- 12024年最全Android学生信息管理系统(1)登录界面设计(1),2024年最新在线面试app_学生信息管理系统安卓
- 2(代码详解)绘制箱线图+找离群点的具体位置+同时绘制多组数据的箱线图_用python绘制箱线图代码
- 3ssm基于微信小程序的音乐播放器(程序+开题)_微信小程序期末大作业音乐小程序需求分析
- 4求职已经3个月,简历大多都石沉大海,一说是手工测试都连连摇头~真的太难了_投了3个月简历,每天的时间都在认真看,太累了
- 5Dev-c++ 5.11版本调试方法(七小时折磨调试成功,超详细版)_dev c++5.11
- 6【主题美化】Java Intellij IDEA 60秒切换全新UI方法_idea新ui设置
- 7【关于web、ios、android和taro小程序PDF预览和下载】_taro如何展示pdf
- 8淦!在外包开发的三年给整废了,备战两个月终拿到Android阿里字节哈啰offer总结_阿里和哈啰去哪个
- 9智能车竞赛圆环、避障等元素方案开源_避障元素
- 10哈尔滨工业大学2020春软件构造、形式语言与自动机及算法设计与分析期末试题_哈工大 算法设计与分析 期末考试
山东大学软件学院项目实训-创新实训-基于大模型的旅游平台(十八)- JUC(4)
赞
踩
线程安全分析
成员变量和静态变量是否线程安全?
-
如果它们没有共享,则线程安全
-
如果它们被共享了,根据它们的状态是否能够改变,又分两种情况
如果只有读操作,则线程安全如果有读写操作,则这段代码是临界区,需要考虑线程安全共享且有读写操作不一定安全。
局部变量是否线程安全?
局部变量是线程安全的
但局部变量引用的对象则未必
如果该对象没有逃离方法的作用访问,它是线程安全的
如果该对象逃离方法的作用范围,需要考虑线程安全
常见线程安全类
-
Integer
-
HashTable
-
String
-
Rando
-
Vector
-
JUC下的类
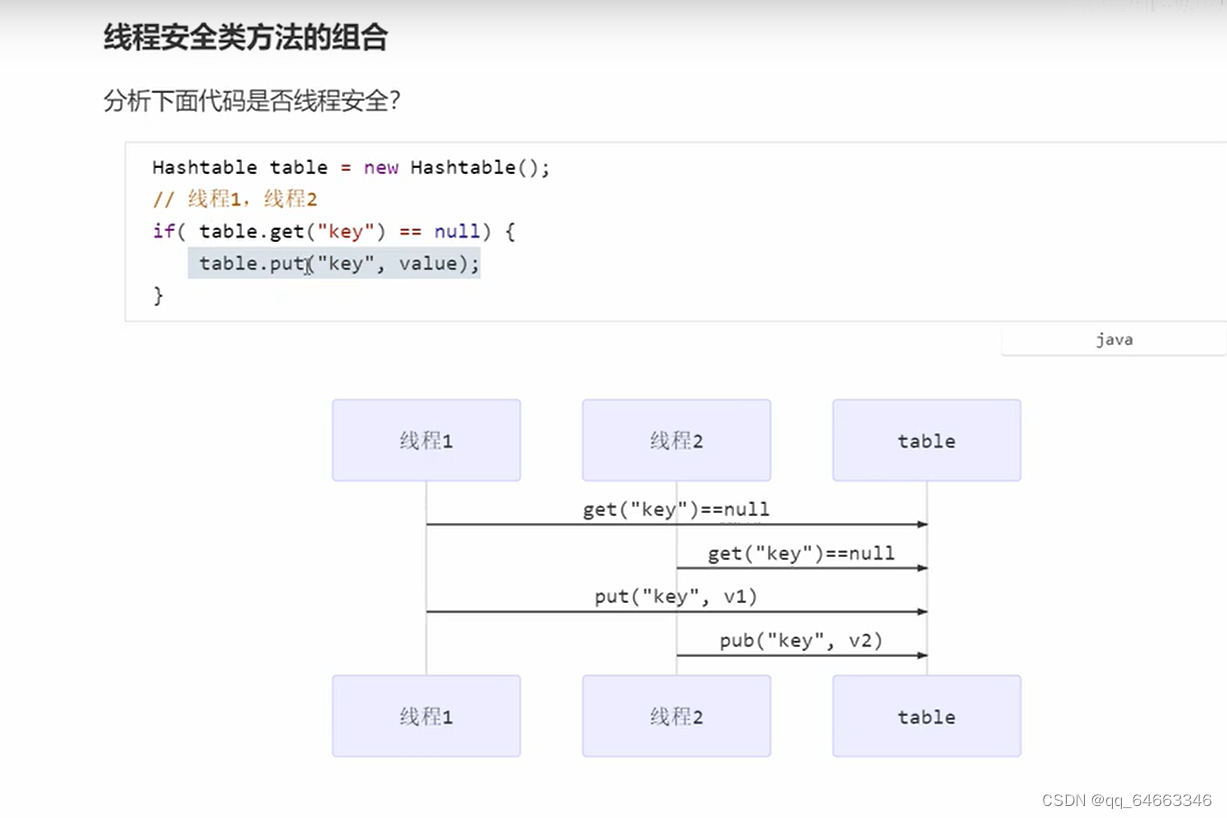
它们单个方法是线程安全的,但是如果多个方法组合的时候就不一样了。下面的代码出现的问题就是线程1判断成功之后切换,刚好释放了锁,然后就是线程2获取锁进行判断,再次切换线程1获取锁处理put,切换线程2也可以获取锁处理put。因为单个方法执行完就会释放锁。所以这样还是需要整体上加锁才能够继续处理
不可变类线程安全
StringString和Integer都是不可变的,String本质上就是一个char[]数组。如果是substring方法实际上就是复制一个新的数组出来,然后再给String的char数组进行赋值。replace也实际上只是创建数组,然后对比原数组的旧值,如果是旧值那么直接给新的数组的那个位置赋值新值
卖票案例
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ExerciseSell")
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// 模拟多人买票
TicketWindow window = new TicketWindow(1000);
// 所有线程的集合
List<Thread> threadList = new ArrayList<>();
// 卖出的票数统计
List<Integer> amountList = new Vector<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
// 买票
try {
Thread.sleep(random(10));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int amount = window.sell(random(5));
// 统计买票数
amountList.add(amount);
});
threadList.add(thread);
thread.start();
}
// 等所有线程执行结束
for (Thread thread : threadList) {
thread.join();
}
// 统计卖出的票数和剩余票数
log.debug("余票:{}",window.getCount());
log.debug("卖出的票数:{}", amountList.stream().mapToInt(i-> i).sum());
}
// Random 为线程安全
static Random random = new Random();
// 产生随机 1~5
public static int random(int amount) {
return random.nextInt(amount) + 1;
}
}
// 售票窗口
class TicketWindow {
private int count;
public TicketWindow(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
// 获取余票数量
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
// 售票 synchronized
public int sell(int amount) {
if (this.count >= amount) {
this.count -= amount;
return amount;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
解决 :
// 售票 synchronized
public synchronized int sell(int amount) {
if (this.count >= amount) {
this.count -= amount;
return amount;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
转账案例
@Slf4j(topic = "c.ExerciseTransfer")
public class ExerciseTransfer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Account a = new Account(1000);
Account b = new Account(1000);
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
a.transfer(b, randomAmount());
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
b.transfer(a, randomAmount());
}
}, "t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
// 查看转账2000次后的总金额
log.debug("total:{}", (a.getMoney() + b.getMoney()));
}
// Random 为线程安全
static Random random = new Random();
// 随机 1~100
public static int randomAmount() {
return random.nextInt(100) + 1;
}
}
// 账户
class Account {
private int money;
public Account(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
public int getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(int money) {
this.money = money;
}
// 转账
public void transfer(Account target, int amount) {
synchronized(Account.class) {
if (this.money >= amount) {
this.setMoney(this.getMoney() - amount);
target.setMoney(target.getMoney() + amount);
}
}
}
}
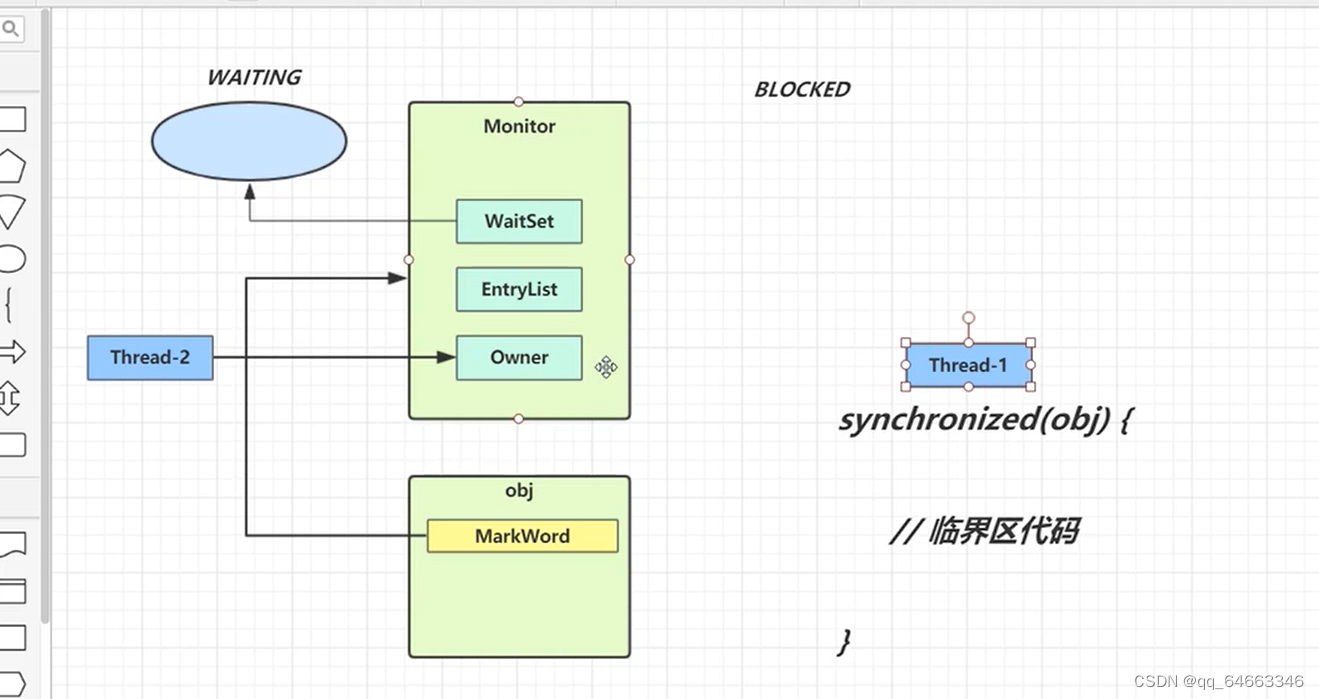
Moniter
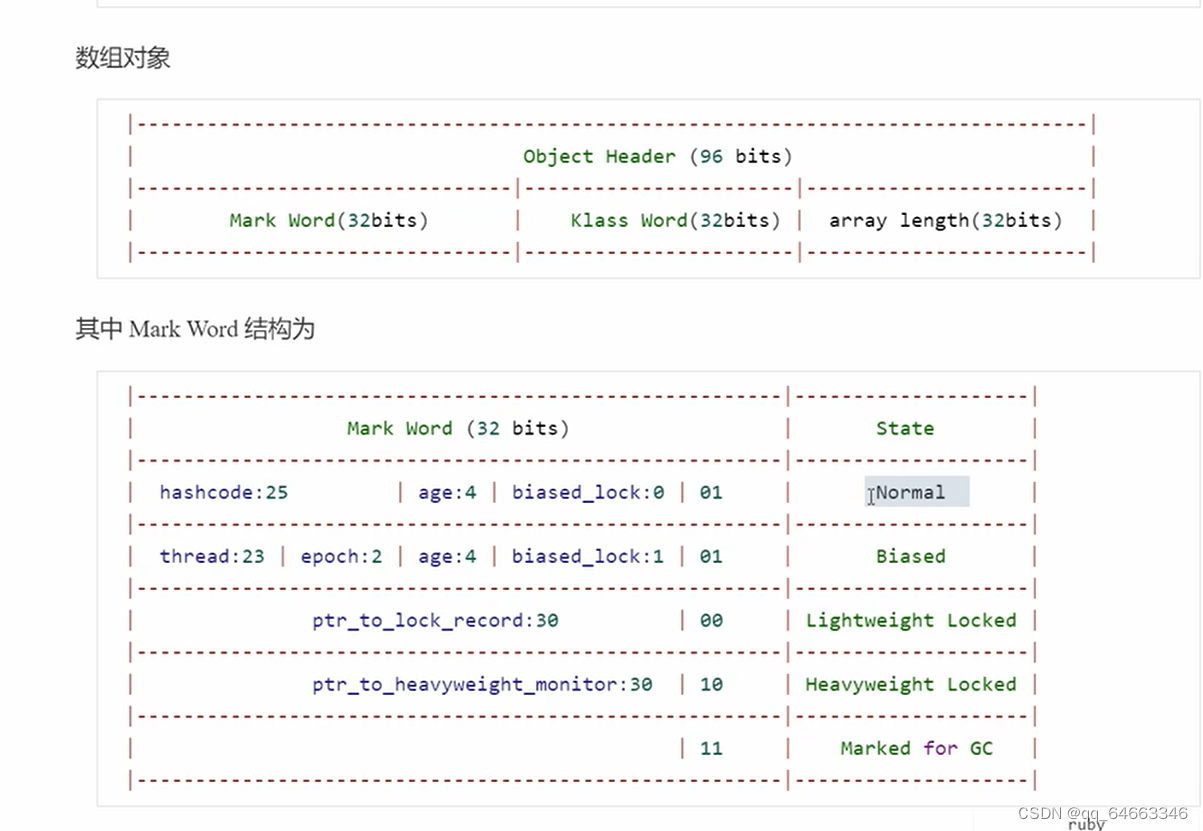
Java对象头
包括了markword主要就是存储hashcode,age(gc生命值),biase_lock是不是偏向锁,01加锁的情况
还有就是klassword只要就是指向类对象(类的信息)。
如果是数组那么就还包括了数组的长度。
Moniter(锁)
Thread1此时进入阻塞队列
工作原理
实际上就是把obj的markword前面30bit记录monitor的地址,指向monitor。然后如果有线程要执行临时区的时候那么就把monitor的owner指向对应的线程。如果又有线程进来,那么会看看obj是否关联锁,然后再看看锁是否有owner,如果有那么就进入到EntryList阻塞等待。等待线程释放锁之后,唤醒entryList然后重新开始竞争。


