- 1android log.d 格式化,如何去掉android.Log.d?
- 2./configure: error: SSL modules require the OpenSSL library. You can either do not enable the module
- 3C语言完整版笔记(初阶,进阶,深刨,初阶数据结构)_c语言代码速记
- 401:WebGL简介、示例、应用场景
- 5【漏洞复现】SpringBlade export-user接口存在SQL注入漏洞_springblade漏洞进阶利用
- 6【0基础入门Python Web笔记】四、python 之计算器的进阶之路_python web 计算器代码
- 7人工智能导论/人工智能及其应用 期末练习题_把下列谓词公式化成子句集:( x)( y)(p(x,y)∧q(x,y))
- 8大数据-计算引擎-Spark(三):RDD编程【离线分析;替代MapReduce编程,使用RDD(弹性分布式数据集)编程;处理非结构化数据;RDD操作算子:transformation、Action】_非结构化数据计算引擎有哪些
- 9珠联壁合地设天造|M1 Mac os(Apple Silicon)基于vscode(arm64)配置搭建Java开发环境(集成web框架Springboot)_m1芯片适配的swt
- 10Elasticsearch机器学习初探:智能数据洞察
CGAN笔记总结第二弹~_cgan的训练过程
赞
踩
一、复习GAN
生成式对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks)是让两个神经网络进行博弈进行学习。基础结构包含生成器和判别器。生成器的目标是生成与真实图片相似的图片,以假乱真,尽可能地让判别器判断生成的图片是真实的。判别器的目标是能够区分真实图片和生成图片。生成器和判别器通过巧妙地设计损失函数,而结合在一起,在相互对抗中不断调整各自的参数,使得判别器难以判断生成器生成的图片是否真实,从而达到欺骗人眼的效果。
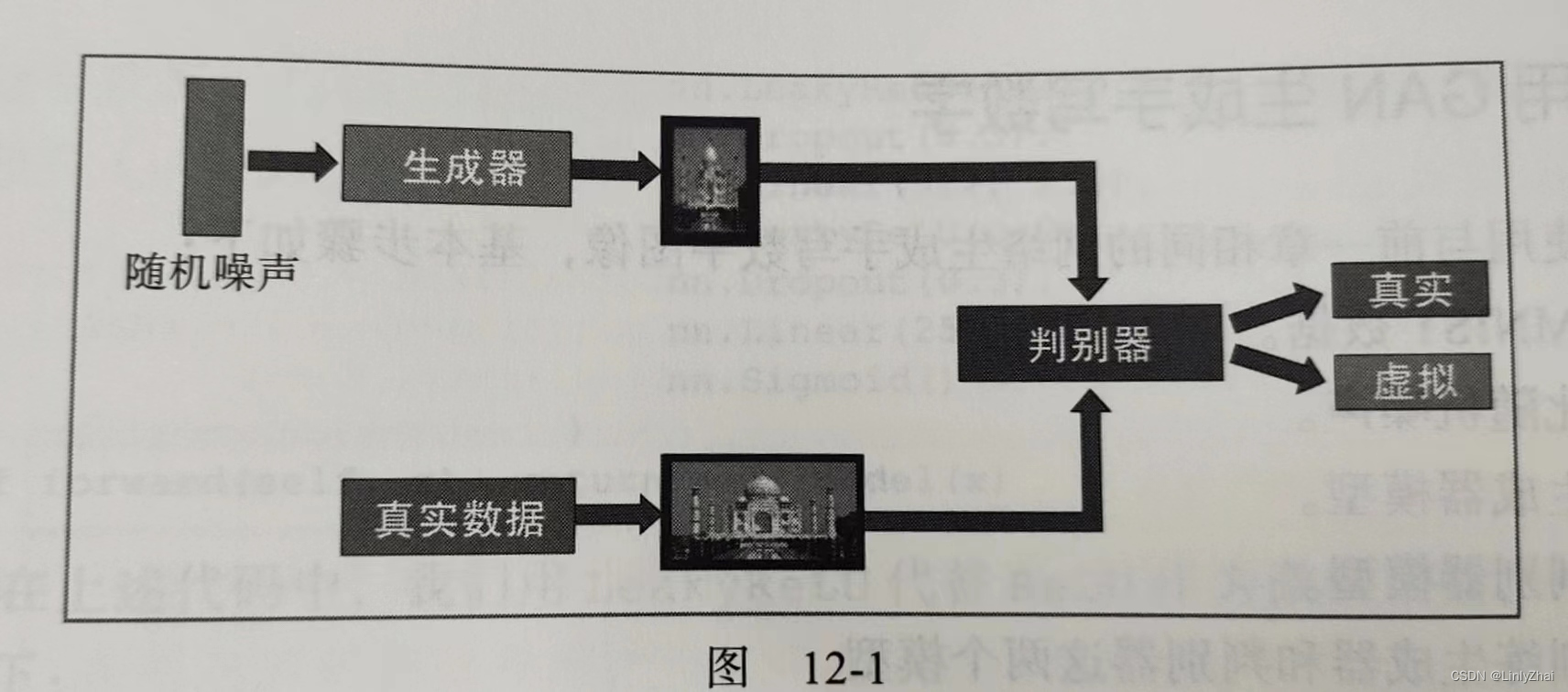
1.1损失函数
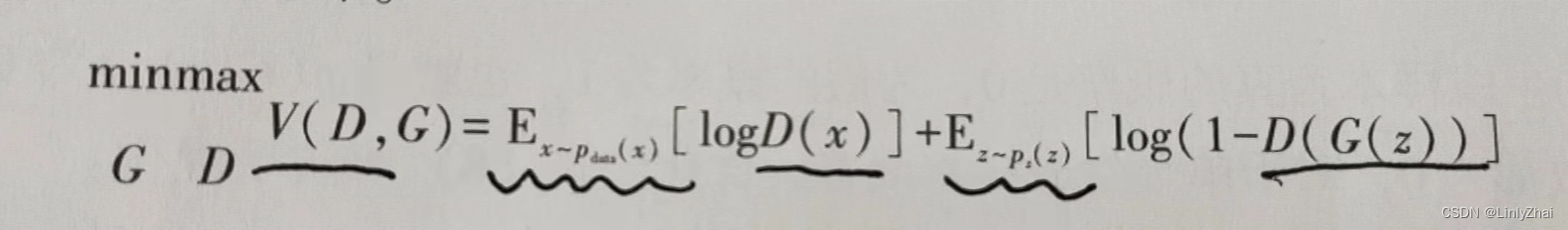
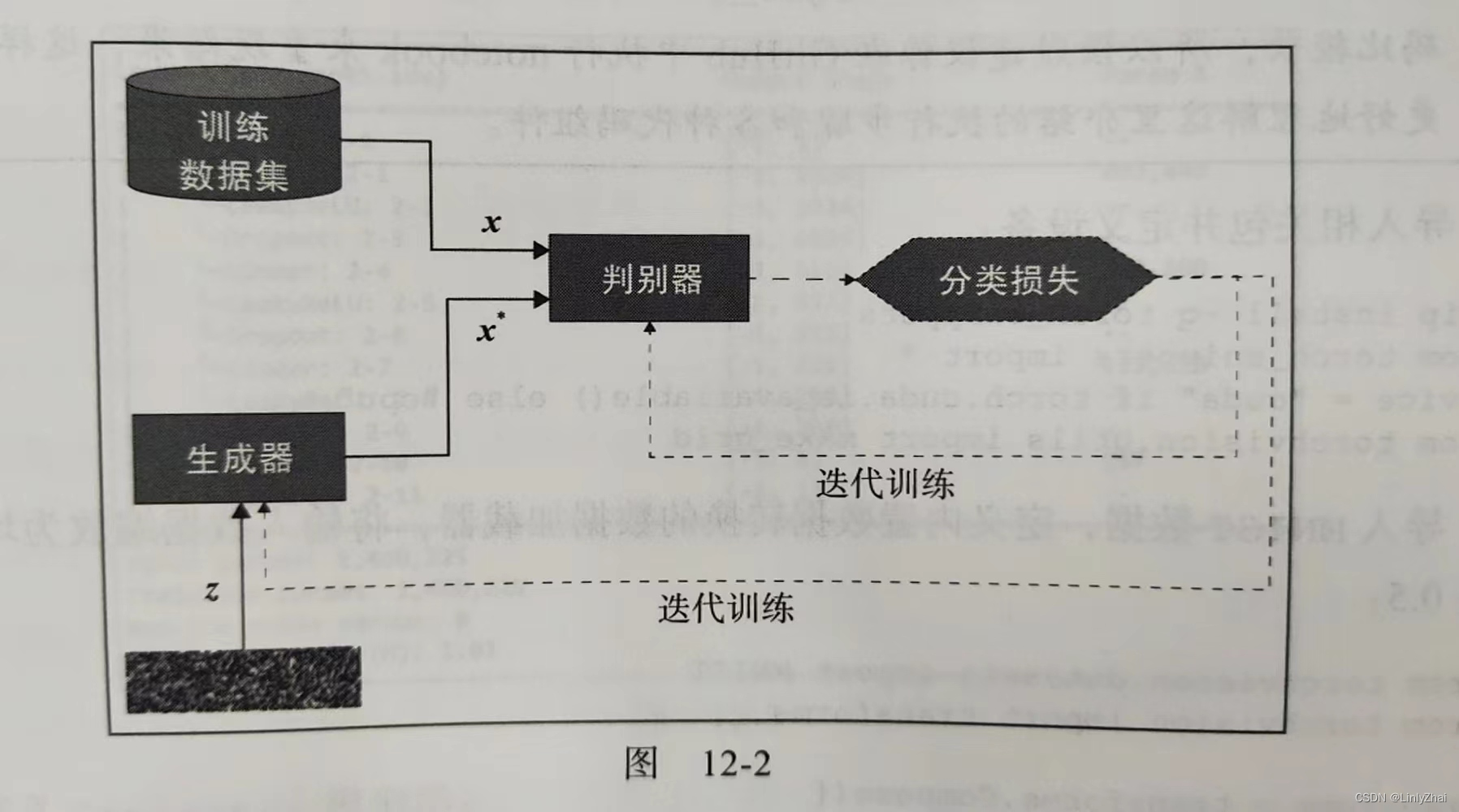
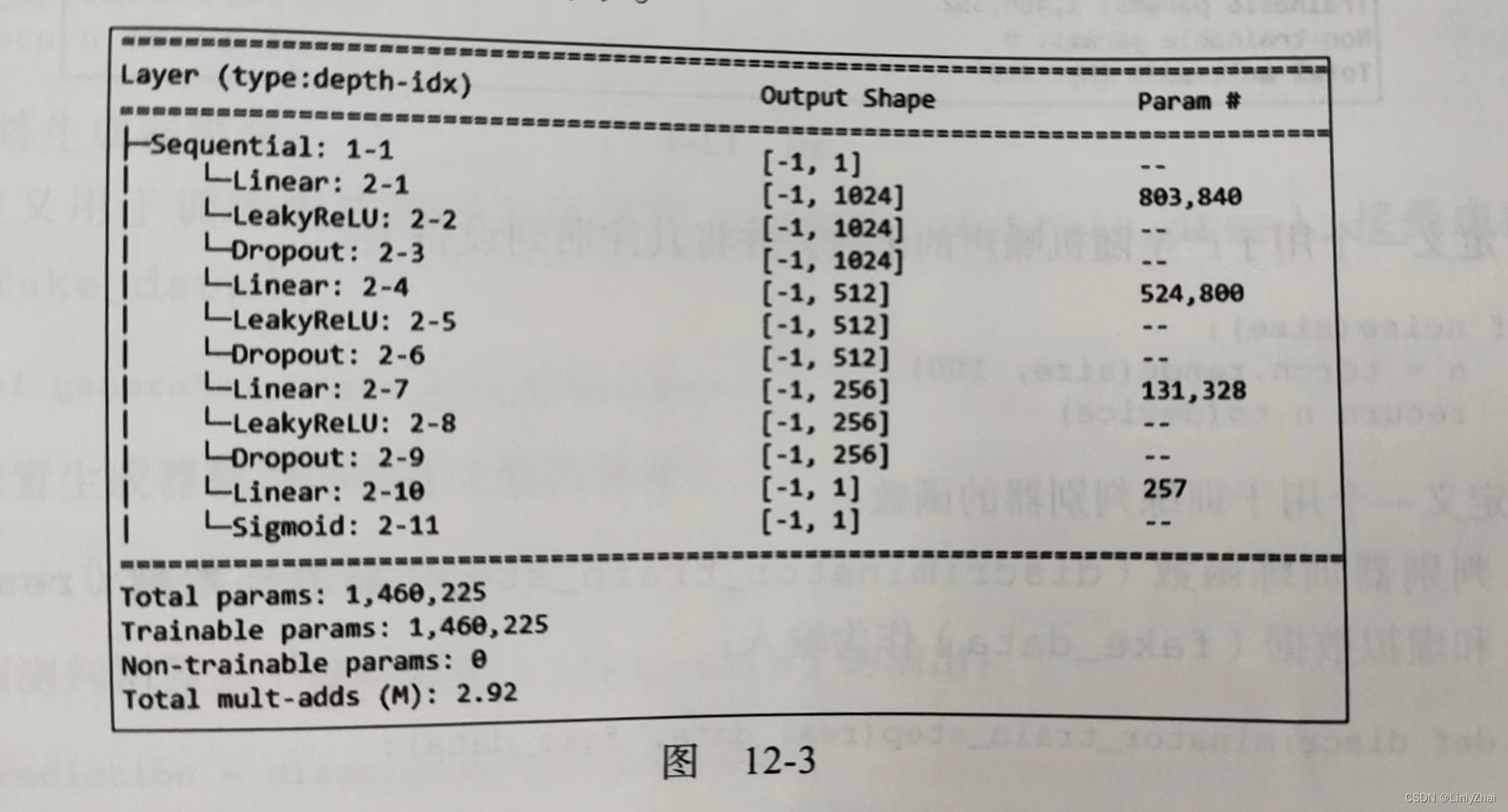
1.2判别器源码
class Discriminator(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.model = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(784,1024), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2), nn.Dropout(0.3), nn.Linear(1024,512), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2), nn.Dropout(0.3), nn.Linear(512,256), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2), nn.Dropout(0.3), nn.Linear(256,1), nn.Sigmoid() ) def forward(self, x): return self.model(x)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
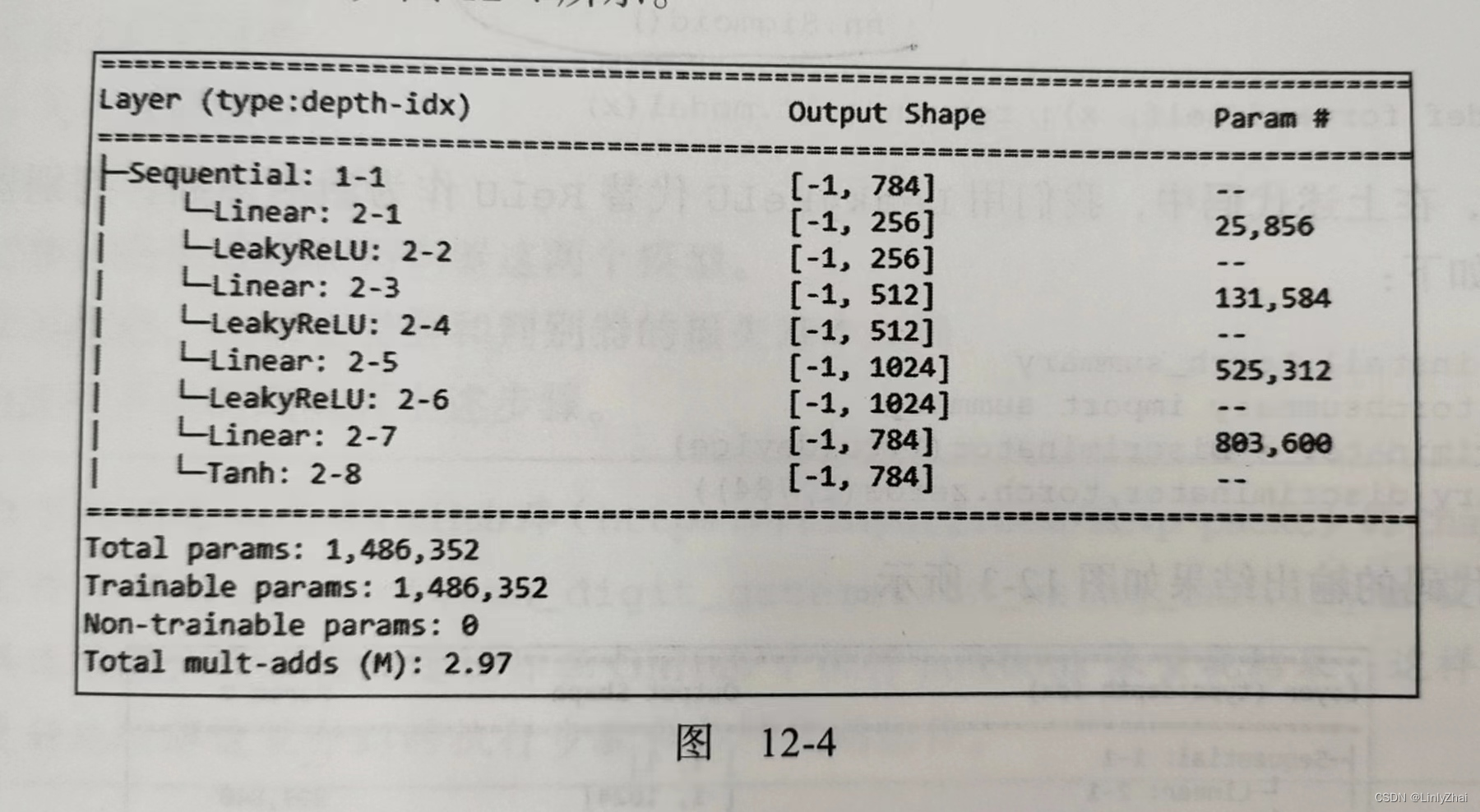
1.3 生成器源码
class Generator(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.model = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(100,256), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2), nn.Linear(256,512), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2), nn.Linear(512,1024), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2), nn.Linear(1024,784), nn.Tahn() ) def forward(self, x): return self.model(x)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18

二、什么是CGAN?
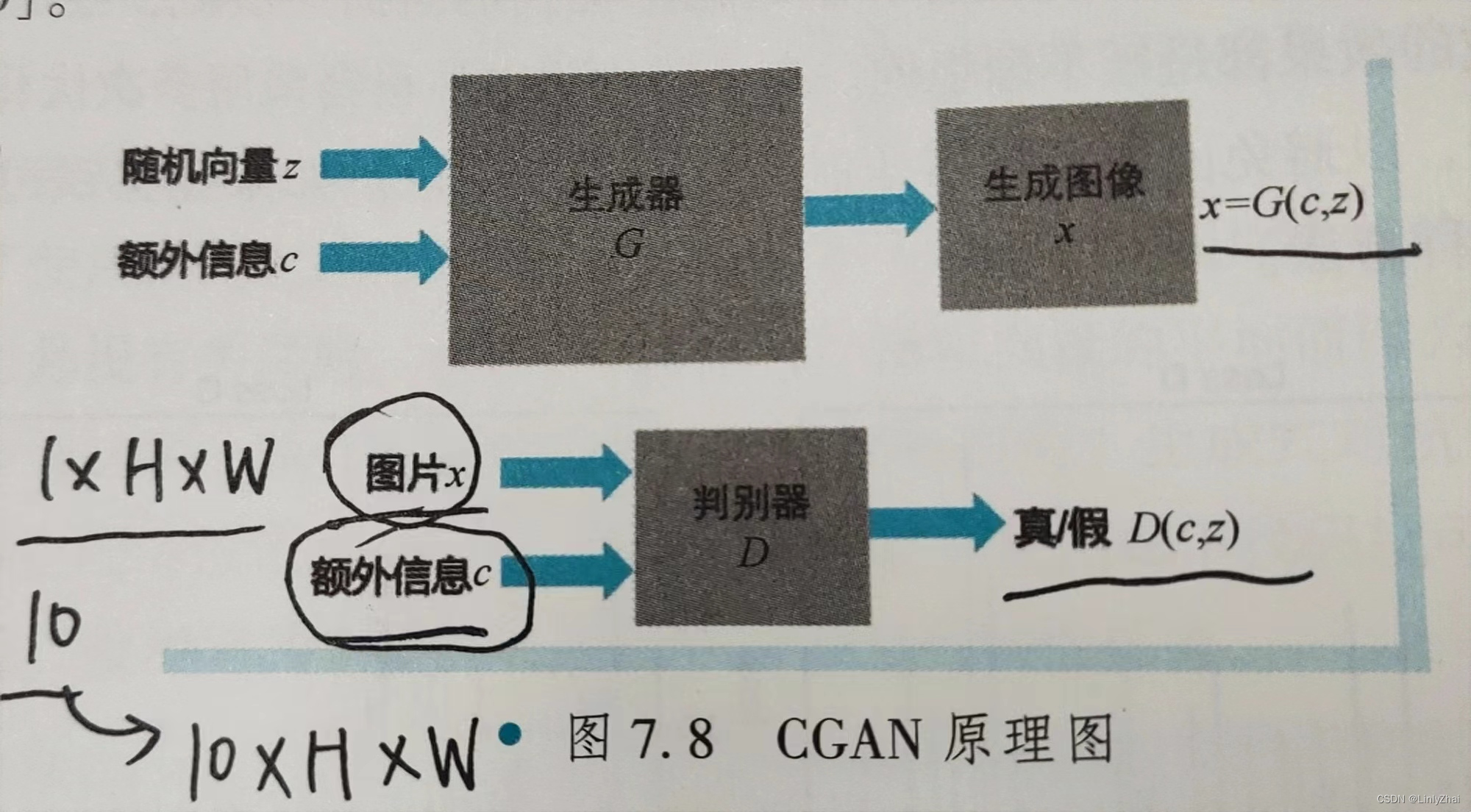
CGAN,全称Conditional Generative Aderversarial Networks.与GAN相比,条件GAN加入了额外信息c,从而能够生成指定的手写数字。
2.1 CGAN原理图
2.2条件GAN的损失函数
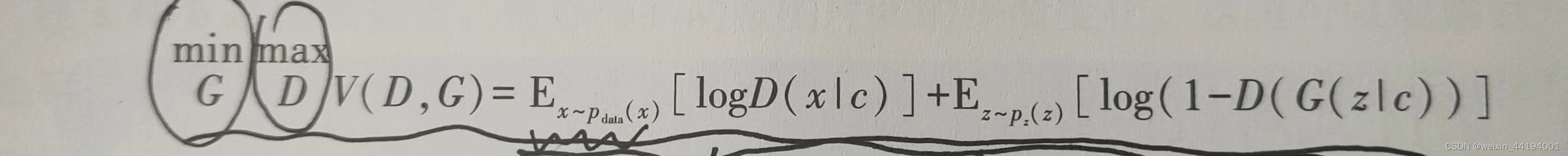
nn.BCELoss()是一个PyTorch中的损失函数,它被用于二分类问题。BCE代表二元交叉熵(Binary Cross Entropy)
这里用到的是二元交叉熵损失函数
D(x)代表的是判别器判别图片是真的概率;
在
2.3 生成器源码
class Generator(nn.Module): def __init__(self, num_channel=1, nz=100, nc=10, ngf=64): super(Generator, self).__init__() self.main = nn.Sequential( # 输入维度 110 x 1 x 1 nn.ConvTranspose2d(nz + nc, ngf * 8, 4, 1, 0, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 8), nn.ReLU(True), # 特征维度 (ngf*8) x 4 x 4 nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 8, ngf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 4), nn.ReLU(True), # 特征维度 (ngf*4) x 8 x 8 nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 4, ngf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 2), nn.ReLU(True), # 特征维度 (ngf*2) x 16 x 16 nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 2, ngf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf), nn.ReLU(True), # 特征维度 (ngf) x 32 x 32 nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf, num_channel, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), nn.Tanh() # 特征维度. (num_channel) x 64 x 64 ) self.apply(weights_init) def forward(self, input_z, onehot_label): input_ = torch.cat((input_z, onehot_label), dim=1) n, c = input_.size() input_ = input_.view(n, c, 1, 1) return self.main(input_)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
在生成器,
随机向量z是100维的,
额外信息c是10维的,(因为手写数字包含0-9,一共10类)
在这里,采用直接拼接的方式,最终形成了110维的输入
2.4 判别器源码
class Discriminator(nn.Module): def __init__(self, num_channel=1, nc=10, ndf=64): super(Discriminator, self).__init__() self.main = nn.Sequential( # 输入维度 (num_c3 # channel+nc) x 64 x 64 1*64*64的图像和10维的类别 10维类别先转换成10*64*64 然后合并就是11*64*64 # 输入通道 输出通道 卷积核的大小 步长 填充 #原始输入张量:b 11 64 64 nn.Conv2d(num_channel + nc, ndf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), #b 64 32 32 nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True), # 特征维度 (ndf) x 32 x 32 nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), #b 64*2 16 16 nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 2), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True), # 特征维度 (ndf*2) x 16 x 16 nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, ndf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), #b 64*4 8 8 nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 4), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True), # 特征维度 (ndf*4) x 8 x 8 nn.Conv2d(ndf * 4, ndf * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), #b 64*8 4 4 nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 8), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True), # 特征维度 (ndf*8) x 4 x 4 nn.Conv2d(ndf * 8, 1, 4, 1, 0, bias=False), #b 1 1 1 其实就是一个数值,区间在正无穷到负无穷之间 nn.Sigmoid() ) self.apply(weights_init) def forward(self, images, onehot_label): device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu' h, w = images.shape[2:] n, nc = onehot_label.shape[:2] label = onehot_label.view(n, nc, 1, 1) * torch.ones([n, nc, h, w]).to(device) input_ = torch.cat([images, label], 1) return self.main(input_)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
在判别器中,输入的数据有
图片x,(可能是来自真实数据集的样本,也可能是来自生成器生成的虚假样本) 维度是1 * H * W
额外信息c,维度是10维,变换到10 * 1 * 1,将后两维进行复制 变换为10 * H * W的张量;
最终拼接在一起,构成11 * H * W的输入。
2.5 训练过程
MODEL_G_PATH = "./" LOG_G_PATH = "Log_G.txt" LOG_D_PATH = "Log_D.txt" IMAGE_SIZE = 64 BATCH_SIZE = 128 WORKER = 1 LR = 0.0002 NZ = 100 NUM_CLASS = 10 EPOCH = 50 data_loader = loadMNIST(img_size=IMAGE_SIZE, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE) #原始图片宽高是28*28的,给改变成64*64 device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") netG = Generator().to(device) netD = Discriminator().to(device) criterion = nn.BCELoss() real_label = 1. fake_label = 0. optimizerD = optim.Adam(netD.parameters(), lr=LR, betas=(0.5, 0.999)) optimizerG = optim.Adam(netG.parameters(), lr=LR, betas=(0.5, 0.999)) g_writer = LossWriter(save_path=LOG_G_PATH) d_writer = LossWriter(save_path=LOG_D_PATH) fix_noise = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, NZ, device=device) fix_input_c = (torch.rand(BATCH_SIZE, 1) * NUM_CLASS).type(torch.LongTensor).squeeze().to(device) fix_input_c = onehot(fix_input_c, NUM_CLASS) img_list = [] G_losses = [] D_losses = [] iters = 0 print("开始训练>>>") for epoch in range(EPOCH): print("正在保存网络并评估...") save_network(MODEL_G_PATH, netG, epoch) with torch.no_grad(): fake_imgs = netG(fix_noise, fix_input_c).detach().cpu() images = recover_image(fake_imgs) full_image = np.full((5 * 64, 5 * 64, 3), 0, dtype="uint8") for i in range(25): row = i // 5 col = i % 5 full_image[row * 64:(row + 1) * 64, col * 64:(col + 1) * 64, :] = images[i] # !!!!!!!!!!!!!! #每一轮次结束后,这里只展示了一批图片的前25张。 plt.imshow(full_image) #plt.show() plt.imsave("{}.png".format(epoch), full_image) for data in data_loader: netD.zero_grad() real_imgs, input_c = data #这里的input_c其实就是数据集每一批中的每个图片对应的标签 input_c = input_c.to(device) input_c = onehot(input_c, NUM_CLASS).to(device) # 1.1 来自数据集的样本 real_imgs = real_imgs.to(device) b_size = real_imgs.size(0) label = torch.full((b_size,), real_label, dtype=torch.float, device=device) #上面的torch.full是生成一维的 b_size这么多的,填充值为1.的张量 # real_label = 1. # fake_label = 0. # 使用判别器对真实数据集样本做判断 #!!!!!!!!!!!!! #output应该是判别器判别一批真图片真实的概率 output = netD(real_imgs, input_c).view(-1) errD_real = criterion(output, label) #!!!!!! #errD_real是判别器识别真图片的误差,为了训练判别器判别真图片为真 errD_real.backward() D_x = output.mean().item() #!!!!!!! #D_x就是判别器判别一批真图片为真的概率的平均值 # 1.2 生成随机向量 这一步想要训练判别器是否能够识别出是虚假图片 noise = torch.randn(b_size, NZ, device=device) # 生成随机标签 input_c = (torch.rand(b_size, 1) * NUM_CLASS).type(torch.LongTensor).squeeze().to(device) input_c = onehot(input_c, NUM_CLASS) # 来自生成器生成的样本 fake = netG(noise, input_c) label.fill_(fake_label) # real_label = 1. # fake_label = 0. # 使用判别器对生成器生成样本做判断 #!!!!!!!!!!! #output应该是判别器判别一批假图片真实的概率 output = netD(fake.detach(), input_c).view(-1) errD_fake = criterion(output, label) # 对判别器进行梯度回传 errD_fake.backward() #!!!!!! #errD_fake是判别器识别假图片的误差,为了训练判别器判别假图片为假 D_G_z1 = output.mean().item() #!!!!!!!!!!!! #D_G_z1就是判别器判别一批假图片为真的概率的平均值 errD = errD_real + errD_fake #!!!!!! #errD是判别器识别真实图片和假图片的误差和 # 更新判别器 optimizerD.step() netG.zero_grad() # 对于生成器训练,令生成器生成的样本为真, label.fill_(real_label) # real_label = 1. # fake_label = 0. #!!!!!!!!!!! #output应该是判别器判别一批假图片真实的概率 output = netD(fake, input_c).view(-1) # 对生成器计算损失 errG = criterion(output, label) #!!!!!! #errG是判别器识别假图片的误差,但是是为了训练生成器生成假图片,以假乱真 # 因为这里判别器的角度label真实应该是0,但是站在生成器的角度,label真实应该是1,即生成器希望生成的虚假图片让判别器识别的时候,会误以为1才比较好,即误以为是真实的图片 # 所以生成器交叉熵也是越小越好 # 对生成器进行梯度回传 errG.backward() D_G_z2 = output.mean().item() #!!!!!!!!!!!! #D_G_z2就是判别器判别一批假图片为真的概率的平均值 # 更新生成器 optimizerG.step() # 输出损失状态 if iters % 5 == 0: print('[%d/%d][%d/%d]\tLoss_D: %.4f\tLoss_G: %.4f\tD(x): %.4f\tD(G(z)): %.4f / %.4f' % (epoch, EPOCH, iters % len(data_loader), len(data_loader), errD.item(), errG.item(), D_x, D_G_z1, D_G_z2)) d_writer.add(loss=errD.item(), i=iters) g_writer.add(loss=errG.item(), i=iters) # 保存损失记录 G_losses.append(errG.item()) D_losses.append(errD.item()) iters += 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
1)这里的训练顺序
这里训练的顺序是
先拿真实图片训练判别器,
再拿假图片训练判别器,
最后,拿假图片让判别器判断,来训练生成器。
2)为什么先训练判别器后训练生成器呢?
试想,假如先训练生成器,但是刚开始判别器还没有判别能力,所以达不到训练生成器,帮助生成器能越来越生成逼真的假图片。
所以,需要先训练判别器,让判别器先具有初步的判别能力,才能训练生成器,帮助生成器能够生成逼真的假图片。
2.6 训练过程运行结果
#errD是判别器识别真实图片和假图片的误差和,是为了训练判别器能够判别真假图片
#errG是判别器识别假图片的误差,但是是为了训练生成器生成假图片,以假乱真
#D_x就是判别器判别一批真图片为真的概率的平均值,训练判别器识别真图片
#D_G_z1就是判别器判别一批假图片为真的概率的平均值,训练判别器识别假图片
#D_G_z2就是判别器判别一批假图片为真的概率的平均值,训练生成器生成逼真的假图片
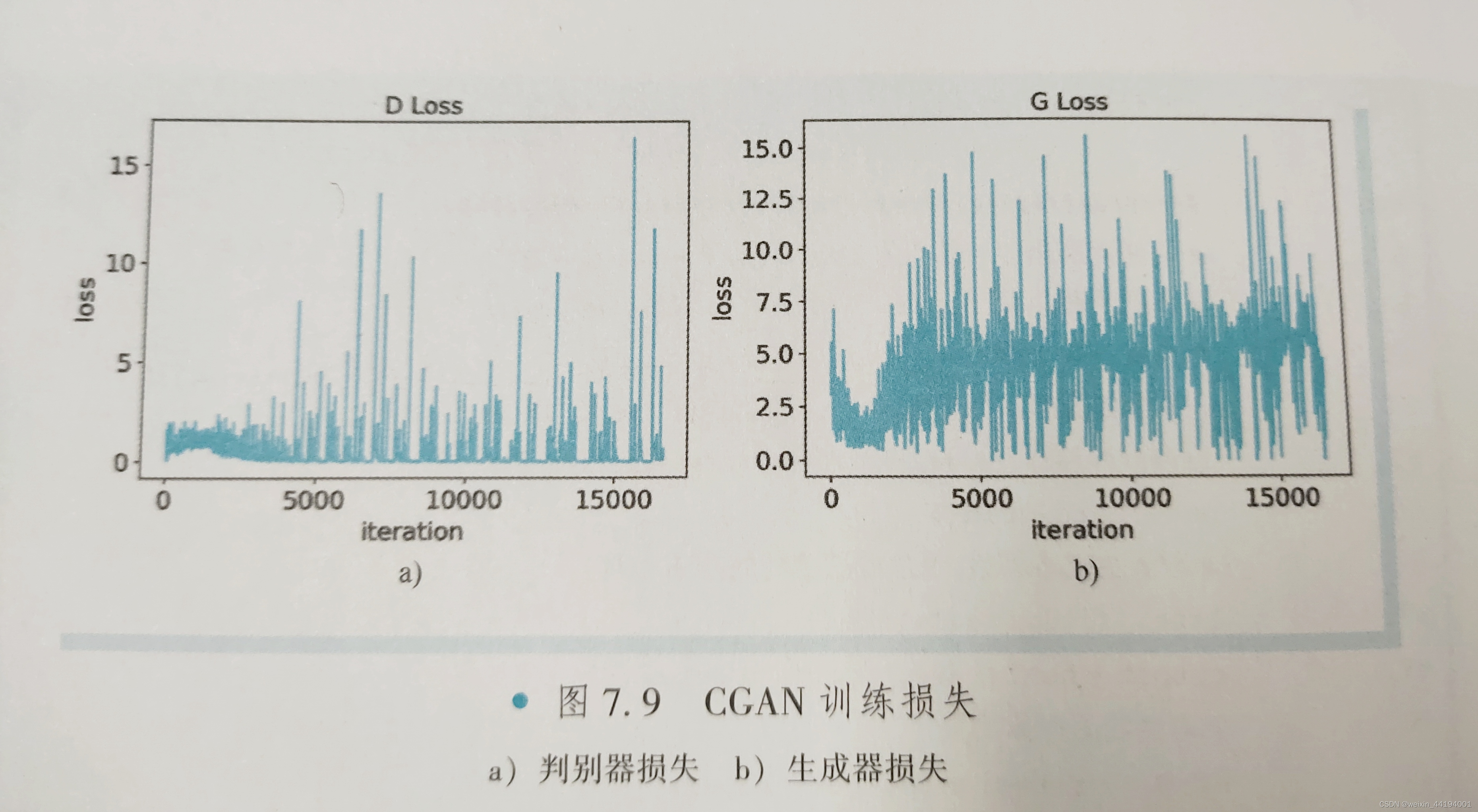

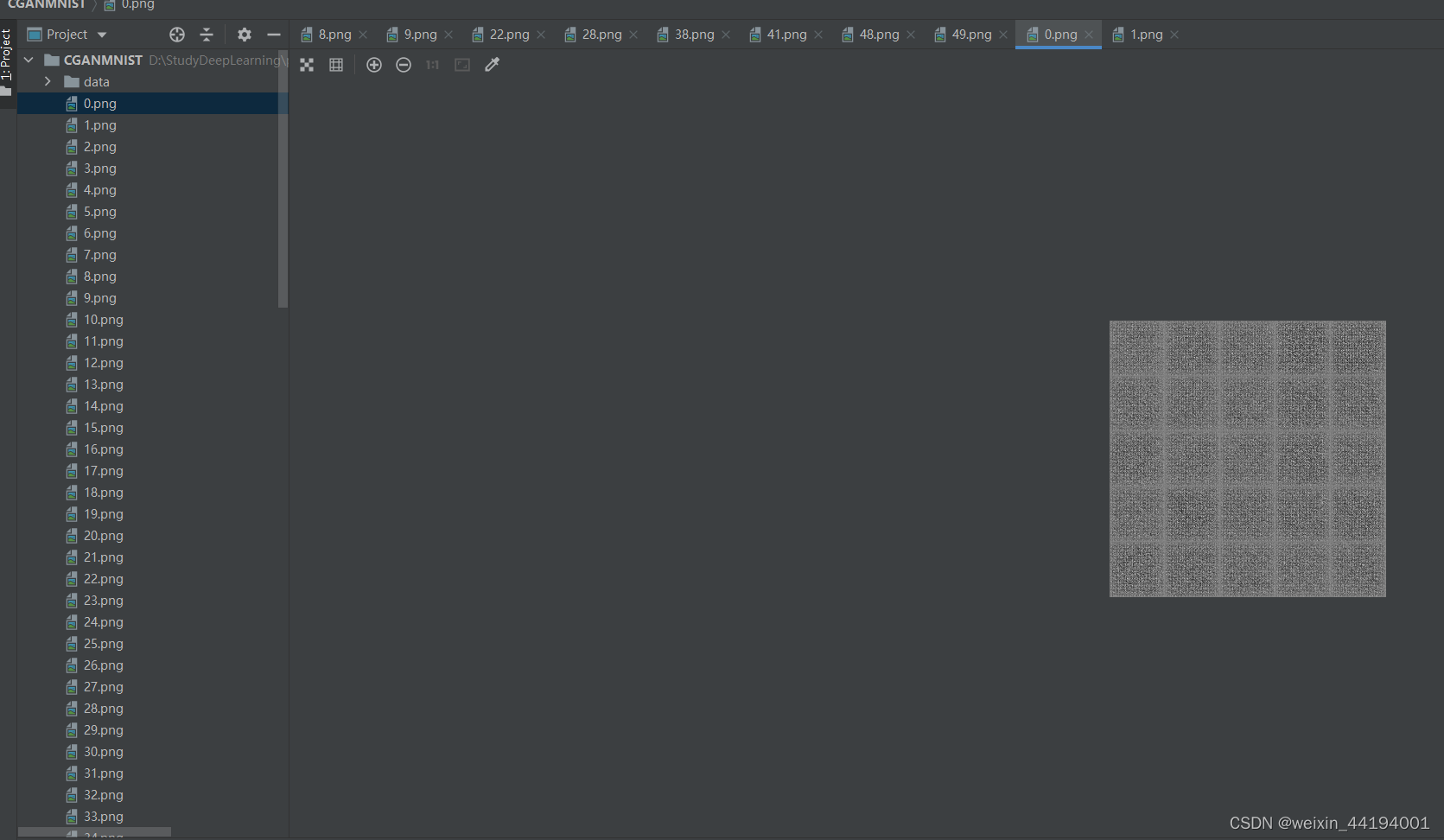
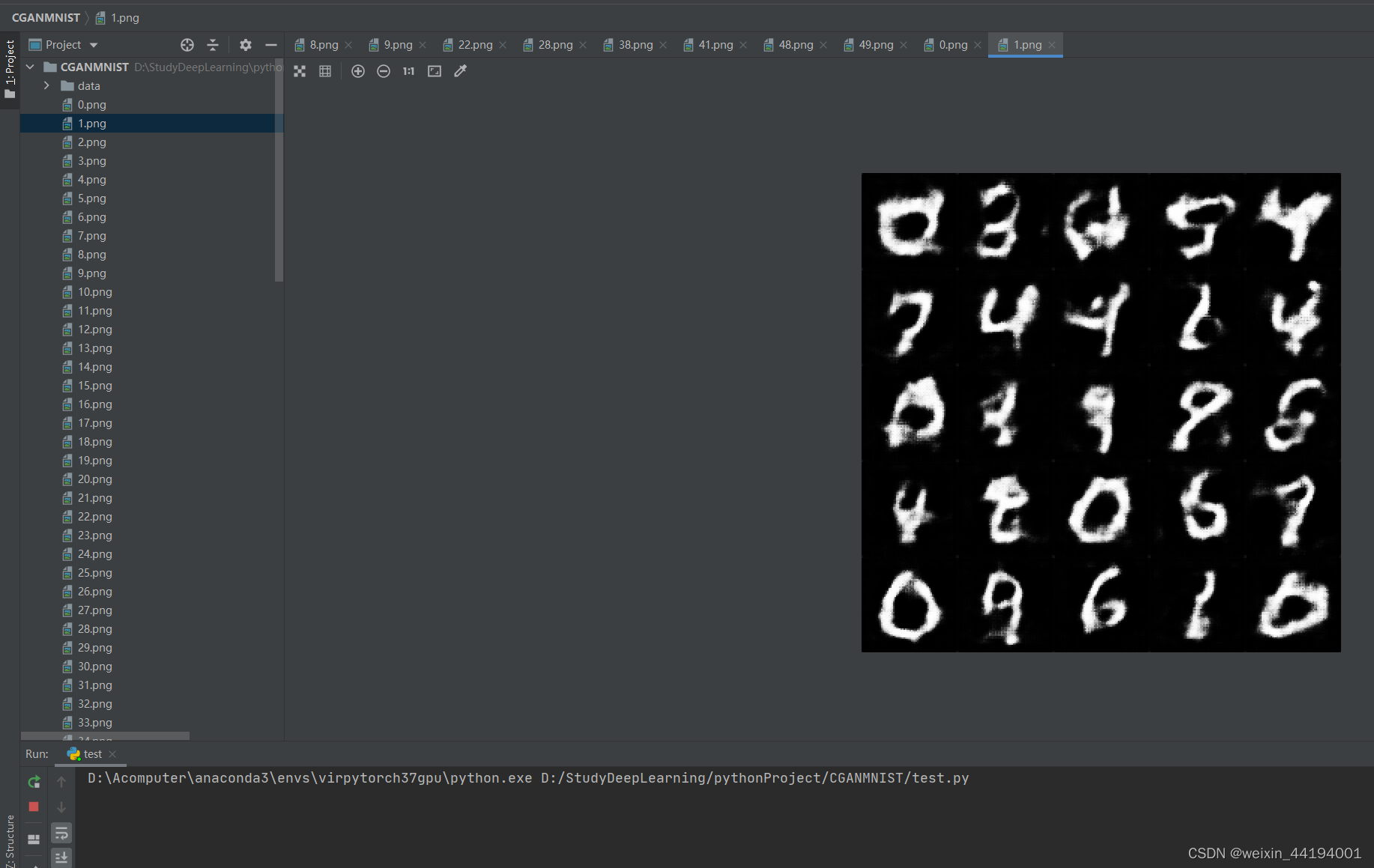
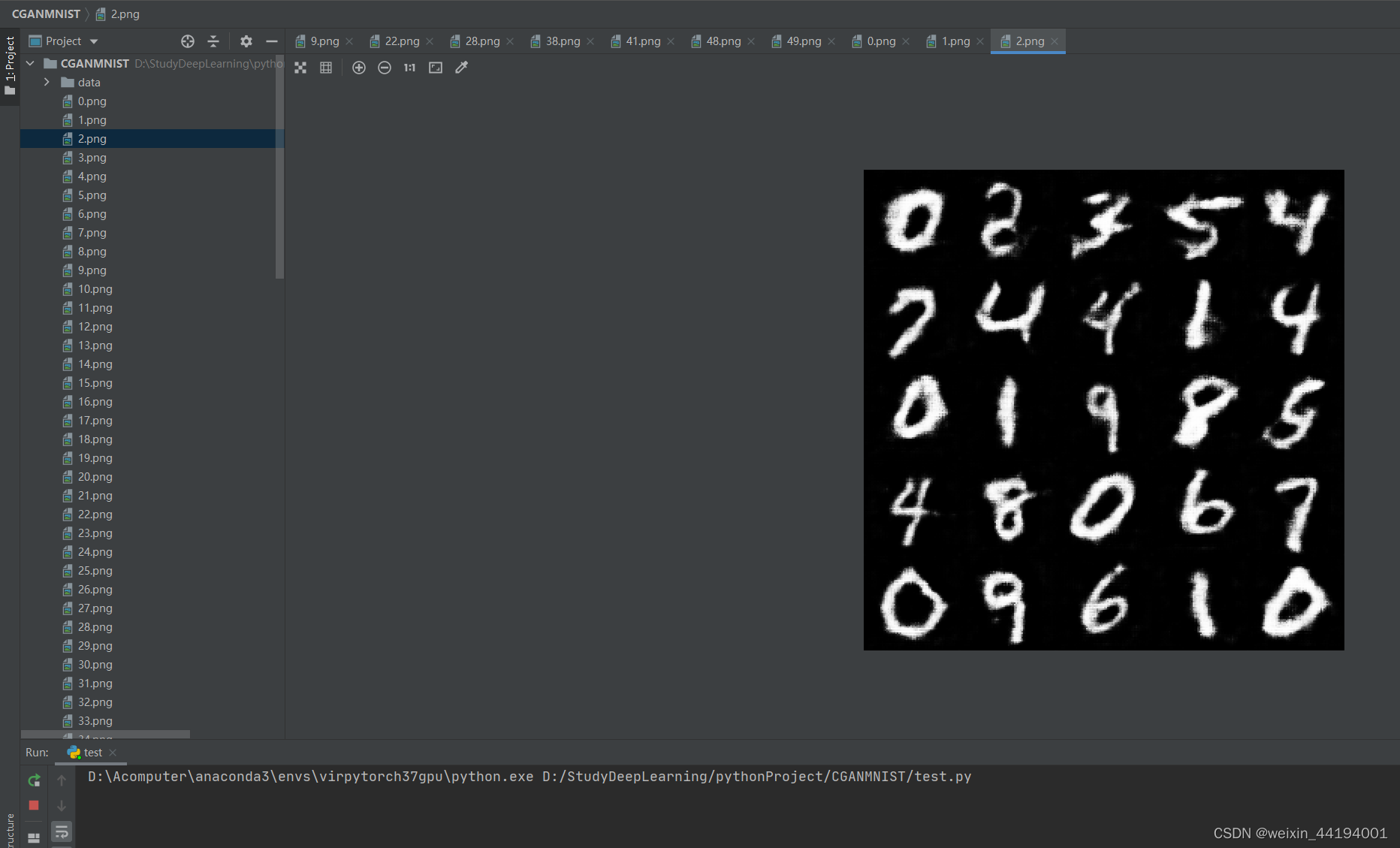
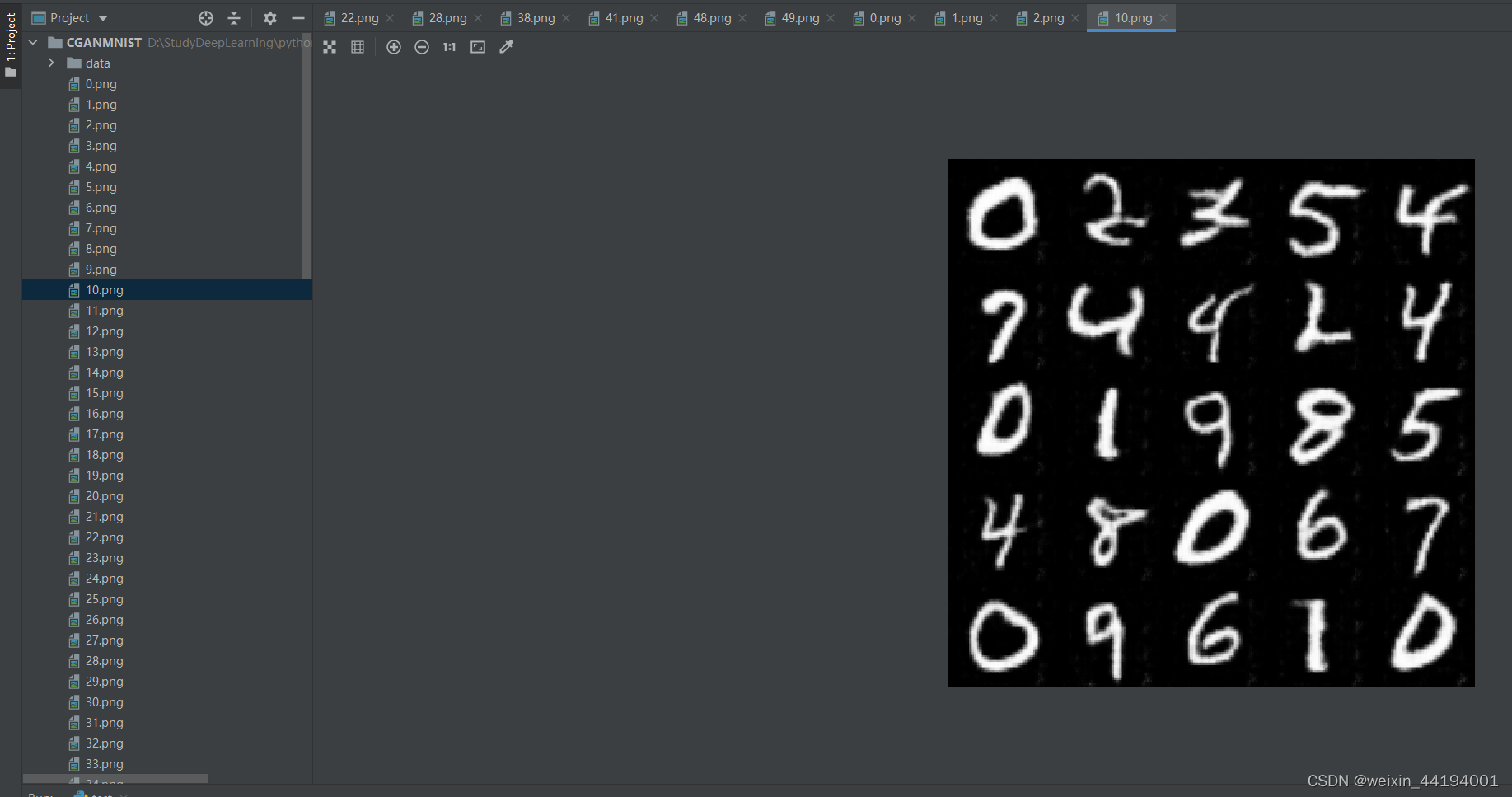
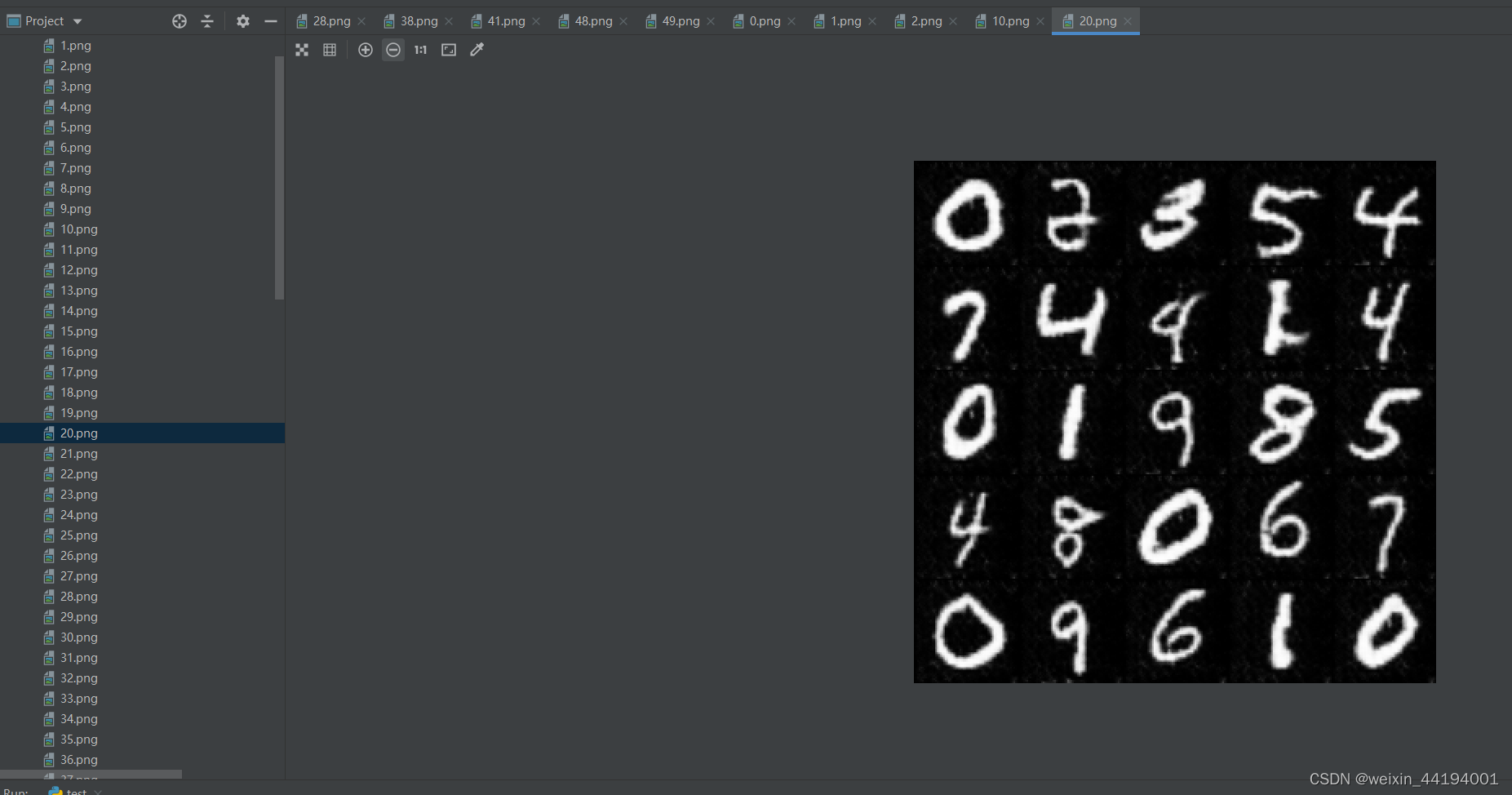
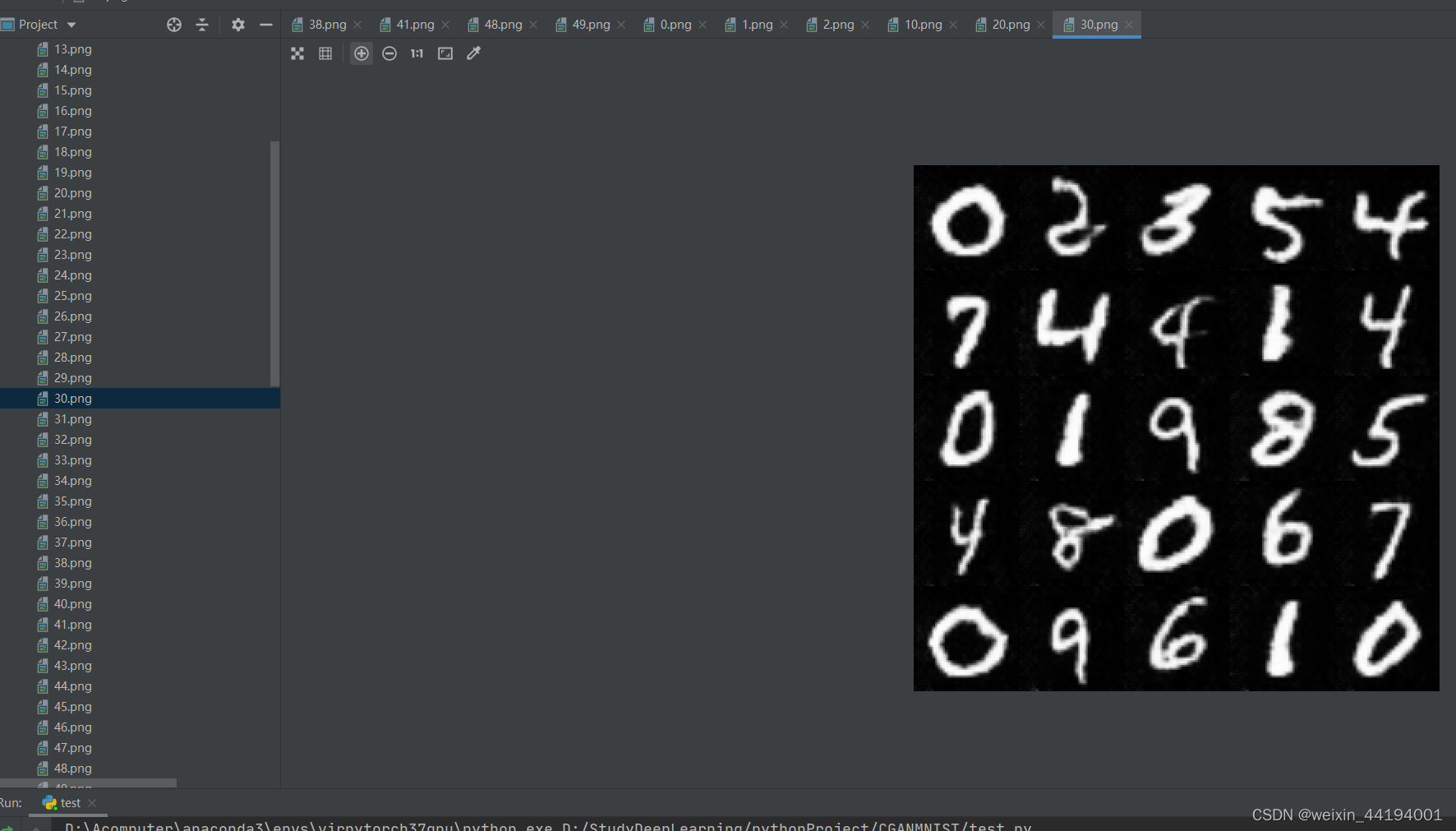
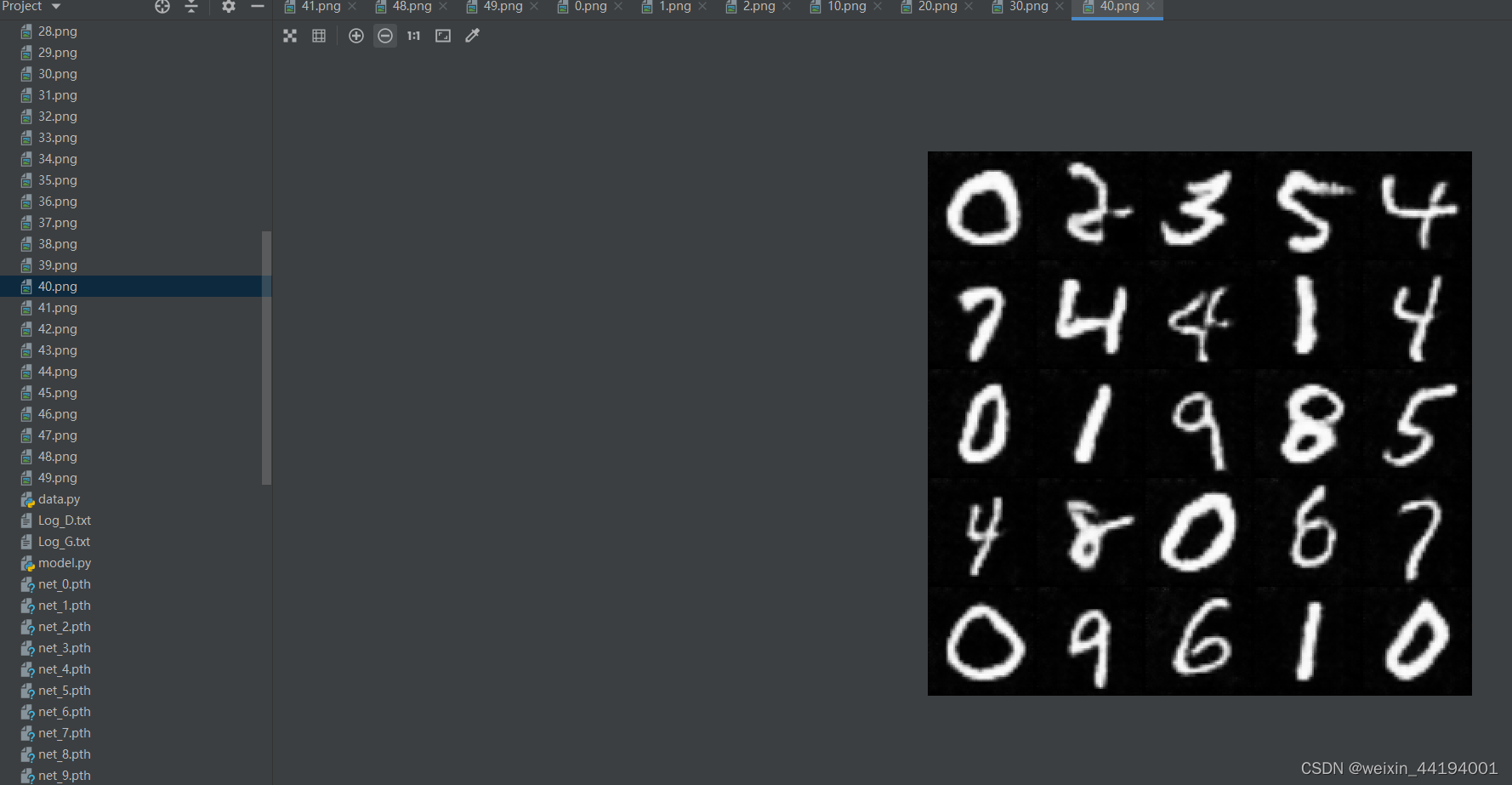
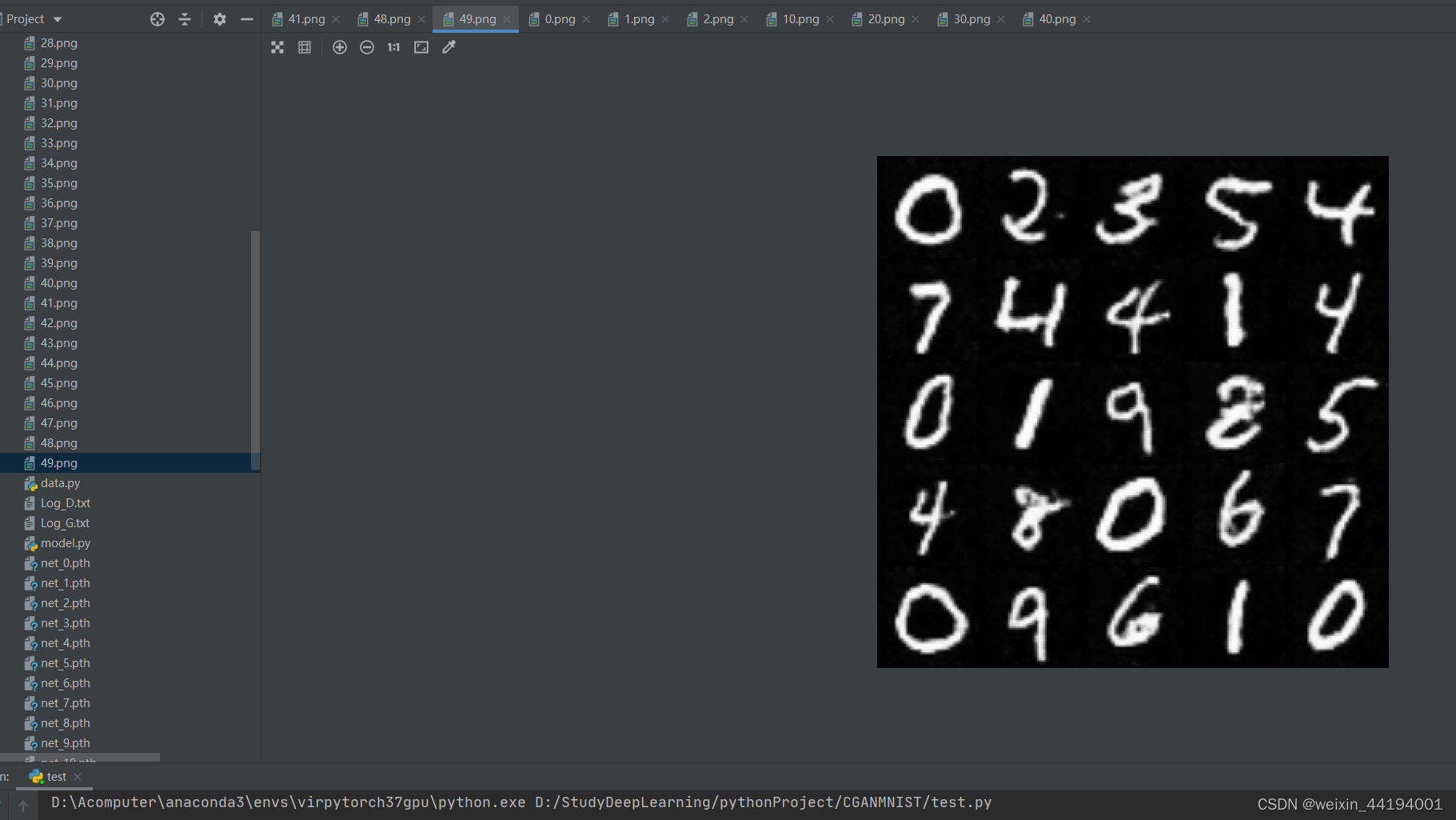
2.7测试结果
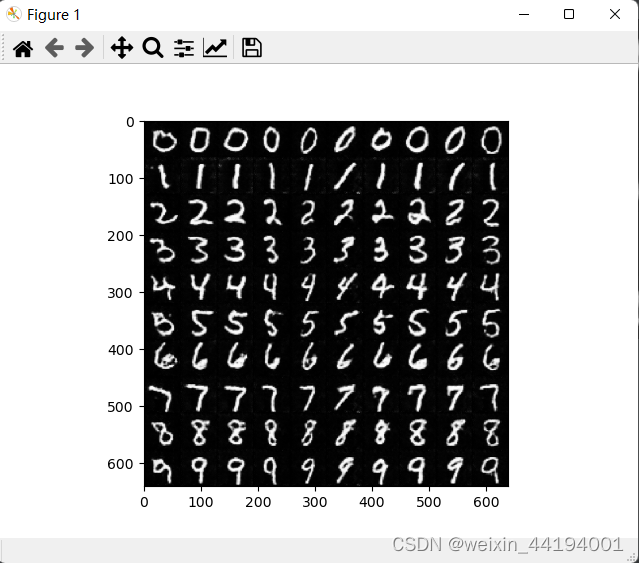
1)测试代码
NZ = 100 NUM_CLASS = 10 BATCH_SIZE = 10 DEVICE = "cpu" netG = Generator() netG = restore_network("./", "49", netG) fix_noise = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, NZ, device=DEVICE) fix_input_c = torch.tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]) device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu" fix_input_c = onehot(fix_input_c, NUM_CLASS) fix_input_c = fix_input_c.to(device) fix_noise = fix_noise.to(device) netG = netG.to(device) #fake_imgs = netG(fix_noise, fix_input_c).detach().cpu() #fix_noise = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, NZ, device=DEVICE) full_image = np.full((10 * 64, 10 * 64, 3), 0, dtype="uint8") for num in range(10): input_c = torch.tensor(np.ones(10, dtype="int64") * num) input_c = onehot(input_c, NUM_CLASS) fix_noise = fix_noise.to(device) input_c = input_c.to(device) fake_imgs = netG(fix_noise, input_c).detach().cpu() images = recover_image(fake_imgs) for i in range(10): row = num col = i % 10 full_image[row * 64:(row + 1) * 64, col * 64:(col + 1) * 64, :] = images[i] plt.imshow(full_image) plt.show() plt.imsave("hah.png", full_image)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38



