热门标签
热门文章
- 1Solr远程命令执行复现(cve-2019-0193)_solr cve-2019-0193
- 2网络安全:NMAP 高级使用技巧和NESSUS漏洞检测_nmap 验证漏洞
- 3unity发布设置解释大全-转载_unity default cursor
- 4如何为网站应用接入第三方微信登录_网站微信登录接入
- 5Leetcode算法-两两交换链表节点(循环法+递归法)_leetcode 交换相邻的2个链表
- 6用while循环语句 做1到10的数字竞猜_随机生成1到10的数字,让用户猜三次,猜成功结束游戏代码,while循环
- 7字母,数字,下划线或者数字的正则表达式_由正则表达式表示 c语言中的标识符,以下划线或字母开头,后跟零个或多个字母数
- 8云计算的可信新边界:边缘计算与协同未来_面向云边端环境的可信协同关键技术
- 9Vue.js - Font Awesome字体图标的使用详解(vue-fontawesome库)_font-awesome-icon
- 10【C++】C++ 引用详解 ④ ( 函数返回 静态变量 / 全局变量 的 引用 / 指针 )_.c++中引用类型的函数返回局部变量
当前位置: article > 正文
pandas学习笔记(一)_pandas 分位数
作者:Cpp五条 | 2024-02-10 18:35:18
赞
踩
pandas 分位数
基本数据结构
1. Series
对于一个Series,其中最常用的属性为值(values)、索引(index)、名字(name),类型(dtype)
s = pd.Series(np.random.randn(5),index=['a','b','c','d','e'],name='这是一个Series',dtype='float64')
s
a -0.152799
b -1.208334
c 0.668842
d 1.547519
e 0.309276
Name: 这是一个Series, dtype: float64
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
访问Series属性
s.values
array([-0.15279875, -1.20833379, 0.6688421 , 1.54751933, 0.30927643])
s.name
'这是一个Series'
s.index
Index(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'], dtype='object')
s.dtype
dtype('float64')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'col1':list('abcde'),'col2':range(5,10),'col3':[1.3,2.5,3.6,4.6,5.8]},
index=list('一二三四五'))
df
- 1
- 2
- 3
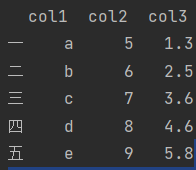
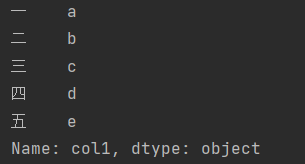
从DataFrame中取出一列为Series
df['coll']
- 1
修改行或列名
df.rename(index={'一':'one'},columns={'col1':'new_col1'})
- 1

调用属性和方法
df.index
Index(['一', '二', '三', '四', '五'], dtype='object')
df.columns
Index(['col1', 'col2', 'col3'], dtype='object')
df.values
array([['a', 5, 1.3],
['b', 6, 2.5],
['c', 7, 3.6],
['d', 8, 4.6],
['e', 9, 5.8]], dtype=object)
df.shape
(5, 3)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
索引的对齐特性
这是Pandas中非常的强大的特性,举例如下
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'A':[1,2,3]},index=[1,2,3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A':[1,2,3]},index=[3,1,2])
df1-df2
- 1
- 2
- 3

列的删除与添加
对于删除而言,可以用drop函数或者del或者pop
当然需要注意的是在运用drop函数时若参数inplace=True后会直接在原DataFrame中改动
df.drop(index='五',columns='col1')
df['col1']=[1,2,3,4,5]
del df['col1']
df
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
pop方法直接在原来的DataFrame上操作,且返回被删除的列,与python中的pop函数类似
df['col1']=[1,2,3,4,5]
df.pop('col1')
- 1
- 2
可以直接增加新的列,也可以使用assign方法
但assign方法不会对原DataFrame做修改
df1['B']=list('abc')
- 1

根据类型选择列
df.select_dtypes(include=['number']).head()
df.select_dtypes(include=['float']).head()
- 1
- 2

最后用T符号可以转置
2.常用函数
head与tail
返回最初行:Head()
返回最后行:Tail()
如果默认括号里不加参数,那么就会默认为前五行或者后五行
unique和nunique
nunique显示有多少个唯一值
unique显示所有的唯一值
count和value_counts
count返回某行某列的元素个数
value_counts返回每个元素有多少个
info和describe
info函数返回有哪些列、有多少非缺失值、每列的类型
describe默认统计数值型数据的各个统计量
df.info()
- 1

df.describe()
- 1

其中还可以自行选择分位数
df.describe(percentiles=[.05, .25, .75, .95])
- 1
对于非数值型也可以用describe函数
idxmax和nlargest
idxmax函数返回最大值所在索引,在某些情况下特别适用,idxmin功能类似
nlargest函数返回前几个大的元素值,nsmallest功能类似
df['ciol1'].nlargest(3)
- 1

clip和replace
clip和replace是两类替换函数
clip是对超过或者低于某些值的数进行截断
replace是对某些值进行替换
7. apply函数
此函数自由度很高,我会专门去讲解。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/Cpp五条/article/detail/74956
推荐阅读
相关标签


