.run(model.initial_state)
-
- # # 使用当前数据训练或测试模型
- for step in range(epoch_size):
- x, y = session.run(data)
- # 在当前批量上运行train_op并计算损失值,交叉熵计算的是下一个单词为给定单词的概率
- cost, state, _ = session.run([model.cost, model.final_state, train_op],
- {model.input_data: x, model.targets: y, model.initial_state: state})
- # 将不同时刻和批量的概率就可得到困惑度的对数形式,将这个和做指数运算就可得到困惑度
- total_costs += cost
- iters += model.num_steps
-
- # 只在训练时输出日志
- if output_log and step % 100 == 0:
- print("After %d steps, perplexity is %.3f" % (step, np.exp(total_costs / iters)))
- return np.exp(total_costs / iters)
- def main():
- train_data, valid_data, test_data, _ = ptb_raw_data(data_path)
-
- # 计算一个epoch需要训练的次数
- train_data_len = len(train_data)
- train_batch_len = train_data_len // train_batch_size
- train_epoch_size = (train_batch_len - 1) // train_num_step
-
- valid_data_len = len(valid_data)
- valid_batch_len = valid_data_len // eval_batch_size
- valid_epoch_size = (valid_batch_len - 1) // eval_num_step
-
- test_data_len = len(test_data)
- test_batch_len = test_data_len // eval_batch_size
- test_epoch_size = (test_batch_len - 1) // eval_num_step
-
- initializer = tf.random_uniform_initializer(-0.05, 0.05)
- with tf.variable_scope("language_model", reuse=None, initializer=initializer):
- train_model = PTBModel(True, train_batch_size, train_num_step)
-
- with tf.variable_scope("language_model", reuse=True, initializer=initializer):
- eval_model = PTBModel(False, eval_batch_size, eval_num_step)
-
- # 训练模型。
- with tf.Session() as session:
- tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
-
- train_queue = ptb_producer(train_data, train_model.batch_size, train_model.num_steps)
- eval_queue = ptb_producer(valid_data, eval_model.batch_size, eval_model.num_steps)
- test_queue = ptb_producer(test_data, eval_model.batch_size, eval_model.num_steps)
-
- coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
- threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=session, coord=coord)
-
- for i in range(num_epoch):
- print("In iteration: %d" % (i + 1))
- run_epoch(session, train_model, train_queue, train_model.train_op, True, train_epoch_size)
-
- valid_perplexity = run_epoch(session, eval_model, eval_queue, tf.no_op(), False, valid_epoch_size)
- print("Epoch: %d Validation Perplexity: %.3f" % (i + 1, valid_perplexity))
-
- test_perplexity = run_epoch(session, eval_model, test_queue, tf.no_op(), False, test_epoch_size)
- print("Test Perplexity: %.3f" % test_perplexity)
-
- coord.request_stop()
- coord.join(threads)
-
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- main()
推荐阅读
相关标签