- 1使用 FasterTransformer 和 Triton 推理服务器加速大型 Transformer 模型的推理
- 2计算机直博毕业要求两篇顶会一作难度如何?
- 3经验篇:朋友成功入职商汤自然语言处理算法工程师,整理了一份自然语言处理入门学习资料(NLP自然语言处理/学习路径)_自然语言处理算法工程师培训见习内容
- 4如何看待第三代神经网络SNN?详解脉冲神经网络的架构原理、数据集和训练方法 原创
- 5Windows环境下搭建chatGLM2-6B-int4量化版模型(图文详解-成果案例)_chatglm 小白搭建
- 6java - 实现list「object」中某个属性的对比_java 判断 list对象中某几个属性值比较大小
- 7大数据毕业设计之Python+Vue.js知识图谱音乐推荐系统 音乐爬虫可视化 音乐数据分析 大数据毕设 大数据毕业设计 机器学习 深度学习 人工智能 数据可视化 计算机毕业设计
- 8MMSegmention系列之四(自定义数据集与自定义数据增强管道)_samples_per_gpu
- 9任务4:ChatGPT文本分类_使用chatglm完成中文文本分类
- 10pycharm复习
Graph Attention Network (GAT) 的Tensorflow版代码解析_in_drop != 0.0啥意思
赞
踩
关于GAT的基本原理解析可查看另一篇博客: Graph Attention Network (GAT) 图注意力模型
这里主要对其Tensorflow版本的代码进行解读,其中也会涉及GAT中的一些核心公式。
首先还是给出GAT的示意图:

GAT的Tensorflow版本实现代码Github地址:https://github.com/PetarV-/GAT
代码结构
.
├── data # Cora数据集
├── models # GAT模型定义 (gat.py)
├── pretrained # 预训练的模型
└── utils # 工具定义
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
参数设置
GAT/execute_cora.py
# training params
batch_size = 1
nb_epochs = 100000
patience = 100
lr = 0.005 # learning rate
l2_coef = 0.0005 # weight decay
hid_units = [8] # numbers of hidden units per each attention head in each layer
n_heads = [8, 1] # additional entry for the output layer
residual = False
nonlinearity = tf.nn.elu
model = GAT
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
数据加载
GAT源码默认使用的是cora数据集。cora的相关介绍可以参考:Cora数据集介绍
数据预处理部分和GCN源码相同:GCN代码分析
最终载入的数据adj为邻接矩阵,表示2708篇文章之间的索引关系。feature表示1433个单词在2708篇文章中是否存在。
GAT/utils/process.py
def load_data(dataset_str):
...
print(adj.shape) # (2708, 2708)
print(features.shape) #(2708, 1433)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
特征预处理
GAT/utils/process.py
def preprocess_features(features):
"""Row-normalize feature matrix and convert to tuple representation"""
rowsum = np.array(features.sum(1))
r_inv = np.power(rowsum, -1).flatten()
r_inv[np.isinf(r_inv)] = 0.
r_mat_inv = sp.diags(r_inv)
features = r_mat_inv.dot(features)
return features.todense(), sparse_to_tuple(features)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
模型定义
GAT核心定义:layers.py
def attn_head(seq, out_sz, bias_mat, activation, in_drop=0.0, coef_drop=0.0, residual=False):
with tf.name_scope('my_attn'):
if in_drop != 0.0:
seq = tf.nn.dropout(seq, 1.0 - in_drop)
seq_fts = tf.layers.conv1d(seq, out_sz, 1, use_bias=False)
# simplest self-attention possible
f_1 = tf.layers.conv1d(seq_fts, 1, 1)
f_2 = tf.layers.conv1d(seq_fts, 1, 1)
logits = f_1 + tf.transpose(f_2, [0, 2, 1])
coefs = tf.nn.softmax(tf.nn.leaky_relu(logits) + bias_mat)
if coef_drop != 0.0:
coefs = tf.nn.dropout(coefs, 1.0 - coef_drop)
if in_drop != 0.0:
seq_fts = tf.nn.dropout(seq_fts, 1.0 - in_drop)
vals = tf.matmul(coefs, seq_fts)
ret = tf.contrib.layers.bias_add(vals)
# residual connection
if residual:
if seq.shape[-1] != ret.shape[-1]:
ret = ret + conv1d(seq, ret.shape[-1], 1) # activation
else:
ret = ret + seq
return activation(ret) # activation
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
这里有 3 个比较核心的参数:
- seq 指的是输入的节点特征矩阵,大小为 [num_graph, num_node, fea_size]
- out_sz 指的是变换后的节点特征维度,也就是 W h i Wh_i Whi 后的节点表示维度。
- bias_mat 是经过变换后的邻接矩阵,大小为 [num_node, num_node]。
下面来看几行重点代码的解读:
seq_fts = tf.layers.conv1d(seq, out_sz, 1, use_bias=False) # [num_graph, num_node, out_sz]
- 1
作者首先对原始节点特征 seq 利用卷积核大小为 1 的 1D 卷积模拟投影变换得到了 seq_fts,投影变换后的维度为 out_sz。注意,这里投影矩阵
W
W
W 是所有节点共享,所以 1D 卷积中的多个卷积核也是共享的。
输出seq_fts 对应于公式中的
W
h
Wh
Wh,shape为 [num_graph, num_node, out_sz]。
f_1 = tf.layers.conv1d(seq_fts, 1, 1) # [num_graph, num_node, 1]
f_2 = tf.layers.conv1d(seq_fts, 1, 1) # [num_graph, num_node, 1]
- 1
- 2
投影变换后得到的seq_fts继续使用卷积核大小为 1 的 1D 卷积处理,得到节点本身的投影f_1 和 其邻居的投影f_2,对应于论文公式中的
a
(
W
h
i
,
W
h
j
)
a(Wh_i, Wh_j)
a(Whi,Whj)。注意这里两个投影的参数是分开的,即有两套投影参数
a
1
a_1
a1和
a
2
a_2
a2,分别对应上面两个conv1d 中的参数。
经过 tf.layers.conv1d(seq_fts, 1, 1) 之后的 f_1 和 f_2 对应于公式中的
a
1
W
h
i
a_1Wh_i
a1Whi 和
a
2
W
h
j
a_2Wh_j
a2Whj,维度均为 [num_graph, num_node, 1]。
logits = f_1 + tf.transpose(f_2, [0, 2, 1]) # [num_graph, num_node, num_node]
- 1
将 f_2 转置之后与 f_1 叠加,通过Tensorflow的广播机制得到的大小为 [num_graph, num_node, num_node] 的 logits,就是一个注意力矩阵:
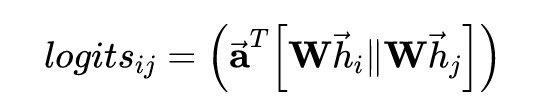
coefs = tf.nn.softmax(tf.nn.leaky_relu(logits) + bias_mat)
- 1
接下来, 按照 GAT 的公式,我们只要对 logits 进行 softmax 归一化就可以得到注意力权重 ,也就是代码里的 coefs。
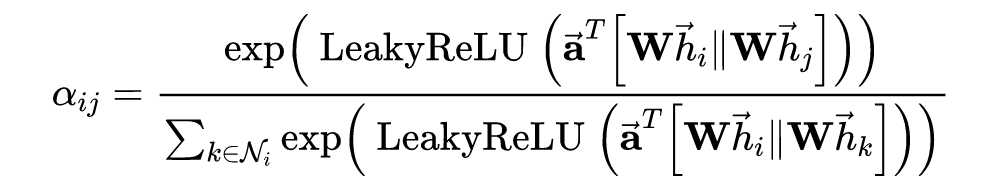 但是,这里为什么会多一项 bias_mat 呢?
但是,这里为什么会多一项 bias_mat 呢?
因为的 logits 存储了任意两个节点之间的注意力值,但是,归一化只需要对每个节点的所有邻居的注意力进行(
k
属于
N
i
k属于N_i
k属于Ni)。所以,引入了 bias_mat 就是将 softmax 的归一化对象约束在每个节点的邻居上,如下式的红色部分。
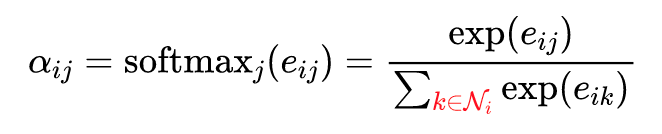
那么,bias_mat 是如何实现的呢?
直接的想法就是只含有 0,1 的邻接矩阵与注意力矩阵相乘,从而对邻居进行 mask。但是,直接用 0,1进行mask,由于softmax中有exp指数操作所以会有问题。
假设注意力权值 [1.2, 0.3, 2.4] 经过 [0,1,1] 的乘法 mask 得到 [0, 0.3, 2.4],再送入到 softmax 归一化,实际上变为 [ e 0 , e 0.3 , e 0.4 ] [e^0, e^{0.3}, e^{0.4}] [e0,e0.3,e0.4],这里本应该被 mask 掉的 1.2 变成了 [ e 0 ] [e^0] [e0]=1,还是参与到了归一化的过程中。
作者这里用一个很大的负数,如
−
1
e
9
-1e9
−1e9,将原始邻居矩阵进行下面的变换。
utils/process.py/adj_to_bias
def adj_to_bias(adj, sizes, nhood=1):
nb_graphs = adj.shape[0] # nb_graphs: 1
# print('adj_to_bias.adj:', adj.shape) # adj: (1, 2708, 2708)
# print('sizes:', sizes) # sizes = nb_nodes : 2708
mt = np.empty(adj.shape) # np.empty返回维度为(1, 2708, 2708)的随机数组
for g in range(nb_graphs): # nb_graphs: 1,此处 g=0 符合循环条件
mt[g] = np.eye(adj.shape[1]) # mt[0]: (2708,2708) 对角线为1的矩阵
for _ in range(nhood): # nhood: 1,此处循环变量=0符合循环条件
mt[g] = np.matmul(mt[g], (adj[g] + np.eye(adj.shape[1]))) # 由于mt[g]为对角阵,故结果仍为(adj[g] + np.eye(adj.shape[1]))
# print(adj[g] + np.eye(adj.shape[1])) # adj(2708,2708) + eye(2708,2708), 实现self-connection自环
for i in range(sizes[g]): # sizes[g]: 2708
for j in range(sizes[g]):
if mt[g][i][j] > 0.0:
mt[g][i][j] = 1.0 # 将大于的0的元素设置为1.0
return -1e9 * (1.0 - mt) # mt中值为1的位置返回0,值为0的位置返回负数-1e9
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
然后,将 bias_mat 和注意力矩阵相加,即 (tf.nn.leaky_relu(logits) + bias_mat), 进而将非节点邻居进行 mask。
例如,[1.2, 0.3, 2.4] 经过
[
−
1
e
9
,
0
,
0
]
[-1e9, 0, 0]
[−1e9,0,0] 的加法 mask 得到
[
e
1.2
−
1
e
9
,
e
0.3
,
e
2.4
]
=
[
0
,
e
0.3
,
e
2.4
]
[e^{1.2-1e9}, e^{0.3}, e^{2.4}]=[0, e^{0.3}, e^{2.4}]
[e1.2−1e9,e0.3,e2.4]=[0,e0.3,e2.4]。这样 softmax 就达到了我们的目的。
vals = tf.matmul(coefs, seq_fts)
- 1
最后,将 mask 之后的注意力矩阵 coefs 与变换后的特征矩阵 seq_fts 相乘,即可得到更新后的节点表示 vals。对应于公式:
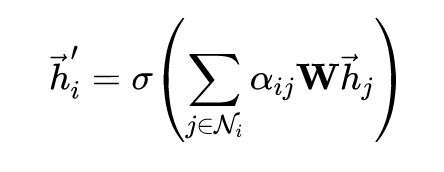
gat.py
logits = model.inference(ftr_in, nb_classes, nb_nodes, is_train,
attn_drop, ffd_drop,
bias_mat=bias_in,
hid_units=hid_units, n_heads=n_heads,
residual=residual, activation=nonlinearity)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
class GAT(BaseGAttN):
def inference(inputs, nb_classes, nb_nodes, training, attn_drop, ffd_drop,
bias_mat, hid_units, n_heads, activation=tf.nn.elu, residual=False):
attns = []
#GAT中预设了8层attention head
for _ in range(n_heads[0]):
attns.append(layers.attn_head(inputs, bias_mat=bias_mat,
out_sz=hid_units[0], activation=activation,
in_drop=ffd_drop, coef_drop=attn_drop, residual=False))
h_1 = tf.concat(attns, axis=-1)
#hid_units表示每一层attention head中的隐藏单元个数
for i in range(1, len(hid_units)):
h_old = h_1
attns = []
for _ in range(n_heads[i]):
attns.append(layers.attn_head(h_1, bias_mat=bias_mat,
out_sz=hid_units[i], activation=activation,
in_drop=ffd_drop, coef_drop=attn_drop, residual=residual))
h_1 = tf.concat(attns, axis=-1)
out = []
#加上输出层
for i in range(n_heads[-1]):
out.append(layers.attn_head(h_1, bias_mat=bias_mat,
out_sz=nb_classes, activation=lambda x: x,
in_drop=ffd_drop, coef_drop=attn_drop, residual=False))
logits = tf.add_n(out) / n_heads[-1]
return logits
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
base_gattn.py
GAT/models/base_gattn.py
定义损失函数。
def loss(logits, labels, nb_classes, class_weights):
sample_wts = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(tf.one_hot(labels, nb_classes), class_weights), axis=-1)
#交叉熵损失函数
xentropy = tf.multiply(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=labels, logits=logits), sample_wts)
return tf.reduce_mean(xentropy, name='xentropy_mean')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
定义训练函数。training最小化损失函数和L2 loss。
def training(loss, lr, l2_coef):
# weight decay
vars = tf.trainable_variables()
lossL2 = tf.add_n([tf.nn.l2_loss(v) for v in vars if v.name not
in ['bias', 'gamma', 'b', 'g', 'beta']]) * l2_coef
# optimizer
opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=lr)
# training op
train_op = opt.minimize(loss+lossL2)
return train_op
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
参考资料:


