- 1微软CEO纳德拉演讲关键词:云计算、人工智能、混合现实
- 2OkHttp基础讲解_openapi okhttp
- 3数字反转(C/C++)_c++实现数字反转
- 4vue3实现路由角色权限
- 5SpringBoot学习(二)_spring.datasource.type
- 6拓尔思测试工程师校招一面面经_ssp面试笔记
- 7Django计算机毕业设计软考刷题小程序python(源码程序+lw+远程部署)_计算机专业毕业设计选题刷题小程序可以做吗
- 8快速构建pyqt5界面UI_pyqt5界面设计
- 9史上最全Java 8新特性总结,助你在工作事半功倍_日常工作中你会用到哪些java新特性,帮助简化不必要的繁琐工作
- 10详解java中,过滤器filter和拦截器interceptor的区别_java拦截器和过滤器
Rust : 与C交互动态库和静态库的尝试_rust使用c代码
赞
踩
rust调用C端的库函数,有很多方法,场景也有所不同。包括windows还是linux,内置库还是自定义库,还是三方库等等。
一、rust调用其内置的C库
这个很简单,直接把extern "C"引入即可:
比如,在rust端main.rs中:
use std::os::raw::c_int;//f32
use std::os::raw:c_double;// f64
extern "C" {
fn abs(num:c_int) ->c_int;
fn sqrt(num:c_double) ->c_double;
}
fn main{
println!("call c->abs :{}",unsafe{abs(-32)});
println!("call c -> sqrt:{}",unsafe{sqrt(36.0)});
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
不需要做其它的处理,直接cargo run 就可以运行。
二、自定义的C库-以windows平台为例
如果rust要调用自建的C库中的函数,情况会较上面复杂一些。今天介绍通过cc库,通过build生成脚本的方式,实现rust调用c端库函数。
1、相关准备:
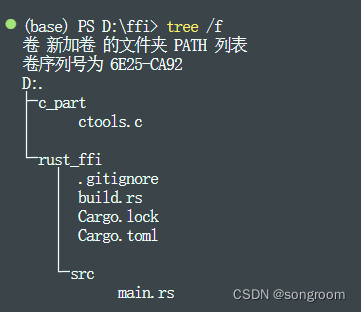
在ffi目录下,创建了c_part和rust_ffi文件夹。 c_part下放了ctools.c文件,里面有一些库函数,需要让rust调用。当然,ctools.c也可以放在其它地方,只需要后面的地址一致即可以。
2、cargo toml部分
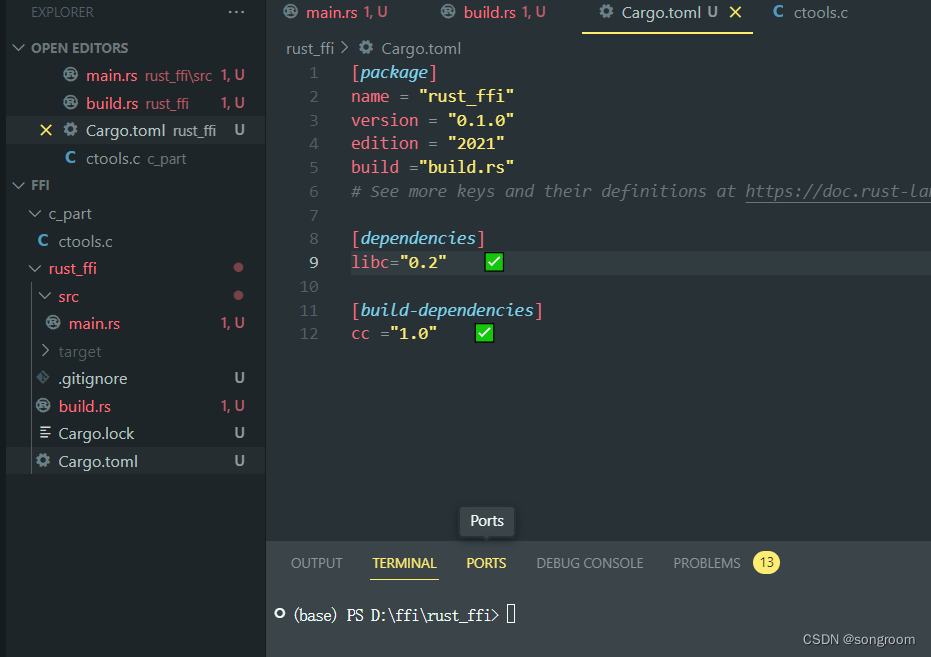 这里需要注意:
这里需要注意:
build="build.rs"
libc ="0.2"
cc ="1.0"
- 1
- 2
- 3
有一些依赖和说明。
3、ctools.c
// ctools.c 代码
int add(int i,int j){
return i+j;
}
int two_times(int input){
return input*2;
}
int three_times(int input){
return input*3;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
4、build.rs文件
extern crate cc;
fn main(){
cc::Build::new().file("../c_part/ctools.c").compile("libctools.a");
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
cc::Build::new().file(“…/c_part/ctools.c”).compile(“libctools.a”);的作用是使用 cc crate 编译 …/c_part/ctools.c文件,并将生成的静态库命名为 libctools.a。
(1)需要注意的是,生成的静态库或动态库的命名和文件格式可能会因操作系统和编译器的不同而有所区别。例如,在 Windows 系统上,静态库的命名通常是 libctools.a,而动态库的命名通常是 ctools.dll。生成静态库或动态库后,就可以使用 Rust 的 #[link(name = “ctools”)] 属性来链接库文件并在 Rust 代码中调用 C 函数了。
如果没有在 Rust 代码中使用 #[link(name = “ctools”)] 属性来指定链接的库的名称,Rust 编译器会默认按照一定的规则搜索系统默认的库文件路径来查找库文件。具体来说,Rust 编译器会按照以下顺序搜索库文件:
在系统默认的库搜索路径中查找:Rust 编译器会搜索系统默认的库文件路径,例如 /usr/lib 和 /usr/local/lib 等目录。
在 Rust 代码所在的目录中查找:如果 Rust 代码和库文件在同一个目录中,Rust 编译器会在该目录中查找库文件。
在指定的搜索路径中查找:如果在编译 Rust 代码时使用了 -L 参数指定了库文件搜索路径,Rust 编译器会在这些路径中查找库文件。
- 1
- 2
- 3
注:此部分内容来源以下链接,在此特别说明。
https://vincebye.github.io/posts/rust%E8%B0%83%E7%94%A8c%E4%BB%A3%E7%A0%81/
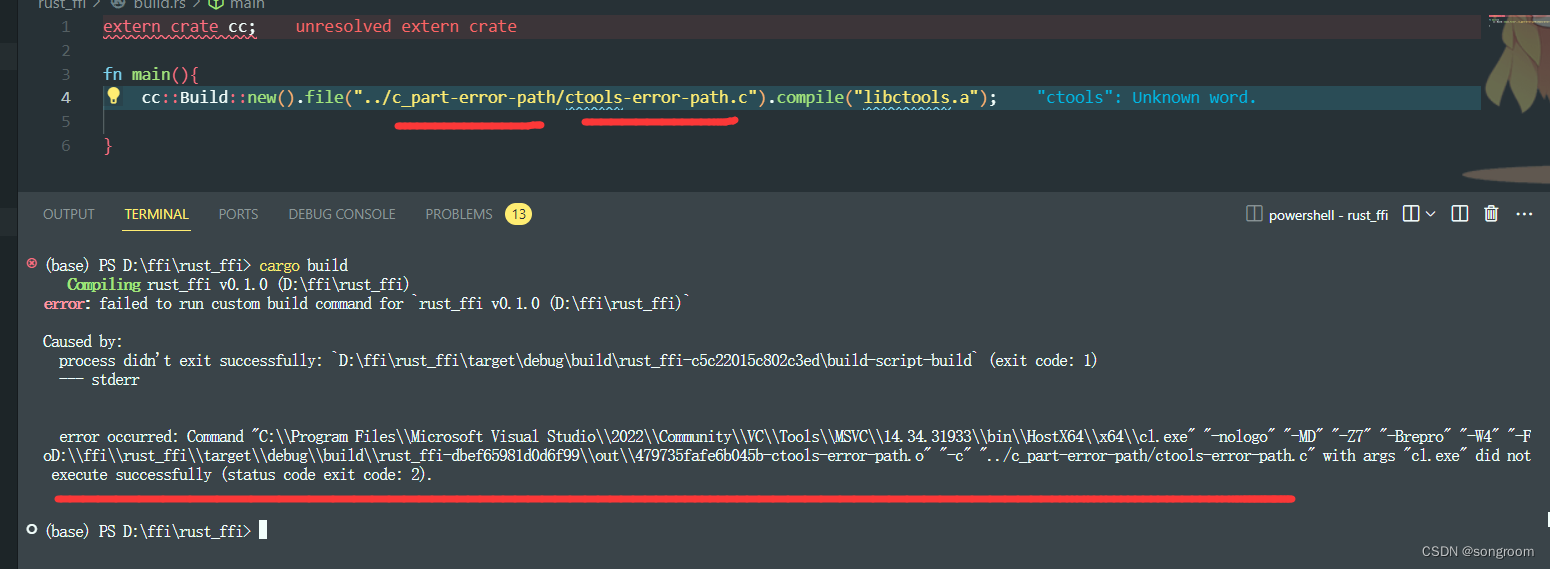
(2 )需要注意的是,file中ctool.c文件地址一定要准确,否则会有如下报错信息(但没有明示说路径不对,找不到文件之类)。报错可能如下(下面标红处路径是故意写错路径的情况):
 5、rust端:main.rs
5、rust端:main.rs
extern crate libc; use libc::c_int; extern "C" { fn add(i:c_int,j:c_int) ->c_int; fn two_times(input:c_int) ->c_int; fn three_times(input:c_int) ->c_int; } fn main() { println!("Hi guys, welcome rust ffi !"); let twotimes_value:i32 = unsafe{two_times(-8)}; println!("twotimes_value : {:?}",twotimes_value); let add_value = unsafe{add(2,3)}; println!("add_value : {:?}",add_value); let threetimes_value = unsafe{three_times(3)}; println!("threetimes_value: {:?}",threetimes_value); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
引入libc库,以及c_int类型。
6、cargo build
如果配置正确,在rust_ffi目录下(build.rs所在目录),运行cargo build: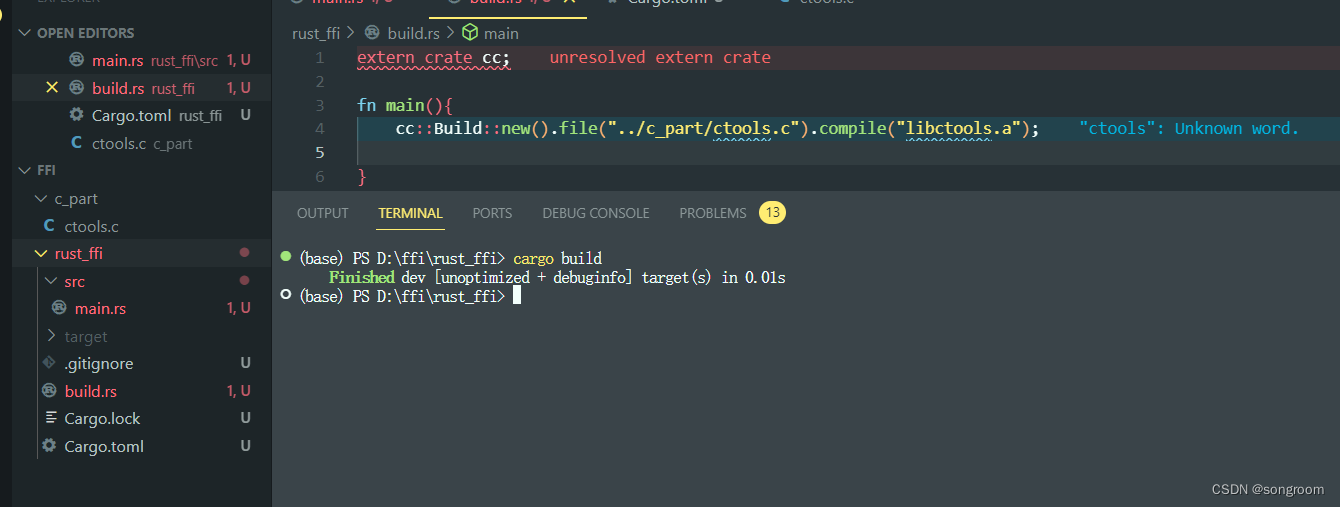 可见build成功。
可见build成功。
7、cargo run
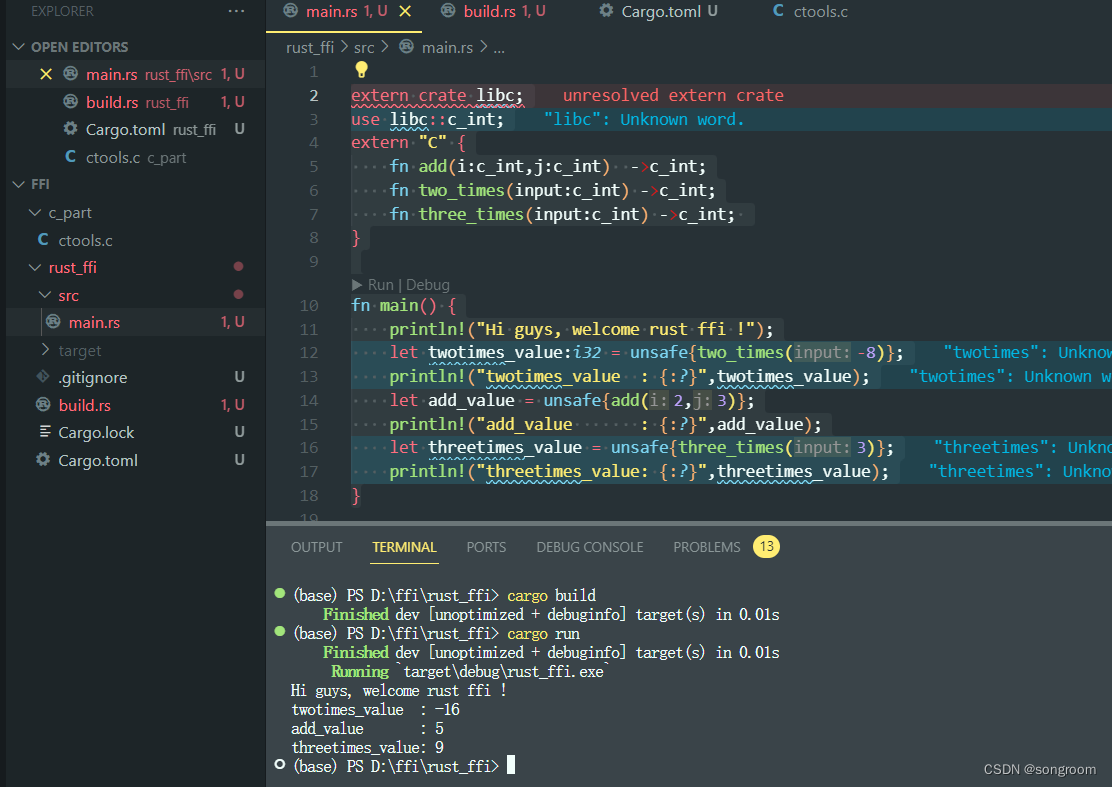 相关结果表明,rust端已经正确调用了ctools.c中几个库函数。
相关结果表明,rust端已经正确调用了ctools.c中几个库函数。
注意的是,因为已经是ffi调用,均需要加unsafe。
三、rust调用C封装好的静态库
(一)、linux平台
总体物料安排和上面windows平台自定义库类似,不再详述。
1、toml文件 , 其实只需要加“build”项,不需要cc库。
[package]
name = "myffi"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
build ="build.rs"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
2、准备生成相应的静态库供调用
在cpart目录下,有ctools.c文件
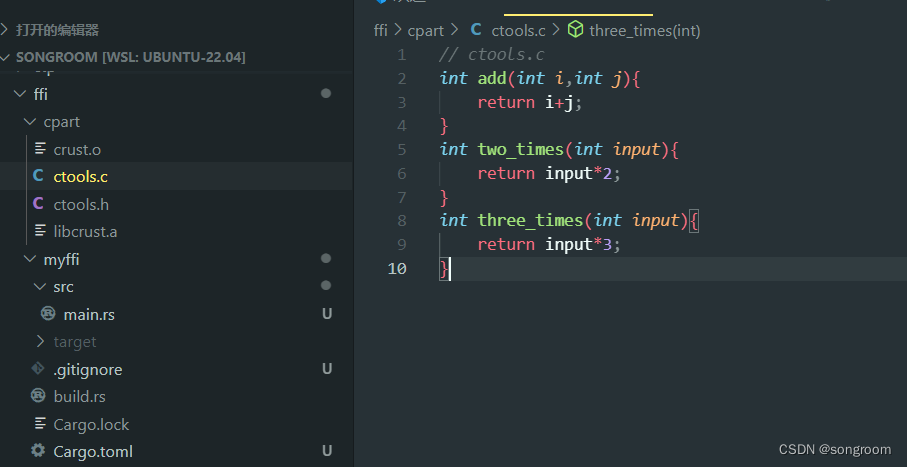
在cpart目录下,运行以下命令,生成了libcrust.a静态链接库。
gcc -c ctools.c -o crust.o
ar -cr libcrust.a crust.o
- 1
- 2
如果发现在对应目录下,已经生成libcrust.a文件,证明已经成功。
3、build.rs
build.rs中,主要一个是rustc-link-lib和rustc-link-search(此处我用了绝对地址)两项即可。具体如下:
fn main(){
println!("cargo:rustc-link-lib=crust");
println!(r"cargo:rustc-link-search=native=/home/songroom/ffi/cpart");
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
值得说明一下,build.rs中println!中"cargo:"的输出,是一种类“告示”通信方式,并不是一种简单的常规的打印。这个是告诉编译器,你去帮我这么干,没有这些,链接就不会成功,绝对不是或有或无的。
4、main.rs
加注了一个#[link=(name=“crust”,kind=“static”)]。
注意,尽管静态库名是libcurst,但在链接属性这,crust前面不要加lib。
extern crate libc; use libc::c_int; #[link=(name="crust",kind="static")] extern "C" { fn add(i:c_int,j:c_int) ->c_int; fn two_times(input:c_int) ->c_int; fn three_times(input:c_int) ->c_int; } fn main() { println!("Hi guys, welcome rust ffi !"); let twotimes_value:i32 = unsafe{two_times(-8)}; println!("twotimes_value : {:?}",twotimes_value); let add_value = unsafe{add(2,3)}; println!("add_value : {:?}",add_value); let threetimes_value = unsafe{three_times(3)}; println!("threetimes_value: {:?}",threetimes_value); }
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
5、配置路径
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:pwd
6、在build.rs的目录下cargo build
root@DESKTOP-MEDPUTU:/home/songroom/ffi/myffi/src# cargo build
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.00s
- 1
- 2
7、cargo run
root@DESKTOP-MEDPUTU:/home/songroom/ffi/myffi/src# cargo run
Compiling myffi v0.1.0 (/home/songroom/ffi/myffi)
Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.44s
Running `/home/songroom/ffi/myffi/target/debug/myffi`
Hi guys, welcome rust ffi !
twotimes_value : -16
add_value : 5
threetimes_value: 9
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
(二)、在windows平台
上面的方式,在windows还未成功,待续。
此外,动态库应差不多,有机会待尝试。
四、C调rust:以linux平台为例
在windows平台操作,不如linux平台方便。
1、结构
建立两个平行目录,c_call下放.c文件;另一个就是rustoc工程(通过cargo new rustoc --lib建立) ,是一个rust lib文件。
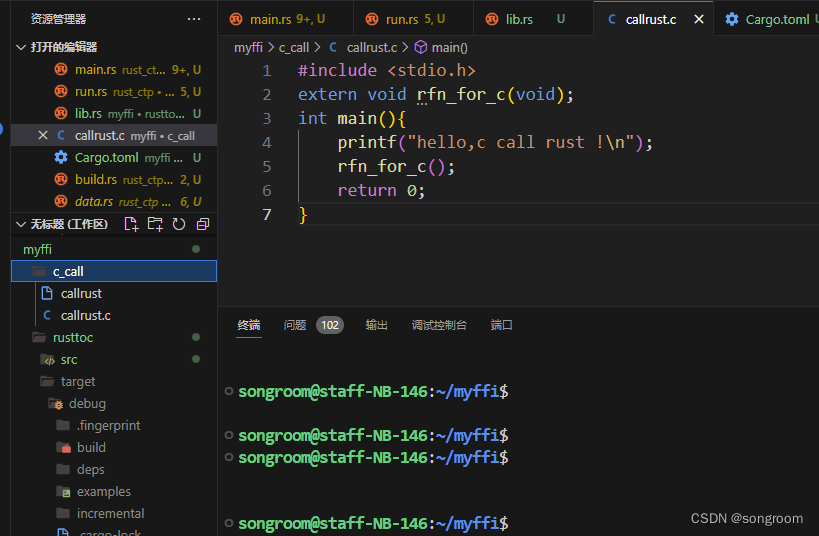 2、rustoc文件夹下lib.rs
2、rustoc文件夹下lib.rs
use std::os::raw::{c_int,c_double};
extern "C"{
fn abs(num:c_int) ->c_int;
fn sqrt(x:c_double) ->c_double;
}
#[no_mangle]
pub extern "C" fn rfn_for_c(){
println!("call from rust fn abs :{}",unsafe{abs(-6)});
println!("call from rust fn sqrt :{}",unsafe{sqrt(36.0)});
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
这个lib.rs中一方面引用了C库中 的两个函数,另一方面, rfn_for_c函数也输出给C调用。
3、rustoc下toml文件
在这里,lib项选择了dylib(动态链接库方式),当然也可以选择staticlib(静态链接库)项。
[package]
name = "rusttoc"
version = "0.1.0"
authors = ["songroom <sognroom@qq.com>"]
edition = "2018"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
[lib]
crate-type =["dylib"]
[dependencies]
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
4、在rusttoc文件夹下,cargo build
查看一下,是否生成相关的.so文件。这个文件后面需要被.c文件调用。
5、c_call文件夹下,建立一个callrust.c文件
#include <stdio.h>
extern void rfn_for_c(void);
int main(){
printf("hello,c call rust !\n");
rfn_for_c();
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
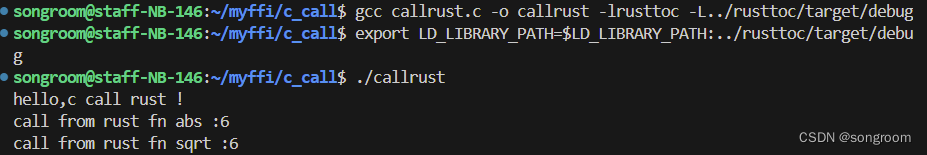
6、c_call文件夹下gcc,并设置.so文件相应的路径临时变量
songroom@staff-NB-146:~/myffi/c_call$ gcc callrust.c -o callrust -lrusttoc -L../rusttoc/target/debug
songroom@staff-NB-146:~/myffi/c_call$ export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:../rusttoc/target/debug
- 1
- 2
关于“-lrusttoc -L…/rusttoc/target/debug”:
(1)-lrusttoc:是指链接rustoc.so
(2)-L…/rusttoc/target/debug:是在“…/rusttoc/target/debug”路径上搜索相应的文件。
可以看到,相应的文件callrust文件已经生成。
LD_LIBRARY_PATH临时设置变量,如果需要设置永久路径, ~/.bashrc 或者 ~/.bash_profile下进行设置。
7、在c_call文件夹下,运行
songroom@staff-NB-146:~/myffi/c_call$ ./callrust
hello,c call rust !
call from rust fn abs :6
call from rust fn sqrt :6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
可见,在linux平台下,c调用rust中的库代码成功。
五、用cbindgen实现rust与c类型交互类型,并实现互调
此外,还有一些场景,有待深入:
1、上面主要讲的rust调C,并没有涉及C如何调Rust。如何实现C和Rust之间的互调?
2、此外,C类库中头文件中有各种不同的复杂自定义类型,且内容很多,如果没有一个自动化的工具来实现对应转换,两者的交互会很困难。
当然,cbindgen 不但可以生成 C 头文件,也可以针对C头文件生成rust的类型,便于交互。
待续。
六、总结及提示
1、和linux相比,windows平台之间RUST与C调用不太友好;如果可以尽可能在linux平台下,windows for linux也是可以的。
2、build.rs在工程中的路径:如果程序入口在rust侧,build.rs则放在rust入口程序同一文件夹下;
3、build.rs中的库中println!中cargo:路径指定是关键之一。具体见build.rs内容。
4、如果多次调用,还是把临时路径变量设置为永久,否则另一次运行仍可能还是找不到相应的库文件。



