- 1最强开源模型来了!一文详解 Stable Diffusion 3 Medium 特点及用法
- 2免费AI网站,AI人工智能写作+在线AI绘画midjourney_免费网页ai
- 3零信任架构的实施规划——针对联邦系统管理员的规划指南_是nist标准《零信任架构》白皮书中列举的技术方案
- 4西门子S7_1200与E6C2_CWZ6C编码器设置_s7-1200与旋转编码器接线图
- 5LVDS硬件设计
- 6使用shedlock实现分布式互斥执行
- 7Git之Idea操作git_idea 登录git
- 82024HVV蓝队初级面试合集(非常详细)零基础入门到精通,收藏这一篇就够了_2024hvv面试题目
- 9毕业设计:基于java的企业员工信息管理系统设计与实现_员工信息查询功能的设计与实现
- 10视频服务器(4) webrtc-streamer(windows下卡住了)
Go语言Redis理解和使用(十)—— Redis_go redis
赞
踩
文章目录
一、重点内容:
知识要点有哪些?
1、redis是什么
2、redis应用案例
3、redis使用注意事项
二、详细知识点介绍:
1、为什么需要Redis
数据从单表,演进出了分库分表:
MySQL从单机演进出了集群:
数据量增长
读写数据压力的不断增加
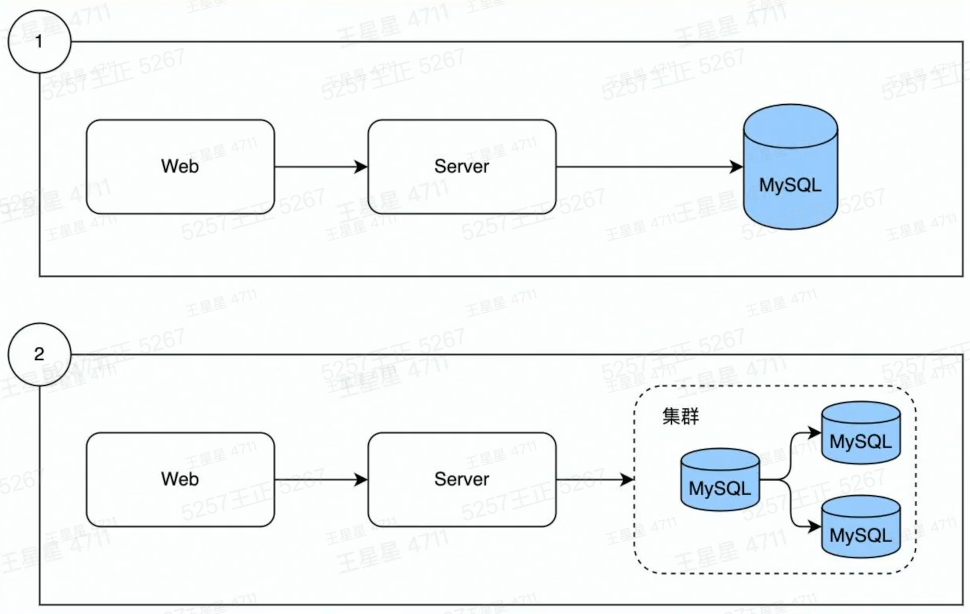
解决问题:
数据分冷热
热数据:经常被访问到的数据
将热数据存储到内存中:
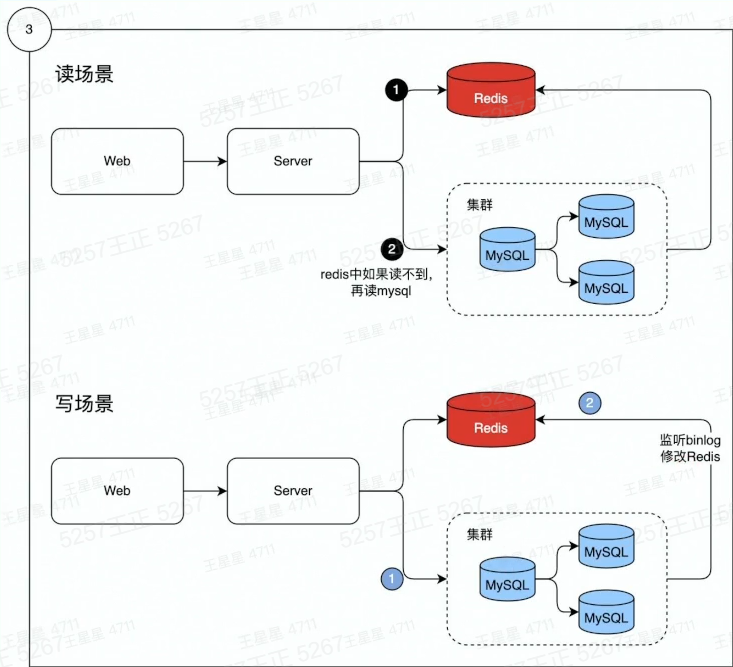
2、redis工作原理
特性:
1、数据从内存中读写
2、数据保存到硬盘上防止重启数据丢失
3、增量数据保存到AOF文件
4、全量数据保存RDB文件
5、单线程处理所有操作命令
图解:
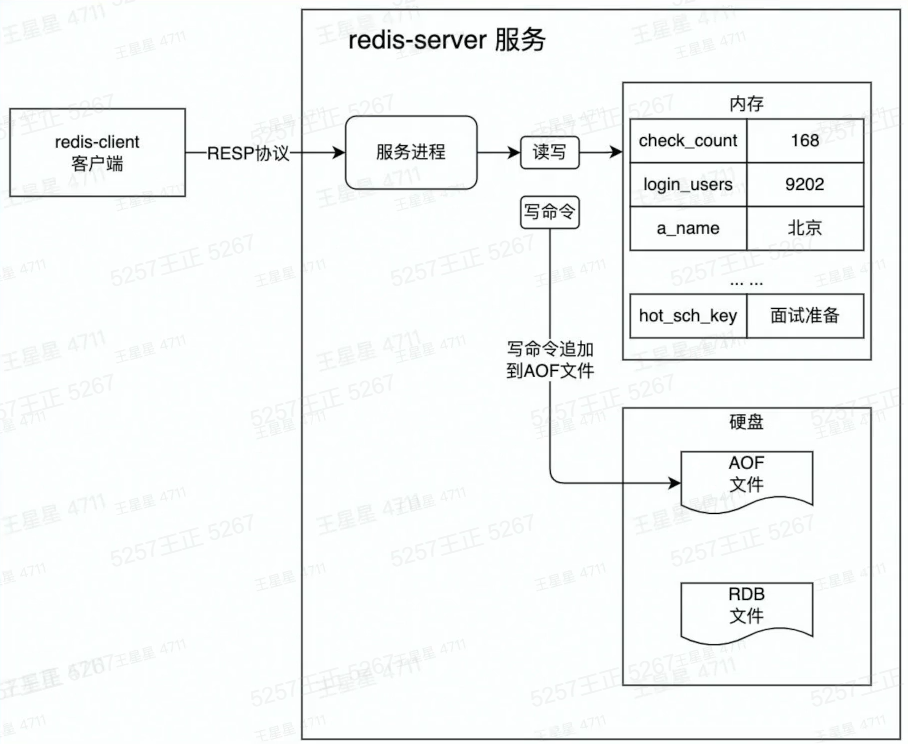
redis启动会首先在硬盘中加载RDB文件、然后加载AOF文件,将数据写入内存中,恢复重启前状态,完成启动。
3、redis安装和配置
安装
熟悉以下命令的操作
- GET/SET/DEL/INCR/SETNX
- HSET/HGET/HINCRBY
- LPUSH/RPOP/LRANGE
- ZADD/ZRANGEBYSCORE/ZREVRANGE/ZINCRBY/ZSCORE
命令使用文档:http://redisdoc.com/
go连接Redis
使用go-redis连接方式:
import ( "fmt" "github.com/go-redis/redis/v8" ) func ConnRedis() { rd := redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{ Addr: "127.0.0.1:6379", // url Password: "", DB:0, // 0号数据库 }) result, err := rd.Ping().Result() if err != nil { fmt.Println("ping err :",err) return } fmt.Println(result) }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
执行后,redis-cli.exe打印了该信息:
1631848109.771606 [0 127.0.0.1:54185] "ping"
- 1
4、redis应用案例
注册全局redis:
package example import ( "github.com/go-redis/redis/v9" ) var RedisClient *redis.Client func init() { rdb := redis.NewClient(&redis.Options{ Addr: "127.0.0.1:6379", Password: "XXXXXX", DB: 1, }) RedisClient = rdb }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
主函数:
输入对应的案例和参数:EXxx和参数。可以运行对应的案例
package main import ( "code.byted.org/wangxingxing.alex/redis_course/example" "context" "fmt" "os" "strings" ) func main() { defer example.RedisClient.Close() argsProg := os.Args var argsWithoutProg []string if len(argsProg) > 0 { argsWithoutProg = os.Args[1:] fmt.Printf("输入参数:\n%s\n----------\n", strings.Join(argsWithoutProg, "\n")) } ctx := context.Background() runExample := argsWithoutProg[0] exampleParams := argsWithoutProg[1:] switch runExample { case "Ex01": example.Ex01(ctx, exampleParams) case "Ex02": example.Ex02(ctx) case "Ex03": example.Ex03(ctx) case "Ex04": example.Ex04(ctx) case "Ex05": example.Ex05(ctx, exampleParams) case "Ex06": example.Ex06(ctx, exampleParams) case "Ex06_2": fmt.Printf("%v\n", exampleParams) example.Ex06_2(ctx, exampleParams) case "Ex07": example.Ex07(ctx) } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
1.连续签到
场景:
掘金每日连续签到
用户每日有一次签到的机会,如果断签,连续签到计数将归0。
连续签到的定义:每天必须在23:59:59前签到
代码:
重点:
1、原有数值加一:
RedisClient.Incr(ctx, key)2、设置过期时间:
RedisClient.ExpireAt(ctx, key, expAt)
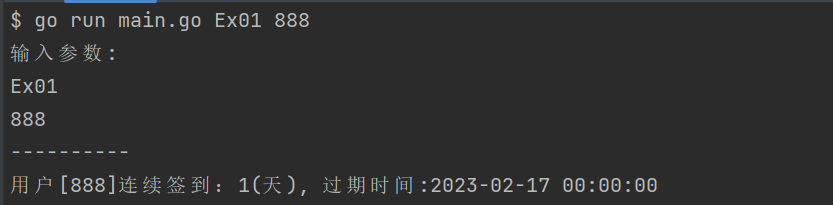
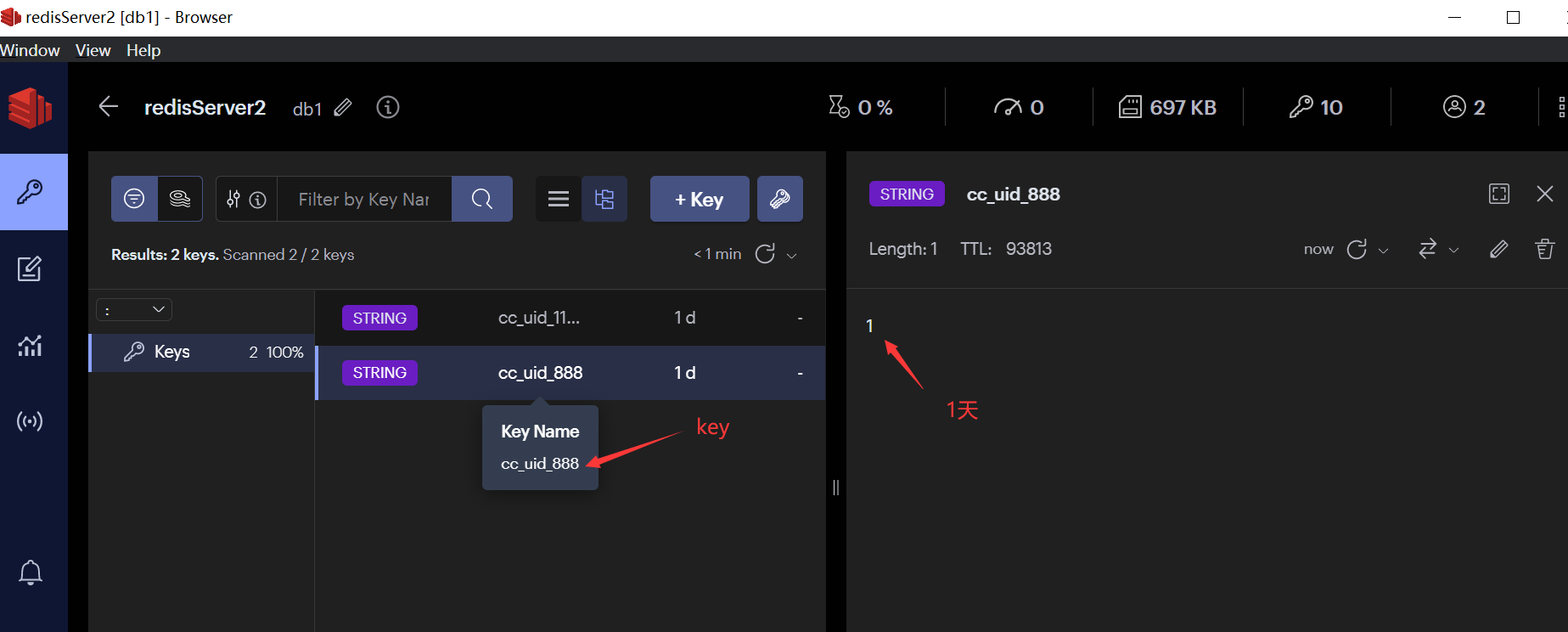
package example import ( "context" "fmt" "strconv" "time" ) var ctx = context.Background() const continuesCheckKey = "cc_uid_%d" // Ex01 连续签到天数 func Ex01(ctx context.Context, params []string) { if userID, err := strconv.ParseInt(params[0], 10, 64); err == nil { addContinuesDays(ctx, userID) } else { fmt.Printf("参数错误, params=%v, error: %v\n", params, err) } } // addContinuesDays 为用户签到续期 func addContinuesDays(ctx context.Context, userID int64) { key := fmt.Sprintf(continuesCheckKey, userID) // 1. 连续签到数+1 err := RedisClient.Incr(ctx, key).Err() if err != nil { fmt.Errorf("用户[%d]连续签到失败", userID) } else { expAt := beginningOfDay().Add(48 * time.Hour) // 2. 设置签到记录在后天的0点到期 if err := RedisClient.ExpireAt(ctx, key, expAt).Err(); err != nil { panic(err) } else { // 3. 打印用户续签后的连续签到天数 day, err := getUserCheckInDays(ctx, userID) if err != nil { panic(err) } fmt.Printf("用户[%d]连续签到:%d(天), 过期时间:%s", userID, day, expAt.Format("2006-01-02 15:04:05")) } } } // getUserCheckInDays 获取用户连续签到天数 func getUserCheckInDays(ctx context.Context, userID int64) (int64, error) { key := fmt.Sprintf(continuesCheckKey, userID) days, err := RedisClient.Get(ctx, key).Result() if err != nil { return 0, err } if daysInt, err := strconv.ParseInt(days, 10, 64); err != nil { panic(err) } else { return daysInt, nil } } // beginningOfDay 获取今天0点时间 func beginningOfDay() time.Time { now := time.Now() y, m, d := now.Date() return time.Date(y, m, d, 0, 0, 0, 0, time.Local) }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
测试:
2.消息通知
使用场景:
消息通知。
例如当文章更新时,将更新后的文章推送到ES,用户就能搜索到最新的文章数据。
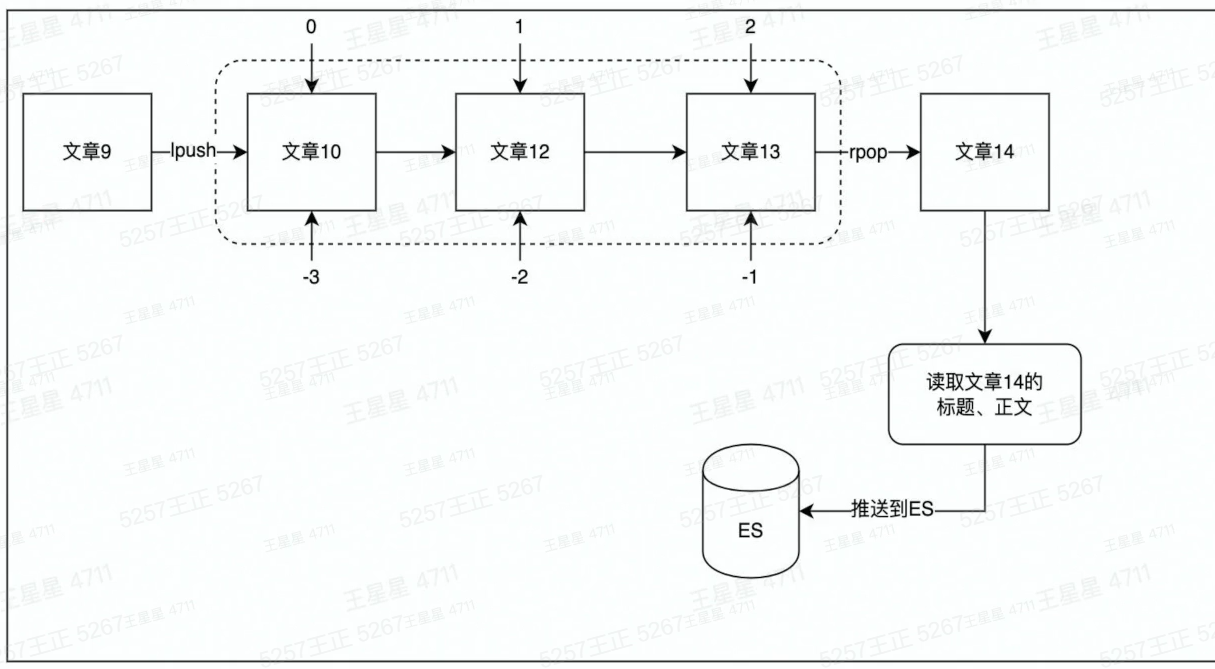
方案:使用list做消息队列
代码:
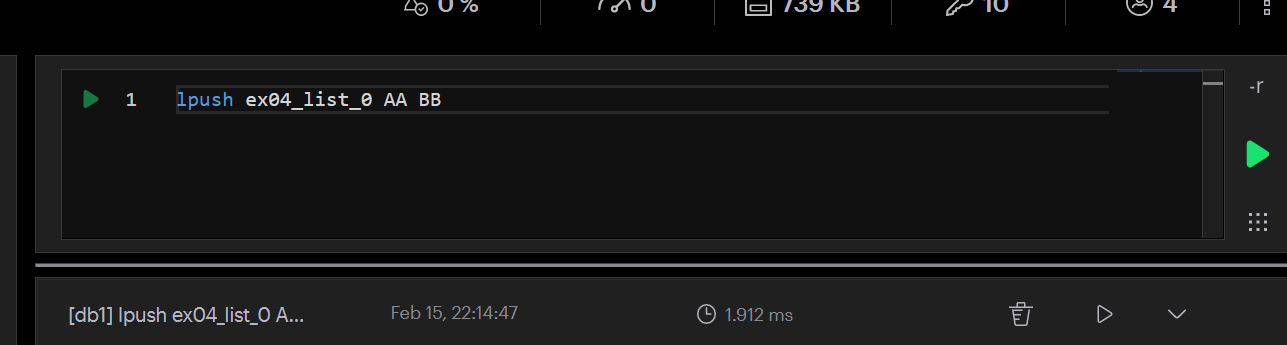
package example import ( "context" "fmt" "strings" "time" "code.byted.org/wangxingxing.alex/redis_course/example/common" ) const ex04ListenList = "ex04_list_0" // lpush ex04_list_0 AA BB // Ex04Params Ex04的自定义函数 type Ex04Params struct { } func Ex04(ctx context.Context) { eventLogger := &common.ConcurrentEventLogger{} // new一个并发执行器 // routineNums是消费端的数量,多消费的场景,可以使用ex04ConsumerPop,使用ex04ConsumerRange存在消息重复消费的问题。 cInst := common.NewConcurrentRoutine(1, eventLogger) // 并发执行用户自定义函数work cInst.Run(ctx, Ex04Params{}, ex04ConsumerPop) // 按日志时间正序打印日志 eventLogger.PrintLogs() } // ex04ConsumerPop 使用rpop逐条消费队列中的信息,数据从队列中移除 // 生成端使用:lpush ex04_list_0 AA BB func ex04ConsumerPop(ctx context.Context, cInstParam common.CInstParams) { routine := cInstParam.Routine for { items, err := RedisClient.BRPop(ctx, 0, ex04ListenList).Result() if err != nil { panic(err) } fmt.Println(common.LogFormat(routine, "读取文章[%s]标题、正文,发送到ES更新索引", items[1])) // 将文章内容推送到ES time.Sleep(1 * time.Second) } }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
测试:
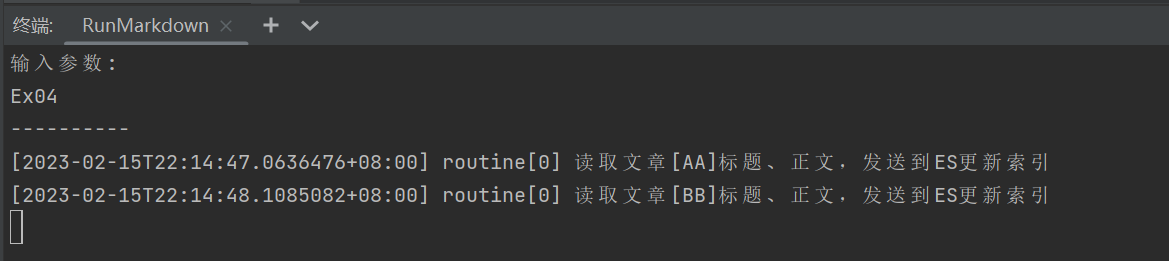
3.计数
场景:
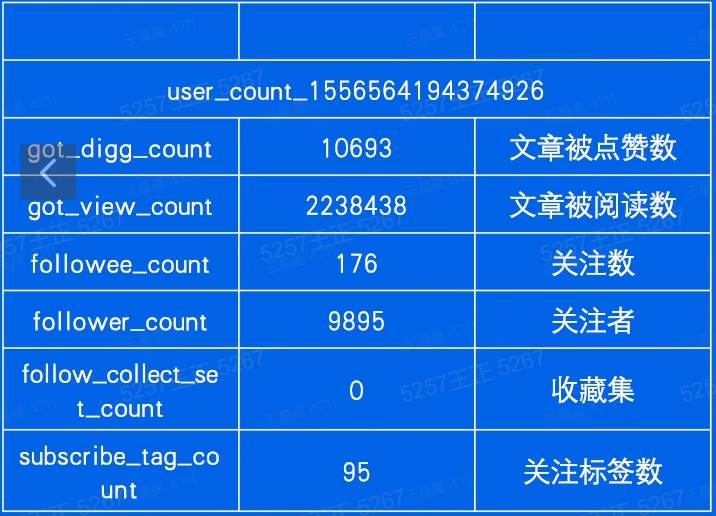
一个用户有多项计数需求,可通过hash结构存储。
代码:
package example import ( "context" "fmt" "os" "strconv" "github.com/go-redis/redis/v9" ) const Ex05UserCountKey = "ex05_user_count" // Ex05 hash数据结果的运用(参考掘金应用) // go run main.go init 初始化用户计数值 // go run main.go get 1556564194374926 // 打印用户(1556564194374926)的所有计数值 // go run main.go incr_like 1556564194374926 // 点赞数+1 // go run main.go incr_collect 1556564194374926 // 点赞数+1 // go run main.go decr_like 1556564194374926 // 点赞数-1 // go run main.go decr_collect 1556564194374926 // 点赞数-1 func Ex05(ctx context.Context, args []string) { if len(args) == 0 { fmt.Printf("args can NOT be empty\n") os.Exit(1) } arg1 := args[0] switch arg1 { case "init": Ex06InitUserCounter(ctx) case "get": userID, err := strconv.ParseInt(args[1], 10, 64) if err != nil { panic(err) } GetUserCounter(ctx, userID) case "incr_like": userID, err := strconv.ParseInt(args[1], 10, 64) if err != nil { panic(err) } IncrByUserLike(ctx, userID) case "incr_collect": userID, err := strconv.ParseInt(args[1], 10, 64) if err != nil { panic(err) } IncrByUserCollect(ctx, userID) case "decr_like": userID, err := strconv.ParseInt(args[1], 10, 64) if err != nil { panic(err) } DecrByUserLike(ctx, userID) case "decr_collect": userID, err := strconv.ParseInt(args[1], 10, 64) if err != nil { panic(err) } DecrByUserCollect(ctx, userID) } } func Ex06InitUserCounter(ctx context.Context) { pipe := RedisClient.Pipeline() userCounters := []map[string]interface{}{ {"user_id": "1556564194374926", "got_digg_count": 10693, "got_view_count": 2238438, "followee_count": 176, "follower_count": 9895, "follow_collect_set_count": 0, "subscribe_tag_count": 95}, {"user_id": "1111", "got_digg_count": 19, "got_view_count": 4}, {"user_id": "2222", "got_digg_count": 1238, "follower_count": 379}, } for _, counter := range userCounters { uid, err := strconv.ParseInt(counter["user_id"].(string), 10, 64) key := GetUserCounterKey(uid) rw, err := pipe.Del(ctx, key).Result() if err != nil { fmt.Printf("del %s, rw=%d\n", key, rw) } _, err = pipe.HMSet(ctx, key, counter).Result() if err != nil { panic(err) } fmt.Printf("设置 uid=%d, key=%s\n", uid, key) } // 批量执行上面for循环设置好的hmset命令 _, err := pipe.Exec(ctx) if err != nil { // 报错后进行一次额外尝试 _, err = pipe.Exec(ctx) if err != nil { panic(err) } } } func GetUserCounterKey(userID int64) string { return fmt.Sprintf("%s_%d", Ex05UserCountKey, userID) } func GetUserCounter(ctx context.Context, userID int64) { pipe := RedisClient.Pipeline() GetUserCounterKey(userID) pipe.HGetAll(ctx, GetUserCounterKey(userID)) cmders, err := pipe.Exec(ctx) if err != nil { panic(err) } for _, cmder := range cmders { counterMap, err := cmder.(*redis.MapStringStringCmd).Result() if err != nil { panic(err) } for field, value := range counterMap { fmt.Printf("%s: %s\n", field, value) } } } // IncrByUserLike 点赞数+1 func IncrByUserLike(ctx context.Context, userID int64) { incrByUserField(ctx, userID, "got_digg_count") } // IncrByUserCollect 收藏数+1 func IncrByUserCollect(ctx context.Context, userID int64) { incrByUserField(ctx, userID, "follow_collect_set_count") } // DecrByUserLike 点赞数-1 func DecrByUserLike(ctx context.Context, userID int64) { decrByUserField(ctx, userID, "got_digg_count") } // DecrByUserCollect 收藏数-1 func DecrByUserCollect(ctx context.Context, userID int64) { decrByUserField(ctx, userID, "follow_collect_set_count") } func incrByUserField(ctx context.Context, userID int64, field string) { change(ctx, userID, field, 1) } func decrByUserField(ctx context.Context, userID int64, field string) { change(ctx, userID, field, -1) } func change(ctx context.Context, userID int64, field string, incr int64) { redisKey := GetUserCounterKey(userID) before, err := RedisClient.HGet(ctx, redisKey, field).Result() if err != nil { panic(err) } beforeInt, err := strconv.ParseInt(before, 10, 64) if err != nil { panic(err) } if beforeInt+incr < 0 { fmt.Printf("禁止变更计数,计数变更后小于0. %d + (%d) = %d\n", beforeInt, incr, beforeInt+incr) return } fmt.Printf("user_id: %d\n更新前\n%s = %s\n--------\n", userID, field, before) _, err = RedisClient.HIncrBy(ctx, redisKey, field, incr).Result() if err != nil { panic(err) } // fmt.Printf("更新记录[%d]:%d\n", userID, num) count, err := RedisClient.HGet(ctx, redisKey, field).Result() if err != nil { panic(err) } fmt.Printf("user_id: %d\n更新后\n%s = %s\n--------\n", userID, field, count) }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
- 154
- 155
- 156
- 157
- 158
- 159
- 160
- 161
- 162
- 163
- 164
- 165
- 166
- 167
- 168
- 169
- 170
- 171
测试:
插入数据:go run main.go Ex05 init
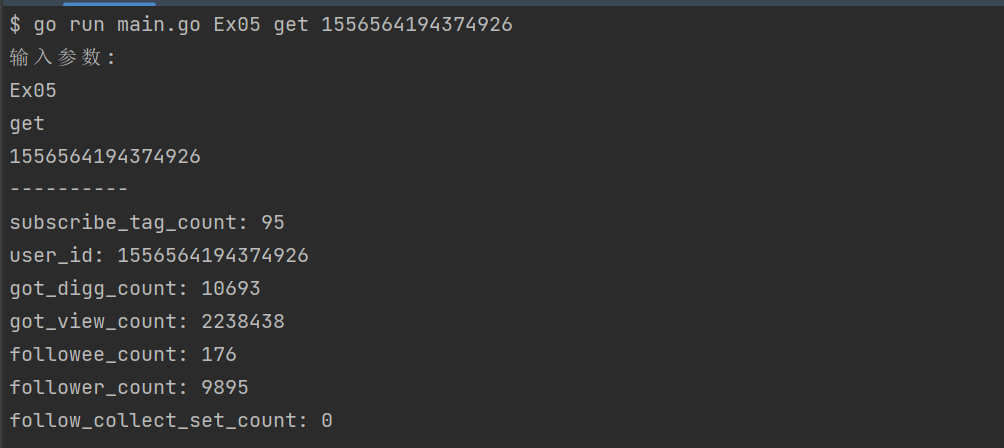
获取数据:go run main.go Ex05 get 1556564194374926
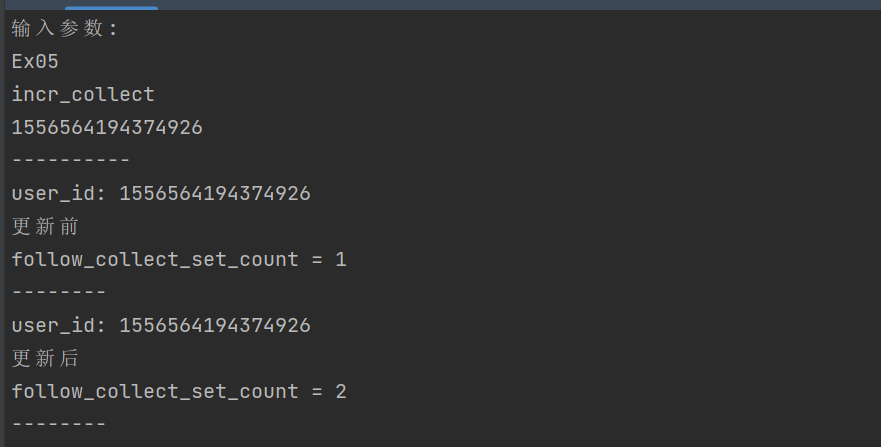
收藏+1:go run main.go Ex05 incr_collect 1556564194374926
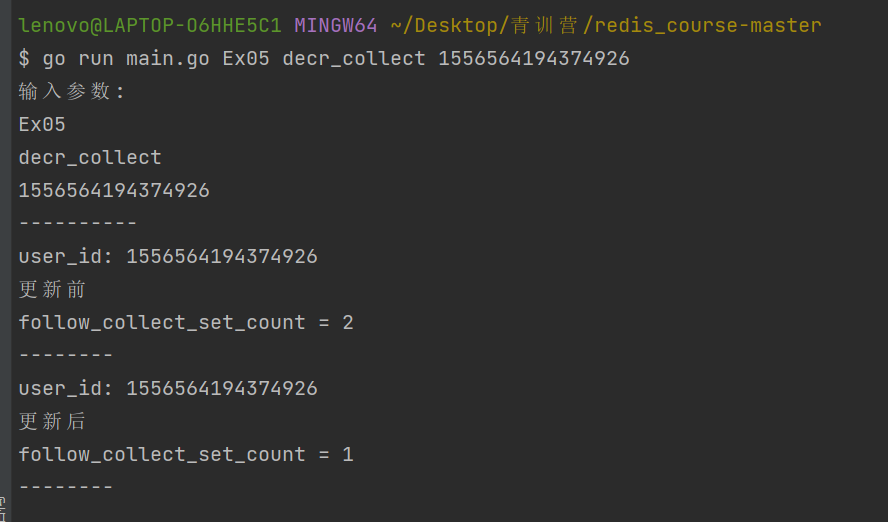
取消收藏:go run main.go Ex05 decr_collect 1556564194374926
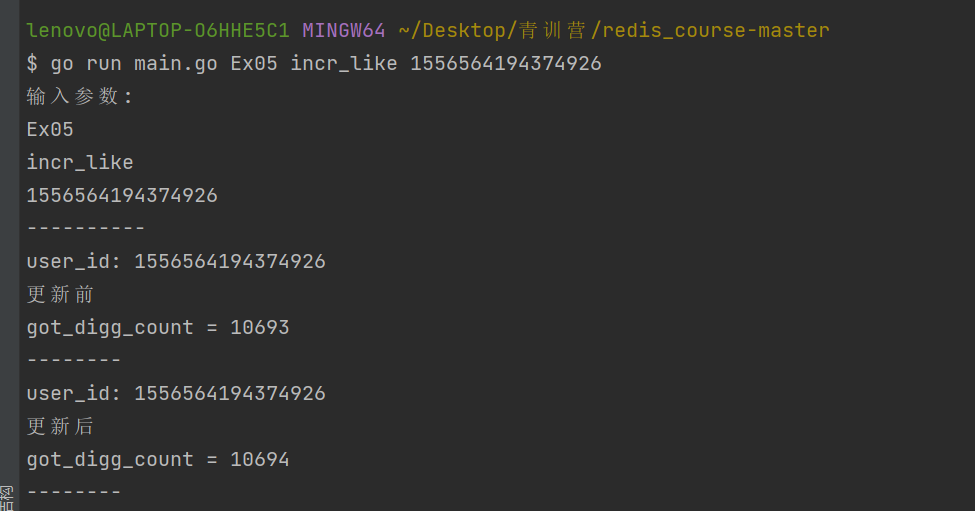
点赞:go run main.go Ex05 incr_like 1556564194374926
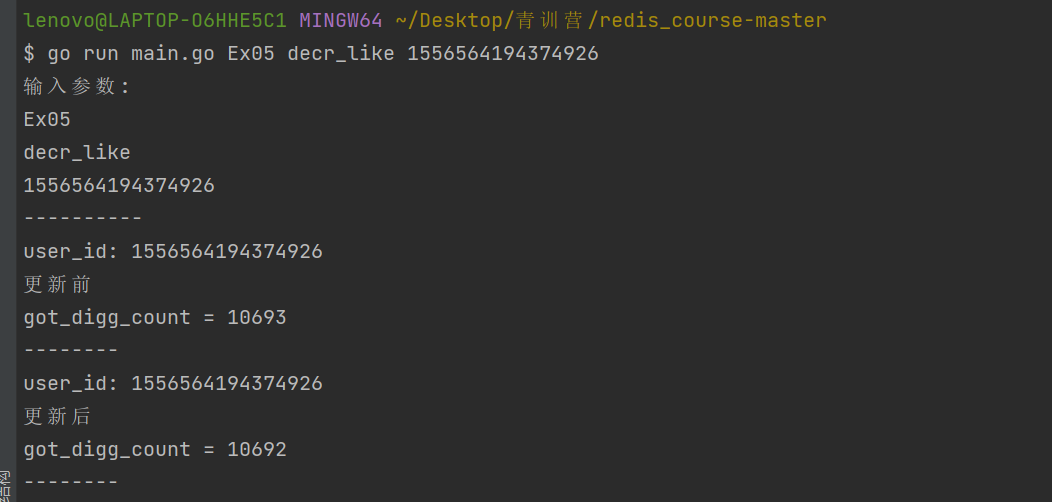
取消点赞:go run main.go Ex05 decr_like 1556564194374926
5、Redis使用注意事项
1、大Key、热Key
大Key的定义:
String类型
大Key标准:value的字节数大于10KB即为大key
Hash/ Set/Zset/list等复杂数据结构类型
大Key标准:元素个数大于5000个或总value字节数大于10MB即为大key
大Key的危害:
1、读取成本高
2、主从复制异常,服务阻塞,无法正常响应请求
3、容易导致慢查询(过期、删除)
4、客户端请求redis超时报错
redis读写过程:
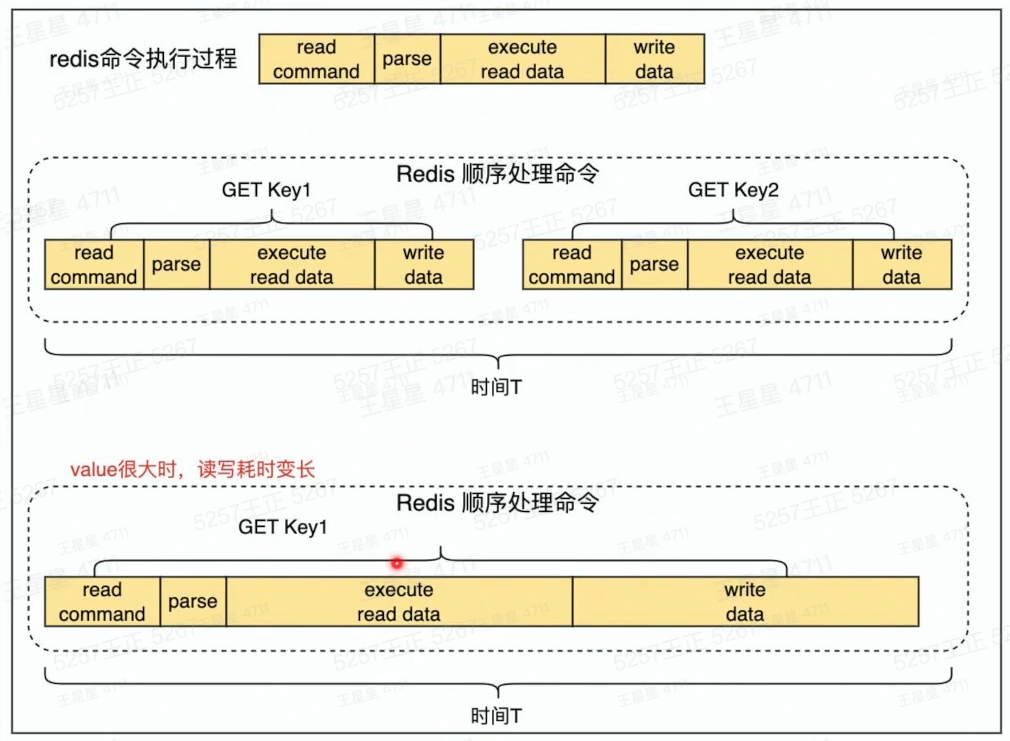
消除大Key
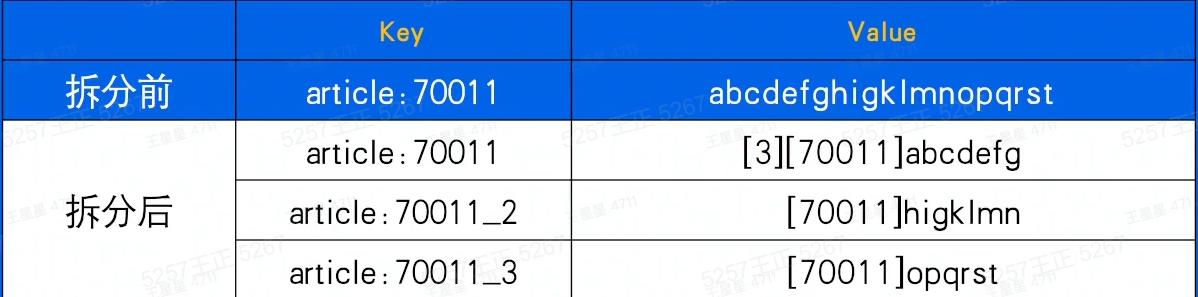
1.拆分
将大key拆分为小key。例如一个String拆分成多个String
2.压缩
将value压缩后写入redis,读取时解压后再使用。
压缩算法可以是gzip、snappy、lz4等。通常情况下,一个压缩算法压缩率高、则解压耗时就长。需要对实际数据进行测试后.选择一个合适的算法。
如果存储的是JSON字符串可以考虑使用MessagePack进行序列化。
3.集合类结构hash、list、set、set
(1)拆分:可以用hash取余、位掩码的方式决定放在哪个key中
(2)区分冷热:如榜单列表场景使用zset,只缓存前10页数据
热Key的定义
用户访问一个Key的QPS特别高,导致Server实例出现CPU负载突增或者不均的情况。热key没有明确的标准,QPS 超过500就有可能被识别为热Key
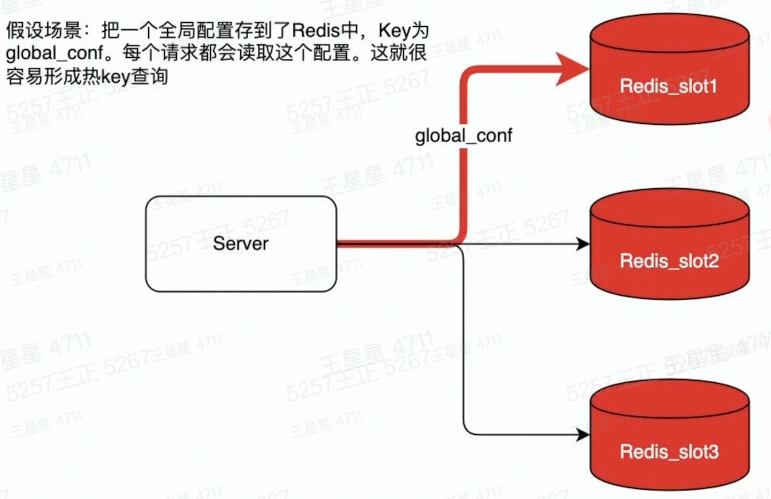
解决热Key的方法
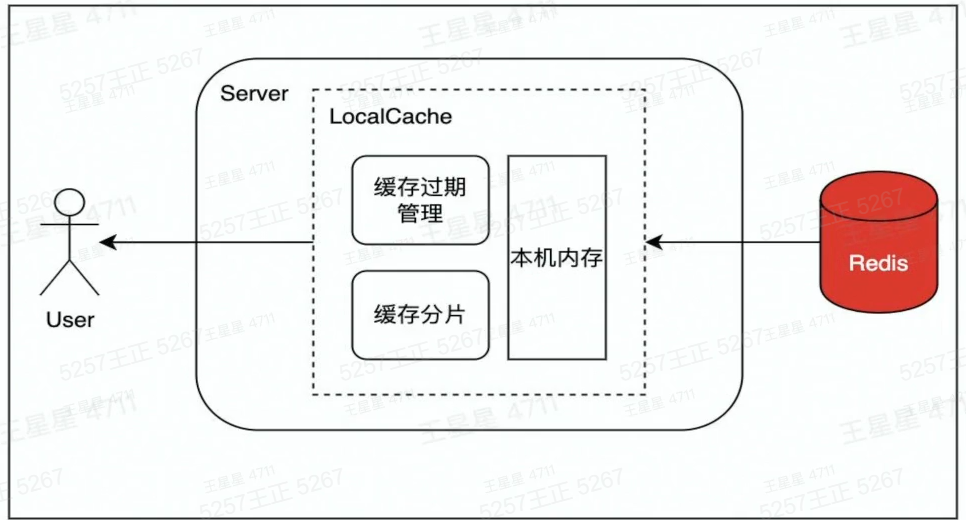
1.设置Localcache
在访问Redis前.在业务服务侧设置Localcache,降低访问Redis的QPS。LocalCache中缓存过期或未命中,则从Redis中将数据更新到LocalCache。Java的Guava、Golang的Bigcache就是这类LocalCache
2.拆分
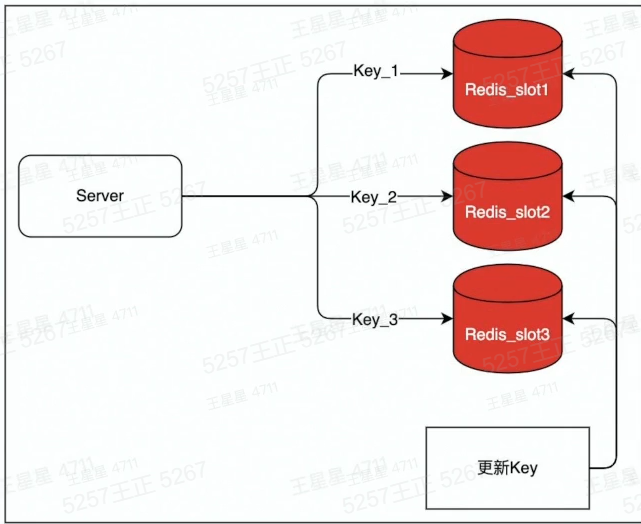
将key :value这一个热Key复制写入多份,例如key1:value,key2:value,访问的时候访问多个key,但value是同一个以此将qps分散到不同实例上.降低负载。代价是,更新时需要更新多个key.存在数据短暂不一致的风险
2、慢查询场景
容易导致redis慢查询的操作:
⑴批量操作一次性传入过多的key/value,如mset/hmset/sadd/zadd等o(n)操作,建议单批次不要超过100,超过100之后性能下降明显。
(2)zset大部分命令都是o(log(n)),当大小超过5k以上时,简单的zadd/zrem也可能导致慢查询。
(3)操作的单个value过大,超过10KB。也即,避免使用大Key
(4)对大key的delete/ expire操作也可能导致慢查询.Redis4.0之前不支持异步删除unlink,大key删除会阻塞Redis
3、缓存穿透、缓存雪崩
缓存穿透:热点数据查询绕过缓存,直接查询数据库
缓存雪崩:大量缓存同时过期
缓存穿透的危害:
(1)查询一个一定不存在的数据
通常不会缓存不存在的数据,这类查询请求都会直接打到db,如果有系统bug或人为攻击.那么容易导致db响应慢甚至宕机。
⑵)缓存过期时
在高并发场景下,一个热key如果过期,会有大量请求同时击穿至db,容易影响db性能和稳定。同一时间有大量key集中过期时,也会导致大量请求落到db上,导致查询变慢,甚至出现db无法响应新的查询。
如何减少缓存穿透:
(1)缓存空值
如一个不存在的userID。这个id在缓存和数据库中都不存在。则可以缓存一个空值,下次再查缓存直接反空值
(2)布隆过滤器
通过bloom filter算法来存储合法Key,得益于该算法超高的压缩率,只需占用极小的空间就能存储大量key值。
三、课后个人总结:
这些内容基本上是第一天的内容,学的真的很过瘾,毕竟对于我来说是干货,能够深入浅出的从案例分析问题。从解决问题中了解设计原理,总结知识。



