- 1Centos 7由于下载软件包信息失败,软件包选择被禁止_centos7由于下载软件包信息失败
- 2Ubuntu18编译jdk8源码
- 3用Docker部署Springboot 项目_spring boot docker部署
- 4如何使用指针交换函数中两个变量的值(指针篇百题1)_指针交换两个变量的值
- 5域运算符::_::域运算符
- 6vscode 运行C++_vscode运行c++代码
- 7STM32CubeMX v6.9.0 BUG:FLASH_LATENCY设置错误导致初始化失败_flash_latency_0
- 8增加swap分区大小_conv swap div
- 9010407-数一数有几个a_通过for循环,遍历此字符,统计有多少个英文字母a
- 10高通Dump分析_高通dump解析
YOLOv5改进系列(六) 更换空间金字塔池化改进 SPP / SPPF / SimSPPF / ASPP / RFB / SPPCSPC / SPPFCSPC_yolov5的spp模块
赞
踩
1 原理
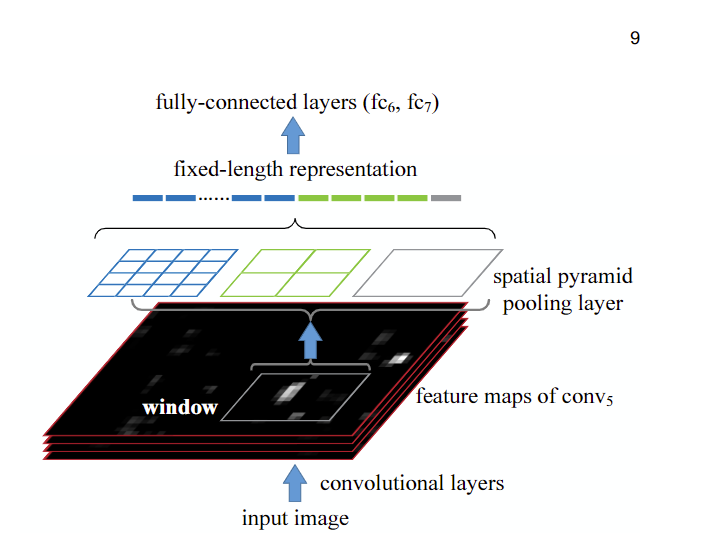
1.1 SPP(Spatial Pyramid Pooling)
SPP模块是何凯明大神在2015年的论文《Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition》中被提出。
SPP全程为空间金字塔池化结构,主要是为了解决两个问题:
- 有效避免了对图像区域裁剪、缩放操作导致的图像失真等问题;
- 解决了卷积神经网络对图相关重复特征提取的问题,大大提高了产生候选框的速度,且节省了计算成本。
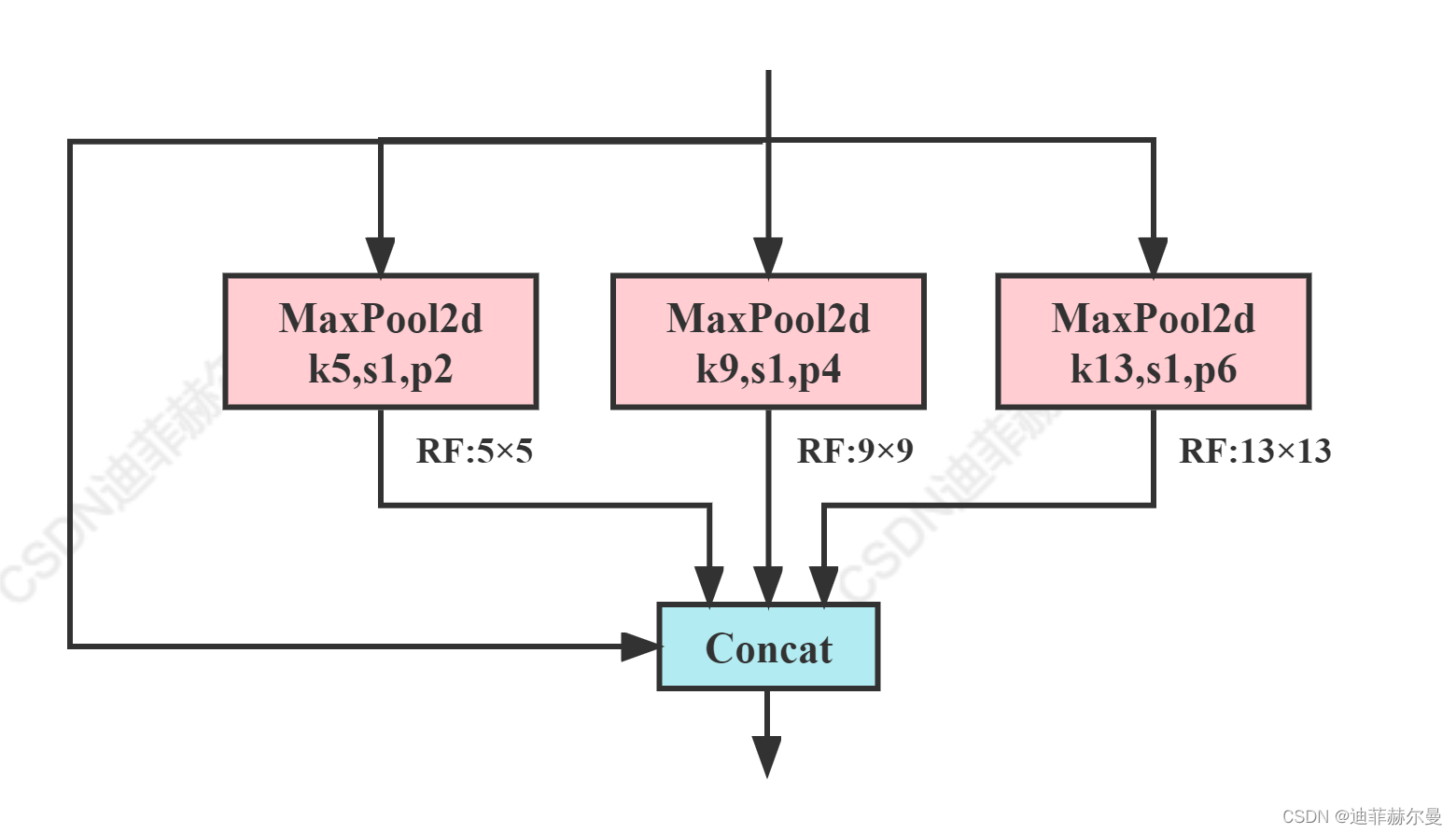
class SPP(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) layer https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.4729
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * (len(k) + 1), c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x] + [m(x) for m in self.m], 1))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
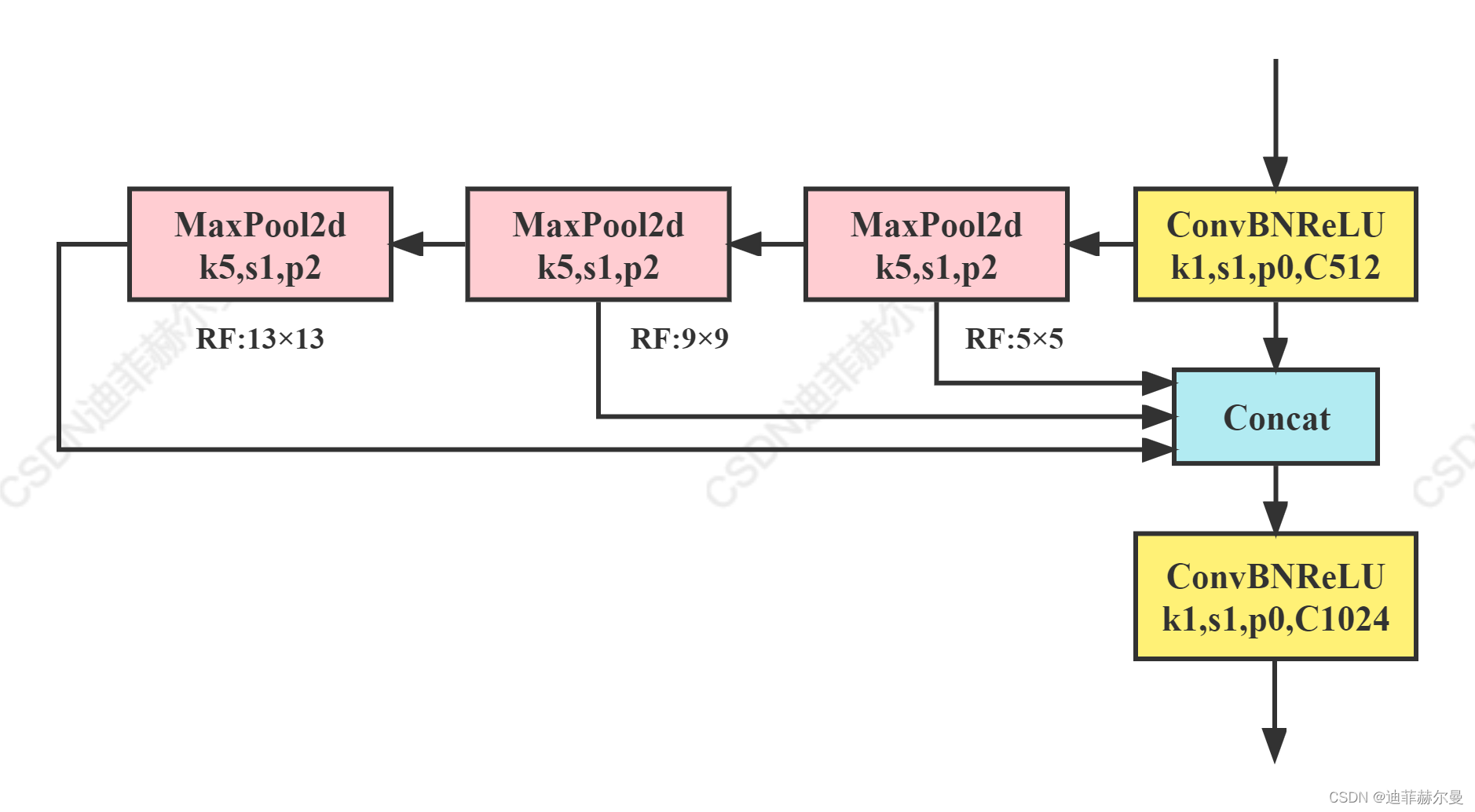
1.2 SPPF(Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast)
这个是YOLOv5作者Glenn Jocher基于SPP提出的,速度较SPP快很多,所以叫SPP-Fast
class SPPF(nn.Module):
# Spatial Pyramid Pooling - Fast (SPPF) layer for YOLOv5 by Glenn Jocher
def __init__(self, c1, c2, k=5): # equivalent to SPP(k=(5, 9, 13))
super().__init__()
c_ = c1 // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c_ * 4, c2, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore') # suppress torch 1.9.0 max_pool2d() warning
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat((x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)), 1))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
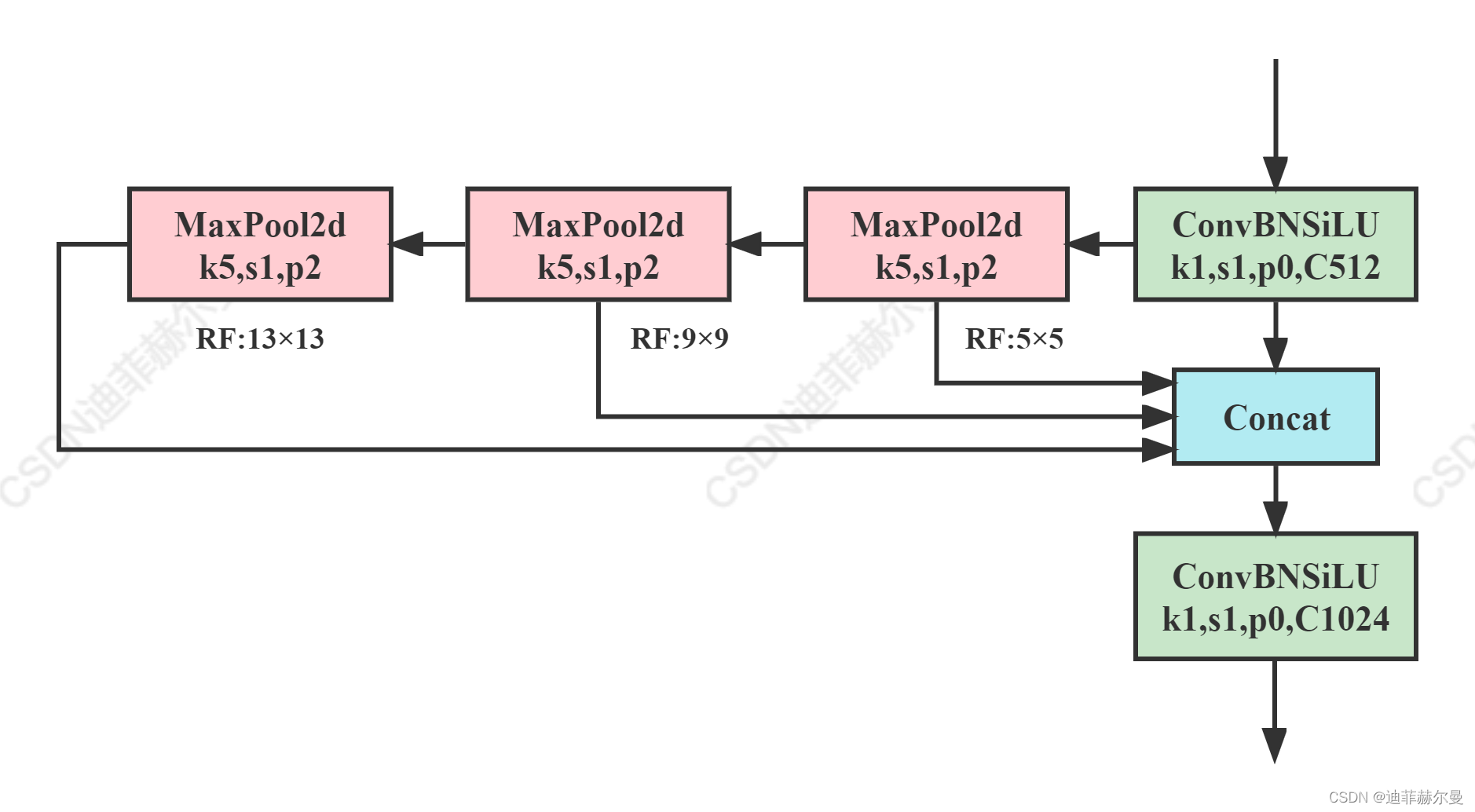
1.3 SimSPPF(Simplified SPPF)
美团YOLOv6提出的模块,感觉和SPPF只差了一个激活函数,简单测试了一下,单个ConvBNReLU速度要比ConvBNSiLU快18%
class SimConv(nn.Module):
'''Normal Conv with ReLU activation'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, groups=1, bias=False):
super().__init__()
padding = kernel_size // 2
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
groups=groups,
bias=bias,
)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.act = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x)))
def forward_fuse(self, x):
return self.act(self.conv(x))
class SimSPPF(nn.Module):
'''Simplified SPPF with ReLU activation'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=5):
super().__init__()
c_ = in_channels // 2 # hidden channels
self.cv1 = SimConv(in_channels, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = SimConv(c_ * 4, out_channels, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=1, padding=kernel_size // 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.cv1(x)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.simplefilter('ignore')
y1 = self.m(x)
y2 = self.m(y1)
return self.cv2(torch.cat([x, y1, y2, self.m(y2)], 1))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
1.4 ASPP(Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling)
受到SPP的启发,语义分割模型DeepLabv2中提出了ASPP模块(空洞空间卷积池化金字塔),该模块使用具有不同采样率的多个并行空洞卷积层。为每个采样率提取的特征在单独的分支中进一步处理,并融合以生成最终结果。该模块通过不同的空洞率构建不同感受野的卷积核,用来获取多尺度物体信息,具体结构比较简单如下图所示:
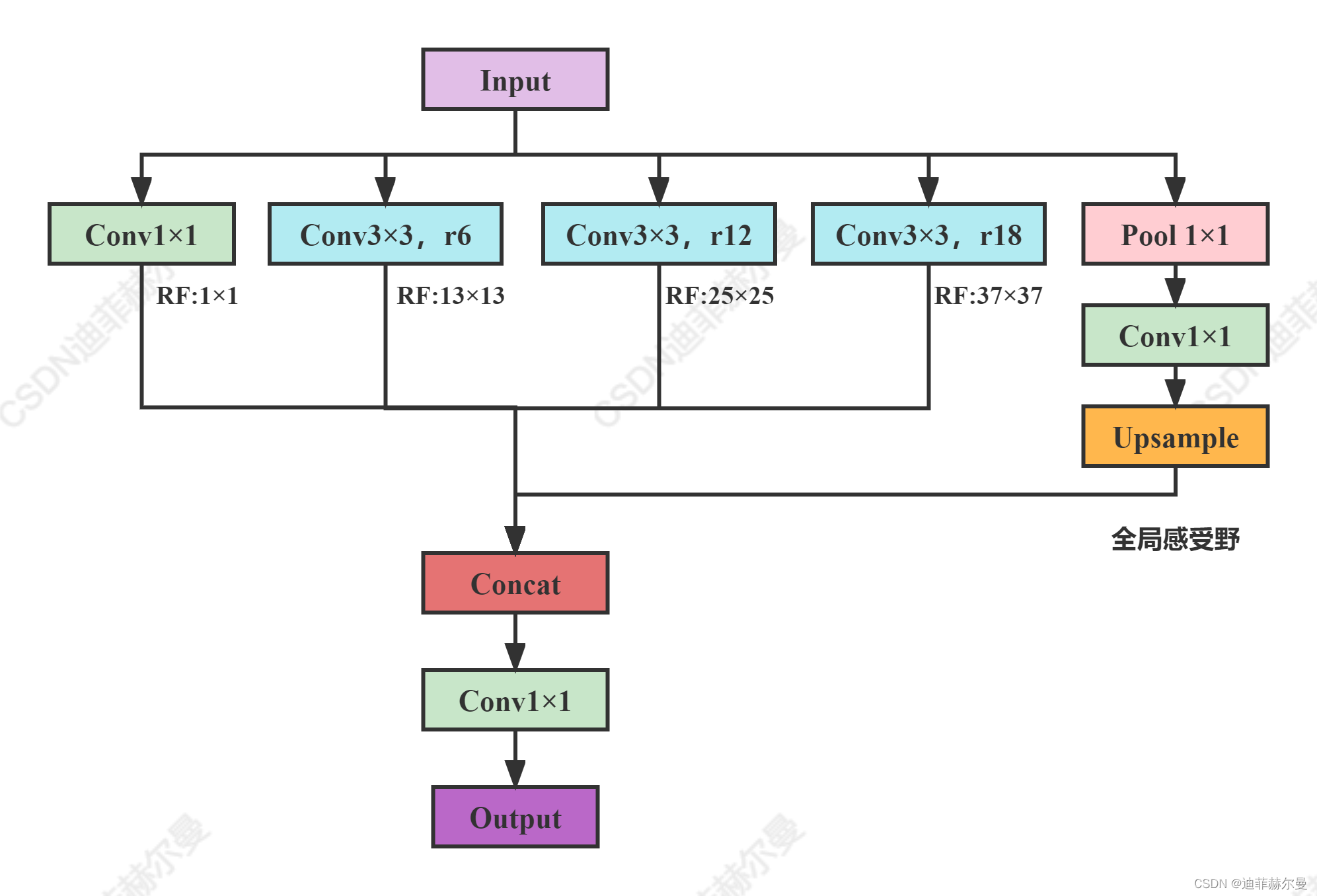
ASPP是在DeepLab中提出来的,在后续的DeepLab版本中对其做了改进,如加入BN层、加入深度可分离卷积等,但基本的思路还是没变。
# without BN version
class ASPP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel=512, out_channel=256):
super(ASPP, self).__init__()
self.mean = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # (1,1)means ouput_dim
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channel,out_channel, 1, 1)
self.atrous_block1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, 1, 1)
self.atrous_block6 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, 3, 1, padding=6, dilation=6)
self.atrous_block12 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, 3, 1, padding=12, dilation=12)
self.atrous_block18 = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, out_channel, 3, 1, padding=18, dilation=18)
self.conv_1x1_output = nn.Conv2d(out_channel * 5, out_channel, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
size = x.shape[2:]
image_features = self.mean(x)
image_features = self.conv(image_features)
image_features = F.upsample(image_features, size=size, mode='bilinear')
atrous_block1 = self.atrous_block1(x)
atrous_block6 = self.atrous_block6(x)
atrous_block12 = self.atrous_block12(x)
atrous_block18 = self.atrous_block18(x)
net = self.conv_1x1_output(torch.cat([image_features, atrous_block1, atrous_block6,
atrous_block12, atrous_block18], dim=1))
return net
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
1.5 RFB(Receptive Field Block)
RFB模块是在《ECCV2018:Receptive Field Block Net for Accurate and Fast Object Detection》一文中提出的,该文的出发点是模拟人类视觉的感受野从而加强网络的特征提取能力,在结构上RFB借鉴了Inception的思想,主要是在Inception的基础上加入了空洞卷积,从而有效增大了感受野
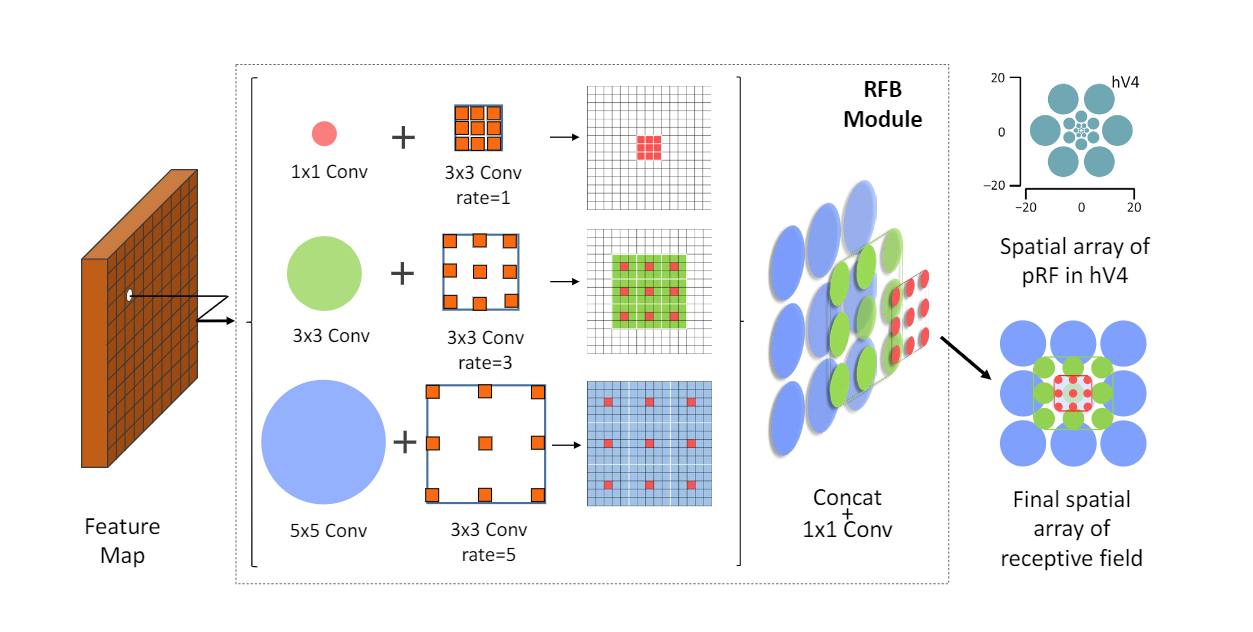
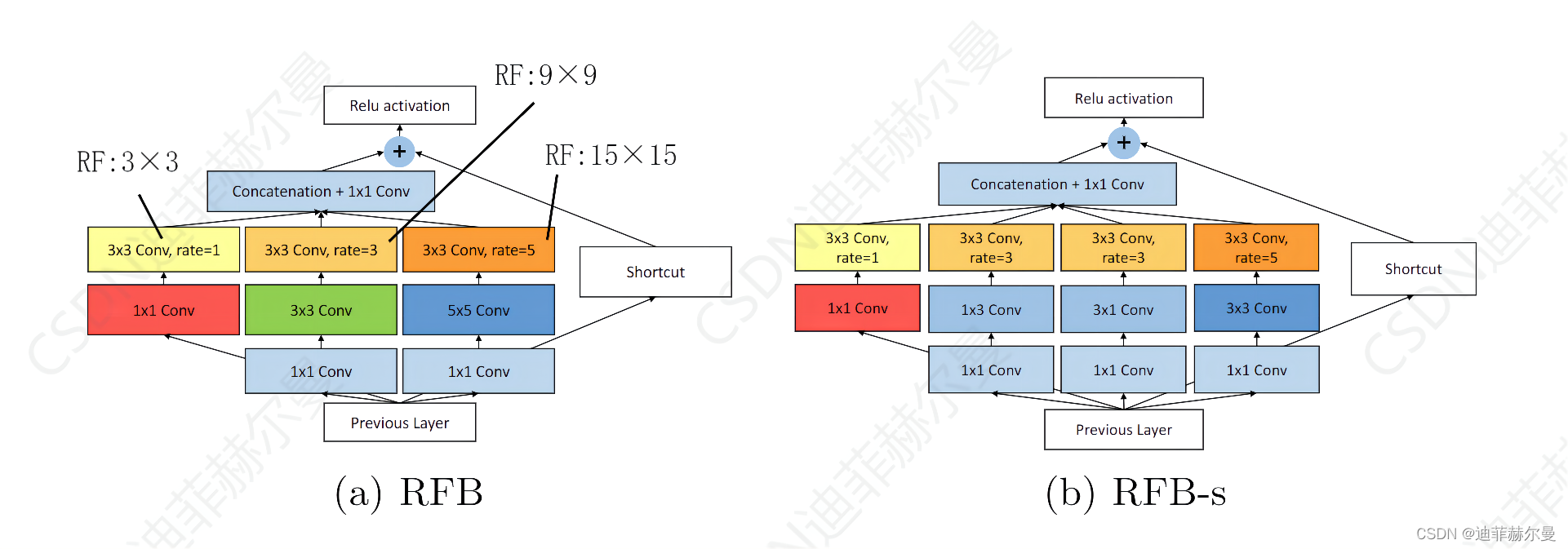
RFB和RFB-s的架构。RFB-s用于在浅层人类视网膜主题图中模拟较小的pRF,使用具有较小内核的更多分支。
class BasicConv(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, relu=True, bn=True):
super(BasicConv, self).__init__()
self.out_channels = out_planes
if bn:
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False)
self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_planes, eps=1e-5, momentum=0.01, affine=True)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else None
else:
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=True)
self.bn = None
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) if relu else None
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
if self.bn is not None:
x = self.bn(x)
if self.relu is not None:
x = self.relu(x)
return x
class BasicRFB(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, scale=0.1, map_reduce=8, vision=1, groups=1):
super(BasicRFB, self).__init__()
self.scale = scale
self.out_channels = out_planes
inter_planes = in_planes // map_reduce
self.branch0 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, groups=groups, relu=False),
BasicConv(inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=stride, padding=(1, 1), groups=groups),
BasicConv(2 * inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=vision, dilation=vision, relu=False, groups=groups)
)
self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, groups=groups, relu=False),
BasicConv(inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=stride, padding=(1, 1), groups=groups),
BasicConv(2 * inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=vision + 2, dilation=vision + 2, relu=False, groups=groups)
)
self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
BasicConv(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, groups=groups, relu=False),
BasicConv(inter_planes, (inter_planes // 2) * 3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, groups=groups),
BasicConv((inter_planes // 2) * 3, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, groups=groups),
BasicConv(2 * inter_planes, 2 * inter_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=vision + 4, dilation=vision + 4, relu=False, groups=groups)
)
self.ConvLinear = BasicConv(6 * inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1, relu=False)
self.shortcut = BasicConv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, relu=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
def forward(self, x):
x0 = self.branch0(x)
x1 = self.branch1(x)
x2 = self.branch2(x)
out = torch.cat((x0, x1, x2), 1)
out = self.ConvLinear(out)
short = self.shortcut(x)
out = out * self.scale + short
out = self.relu(out)
return out
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
1.6 SPPCSPC
该模块是YOLOv7中使用的SPP结构,表现优于SPPF,但参数量和计算量提升了很多
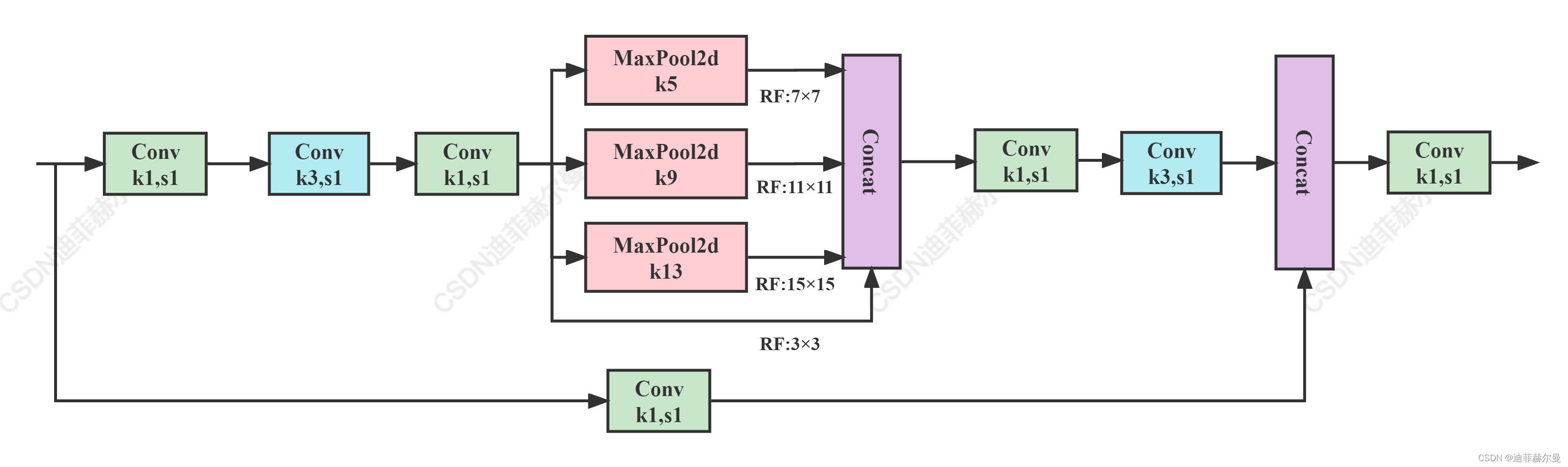
class SPPCSPC(nn.Module):
# CSP https://github.com/WongKinYiu/CrossStagePartialNetworks
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super(SPPCSPC, self).__init__()
c_ = int(2 * c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv4 = Conv(c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
self.cv5 = Conv(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv6 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv7 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))
y1 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat([x1] + [m(x1) for m in self.m], 1)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv7(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))
#分组SPPCSPC 分组后参数量和计算量与原本差距不大,不知道效果怎么样
class SPPCSPC_group(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5, k=(5, 9, 13)):
super(SPPCSPC_group, self).__init__()
c_ = int(2 * c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1, g=4)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1, g=4)
self.cv3 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1, g=4)
self.cv4 = Conv(c_, c_, 1, 1, g=4)
self.m = nn.ModuleList([nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=x, stride=1, padding=x // 2) for x in k])
self.cv5 = Conv(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1, g=4)
self.cv6 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1, g=4)
self.cv7 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1, g=4)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))
y1 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat([x1] + [m(x1) for m in self.m], 1)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv7(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
1.7 SPPFCSPC
我借鉴了SPPF的思想将SPPCSPC优化了一下,得到了SPPFCSPC,在保持感受野不变的情况下获得速度提升;我把这个模块给v7作者看了,并没有得到否定,详细回答可以看4 Issue
目前这个结构被YOLOv6 3.0版本使用了,效果很不错,大家可以看一下YOLOv6 3.0的论文,里面有详细的实验结果。
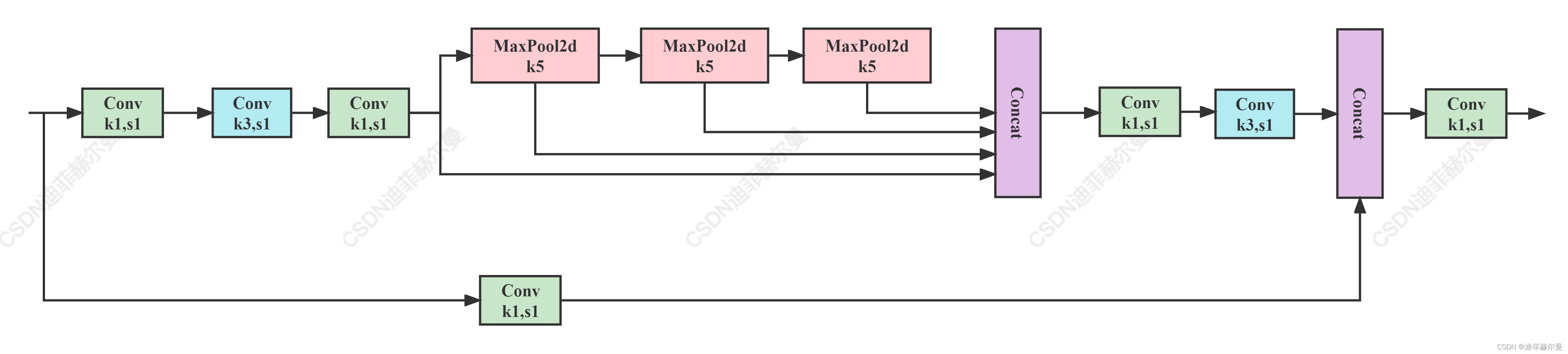
class SPPFCSPC(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, n=1, shortcut=False, g=1, e=0.5, k=5):
super(SPPFCSPC, self).__init__()
c_ = int(2 * c2 * e) # hidden channels
self.cv1 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv2 = Conv(c1, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv3 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv4 = Conv(c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.m = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=k, stride=1, padding=k // 2)
self.cv5 = Conv(4 * c_, c_, 1, 1)
self.cv6 = Conv(c_, c_, 3, 1)
self.cv7 = Conv(2 * c_, c2, 1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.cv4(self.cv3(self.cv1(x)))
x2 = self.m(x1)
x3 = self.m(x2)
y1 = self.cv6(self.cv5(torch.cat((x1,x2,x3, self.m(x3)),1)))
y2 = self.cv2(x)
return self.cv7(torch.cat((y1, y2), dim=1))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
2 参数量对比
这里我在yolov5s.yaml中使用各个模型替换SPP模块
| 模型 | 参数量(parameters) | 计算量(GFLOPs) |
|---|---|---|
| SPP | 7225885 | 16.5 |
| SPPF | 7235389 | 16.5 |
| SimSPPF | 7235389 | 16.5 |
| ASPP | 15485725 | 23.1 |
| BasicRFB | 7895421 | 17.1 |
| SPPCSPC | 13663549 | 21.7 |
| SPPFCSPC | 13663549 | 21.7 |
| 分组SPPCSPC | 8355133 | 17.4 |
3 改进方式
第一步;各个代码放入common.py中
第二步;yolo.py中加入类名
第三步;修改配置文件
yolov5配置文件如下:
# YOLOv5 声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:【wpsshop博客】Copyright © 2003-2013 www.wpsshop.cn 版权所有,并保留所有权利。


