- 1干货文:在 Mac 中卸载 Python 的方式_mac卸载python
- 2C语言经典算法之A*搜索算法_c语言a*算法
- 3安装Docker报错TCP connection reset by peer或者Timeout_docker push write: connection reset by peer
- 4ChatGPT高效提问—prompt实践(绘画、Logo设计)_logo生成的prompt
- 5VSCode 配置 CMake_vscode设置cmake
- 6机器人开发--AGV控制系统_agv使用工控机方案
- 7为什么-关于因果关系的新科学 | 01 因果关系之梯_为什么 因果关系的新科学
- 8OceanBase4.1社区版(单节点集群)安装_oceanbase社区版安装
- 9物联网毕设 -- 智能家居控制系统(APP+OneNET+WIFI)_智能设备控制的需求和原理,完成一个控制模块以及app小程序,app与控制模块通过wifi
- 10NLP LLM(Pretraining + Finetuning)——HuggingFace Transformer代码篇_directionality": "bidi",
c++的学习之路:28、哈希表
赞
踩
摘要
本章主要是说一下哈希的实现
目录
一、哈希表
1、哈希概念
顺序结构以及平衡树中,元素关键码与其存储位置之间没有对应的关系,因此在查找一个元素
时,必须要经过关键码的多次比较。顺序查找时间复杂度为O(N),平衡树中为树的高度,即
O($log_2 N$),搜索的效率取决于搜索过程中元素的比较次数。
理想的搜索方法:可以不经过任何比较,一次直接从表中得到要搜索的元素。如果构造一种存储结构,通过某种函数(hashFunc)使元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间能够建立一一映射的关系,那么在查找时通过该函数可以很快找到该元素。当向该结构中:
1、插入元素
根据待插入元素的关键码,以此函数计算出该元素的存储位置并按此位置进行存放
2、搜索元素
对元素的关键码进行同样的计算,把求得的函数值当做元素的存储位置,在结构中按此位置取元素比较,若关键码相等,则搜索成功
该方式即为哈希(散列)方法,哈希方法中使用的转换函数称为哈希(散列)函数,构造出来的结构称
为哈希表(Hash Table)(或者称散列表)
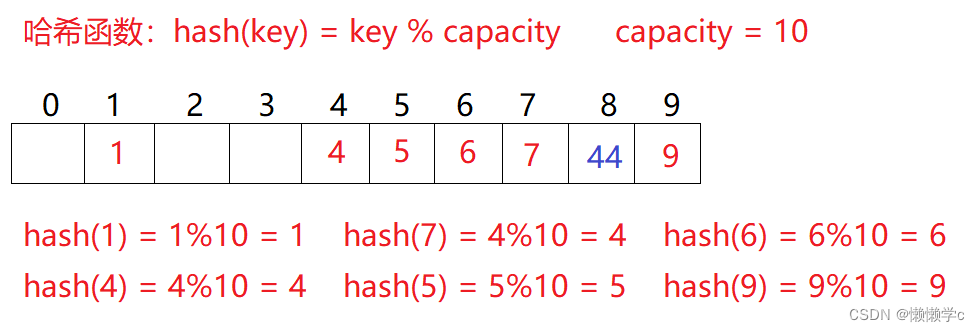
例如:数据集合{1,7,6,4,5,9};
哈希函数设置为:hash(key) = key % capacity; capacity为存储元素底层空间总的大小,用该方法进行搜索不必进行多次关键码的比较,因此搜索的速度比较快
 对于两个数据元素的关键字$k_i$和 $k_j$(i != j),有$k_i$ != $k_j$,但有:Hash($k_i$) ==Hash($k_j$),即:不同关键字通过相同哈希哈数计算出相同的哈希地址,该种现象称为哈希冲突或哈希碰撞
对于两个数据元素的关键字$k_i$和 $k_j$(i != j),有$k_i$ != $k_j$,但有:Hash($k_i$) ==Hash($k_j$),即:不同关键字通过相同哈希哈数计算出相同的哈希地址,该种现象称为哈希冲突或哈希碰撞
解决哈希冲突两种常见的方法是:闭散列和开散列,下面将会讲
2、闭散列
闭散列:也叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有
空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置中的“下一个” 空位置中去。
线性探测法
比如下图中的场景,现在需要插入元素44,先通过哈希函数计算哈希地址,hashAddr为4,因此44理论上应该插在该位置,但是该位置已经放了值为4的元素,即发生哈希冲突。
线性探测:从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻找到下一个空位置为止。
插入:通过哈希函数获取待插入元素在哈希表中的位置,如果该位置中没有元素则直接插入新元素,如果该位置中有元素发生哈希冲突,使用线性探测找到下一个空位置,插入新元素
下面将会讲一下闭散列的代码实现
1、节点创建
这里是创建了一个枚举的表,里面存着三种状态,分别是空、存在和删除,分别代表这数据是否存在哈希表里面,节点里面存着pair创建的键值对和状态,这里默认初始为空的状态也就是EMPTY
enum State//记录状态,空、存在、删除
{
EMPTY,
EXIST,
DELETE
};template<class K, class V>
struct HashData
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state = EMPTY;
};
2、插入
这个插入的写法,首先是判断是否有重复的,这里重复就直接返回flase,然后判断吧哈希表是否为空或者平衡因子是否等于0.7,当这两个条件,任意一个达成的时候,就可以进行扩容,这里是直接而被扩容,然后复用插入这个函数,然后再把两个表进行交换,这里是插入位置的计算是直接%上哈希表的大小,然后才直接找到映射的位置,然后进行插入,如果当前位置已经有数据的时候,就向后进行++找到没有数据的位置插入。
bool Insert(const pair<K, V> kv)//插入
{
if (Find(kv.first))//判断是否重复
return false;
if (_tables.size() == 0 || _n * 10 / _tables.size() == 7)//判断平衡因子或者刚开始的时候扩容,平衡因子是0.7
{
size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;//二倍扩容
HashTable<K, V> newhs;//新表
newhs._tables.resize(newsize);//开辟空间
for (auto e : _tables)
{
if (e._state == EXIST)
{
newhs.Insert(e._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newhs._tables);//交换两个表
}
size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();//进行位置映射
size_t i = 1;
size_t index = hashi;
while (_tables[index]._state == EXIST)//如果存在就进行向后面进行++找到没使用的格子插入
{
index = hashi + i;
index %= _tables.size();
++i;
}
_tables[index]._kv = kv;
_tables[index]._state = EXIST;
_n++;
return true;
}
3、查找
这个查找也是利用映射位置进行查找,如果没有就进行向后遍历去查找,如果还是没有找到就返回空,找到就返回当前节点的位置
HashData<K, V>* Find(const K& key)//查找
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)
{
return nullptr;
}
size_t hashi = key % _tables.size();
size_t i = 1;
size_t index = hashi;
while (_tables[index]._state != EMPTY)//不等于空就继续查找
{
if (_tables[index]._state == EXIST && _tables[index]._kv.first == key)
{//状态等于插入并且key值相等
return&_tables[index];
}
index = hashi + i;
index %= _tables.size();
i++;
if (index == hashi)
{
break;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
4、删除
这个删除就是进行查找,查到就进行删除,这里需要把状态置为删除,然后n--
bool Erase(const K& key)//删除
{
HashData<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_state = DELETE;
_n--;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
5、测试
这里就是进行插入,插入结束后,就进行查找,找到后就是打印在,然后再把13删除,然后就再次查找,这次肯定是找不到,也就是打印不在
void TestHashTable1()
{
int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
HashTable<int, int> ht;
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
if (ht.Find(13))
{
cout << "13在" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "13不在" << endl;
}ht.Erase(13);
if (ht.Find(13))
{
cout << "13在" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "13不在" << endl;
}
}

3、开散列
1、创建
这里是进行创建一个节点,里面存放的是下一个节点的地址和键值对,然后这里也是创建了一个仿函数,然后用以后续使用的方便,这里也是进行特化了一个字符串的。
template<class K, class V>
struct HashNode//哈希节点
{
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
pair<K, V> _kv;HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_next(nullptr)
, _kv(kv)
{}
};template<class K>
struct HashFunc//仿函数进行使用,方便访问,重载了(),这样就可以传入各种类型的参数
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return key;
}
};template<>// 特化
struct HashFunc<string>//特化一个字符串类型
{
// BKDR
size_t operator()(const string& s)//这里是利用ASCLL码值存储
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : s)
{
hash += ch;
hash *= 31;//BKDR的参考数字是31
}
return hash;
}
};
2、插入
这个插入和闭散列差不多,但是他是一个节点下面挂着一串一串的,这样就会减少冲突,这里的计算扩容就是按照大佬的写法就是利用素数进行扩容
size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)//素数,这里就是用来计算表扩容需要的大小,这里就是利用素数进行扩容的
{
static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;
static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
{
53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
};
size_t i = 0;
for (; i < __stl_num_primes; ++i)
{
if (__stl_prime_list[i] > prime)
return __stl_prime_list[i];
}
return __stl_prime_list[i];//找到下一个素数进行返回
}bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)//插入
{
if (Find(kv.first))//去查找需要插入的数,如果找到了就直接返回
return false;
Hash hash;
if (_n == _tables.size())// 负载因因子==1时扩容
{
size_t newsize = GetNextPrime(_tables.size());//进行获取下一个素数
vector<Node*> newtables(newsize, nullptr);//按照这个素数的大小进行创建新的表
for (auto& cur : _tables)//遍历旧的表进行把之前的表插入在新的表
{
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = hash(cur->_kv.first) % newtables.size();
cur->_next = newtables[hashi];
newtables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
}
_tables.swap(newtables);//交换两个表
}
size_t hashi = hash(kv.first) % _tables.size();//计算需要插入的映射位置
Node* newnode = new Node(kv);//创建一个新的节点
newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];//然后进行头插
_tables[hashi] = newnode;
++_n;//这里不能忘了把n进行++
return true;
}
3、查找
这个就是查找就是首先计算到映射的位置,因为开散列的情况下,就是下面在相应的映射位置下面挂着一长串节点,这里就是找到映射节点在进行遍历寻找。
Node* Find(const K& key)//查找
{
if (_tables.size() == 0)//表里面如果是空就返回空
return nullptr;
Hash hash;//利用仿函数创建key值
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();//这个就是计算需要映射的地址
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];//然后记录当前节点
while (cur)//利用这个节点进行遍历桶
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)//如果找到相等key值的时候就返回当前节点
return cur;
cur = cur->_next;//进行迭代
}
return nullptr;//找不到就返回空
}
4、删除
这个删除的函数写法就是首先找到映射位置,然后这里需要注意的是要创建两个节点,以防在后面还有节点就给释放了,出现野指针的情况,这里是用两个接待你进行迭代,以防出现也野指针的情况
bool Erase(const K& key)//删除
{
Hash hash;//利用仿函数创建key值
size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();//计算映射的地址
Node* prev = nullptr;//这里是创建一个节点用来记录,以防删除的时候会造成野指针
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];//利用cur记录桶的当前节点
while (cur)//进行遍历
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)//找到了
{
if (prev == nullptr)//这时就进行判断perv是不是空节点,如果是就直接把桶的下一个节点挂在桶原来的节点
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
}
else//如果perv不是空节点,就把cur的下一个节点挂在了perv节点上面
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
else//没找到就进行迭代
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_next;
}
}
return false;//全部遍历完还没有找到就返回false
}
5、析构函数
这个析构函数的遍历是为把整个表全部都清理干净
~HashTable()//这个析构函数是为了把整个哈希表都清理干净
{
for (auto& cur : _tables)//遍历整个表
{
while (cur)//表里面的桶进行把那一串全删了,迭代进行
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
cur = nullptr;
}
}
二、map
这个map的封装和上章的差不多,这里直接放测试了,然后代码放在文章末
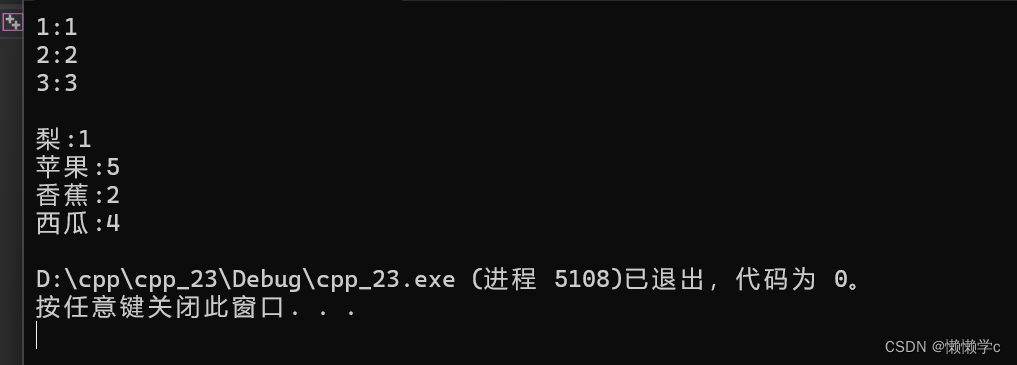
void test_unordered_map1()
{
unordered_map<int, int> m;
m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
m.insert(make_pair(3, 3));
m.insert(make_pair(2, 2));unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}void test_unordered_map2()
{
string arr[] = { "西瓜", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉", "梨" };
unordered_map<string, int> countMap;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
countMap[e]++;
}for (auto& kv : countMap)
{
cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
}
}
三、set
这个set的封装和上章的差不多,这里直接放测试了,然后代码放在文章末
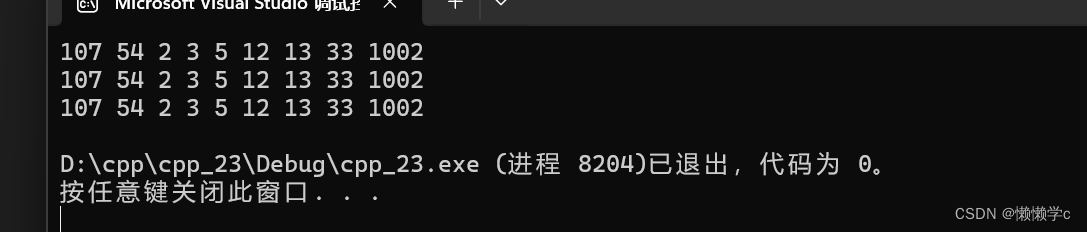
void test_unordered_set1()
{
int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
unordered_set<int> s;
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}s.insert(54);
s.insert(107);unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;print(s);
}
四、位图与布隆过滤器
所谓位图,就是用每一位来存放某种状态,适用于海量数据,数据无重复的场景。通常是用
来判断某个数据存不存在的。
布隆过滤器提出:
我们在使用新闻客户端看新闻时,它会给我们不停地推荐新的内容,它每次推荐时要去重,去掉那些已经看过的内容。问题来了,新闻客户端推荐系统如何实现推送去重的? 用服务器记录了用户看过的所有历史记录,当推荐系统推荐新闻时会从每个用户的历史记录里进行筛选,过滤掉那些已经存在的记录。 如何快速查找呢?
1、用哈希表存储用户记录,缺点:浪费空间
2、用位图存储用户记录,缺点:位图一般只能处理整形,如果内容编号是字符串,就无法处理了。
3、将哈希与位图结合,即布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器概念:
布隆过滤器是由布隆(Burton Howard Bloom)在1970年提出的 一种紧凑型的、比较巧妙的概
率型数据结构,特点是高效地插入和查询,可以用来告诉你 “某样东西一定不存在或者可能存
在”,它是用多个哈希函数,将一个数据映射到位图结构中。此种方式不仅可以提升查询效率,也
可以节省大量的内存空间。
五、代码
test.cpp
- #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- #include <vector>
- using namespace std;
- #include "HashTable.h"
- #include "HashTable - 副本.h"
- #include "UnorderedMap.h"
- #include "UnorderedSet.h"
-
- int main()
- {
- //ly1::TestHashTable1();
- //ly2::TestHashTable1();
- //ly2::TestHashTable2();
- //ly2::TestHashTable3();
- lyset::test_unordered_set1();
- //lymap::test_unordered_map1();
- //lymap::test_unordered_map2();
- }

HashTable.h
- #pragma once
-
- namespace ly3
- {
- template<class T>
- struct HashNode//哈希节点
- {
- HashNode<T>* _next;
- T _data;
-
- HashNode(const T& data)
- :_next(nullptr)
- , _data(data)
- {}
- };
-
- template<class K>
- struct HashFunc//仿函数进行使用,方便访问,重载了(),这样就可以传入各种类型的参数
- {
- size_t operator()(const K& key)
- {
- return key;
- }
- };
-
- // 特化
- template<>// 特化
- struct HashFunc<string>//特化一个字符串类型
- {
- // BKDR
- size_t operator()(const string& s)//这里是利用ASCLL码值存储
- {
- size_t hash = 0;
- for (auto ch : s)
- {
- hash += ch;
- hash *= 31;//BKDR的参考数字是31
- }
- return hash;
- }
- };
-
- //前置声明
- template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
- class HashTable;
-
- template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
- struct __HashIterator//迭代器
- {//下面是一堆重定义,方便编写
- typedef HashNode<T> Node;
- typedef HashTable<K, T, KeyOfT, Hash> HT;
- typedef __HashIterator<K, T, Ref, Ptr, KeyOfT, Hash> Self;
- typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> Iterator;
-
- Node* _node;
- const HT* _ht;
- //下面都是两种,一个是普通迭代器,一个是const迭代器
- __HashIterator(Node* node, const HT* ht)
- :_node(node)
- , _ht(ht)
- {}
-
- __HashIterator(const Iterator& it)
- :_node(it._node)
- , _ht(it._ht)
- {}
-
- Ref operator*()
- {
- return _node->_data;
- }
-
- Ptr operator->()
- {
- return &_node->_data;
- }
-
- bool operator!=(const Self& s)//判断是否相等,直接判断地址就可以
- {
- return _node != s._node;
- }
-
- Self& operator++()//这个++就是用来继续遍历的,就是首先把桶内的数据遍历完,地址在进行++
- {
- if (_node->_next != nullptr)//下一个节点不是空就继续迭代
- {
- _node = _node->_next;
- }
- else//如果是有就进行查找下一个不为空的地址
- {
- KeyOfT kot;
- Hash hash;
- size_t hashi = hash(kot(_node->_data)) % _ht->_tables.size();//记录映射的地址
- ++hashi;
- while (hashi < _ht->_tables.size())//进行迭代
- {
- if (_ht->_tables[hashi])
- {
- _node = _ht->_tables[hashi];
- break;
- }
- else
- {
- ++hashi;
- }
- }
- if (hashi == _ht->_tables.size())//如果到最后,也就是满的地方,就把node置为空
- {
- _node = nullptr;
- }
- }
-
- return *this;
- }
- };
-
- template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
- class HashTable
- {
- template<class K, class T, class Ref, class Ptr, class KeyOfT, class Hash>
- friend struct __HashIterator;
-
- typedef HashNode<T> Node;
- public:
- typedef __HashIterator<K, T, T&, T*, KeyOfT, Hash> iterator;
- typedef __HashIterator<K, T, const T&, const T*, KeyOfT, Hash> const_iterator;
-
- iterator begin()//begin迭代器
- {
- Node* cur = nullptr;
- for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)//遍历找到第一个不为空的直接返回
- {
- cur = _tables[i];
- if (cur)
- {
- break;
- }
- }
-
- return iterator(cur, this);
- }
-
- iterator end()//返回最后一个迭代器
- {
- return iterator(nullptr, this);
- }
-
- const_iterator begin() const//const版本的
- {
- Node* cur = nullptr;
- for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
- {
- cur = _tables[i];
- if (cur)
- {
- break;
- }
- }
-
- return const_iterator(cur, this);
- }
-
- const_iterator end() const
- {
- return const_iterator(nullptr, this);
- }
-
- ~HashTable()//这个析构函数是为了把整个哈希表都清理干净
- {
- for (auto& cur : _tables)//遍历整个表
- {
- while (cur)//表里面的桶进行把那一串全删了,迭代进行
- {
- Node* next = cur->_next;
- delete cur;
- cur = next;
- }
- cur = nullptr;
- }
- }
-
- iterator Find(const K& key)//查找,这个就是利用迭代器查找,原理和上面一个没有封装版本差不多
- {
- if (_tables.size() == 0)
- return end();
- KeyOfT kot;
- Hash hash;
- size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
- Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
- while (cur)
- {
- if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
- {
- return iterator(cur, this);
- }
- cur = cur->_next;
- }
- return end();
- }
-
- bool Erase(const K& key)//删除的也是和原始版本差不多
- {
- Hash hash;
- KeyOfT kot;
- size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();
- Node* prev = nullptr;
- Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
- while (cur)
- {
- if (kot(cur->_data) == key)
- {
- if (prev == nullptr)
- {
- _tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
- }
- else
- {
- prev->_next = cur->_next;
- }
- delete cur;
- return true;
- }
- else
- {
- prev = cur;
- cur = cur->_next;
- }
- }
- return false;
- }
-
- size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)
- {
- static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;
- static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
- {
- 53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
- 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
- 49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
- 1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
- 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
- 1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
- };
-
- size_t i = 0;
- for (; i < __stl_num_primes; ++i)
- {
- if (__stl_prime_list[i] > prime)
- return __stl_prime_list[i];
- }
- return __stl_prime_list[i];
- }
-
- pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data)
- {
- KeyOfT kot;
- iterator it = Find(kot(data));
- if (it != end())
- {
- return make_pair(it, false);
- }
- Hash hash;
- if (_n == _tables.size())
- {
- size_t newsize = GetNextPrime(_tables.size());
- vector<Node*> newtables(newsize, nullptr);
- for (auto& cur : _tables)
- {
- while (cur)
- {
- Node* next = cur->_next;
- size_t hashi = hash(kot(cur->_data)) % newtables.size();
- cur->_next = newtables[hashi];
- newtables[hashi] = cur;
- cur = next;
- }
- }
- _tables.swap(newtables);
- }
- size_t hashi = hash(kot(data)) % _tables.size();
- Node* newnode = new Node(data);
- newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];
- _tables[hashi] = newnode;
- ++_n;
- return make_pair(iterator(newnode, this), false);;
- }
-
- size_t MaxBucketSize()
- {
- size_t max = 0;
- for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)
- {
- auto cur = _tables[i];
- size_t size = 0;
- while (cur)
- {
- ++size;
- cur = cur->_next;
- }
- if (size > max)
- {
- max = size;
- }
- }
- return max;
- }
- private:
- vector<Node*> _tables; // 指针数组
- size_t _n = 0; // 存储有效数据个数
- };
- }

HashTable副本.h
- #pragma once
-
- namespace ly1//散列
- {
- enum State//记录状态,空、存在、删除
- {
- EMPTY,
- EXIST,
- DELETE
- };
-
- template<class K, class V>
- struct HashData
- {
- pair<K, V> _kv;
- State _state = EMPTY;
- };
-
- template<class K, class V>
- class HashTable
- {
- public:
- bool Insert(const pair<K, V> kv)//插入
- {
- if (Find(kv.first))//判断是否重复
- return false;
- if (_tables.size() == 0 || _n * 10 / _tables.size() == 7)//判断平衡因子或者刚开始的时候扩容,平衡因子是0.7
- {
- size_t newsize = _tables.size() == 0 ? 10 : _tables.size() * 2;//二倍扩容
- HashTable<K, V> newhs;//新表
- newhs._tables.resize(newsize);//开辟空间
- for (auto e : _tables)
- {
- if (e._state == EXIST)
- {
- newhs.Insert(e._kv);
- }
- }
- _tables.swap(newhs._tables);//交换两个表
- }
- size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();//进行位置映射
- size_t i = 1;
- size_t index = hashi;
- while (_tables[index]._state == EXIST)//如果存在就进行向后面进行++找到没使用的格子插入
- {
- index = hashi + i;
- index %= _tables.size();
- ++i;
- }
- _tables[index]._kv = kv;
- _tables[index]._state = EXIST;
- _n++;
- return true;
- }
-
- HashData<K, V>* Find(const K& key)//查找
- {
- if (_tables.size() == 0)
- {
- return nullptr;
- }
- size_t hashi = key % _tables.size();
- size_t i = 1;
- size_t index = hashi;
- while (_tables[index]._state != EMPTY)//不等于空就继续查找
- {
- if (_tables[index]._state == EXIST && _tables[index]._kv.first == key)
- {//状态等于插入并且key值相等
- return&_tables[index];
- }
- index = hashi + i;
- index %= _tables.size();
- i++;
- if (index == hashi)
- {
- break;
- }
- }
- return nullptr;
- }
-
- bool Erase(const K& key)//删除
- {
- HashData<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
- if (ret)
- {
- ret->_state = DELETE;
- _n--;
- return true;
- }
- else
- {
- return false;
- }
- }
- private:
- vector<HashData<K, V>> _tables;
- size_t _n = 0; // 存储的数据个数
- };
-
- void TestHashTable1()
- {
- int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
- HashTable<int, int> ht;
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
- }
-
- ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
-
- if (ht.Find(13))
- {
- cout << "13在" << endl;
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "13不在" << endl;
- }
-
- ht.Erase(13);
-
- if (ht.Find(13))
- {
- cout << "13在" << endl;
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "13不在" << endl;
- }
- }
- }
-
-
- namespace ly2
- {
- template<class K, class V>
- struct HashNode//哈希节点
- {
- HashNode<K, V>* _next;
- pair<K, V> _kv;
-
- HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
- :_next(nullptr)
- , _kv(kv)
- {}
- };
-
- template<class K>
- struct HashFunc//仿函数进行使用,方便访问,重载了(),这样就可以传入各种类型的参数
- {
- size_t operator()(const K& key)
- {
- return key;
- }
- };
-
- template<>// 特化
- struct HashFunc<string>//特化一个字符串类型
- {
- // BKDR
- size_t operator()(const string& s)//这里是利用ASCLL码值存储
- {
- size_t hash = 0;
- for (auto ch : s)
- {
- hash += ch;
- hash *= 31;//BKDR的参考数字是31
- }
- return hash;
- }
- };
-
- template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
- class HashTable
- {
- typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
- public:
- Node* Find(const K& key)//查找
- {
- if (_tables.size() == 0)//表里面如果是空就返回空
- return nullptr;
- Hash hash;//利用仿函数创建key值
- size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();//这个就是计算需要映射的地址
- Node* cur = _tables[hashi];//然后记录当前节点
- while (cur)//利用这个节点进行遍历桶
- {
- if (cur->_kv.first == key)//如果找到相等key值的时候就返回当前节点
- return cur;
- cur = cur->_next;//进行迭代
- }
- return nullptr;//找不到就返回空
- }
-
- bool Erase(const K& key)//删除
- {
- Hash hash;//利用仿函数创建key值
- size_t hashi = hash(key) % _tables.size();//计算映射的地址
- Node* prev = nullptr;//这里是创建一个节点用来记录,以防删除的时候会造成野指针
- Node* cur = _tables[hashi];//利用cur记录桶的当前节点
- while (cur)//进行遍历
- {
- if (cur->_kv.first == key)//找到了
- {
- if (prev == nullptr)//这时就进行判断perv是不是空节点,如果是就直接把桶的下一个节点挂在桶原来的节点
- {
- _tables[hashi] = cur->_next;
- }
- else//如果perv不是空节点,就把cur的下一个节点挂在了perv节点上面
- {
- prev->_next = cur->_next;
- }
- delete cur;
- return true;
- }
- else//没找到就进行迭代
- {
- prev = cur;
- cur = cur->_next;
- }
- }
- return false;//全部遍历完还没有找到就返回false
- }
-
- size_t GetNextPrime(size_t prime)//素数,这里就是用来计算表扩容需要的大小,这里就是利用素数进行扩容的
- {
- static const int __stl_num_primes = 28;
- static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
- {
- 53, 97, 193, 389, 769,
- 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
- 49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433,
- 1572869, 3145739, 6291469, 12582917, 25165843,
- 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457,
- 1610612741, 3221225473, 4294967291
- };
- size_t i = 0;
- for (; i < __stl_num_primes; ++i)
- {
- if (__stl_prime_list[i] > prime)
- return __stl_prime_list[i];
- }
- return __stl_prime_list[i];//找到下一个素数进行返回
- }
-
- bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)//插入
- {
- if (Find(kv.first))//去查找需要插入的数,如果找到了就直接返回
- return false;
- Hash hash;
- if (_n == _tables.size())// 负载因因子==1时扩容
- {
- size_t newsize = GetNextPrime(_tables.size());//进行获取下一个素数
- vector<Node*> newtables(newsize, nullptr);//按照这个素数的大小进行创建新的表
- for (auto& cur : _tables)//遍历旧的表进行把之前的表插入在新的表
- {
- while (cur)
- {
- Node* next = cur->_next;
- size_t hashi = hash(cur->_kv.first) % newtables.size();
- cur->_next = newtables[hashi];
- newtables[hashi] = cur;
- cur = next;
- }
- }
- _tables.swap(newtables);//交换两个表
- }
- size_t hashi = hash(kv.first) % _tables.size();//计算需要插入的映射位置
- Node* newnode = new Node(kv);//创建一个新的节点
- newnode->_next = _tables[hashi];//然后进行头插
- _tables[hashi] = newnode;
- ++_n;//这里不能忘了把n进行++
- return true;
- }
-
- size_t MaxBucketSize()//获取最大桶的大小
- {
- size_t max = 0;//用来记录最大的大小
- for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); ++i)//首先就是遍历整个表
- {
- auto cur = _tables[i];//获取表的每个节点
- size_t size = 0;//每一遍的大小
- while (cur)//进行迭代
- {
- ++size;
- cur = cur->_next;
- }
- if (size > max)//如果这一遍的大小比之前记录的大小大就把这个数值给记录最大数的变量
- {
- max = size;
- }
- return max;
- }
- }
-
- ~HashTable()//这个析构函数是为了把整个哈希表都清理干净
- {
- for (auto& cur : _tables)//遍历整个表
- {
- while (cur)//表里面的桶进行把那一串全删了,迭代进行
- {
- Node* next = cur->_next;
- delete cur;
- cur = next;
- }
- cur = nullptr;
- }
- }
- private:
- vector<Node*> _tables; // 指针数组
- size_t _n = 0; // 存储有效数据个数
- };
-
- void TestHashTable1()
- {
- int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
- HashTable<int, int> ht;
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
- }
-
- ht.Insert(make_pair(15, 15));
- ht.Insert(make_pair(25, 25));
- ht.Insert(make_pair(35, 35));
- ht.Insert(make_pair(45, 45));
- ht.Erase(12);
- ht.Erase(3);
- ht.Erase(33);
- }
-
- void TestHashTable2()
- {
- HashTable<string, string> ht;
- ht.Insert(make_pair("sort", "排序"));
- ht.Insert(make_pair("string", "字符串"));
- ht.Insert(make_pair("left", "左边"));
- ht.Insert(make_pair("right", "右边"));
- ht.Insert(make_pair("", "右边"));
- }
-
- void TestHashTable3()
- {
- size_t N = 900000;
- HashTable<int, int> ht;
- srand((unsigned)time(0));
- for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- {
- size_t x = rand() + i;
- ht.Insert(make_pair(x, x));
- }
- cout << ht.MaxBucketSize() << endl;
- }
- }

UnorderedMap.h
- #pragma once
-
- namespace lymap
- {
- template<class K, class V, class Hash = ly3::HashFunc<K>>
- class unordered_map
- {
- public:
- struct MapKeyOfT
- {
- const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)
- {
- return kv.first;
- }
- };
- public:
- typedef typename ly3::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash>::iterator iterator;
- typedef typename ly3::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
-
- iterator begin()
- {
- return _ht.begin();
- }
-
- iterator end()
- {
- return _ht.end();
- }
-
- const_iterator begin() const
- {
- return _ht.begin();
- }
-
- const_iterator end() const
- {
- return _ht.end();
- }
-
- pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
- {
- return _ht.Insert(kv);
- }
-
- V& operator[](const K& key)
- {
- pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V()));
- return ret.first->second;
- }
-
- iterator find(const K& key)
- {
- return _ht.Find(key);
- }
-
- bool erase(const K& key)
- {
- return _ht.Erase(key);
- }
-
- private:
- ly3::HashTable<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
- };
-
- void test_unordered_map1()
- {
- unordered_map<int, int> m;
- m.insert(make_pair(1, 1));
- m.insert(make_pair(3, 3));
- m.insert(make_pair(2, 2));
-
- unordered_map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();
- while (it != m.end())
- {
-
- cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
- ++it;
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
-
- void test_unordered_map2()
- {
- string arr[] = { "西瓜", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉", "梨" };
- unordered_map<string, int> countMap;
- for (auto& e : arr)
- {
- countMap[e]++;
- }
-
- for (auto& kv : countMap)
- {
- cout << kv.first << ":" << kv.second << endl;
- }
- }
- }

UnorderedSet.h
- #pragma once
- namespace lyset
- {
- template<class K, class Hash = ly3::HashFunc<K>>
- class unordered_set
- {
- public:
- struct SetKeyOfT
- {
- const K& operator()(const K& key)
- {
- return key;
- }
- };
- public:
- typedef typename ly3::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator iterator;
- typedef typename ly3::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash>::const_iterator const_iterator;
-
-
- iterator begin()
- {
- return _ht.begin();
- }
-
- iterator end()
- {
- return _ht.end();
- }
-
- const_iterator begin() const
- {
- return _ht.begin();
- }
-
- const_iterator end() const
- {
- return _ht.end();
- }
-
- pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
- {
- return _ht.Insert(key);
- }
-
- iterator find(const K& key)
- {
- return _ht.Find(key);
- }
-
- bool erase(const K& key)
- {
- return _ht.Erase(key);
- }
-
- private:
- ly3::HashTable<K, K, SetKeyOfT, Hash> _ht;
- };
-
- void print(const unordered_set<int>& s)
- {
- unordered_set<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin();
- while (it != s.end())
- {
- cout << *it << " ";
- ++it;
- }
- cout << endl;
- }
-
- void test_unordered_set1()
- {
- int a[] = { 3, 33, 2, 13, 5, 12, 1002 };
- unordered_set<int> s;
- for (auto e : a)
- {
- s.insert(e);
- }
-
- s.insert(54);
- s.insert(107);
-
- unordered_set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
- while (it != s.end())
- {
- cout << *it << " ";
- ++it;
- }
- cout << endl;
-
- for (auto e : s)
- {
- cout << e << " ";
- }
- cout << endl;
-
- print(s);
- }
- }



