- 1Vim 编辑器中大写键的命令
- 22022“高考记忆” 已打包完成,请查收!_你有一份“高考回忆”已打包完成,请查收!
- 3TwoSampleMR安装R包(devtools辅助从GitHub上安装R包)_twosamplemr包官网
- 4EXCEL中sum、sumif、sumifs、if、subtotal、vlookup、match、index函数使用方法详解。_subtotal嵌套sumif使用
- 5IOS 纯代码自定义UIView案例
- 6机器学习环境初步搭建(conda和Visual Studio Code安装教程超详细版)_vscode conda
- 7TestFlight 如何获取邀请码
- 8Rabbitmq消息重复消费问题(幂等性保障)_rabbitmq 重复消费幂等校验
- 9毕业设计商城小程序练习_vscode些购物车代码
- 10mysql导出数据1049_mysql备份数据出现mysqldump: Got error: 1049: Unknown database ‘jxgl>jxgl.sql‘ when selecting...
人工智能之蚁群算法_蚁群算法是人工智能吗
赞
踩
蚁群算法简介
蚁群算法(Ant Clony Optimization, ACO)是一种群智能算法,它是由一群无智能或有轻微智能的个体(Agent)通过相互协作而表现出智能行为,从而为求解复杂问题提供了一个新的可能性。蚁群算法最早是由意大利学者Colorni A., Dorigo M. 等于1991年提出。经过20多年的发展,蚁群算法在理论以及应用研究上已经得到巨大的进步。
蚁群算法是一种仿生学算法,是由自然界中蚂蚁觅食的行为而启发的。在自然界中,蚂蚁觅食过程中,蚁群总能够按照寻找到一条从蚁巢和食物源的最优路径。下图显示了这样一个觅食的过程。
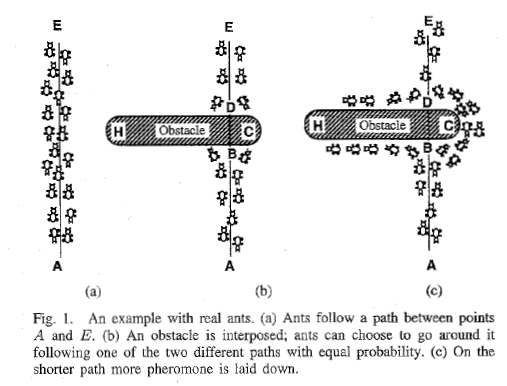
在图(a)中,有一群蚂蚁,假如A是蚁巢,E是食物源(反之亦然)。这群蚂蚁将沿着蚁巢和食物源之间的直线路径行驶。假如在A和E之间突然出现了一个障碍物(图(b)),那么,在B点(或D点)的蚂蚁将要做出决策,到底是向左行驶还是向右行驶?由于一开始路上没有前面蚂蚁留下的 信息素(pheromone) ,蚂蚁朝着两个方向行进的概率是相等的。但是当有蚂蚁走过时,它将会在它行进的路上释放出信息素,并且这种信息素会议一定的速率散发掉。信息素是蚂蚁之间交流的工具之一。它后面的蚂蚁通过路上信息素的浓度,做出决策,往左还是往右。很明显,沿着短边的的路径上信息素将会越来越浓(图(c)),从而吸引了越来越多的蚂蚁沿着这条路径行驶。
TSP问题描述
蚁群算法最早用来求解TSP问题,并且表现出了很大的优越性,因为它分布式特性,鲁棒性强并且容易与其它算法结合,但是同时也存在这收敛速度慢,容易陷入局部最优(local optimal)等缺点。
TSP问题(Travel Salesperson Problem,即旅行商问题或者称为中国邮递员问题),是一种NP-hard问题,此类问题用一般的算法是很难得到最优解的,所以一般需要借助一些启发式算法求解,例如遗传算法(GA),蚁群算法(ACO),微粒群算法(PSO)等等。
TSP问题(旅行商问题)是指旅行家要旅行n个城市,要求各个城市经历且仅经历一次 然后回到出发城市,并要求所走的路程最短。
一个TSP问题可以表达为:求解遍历图G=(V,E,C),所有的节点一次并且回到起始节点,使得连接这些节点的路径成本最低。
蚁群算法原理
假如蚁群中所有蚂蚁的数量为m,所有城市之间的信息素用矩阵pheromone表示,最短路径为bestLength,最佳路径为bestTour。每只蚂蚁都有自己的内存,内存中用一个禁忌表(Tabu)来存储该蚂蚁已经访问过的城市,表示其在以后的搜索中将不能访问这些城市;还有用另外一个允许访问的城市表(Allowed)来存储它还可以访问的城市;另外还用一个矩阵(Delta)来存储它在一个循环(或者迭代)中给所经过的路径释放的信息素;还有另外一些数据,例如一些控制参数(α,β,ρ,Q),该蚂蚁行走玩全程的总成本或距离(tourLength),等等。假定算法总共运行MAX_GEN次,运行时间为t。
蚁群算法计算过程如下:
(1)初始化。
(2)为每只蚂蚁选择下一个节点。
(3)更新信息素矩阵。
(4)检查终止条件
如果达到最大代数MAX_GEN,算法终止,转到第(5)步;否则,重新初始化所有的蚂蚁的Delt矩阵所有元素初始化为0,Tabu表清空,Allowed表中加入所有的城市节点。随机选择它们的起始位置(也可以人工指定)。在Tabu中加入起始节点,Allowed中去掉该起始节点,重复执行(2),(3),(4)步。
(5)输出最优值
代码实现
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import random
import copy
import time
import sys
import math
import tkinter #//GUI模块
import threading
from functools import reduce
# 参数
'''
ALPHA:信息启发因子,值越大,则蚂蚁选择之前走过的路径可能性就越大
,值越小,则蚁群搜索范围就会减少,容易陷入局部最优
BETA:Beta值越大,蚁群越就容易选择局部较短路径,这时算法收敛速度会
加快,但是随机性不高,容易得到局部的相对最优
'''
(ALPHA, BETA, RHO, Q) = (1.0,2.0,0.5,100.0)
# 城市数,蚁群
(city_num, ant_num) = (50,50)
distance_x = [
178,272,176,171,650,499,267,703,408,437,491,74,532,
416,626,42,271,359,163,508,229,576,147,560,35,714,
757,517,64,314,675,690,391,628,87,240,705,699,258,
428,614,36,360,482,666,597,209,201,492,294]
distance_y = [
170,395,198,151,242,556,57,401,305,421,267,105,525,
381,244,330,395,169,141,380,153,442,528,329,232,48,
498,265,343,120,165,50,433,63,491,275,348,222,288,
490,213,524,244,114,104,552,70,425,227,331]
#城市距离和信息素
distance_graph = [ [0.0 for col in range(city_num)] for raw in range(city_num)]
pheromone_graph = [ [1.0 for col in range(city_num)] for raw in range(city_num)]
#----------- 蚂蚁 -----------
class Ant(object):
# 初始化
def __init__(self,ID):
self.ID = ID # ID
self.__clean_data() # 随机初始化出生点
# 初始数据
def __clean_data(self):
self.path = [] # 当前蚂蚁的路径
self.total_distance = 0.0 # 当前路径的总距离
self.move_count = 0 # 移动次数
self.current_city = -1 # 当前停留的城市
self.open_table_city = [True for i in range(city_num)] # 探索城市的状态
city_index = random.randint(0,city_num-1) # 随机初始出生点
self.current_city = city_index
self.path.append(city_index)
self.open_table_city[city_index] = False
self.move_count = 1
# 选择下一个城市
def __choice_next_city(self):
next_city = -1
select_citys_prob = [0.0 for i in range(city_num)] #存储去下个城市的概率
total_prob = 0.0
# 获取去下一个城市的概率
for i in range(city_num):
if self.open_table_city[i]:
try :
# 计算概率:与信息素浓度成正比,与距离成反比
select_citys_prob[i] = pow(pheromone_graph[self.current_city][i], ALPHA) * pow((1.0/distance_graph[self.current_city][i]), BETA)
total_prob += select_citys_prob[i]
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print ('Ant ID: {ID}, current city: {current}, target city: {target}'.format(ID = self.ID, current = self.current_city, target = i))
sys.exit(1)
# 轮盘选择城市
if total_prob > 0.0:
# 产生一个随机概率,0.0-total_prob
temp_prob = random.uniform(0.0, total_prob)
for i in range(city_num):
if self.open_table_city[i]:
# 轮次相减
temp_prob -= select_citys_prob[i]
if temp_prob < 0.0:
next_city = i
break
# 未从概率产生,顺序选择一个未访问城市
# if next_city == -1:
# for i in range(city_num):
# if self.open_table_city[i]:
# next_city = i
# break
if (next_city == -1):
next_city = random.randint(0, city_num - 1)
while ((self.open_table_city[next_city]) == False): # if==False,说明已经遍历过了
next_city = random.randint(0, city_num - 1)
# 返回下一个城市序号
return next_city
# 计算路径总距离
def __cal_total_distance(self):
temp_distance = 0.0
for i in range(1, city_num):
start, end = self.path[i], self.path[i-1]
temp_distance += distance_graph[start][end]
# 回路
end = self.path[0]
temp_distance += distance_graph[start][end]
self.total_distance = temp_distance
# 移动操作
def __move(self, next_city):
self.path.append(next_city)
self.open_table_city[next_city] = False
self.total_distance += distance_graph[self.current_city][next_city]
self.current_city = next_city
self.move_count += 1
# 搜索路径
def search_path(self):
# 初始化数据
self.__clean_data()
# 搜素路径,遍历完所有城市为止
while self.move_count < city_num:
# 移动到下一个城市
next_city = self.__choice_next_city()
self.__move(next_city)
# 计算路径总长度
self.__cal_total_distance()
#----------- TSP问题 -----------
class TSP(object):
def __init__(self, root, width = 800, height = 600, n = city_num):
# 创建画布
self.root = root
self.width = width
self.height = height
# 城市数目初始化为city_num
self.n = n
# tkinter.Canvas
self.canvas = tkinter.Canvas(
root,
width = self.width,
height = self.height,
bg = "#EBEBEB", # 背景白色
xscrollincrement = 1,
yscrollincrement = 1
)
self.canvas.pack(expand = tkinter.YES, fill = tkinter.BOTH)
self.title("TSP蚁群算法(n:初始化 e:开始搜索 s:停止搜索 q:退出程序)")
self.__r = 5
self.__lock = threading.RLock() # 线程锁
self.__bindEvents()
self.new()
# 计算城市之间的距离
for i in range(city_num):
for j in range(city_num):
temp_distance = pow((distance_x[i] - distance_x[j]), 2) + pow((distance_y[i] - distance_y[j]), 2)
temp_distance = pow(temp_distance, 0.5)
distance_graph[i][j] =float(int(temp_distance + 0.5))
# 按键响应程序
def __bindEvents(self):
self.root.bind("q", self.quite) # 退出程序
self.root.bind("n", self.new) # 初始化
self.root.bind("e", self.search_path) # 开始搜索
self.root.bind("s", self.stop) # 停止搜索
# 更改标题
def title(self, s):
self.root.title(s)
# 初始化
def new(self, evt = None):
# 停止线程
self.__lock.acquire()
self.__running = False
self.__lock.release()
self.clear() # 清除信息
self.nodes = [] # 节点坐标
self.nodes2 = [] # 节点对象
# 初始化城市节点
for i in range(len(distance_x)):
# 在画布上随机初始坐标
x = distance_x[i]
y = distance_y[i]
self.nodes.append((x, y))
# 生成节点椭圆,半径为self.__r
node = self.canvas.create_oval(x - self.__r,
y - self.__r, x + self.__r, y + self.__r,
fill = "#ff0000", # 填充红色
outline = "#000000", # 轮廓白色
tags = "node",
)
self.nodes2.append(node)
# 显示坐标
self.canvas.create_text(x,y-10, # 使用create_text方法在坐标(302,77)处绘制文字
text = '('+str(x)+','+str(y)+')', # 所绘制文字的内容
fill = 'black' # 所绘制文字的颜色为灰色
)
# 顺序连接城市
#self.line(range(city_num))
# 初始城市之间的距离和信息素
for i in range(city_num):
for j in range(city_num):
pheromone_graph[i][j] = 1.0
self.ants = [Ant(ID) for ID in range(ant_num)] # 初始蚁群
self.best_ant = Ant(-1) # 初始最优解
self.best_ant.total_distance = 1 << 31 # 初始最大距离
self.iter = 1 # 初始化迭代次数
# 将节点按order顺序连线
def line(self, order):
# 删除原线
self.canvas.delete("line")
def line2(i1, i2):
p1, p2 = self.nodes[i1], self.nodes[i2]
self.canvas.create_line(p1, p2, fill = "#000000", tags = "line")
return i2
# order[-1]为初始值
reduce(line2, order, order[-1])
# 清除画布
def clear(self):
for item in self.canvas.find_all():
self.canvas.delete(item)
# 退出程序
def quite(self, evt):
self.__lock.acquire()
self.__running = False
self.__lock.release()
self.root.destroy()
print (u"\n程序已退出...")
sys.exit()
# 停止搜索
def stop(self, evt):
self.__lock.acquire()
self.__running = False
self.__lock.release()
# 开始搜索
def search_path(self, evt = None):
# 开启线程
self.__lock.acquire()
self.__running = True
self.__lock.release()
while self.__running:
# 遍历每一只蚂蚁
for ant in self.ants:
# 搜索一条路径
ant.search_path()
# 与当前最优蚂蚁比较
if ant.total_distance < self.best_ant.total_distance:
# 更新最优解
self.best_ant = copy.deepcopy(ant)
# 更新信息素
self.__update_pheromone_gragh()
print (u"迭代次数:",self.iter,u"最佳路径总距离:",int(self.best_ant.total_distance))
# 连线
self.line(self.best_ant.path)
# 设置标题
self.title("TSP蚁群算法(n:随机初始 e:开始搜索 s:停止搜索 q:退出程序) 迭代次数: %d" % self.iter)
# 更新画布
self.canvas.update()
self.iter += 1
# 更新信息素
def __update_pheromone_gragh(self):
# 获取每只蚂蚁在其路径上留下的信息素
temp_pheromone = [[0.0 for col in range(city_num)] for raw in range(city_num)]
for ant in self.ants:
for i in range(1,city_num):
start, end = ant.path[i-1], ant.path[i]
# 在路径上的每两个相邻城市间留下信息素,与路径总距离反比
temp_pheromone[start][end] += Q / ant.total_distance
temp_pheromone[end][start] = temp_pheromone[start][end]
# 更新所有城市之间的信息素,旧信息素衰减加上新迭代信息素
for i in range(city_num):
for j in range(city_num):
pheromone_graph[i][j] = pheromone_graph[i][j] * RHO + temp_pheromone[i][j]
# 主循环
def mainloop(self):
self.root.mainloop()
#----------- 程序的入口处 -----------
if __name__ == '__main__':
TSP(tkinter.Tk()).mainloop()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
- 172
- 173
- 174
- 175
- 176
- 177
- 178
- 179
- 180
- 181
- 182
- 183
- 184
- 185
- 186
- 187
- 188
- 189
- 190
- 191
- 192
- 193
- 194
- 195
- 196
- 197
- 198
- 199
- 200
- 201
- 202
- 203
- 204
- 205
- 206
- 207
- 208
- 209
- 210
- 211
- 212
- 213
- 214
- 215
- 216
- 217
- 218
- 219
- 220
- 221
- 222
- 223
- 224
- 225
- 226
- 227
- 228
- 229
- 230
- 231
- 232
- 233
- 234
- 235
- 236
- 237
- 238
- 239
- 240
- 241
- 242
- 243
- 244
- 245
- 246
- 247
- 248
- 249
- 250
- 251
- 252
- 253
- 254
- 255
- 256
- 257
- 258
- 259
- 260
- 261
- 262
- 263
- 264
- 265
- 266
- 267
- 268
- 269
- 270
- 271
- 272
- 273
- 274
- 275
- 276
- 277
- 278
- 279
- 280
- 281
- 282
- 283
- 284
- 285
- 286
- 287
- 288
- 289
- 290
- 291
- 292
- 293
- 294
- 295
- 296
- 297
- 298
- 299
- 300
- 301
- 302
- 303
- 304
- 305
- 306
- 307
- 308
- 309
- 310
- 311
- 312
- 313
- 314
- 315
- 316
- 317
- 318
- 319
- 320
- 321
- 322
- 323
- 324
- 325
- 326


