热门标签
热门文章
- 1【深度学习笔记】6_7 门控循环单元(GRU)
- 2LeetCode(Python)—— 二叉树的中序遍历(简单)_python二叉树中序遍历
- 3vision transformer 剪枝论文汇总_vision transformer slimming: multi-dimension searc
- 4Python中的f字符串的用法_python f
- 5索引的数据结构
- 6在ffmpeg中添加编解码器_ffdecoder.lib
- 7【Matlab群体智能算法第二期】基于反向学习的改进粒子群算法(含matlab代码)_改进粒子群算法matlab代码
- 8bat, shell脚本ssh自动输入密码_bat自动输入用户名和密码
- 9单片机和嵌入式设计的区别
- 10大型语言模型的语义搜索(一):关键词搜索_如何查看大模型的关键词
当前位置: article > 正文
Yolov5训练自己的数据集(最详细教程)
作者:我家小花儿 | 2024-04-19 15:55:27
赞
踩
yolov5训练自己的数据集
一、环境配置部分
默认使用anaconda来管理python环境。
1.创建虚拟环境
conda create -n yolov5 python=3.82.根据自己安装的CUDA版本去pytorch官网下载torch等。
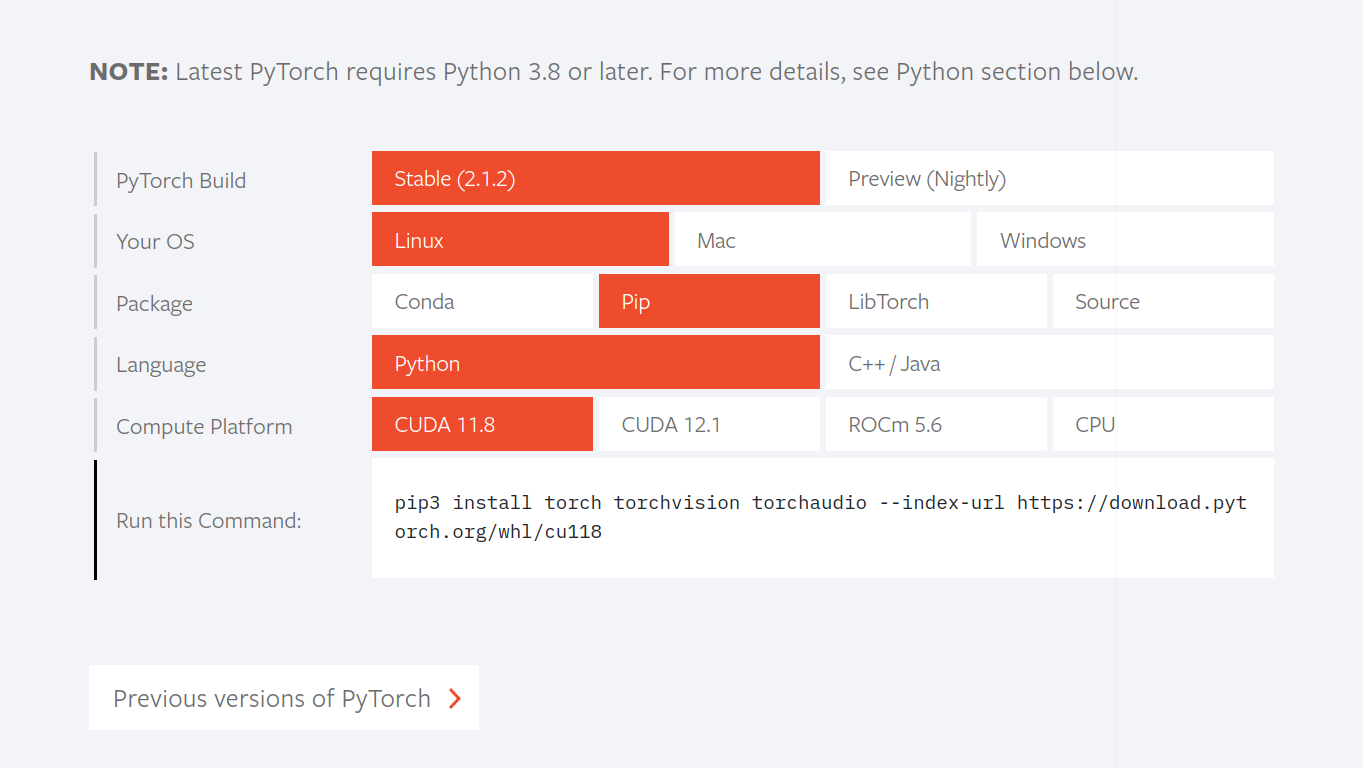
因为我的CUDA是11.1,默认的没有,点击下面的previous versions of pytorch看以前的版本。发现torch1.10.1可以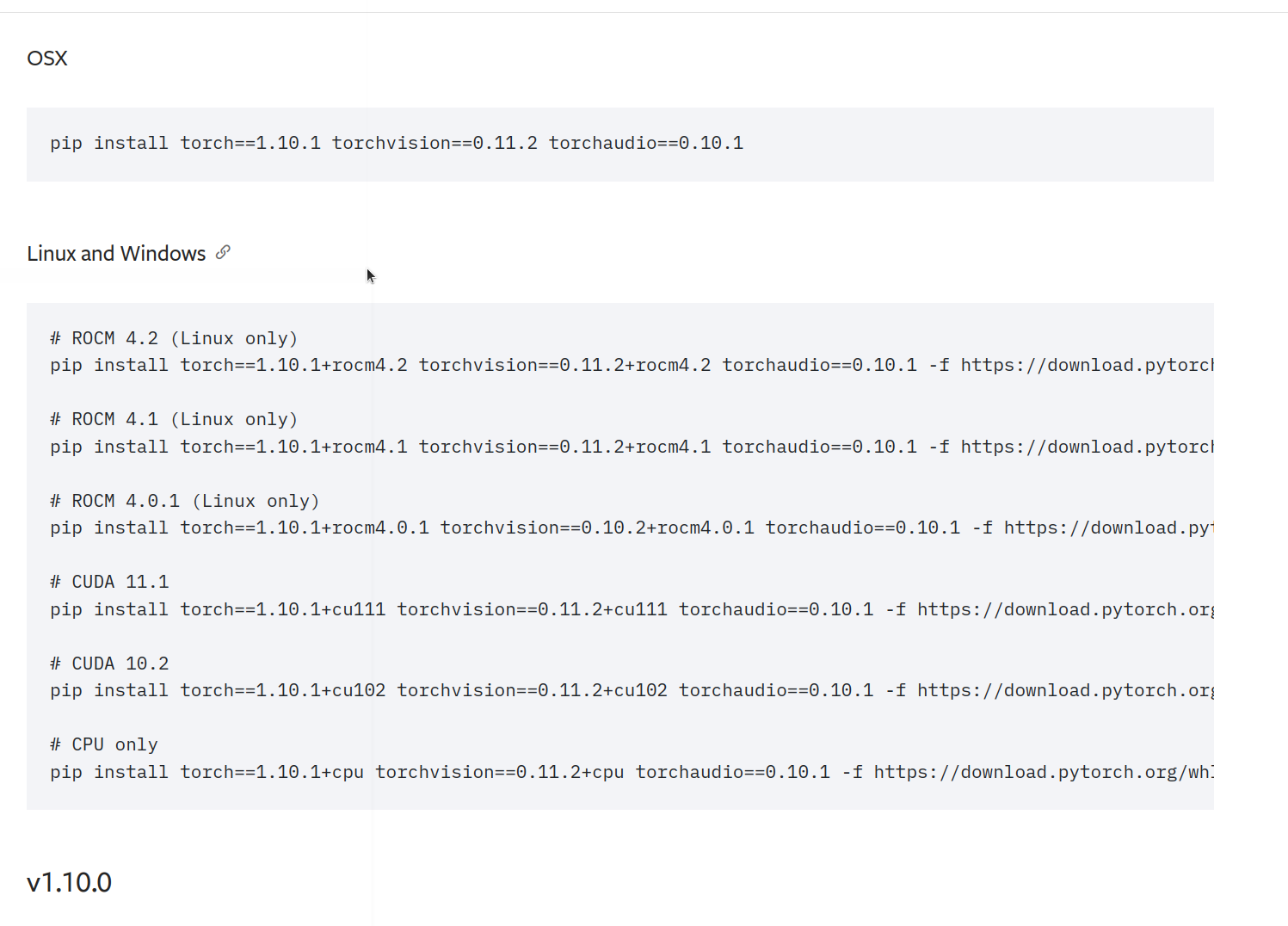
pip install torch==1.10.1+cu111 torchvision==0.11.2+cu111 torchaudio==0.10.1 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu111/torch_stable.html3.下载yolov5代码
- git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 # clone
- cd yolov5
- pip install -r requirements.txt # install
二、数据集制作部分
先用labelimage标注自己的数据,尽量是yolo格式的,也就是标注文件是txt形式,如果有voc格式也没关系,可以进行转换。
2.1voc格式
第一步:把JPEGImages、Annotations、ImageSets(他们的说明见下面代码)和下面的代码放在一个目录下。运行下面的代码,就会在ImageSets/Main/下得到训练和验证的txt文件。
- import os
- import random
-
- images_path = "JPEGImages/" #里面放的图片
- xmls_path = "Annotations/" #里面放的xml格式标注文件
- train_val_txt_path = "ImageSets/Main/" #这个就是一个空的文件夹,运行这个代码后在Main文件夹下有两个训练的txt文件
- val_percent = 0.1 #验证集的比例。
-
- images_list = os.listdir(images_path)
- random.shuffle(images_list)
-
- train_images_count = int((1 - val_percent) * len(images_list))
- val_images_count = int(val_percent * len(images_list))
-
- train_txt = open(os.path.join(train_val_txt_path, "train.txt"), "w")
- train_count = 0
- for i in range(train_images_count):
- text = images_list[i].split(".png")[0] + "\n"
- train_txt.write(text)
- train_count += 1
- print("train_count : " + str(train_count))
- train_txt.close()
-
- val_txt = open(os.path.join(train_val_txt_path, "val.txt"), "w")
- val_count = 0
- for i in range(val_images_count):
- text = images_list[i + train_images_count].split(".png")[0] + "\n"
- val_txt.write(text)
- val_count += 1
- print("val_count : " + str(val_count))
- val_txt.close()

第二步:标注文件voc格式转yolo格式
我们只需要在main函数里指定两个参数,一个是VOC标注文件地址,一个是yolo输出文件地址
- import os
- import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
-
- def convert_folder_to_yolov5(input_folder, output_folder):
- # Ensure output folder exists
- if not os.path.exists(output_folder):
- os.makedirs(output_folder)
-
- # Loop through each XML file in the input folder
- for xml_file_name in os.listdir(input_folder):
- if xml_file_name.endswith('.xml'):
- xml_file_path = os.path.join(input_folder, xml_file_name)
-
- # Generate corresponding output txt file path
- txt_file_name = os.path.splitext(xml_file_name)[0] + '.txt'
- txt_file_path = os.path.join(output_folder, txt_file_name)
-
- # Convert XML to Yolov5 format and save to txt file
- convert_to_yolov5(xml_file_path, txt_file_path)
-
- def convert_to_yolov5(xml_file, output_file):
- tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
- root = tree.getroot()
-
- with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
- for obj in root.findall('object'):
- class_name = obj.find('name').text
- if class_name == 'cone': # Assuming 'disease' is the class of interest
- xmin = int(obj.find('bndbox/xmin').text)
- ymin = int(obj.find('bndbox/ymin').text)
- xmax = int(obj.find('bndbox/xmax').text)
- ymax = int(obj.find('bndbox/ymax').text)
-
- width = xmax - xmin
- height = ymax - ymin
- x_center = (xmin + xmax) / 2.0
- y_center = (ymin + ymax) / 2.0
-
- # Normalize coordinates and dimensions
- x_center /= int(root.find('size/width').text)
- y_center /= int(root.find('size/height').text)
- width /= int(root.find('size/width').text)
- height /= int(root.find('size/height').text)
-
- line = f"{0} {x_center} {y_center} {width} {height}\n"
- f.write(line)
-
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- input_folder_path = "/home/wangchen/YOLOX/cone/Annotations" #voc格式标注文件
- output_folder_path = "/home/wangchen/YOLOX/cone/YOLOLabels" #yolo格式保存地址
-
- convert_folder_to_yolov5(input_folder_path, output_folder_path)

第三步:根据第一步的生成的voc索引,来将yolo数据划分为train和val两部分。
下面这个代码运行完,会在output_dataset_path里面产生两个文件夹,一个train,一个val,每一个里面又都有一个images和labels。这个数据集目录结构是不对的,需要调整一下。改成下图结构
- import os
- import random
- from shutil import copyfile
-
-
- def split_dataset(image_folder, txt_folder, output_folder, split_index):
- # Ensure output folders exist
- for dataset in ['train', 'val']:
- if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(output_folder, dataset, 'images')):
- os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_folder, dataset, 'images'))
- if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(output_folder, dataset, 'txt')):
- os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_folder, dataset, 'txt'))
- train_index = os.path.join(split_index, 'train.txt')
- val_index = os.path.join(split_index, 'val.txt')
- with open(train_index, 'r') as file:
- train_images = [i.strip() for i in file.readlines()]
- with open(val_index, 'r') as file:
- val_images = [i.strip() for i in file.readlines()]
-
- # Copy images to respective folders
- for dataset, images_list in zip(['train', 'val'], [train_images, val_images]):
- for image_file in images_list:
- image_path = os.path.join(image_folder, image_file + '.png')
- copyfile(image_path, os.path.join(output_folder, dataset, 'images', image_file + '.png'))
- txt_file = image_file + '.txt'
- txt_path = os.path.join(txt_folder, txt_file)
-
- # Copy corresponding txt file if exists
- if os.path.exists(txt_path):
- copyfile(txt_path, os.path.join(output_folder, dataset, 'txt', txt_file))
-
-
- if __name__ == "__main__":
- image_folder_path = "/home/wangchen/YOLOX/cone/JPEGImages"
- txt_folder_path = "/home/wangchen/YOLOX/cone/YOLOLabels"
- output_dataset_path = "/home/wangchen/YOLOX/yolo_data"
- split_index = "/home/wangchen/YOLOX/cone/ImageSets/Main"
-
- split_dataset(image_folder_path, txt_folder_path, output_dataset_path, split_index)

2.2YOLO格式
直接按照上面第三步目录结构划分就行。
三、yolov5配置文件修改
修改data/VOC.yaml.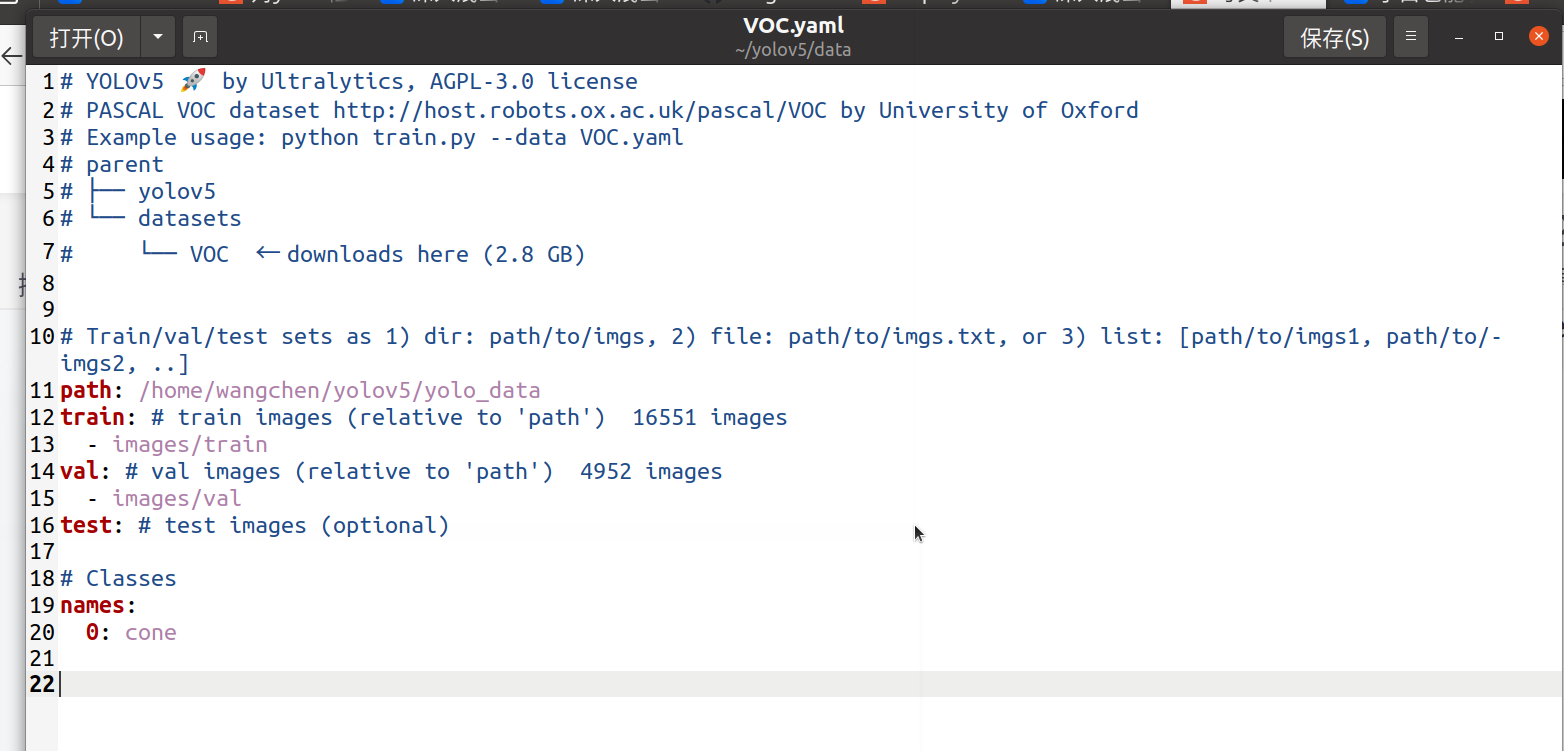
修改models/yolov5_s.yaml里面的类别个数。修改train.py里面的相关超参数即可。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/我家小花儿/article/detail/452539
推荐阅读
相关标签



