- 1知识图谱的概述_知识图谱概念
- 22021 Java面试真题集锦_():弹出最上层的数据,其他的各层内容依次上移一个层。
- 3SpringBoot整合GraphQL第(二)章节_springboot graphql 发送请求
- 4linux docker 软路由,OpenWrt软路由使用docker安装jellyfin影音中心
- 5CSS进阶平面转换
- 6Cocos 深圳沙龙回顾丨探索技术边界,领略大神眼中的 Cocos 世界
- 7解决Windows11/10本地账户改用Microsoft账户登录显示“发生了错误”的问题_改用microsoft账户登录 发生了错误
- 8Oracle EBS SOA 接口删除及发布_ebs soa 删除
- 9STM32F4XX - CAN设置
- 10港台术语与内地术语之对照_测土体high8”hhhhh
bisect_left,bisect_right,bisect的用法,区别以源码分析_bisect_left和bisect_right区别
赞
踩
bisect_left(*args, **kwargs)
向一个数组插入一个数字,返回应该插入的位置。
如果这个数字不存在于这个数组中,则返回第一个比这个数大的数的索引
如果这个数字存在,则返回数组中这个数的位置的最小值(即最左边那个索引)
案例1:这个数在数组中不存在
arr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11]
# 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置
index = bisect_left(arr, 5.5)
print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
执行结果:
Insert 6 at index 4 to maintain sorted order.
我们找到了第一个大于5.5的数字6的位置,输出4
案例2:这个数在数组中存在
我们修改一下代码,寻找6的位置
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect, bisect_right
arr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11]
# 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置
index = bisect_left(arr, 6)
print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
执行结果:
Insert 6 at index 4 to maintain sorted order.
我们发现还是4
bisect_right(*args, **kwargs)
向一个数组插入一个数字,返回应该插入的位置。
作用:返回第一个比这个数大的数的索引
案例1:这个数在数组中不存在
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect, bisect_right
arr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11]
# 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置
index = bisect_right(arr, 6.5)
print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
执行结果:
Insert 6 at index 6 to maintain sorted order.
数字7的位置被输出
案例2:这个数在数组中存在
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect, bisect_right
arr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11]
# 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置
index = bisect_right(arr, 6)
print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
执行结果:
Insert 6 at index 6 to maintain sorted order.
数字7的位置被输出
对比bisect_left 和 bisect_right
相同点:
当第二个参数数字x不在第一个参数数组arr中时候,二者都会返回arr中第一个比x大的数的位置
不同点:
当arr中存在x,bisect_left会返回arr中x的最小索引,而bisect_right会返回第一个比x大的数的位置
bisect()
我们查看源码发现:
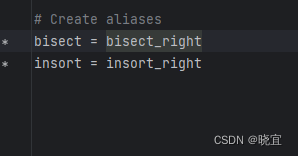
bisect就是bisect_right
完整代码
from bisect import bisect_left, bisect, bisect_right arr = [1, 3, 3, 5, 6, 6, 7, 9, 11] # 在已排序的列表中查找元素 6 的插入位置 index = bisect_right(arr, 6) print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.") index = bisect(arr, 6) print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.") index = bisect_left(arr, 6) print(f"Insert 6 at index {index} to maintain sorted order.")
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
结果:
Insert 6 at index 6 to maintain sorted order.
Insert 6 at index 6 to maintain sorted order.
Insert 6 at index 4 to maintain sorted order.
源码分析
我们先来看 bisect_right 的源码
def bisect_right(a, x, lo=0, hi=None): """Return the index where to insert item x in list a, assuming a is sorted. The return value i is such that all e in a[:i] have e <= x, and all e in a[i:] have e > x. So if x already appears in the list, a.insert(x) will insert just after the rightmost x already there. Optional args lo (default 0) and hi (default len(a)) bound the slice of a to be searched. """ if lo < 0: raise ValueError('lo must be non-negative') if hi is None: hi = len(a) while lo < hi: mid = (lo+hi)//2 # Use __lt__ to match the logic in list.sort() and in heapq if x < a[mid]: hi = mid else: lo = mid+1 return lo
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
bisect_left 的源码
def bisect_left(a, x, lo=0, hi=None): """Return the index where to insert item x in list a, assuming a is sorted. The return value i is such that all e in a[:i] have e < x, and all e in a[i:] have e >= x. So if x already appears in the list, a.insert(x) will insert just before the leftmost x already there. Optional args lo (default 0) and hi (default len(a)) bound the slice of a to be searched. """ if lo < 0: raise ValueError('lo must be non-negative') if hi is None: hi = len(a) while lo < hi: mid = (lo+hi)//2 # Use __lt__ to match the logic in list.sort() and in heapq if a[mid] < x: lo = mid+1 else: hi = mid return lo
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
我们观察到这两种实现方式主要在于下面两行:
bisect_right:
if x < a[mid]: hi = mid
else: lo = mid+1
- 1
- 2
bisect_left:
if a[mid] < x: lo = mid+1
else: hi = mid
- 1
- 2
我们观察到,两段源码都会返回lo,即左边界,所以我们关注一下这两行代码对于左边界的影响:
在bisect_right中,只有当 x=a[mid] or x>a[mid]时,lo才会更新为mid+1,所以最终的lo只可能是第一个大于x的索引
在bisect_left中,当 a[mid] < x时,lo会更新为mid+1,此时我们想要的索引位置必然在mid右侧,所以lo可以为相同的x的第一次出现的位置;同时我们注意到当 a[mid] >= x时,hi=mid,说明当lo取到了相同的数的最左侧时,hi右端点其实会向左平移的,所以lo既可以是数组中第一个大于x的数的索引,也可以是相同的x的最左侧第一个x的索引



