热门标签
当前位置: article > 正文
模型蒸馏技术实践
作者:不正经 | 2024-05-07 10:55:17
赞
踩
模型蒸馏

学习目标
- 了解什么是模型蒸馏(model distillation)技术和相关原理。
- 掌握使用Textbrewer进行模型蒸馏。
什么是模型蒸馏
- Hinton(AI教父)在NIPS2014提出了知识蒸馏(Knowledge Distillation)的概念,至此开启了该领域的深入研究。我们将模型蒸馏看作是知识蒸馏体系的重要分支。
- 它的目的是:进行模型压缩,就和模型量化和剪枝一样。
- 它实现的方式是将预压缩模型定义为teacher model,这个teacher model在蒸馏过程中参数一般是不变的(离线蒸馏,即预压缩模型已是是评估指标很高且参数不变的模型)。之后再定义一个student model,这也是我们最终要得到的模型。它将使用部分的真实数据以及使用teacher model预测出结果的数据作为预训练数据进行训练。
- 使用部分真实数据是为了让student model具有一定的拟合能力。
- 使用teacher model预测出结果的数据是为了让student model学习其泛化能力。
- 最后我们可以使用与teacher model相同的验证集上进行student model的评估。
- 之后,我们仍然可以在蒸馏之后得到的student model上进行微调。
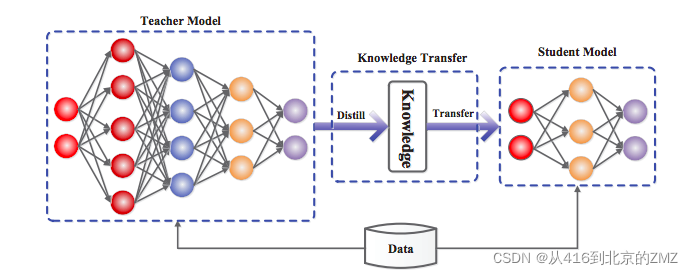
TextBrewer工作流
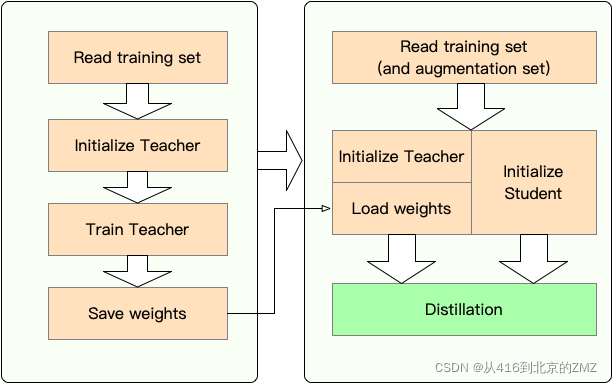
TextBrewer安装
- 安装必备的工具包
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
- 1
- requirements.txt
pyTorch=1.6.0
TensorboardX
numPy
tqdm
transformers>=2.3.0
textbrewer==0.2.1.post1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 注:python >= 3.6
TextBrewer使用步骤
- 第一步:根据配置获得模型teacher model和student model
- 第二步:准备指定格式的训练和验证数据
- 第三步:指定基本的训练配置
- 第四步:自定义蒸馏适配器
- 第五步:自定义蒸馏回调函数
- 第六步:初始化蒸馏配置
- 第七步:整合蒸馏处理器并进行训练
NLP transformer示例
第一步:根据配置获得模型teacher model和student model
import textbrewer from textbrewer import GeneralDistiller from textbrewer import TrainingConfig, DistillationConfig from transformers import BertForSequenceClassification, BertConfig, AdamW from transformers import get_linear_schedule_with_warmup import torch from torch.utils.data import Dataset,DataLoader import numpy as np device = torch.device('cpu') # 读取T模型与S模型的配置 """ T-model: { # 多头注意力机制中输出注意力张量的dropout比率 "attention_probs_dropout_prob": 0.1, # 使用的激活函数为gelu # def gelu_new(x): # Implementation of the gelu activation function currently in Google Bert repo (identical to OpenAI GPT). # Also see https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.08415 # # return 0.5 * x * (1 + torch.tanh(math.sqrt(2 / math.pi) * (x + 0.044715 * torch.pow(x, 3)))) "hidden_act": "gelu", # 前馈全连接层的dropout比率 "hidden_dropout_prob": 0.1, # 前馈全连接的输出维度 "hidden_size": 768, # 参数初始化时使用正态分布,标准差的取值 "initializer_range": 0.02, # 中间全连接层的维度 "intermediate_size": 3072, # 运行位置编码的最大文本长度 "max_position_embeddings": 512, # 多头注意力的头数 "num_attention_heads": 12, # transformer encoder的数量 "num_hidden_layers": 12, # 是指token_type_ids的数量,即句子分隔标记的数量,2代表双句输入,两句话用00001111来区分 "type_vocab_size": 2, # vocab_size的大小 "vocab_size": 30522 } S-model: { "attention_probs_dropout_prob": 0.1, "hidden_act": "gelu", "hidden_dropout_prob": 0.1, "hidden_size": 768, "initializer_range": 0.02, "intermediate_size": 3072, "max_position_embeddings": 512, "num_attention_heads": 12, # 层数变成了3 "num_hidden_layers": 3, "type_vocab_size": 2, "vocab_size": 30522 } """ # 封装成huggingface需要的格式对象 bert_config = BertConfig.from_json_file('bert_config/bert_config.json') bert_config_T3 = BertConfig.from_json_file('bert_config/bert_config_T3.json') # 设定输出时带有隐层的输出 bert_config.output_hidden_states = True bert_config_T3.output_hidden_states = True # 通过huggingface根据配置来加载bert模型 teacher_model = BertForSequenceClassification(bert_config) student_model = BertForSequenceClassification(bert_config_T3) # 发送到设备上 teacher_model.to(device=device) student_model.to(device=device)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
第二步:准备指定格式的训练和验证数据
# 自定义Dataset,该类型的dataset可以被dataloader封装进而被模型加载数据时使用 # 怎么样的Dataset时符合要求的呢? # pytorch官网有一些说明:https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/basics/data_tutorial.html?highlight=dataset # 该类 需要存在__init__(初始化包括输入文本对应的id与对应的标签) # 需要__getitem__根据索引能够取到单条样本 # 需要__len__能够获得全部数据的数量 class DictDataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, all_input_ids, all_labels): self.all_input_ids = all_input_ids self.all_labels = all_labels def __getitem__(self, index): return {'input_ids': self.all_input_ids[index], 'labels': self.all_labels[index]} def __len__(self): return self.all_input_ids.size(0) # 准备数据 # 随机初始化size=(100,128),代表100条样本,每条样本128个字 all_input_ids = torch.randint(low=0,high=100,size=(100,128)) # 因为二分类任务,同样是100个标签,每个结果为0/1 all_labels = torch.randint(low=0,high=2,size=(100,)) # 我们将其放在dataset之中,并分为训练集和验证集 dataset = DictDataset(all_input_ids, all_labels) eval_dataset = DictDataset(all_input_ids, all_labels) # 使用DataLoader封装,指定必要的参数,如batch_size dataloader = DataLoader(dataset,batch_size=32)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
第三步:指定基本的训练配置
# 指定训练轮数和步数
num_epochs = 10
num_training_steps = len(dataloader) * num_epochs
# 指定优化器
optimizer = AdamW(student_model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
# 指定步长调节器(步数用在热启动中使用,即模型在热启动规定的步数内,学习率保持初始值而不被调节或线性增加,防止早期数据无规律而造成的无序波动)
scheduler_class = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
scheduler_args = {'num_warmup_steps':int(0.1*num_training_steps), 'num_training_steps':num_training_steps}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
第四步:自定义蒸馏适配器
# 为了能够满足蒸馏框架的需求,需要自定义适配器
# 这里适配器的作用就是重新定义模型的输出,简化输出,方便计算损失
# 框架要求必须是两个参数,第二个为模型的真实输出
# 这里我们的适配器要以字典输出,'logits'是模型softmax前的输出
# 'hidden'是所有的隐层输出
def simple_adaptor(_, model_outputs):
return {'logits': model_outputs[1],
'hidden': model_outputs[2],}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
第五步:自定义蒸馏回调函数
# 定义回调函数,这里训练后的回调就是进行预测 # 参数包括训练后的模型,验证集,步数,以及设备 def predict(model, eval_dataset, step, device): # 进行评估状态 model.eval() # 预测的logits列表 pred_logits = [] # 真实的标签列表 label_ids =[] # 封装数据集 dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset,batch_size=32) for batch in dataloader: # 在每一个batch里区别输入和标签 input_ids = batch['input_ids'].to(device) labels = batch['labels'] with torch.no_grad(): # 获得logits logits, _ = model(input_ids=input_ids) # 因为可能在gpu上预测,所以要转发回CPU cpu_logits = logits.detach().cpu() # 填充在列表中,准备计算准确率 for i in range(len(cpu_logits)): pred_logits.append(cpu_logits[i].numpy()) label_ids.append(labels[i]) # 模型状态切换,因为该预测只是训练过程中的一次评估,之后还有可能继续训练 model.train() pred_logits = np.array(pred_logits) label_ids = np.array(label_ids) # 取最大值所在索引 y_p = pred_logits.argmax(axis=-1) # 与真实标签对比准确率 accuracy = (y_p==label_ids).sum()/len(label_ids) print ("Number of examples: ",len(y_p)) print ("Acc: ", accuracy) # 回调使用偏函数 from functools import partial # 在回调过程中,每次都可以重写参数eval_dataset和device callback_func = partial(predict, eval_dataset=eval_dataset, device=device)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
第六步:初始化蒸馏配置
# 框架要求初始化两项配置: 训练配置和蒸馏配置
# 训练配置可以指定训练模型的保存路径
# 是否使用混合精度训练,以及分布式训练等等
train_config = TrainingConfig(output_dir="saved_models", device=device)
## 蒸馏配置参数
distill_config = DistillationConfig(
temperature=8,
hard_label_weight=0,
kd_loss_type='mse',
intermediate_matches=[
{'layer_T':0, 'layer_S':0, 'feature':'hidden', 'loss': 'hidden_mse','weight' : 1},
{'layer_T':11, 'layer_S':2, 'feature':'hidden', 'loss': 'hidden_mse', 'weight' : 1}]
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 蒸馏配置参数:
-
temperature: 温度,它是T model蒸馏时输出softamx层中的参数,是对原生softmax的改进而衍生的概念。
![(img-FewabsXd-1639286376010)(./img/gongshi0.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fb406d14a79c4b129d95dfedc5ff18f4.png)
- T越大使得结果概率分布约均匀(平缓),T的作用是改变输出的分布,使得模型原本明朗的正负结果变得模糊,本质是想增大S模型的识别难度,从而增强泛化。
- 我们将训练T model时的准确标签分布,如[1,0]称为硬标签(此时使用原生softmax输出),而使用带有温度参数的softmax的输出,如[0.6,0.4]称为软标签。
-
hard_label_weight:硬标签损失所占的权重
- S model一般使用带有软硬标签的数据进行训练,蒸馏的总损失函数是由三部分组成,软标签部分,硬标签部分和内部网络计算和。软硬标签损失都带有各自的权重。
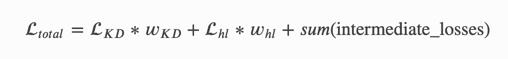
- S model一般使用带有软硬标签的数据进行训练,蒸馏的总损失函数是由三部分组成,软标签部分,硬标签部分和内部网络计算和。软硬标签损失都带有各自的权重。
-
kd_loss_type:软标签损失函数类型,计算软标签的方法,这里是mse。
-
intermediate_matches:模型内部层匹配损失计算规则
- 这里表示:T model第一层输出与S model第一层输出计算mse,T model最后一层输出与S model最后一层输出计算mse,最后加权求和纳入总损失之中。
-
第七步:整合蒸馏处理器并进行训练
# 整合蒸馏处理器
distiller = GeneralDistiller(
train_config=train_config, distill_config = distill_config,
model_T = teacher_model, model_S = student_model,
adaptor_T = simple_adaptor, adaptor_S = simple_adaptor)
# 进行蒸馏训练
with distiller:
distiller.train(optimizer,dataloader, num_epochs=num_epochs,
scheduler_class=scheduler_class, scheduler_args = scheduler_args, callback=callback_func)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
效果对比
- 我们将在路径saved_models中生成若干参数文件,它们是蒸馏后的bert模型的参数文件,大小为175M,而原生的bert参数大小为391M。
| bert | 蒸馏后的bert | |
|---|---|---|
| 大小 | 391M | 175M |
- 如何使用蒸馏后的pkl文件:
# 加载蒸馏后的模型
bert_config_T3 = BertConfig.from_json_file('bert_config/bert_config_T3.json')
bert_config_T3.output_hidden_states = True
model = BertForSequenceClassification(bert_config_T3)
PATH = './saved_models/gs40.pkl'
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(PATH))
model.eval()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
CV resnet示例
第一步:根据配置获得模型teacher model和student model
import textbrewer from textbrewer import GeneralDistiller from textbrewer import TrainingConfig, DistillationConfig from transformers import AdamW from transformers import get_linear_schedule_with_warmup import torch from torch.utils.data import Dataset,DataLoader import numpy as np device = torch.device('cpu') import torch.nn as nn import torchvision.models as models # teacher模型使用resnet152 # student模型使用resnet18 model_fe_152 = models.resnet152(pretrained=True) num_ftrs_152 = model_fe_152.fc.in_features model_fe_152.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs_152, 2) teacher_model = model_fe_152.to(device) model_fe_18 = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) num_ftrs_18 = model_fe_18.fc.in_features model_fe_18.fc = nn.Linear(num_ftrs_18, 2) student_model = model_fe_18.to(device) from torchsummary import summary # 在蒸馏前可以看到二者模型的参数大小 # teacher为221.82,student为42.64 summary(teacher_model, (3, 7, 7)) summary(student_model, (3, 7, 7))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 输出效果:
================================================================ Total params: 58,147,906 Trainable params: 58,147,906 Non-trainable params: 0 ---------------------------------------------------------------- Input size (MB): 0.00 Forward/backward pass size (MB): 2.23 Params size (MB): 221.82 Estimated Total Size (MB): 224.04 ---------------------------------------------------------------- ================================================================ Total params: 11,177,538 Trainable params: 11,177,538 Non-trainable params: 0 ---------------------------------------------------------------- Input size (MB): 0.00 Forward/backward pass size (MB): 0.17 Params size (MB): 42.64 Estimated Total Size (MB): 42.81 ----------------------------------------------------------------
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
第二步:准备指定格式的训练和验证数据
# 自定义Dataset,该类型的dataset可以被dataloader封装进而被模型加载数据时使用 # 怎么样的Dataset时符合要求的呢? # pytorch官网有一些说明:https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/basics/data_tutorial.html?highlight=dataset # 该类 需要存在__init__(初始化包括输入文本对应的id与对应的标签) # 需要__getitem__根据索引能够取到单条样本 # 需要__len__能够获得全部数据的数量 class DictDataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, all_input_ids, all_labels): self.all_input_ids = all_input_ids self.all_labels = all_labels def __getitem__(self, index): return [self.all_input_ids[index]] def __len__(self): return self.all_input_ids.size(0) # 准备数据 # 随机初始化size=(128),代表128条样本 all_input_ids = torch.rand(size=(128, 3, 7, 7)) # 因为二分类任务,同样是128个标签,每个结果为0/1 all_labels = torch.randint(low=0,high=2,size=(128,)) # 我们将其放在dataset之中,并分为训练集和验证集 dataset = DictDataset(all_input_ids, all_labels) eval_dataset = DictDataset(all_input_ids, all_labels) # 使用DataLoader封装,指定必要的参数,如batch_size dataloader = DataLoader(dataset,batch_size=64) labelloader = DataLoader(all_labels,batch_size=64)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
第三步:指定基本的训练配置
# 指定训练轮数和步数
num_epochs = 10
num_training_steps = len(dataloader) * num_epochs
# 指定优化器
optimizer = AdamW(student_model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
# 指定步长调节器(步数用在热启动中使用,即模型在热启动规定的步数内,学
# 习率保持初始值而不被调节或线性增加,防止早期数据无规律而造成的无序波动)
scheduler_class = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
scheduler_args = {'num_warmup_steps':int(0.1*num_training_steps), 'num_training_steps':num_training_steps}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
第四步:自定义蒸馏适配器
# 为了能够满足蒸馏框架的需求,需要自定义适配器
# 这里适配器的作用就是重新定义模型的输出,简化输出,方便计算损失
# 框架要求必须是两个参数,第二个为模型的真实输出
# 这里我们的适配器要以字典输出,'logits'是模型softmax前的输出
def simple_adaptor(_, model_outputs):
return {'logits': model_outputs[0]}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
第五步:自定义蒸馏回调函数
# 定义回调函数,这里训练后的回调就是进行预测 # 参数包括训练后的模型,验证集,步数,以及设备 def predict(model, eval_dataset, step, device): # 进行评估状态 model.eval() # 预测的logits列表 pred_logits = [] # 真实的标签列表 label_ids =[] # 封装数据集 dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset,batch_size=64) for batch in dataloader: # 在每一个batch里区别输入和标签 input_ids = batch[0] labels = next(iter(labelloader)) with torch.no_grad(): # 获得logits logits = model(torch.tensor(input_ids)) # 因为可能在gpu上预测,所以要转发回CPU cpu_logits = logits.detach().cpu() # 填充在列表中,准备计算准确率 for i in range(len(cpu_logits)): pred_logits.append(cpu_logits[i].numpy()) label_ids.append(labels[i]) # 模型状态切换,因为该预测只是训练过程中的一次评估,之后还有可能继续训练 model.train() pred_logits = np.array(pred_logits) label_ids = np.array(label_ids) # 取最大值所在索引 y_p = pred_logits.argmax(axis=-1) # 与真实标签对比准确率 accuracy = (y_p==label_ids).sum()/len(label_ids) print ("Number of examples: ",len(y_p)) print ("Acc: ", accuracy) # 回调使用偏函数 from functools import partial # 在回调过程中,每次都可以重写参数eval_dataset和device callback_func = partial(predict, eval_dataset=eval_dataset, device=device)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
第六步:初始化蒸馏配置
# 框架要求初始化两项配置
# 训练配置和蒸馏配置
## 训练配置可以指定训练模型的保存路径
## 是否使用混合精度训练,以及分布式训练等等
train_config = TrainingConfig(output_dir="saved_models", device=device)
distill_config = DistillationConfig(
temperature=8,
hard_label_weight=0,
kd_loss_type='mse',
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 蒸馏配置参数:
-
temperature: 温度,它是T model蒸馏时输出softamx层中的参数,是>对原生softmax的改进而衍生的概念。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jjRQXjtR-1639286376015)(./img/gongshi0.png)]- T越大使得结果概率分布约均匀(平缓),T的作用是改变输出>的分布,使得模型原本明朗的正负结果变得模糊,本质是想增大S模型的识别难度,从而增强泛化。
- 我们将训练T model时的准确标签分布,如[1,0]称为硬标签>(此时使用原生softmax输出),而使用带有温度参数的softmax的输出,如[0.6>,0.4]称为软标签。
-
hard_label_weight:硬标签损失所占的权重
- S model一般使用带有软硬标签的数据进行训练,蒸馏的总损
失函数是由三部分组成,软标签部分,硬标签部分和内部网络计算和。软硬标签>损失都带有各自的权重。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8WUDkYGt-1639286376017)(./img/gongshi1.png)]
- S model一般使用带有软硬标签的数据进行训练,蒸馏的总损
-
kd_loss_type:软标签损失函数类型,计算软标签的方法,这里是mse。
-
intermediate_matches:模型内部层匹配损失计算规则
- 这里表示:T model第一层输出与S model第一层输出计算mse,T model最后一层输出与S model最后一层输出计算mse,最后加权求和纳入总损失之中。
-
第七步:整合蒸馏处理器并进行训练
# 整合蒸馏处理器
distiller = GeneralDistiller(
train_config=train_config, distill_config = distill_config,
model_T = teacher_model, model_S = student_model,
adaptor_T = simple_adaptor, adaptor_S = simple_adaptor)
# 进行蒸馏训练
with distiller:
distiller.train(optimizer,dataloader, num_epochs=num_epochs,
scheduler_class=scheduler_class, scheduler_args = scheduler_args, callback=callback_func)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 输出效果:
Number of examples: 128 Acc: 0.4453125 10%|███▍ Number of examples: 128[00:00<00:04, 2.14it/s] Acc: 0.523437524it/s] 20%|██████▊ Number of examples: 128[00:00<00:03, 2.11it/s] Acc: 0.523437531it/s] 30%|██████████▏ Number of examples: 128[00:01<00:03, 2.03it/s] Acc: 0.531253.92it/s] 40%|█████████████▌ Number of examples: 128[00:02<00:03, 1.84it/s] Acc: 0.531254.22it/s] 50%|█████████████████Number of examples: 128[00:02<00:02, 1.86it/s] Acc: 0.523437533it/s] 60%|█████████████████Number of examples: 128[00:03<00:02, 1.86it/s] Acc: 0.507812533it/s] 70%|█████████████████Number of examples: 128[00:03<00:01, 1.88it/s] Acc: 0.492187536it/s] 80%|█████████████████Number of examples: 128[00:04<00:01, 1.97it/s] Acc: 0.484375.35it/s] 90%|█████████████████Number of examples: 128[00:04<00:00, 1.92it/s] Acc: 0.484375.26it/s] 100%|█████████████████████████████████| 10/10 [00:05<00:00, 1.91it/s]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
小节总结
- 学习了什么是模型蒸馏。
- 掌握了使用textbrewer进行模型蒸馏的步骤。

声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/不正经/article/detail/548817
推荐阅读
相关标签



