- 1Docker-高级篇(1)-Dockerfile(核心&构建Redis&构建JDK8)_dockerfile 打包 jdk jar mysql redis
- 22021蓝桥杯(Python)骗分指南_蓝桥杯骗分导论
- 3时间序列 工具库学习(1) tsfresh特征提取、特征选择
- 4物流行业分析数据集分享_物流数据集
- 5ELEMENTUI奇葩坑爬出,遇到根本无从下手的问题之解答_elementui做的不好的地方
- 6大数据和人工智能概念全面解析_人工智能 大数据 电动车
- 7【Jenkins】持续集成与交付 (七):Gitlab添加组、创建用户、创建项目和源码上传到Gitlab仓库
- 8@param注解_Spring 自定义注解从入门到精通
- 9Hive之复杂字段分隔符
- 10Python 实现图书馆管理系统登录界面_关于python制作系统的登录界面和应用
数据结构的堆(c语言版)
赞
踩
一.堆的概念
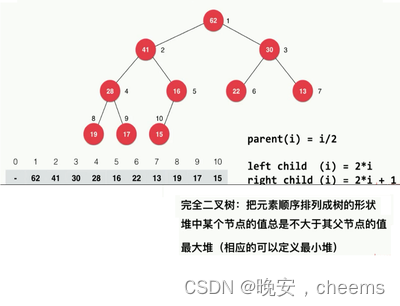
1.堆的基本概念
在计算机科学中,堆是一种特殊的数据结构,通常用于实现优先队列和动态分配内存。
2.堆的特征
堆是一个完全二叉树,它具有以下两个主要特性:
-
堆序性:对于最大堆,在堆中的任意节点i,其父节点的值大于等于节点i的值;对于最小堆,在堆中的任意节点i,其父节点的值小于等于节点i的值。这意味着在最大堆中,根节点是堆中最大的元素;在最小堆中,根节点是堆中最小的元素。
-
完全二叉树性质:除了最底层外,堆的其他层都是满的,并且最底层的节点集中在左侧。
3.堆的性质
根据堆序性质,我们可以高效地找到堆中的最大(最小)元素。这使得堆非常适用于解决一些需要高效获取最大(最小)元素的问题,例如优先队列和排序算法(如堆排序)。
堆可以用数组来实现,其中父节点和子节点之间的关系可以通过索引计算得出。通常,堆的插入和删除操作会触发堆的调整,以维持堆序性质。
需要注意的是,堆和操作系统中的堆内存分配是不同的概念。在操作系统中,堆内存指的是动态分配的内存区域,而在数据结构中,堆是一种数据结构。
4.堆的优缺点
优点:
-
高效的插入和删除操作:在堆中,插入和删除元素的时间复杂度为O(log n),其中n是堆中元素的个数。这是由于堆的调整过程只需要对树的高度进行操作,堆的高度通常比较小。
-
快速获取最大(最小)元素:在最大堆中,根节点是堆中的最大元素;在最小堆中,根节点是堆中的最小元素。因此,可以在O(1)的时间复杂度内获取最大(最小)元素。
-
实现优先队列:堆常用于实现优先队列,其中元素按照优先级进行排序。优先队列可以在O(1)的时间复杂度内获取最高优先级的元素,并且在O(log n)的时间复杂度内插入和删除元素。
缺点:
-
不支持快速查找:堆并不提供快速查找指定元素的功能。如果需要在堆中进行查找操作,时间复杂度为O(n),需要遍历整个堆。
-
内存空间的浪费:堆使用数组来存储元素,如果事先不知道元素的个数,需要预分配一个较大的数组空间。这可能会导致内存空间的浪费。
-
不稳定性:堆排序算法是一种不稳定的排序算法。在排序过程中,相等元素的相对顺序可能会改变。
二.堆的功能
-
插入元素:向堆中插入一个新元素。插入操作会根据堆的特性进行调整,以保持堆的性质。
-
删除最大(最小)元素:从堆中删除并返回最大(最小)元素。删除操作会将堆的最后一个元素移到堆顶,并根据堆的特性进行调整,以保持堆的性质。
-
获取最大(最小)元素:返回堆中的最大(最小)元素,而不删除它。获取操作只是简单地返回堆的根节点的值。
-
堆排序:使用堆进行排序。堆排序是一种基于堆的排序算法,它利用堆的性质进行排序操作。
-
构建堆:将一个无序的数组转换为一个堆。构建堆的过程会进行堆调整,以满足堆的性质。
-
堆化:对一个已有的堆进行调整,以满足堆的性质。堆化可以通过自上而下或自下而上的方式进行。
-
堆的合并:将两个堆合并为一个堆。堆的合并操作通常用于合并多个优先队列。
-
查找元素:在堆中查找指定元素。由于堆并不提供快速查找功能,查找操作需要遍历整个堆,时间复杂度为O(n)。
三.堆的代码实现
1.堆的定义
创建一个结构体,其中成员如下:
array:一个指向整型数组的指针,用于存储堆中的元素。capacity:一个整数,表示堆的容量,即array数组的最大长度。size:一个整数,表示当前堆中的元素个数,即array数组中实际存储的元素数量。
- typedef struct {
- int* array; // 存储堆元素的数组
- int capacity; // 堆的容量
- int size; // 堆中当前元素的个数
- } Heap;
2.创建堆
创建堆。该函数接受一个整数参数 capacity,表示堆的容量。它会分配堆所需的内存,并返回指向堆结构的指针。
- // 创建堆
- Heap* createHeap(int capacity) {
- Heap* heap = (Heap*)malloc(sizeof(Heap));
- heap->array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * capacity);
- heap->capacity = capacity;
- heap->size = 0;
- return heap;
- }
3.交换两个数值
交换两个元素的值。该函数接受两个整型指针作为参数,通过引用交换指针所指向的两个整数的值。
- // 交换两个元素
- void swap(int* a, int* b) {
- int temp = *a;
- *a = *b;
- *b = temp;
- }
4.入堆
向堆中插入元素。该函数接受一个指向堆结构的指针 heap 和要插入的整数值 value。它将元素插入到堆的最后位置,并通过自上而下的调整操作,保持堆的性质。
- // 向堆中插入元素
- void insert(Heap* heap, int value) {
- if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
- printf("堆已满,无法插入新元素。\n");
- return;
- }
-
- // 将新元素插入到堆的最后位置
- heap->array[heap->size] = value;
-
- int currentIndex = heap->size;
- int parentIndex = (currentIndex - 1) / 2;
-
- // 自下而上调整堆结构
- while (currentIndex > 0 && heap->array[currentIndex] > heap->array[parentIndex]) {
- swap(&heap->array[currentIndex], &heap->array[parentIndex]);
- currentIndex = parentIndex;
- parentIndex = (currentIndex - 1) / 2;
- }
-
- heap->size++;
- }

5.出堆
从堆中删除并返回最大元素。该函数接受一个指向堆结构的指针 heap。它将堆顶元素(最大元素)删除,并将最后一个元素移到堆顶,然后通过自上而下的调整操作,保持堆的性质。
- // 从堆中删除并返回最大元素
- int deleteMax(Heap* heap) {
- if (heap->size == 0) {
- printf("堆为空,无法删除元素。\n");
- return -1;
- }
-
- int maxValue = heap->array[0];
-
- // 将最后一个元素移到堆顶
- heap->array[0] = heap->array[heap->size - 1];
- heap->size--;
-
- int currentIndex = 0;
- int leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
- int rightChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 2;
-
- // 自上而下调整堆结构
- while (1) {
- int maxIndex = currentIndex;
-
- // 与左子节点比较
- if (leftChildIndex < heap->size && heap->array[leftChildIndex] > heap->array[maxIndex]) {
- maxIndex = leftChildIndex;
- }
-
- // 与右子节点比较
- if (rightChildIndex < heap->size && heap->array[rightChildIndex] > heap->array[maxIndex]) {
- maxIndex = rightChildIndex;
- }
-
- // 如果当前节点已经是最大值,则堆已调整完毕
- if (maxIndex == currentIndex) {
- break;
- }
-
- // 否则,交换当前节点与最大子节点的位置
- swap(&heap->array[currentIndex], &heap->array[maxIndex]);
- currentIndex = maxIndex;
- leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
- rightChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 2;
- }
-
- return maxValue;
- }

6.打印堆
打印堆元素。该函数接受一个指向堆结构的指针 heap。它会遍历堆中的元素,并将它们打印出来。
- // 打印堆元素
- void printHeap(Heap* heap) {
- printf("堆元素:");
- for (int i = 0; i < heap->size; i++) {
- printf("%d ", heap->array[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
7.销毁堆
释放堆内存。该函数接受一个指向堆结构的指针 heap。它会释放堆所占用的内存,防止内存泄漏。
- // 释放堆内存
- void destroyHeap(Heap* heap) {
- free(heap->array);
- free(heap);
- }
四.堆的源码呈现
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
-
- // 定义堆结构
- typedef struct {
- int* array; // 存储堆元素的数组
- int capacity; // 堆的容量
- int size; // 堆中当前元素的个数
- } Heap;
-
- // 创建堆
- Heap* createHeap(int capacity) {
- Heap* heap = (Heap*)malloc(sizeof(Heap));
- heap->array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * capacity);
- heap->capacity = capacity;
- heap->size = 0;
- return heap;
- }
-
- // 交换两个元素
- void swap(int* a, int* b) {
- int temp = *a;
- *a = *b;
- *b = temp;
- }
-
- // 向堆中插入元素
- void insert(Heap* heap, int value) {
- if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
- printf("堆已满,无法插入新元素。\n");
- return;
- }
-
- // 将新元素插入到堆的最后位置
- heap->array[heap->size] = value;
-
- int currentIndex = heap->size;
- int parentIndex = (currentIndex - 1) / 2;
-
- // 自下而上调整堆结构
- while (currentIndex > 0 && heap->array[currentIndex] > heap->array[parentIndex]) {
- swap(&heap->array[currentIndex], &heap->array[parentIndex]);
- currentIndex = parentIndex;
- parentIndex = (currentIndex - 1) / 2;
- }
-
- heap->size++;
- }
-
- // 从堆中删除并返回最大元素
- int deleteMax(Heap* heap) {
- if (heap->size == 0) {
- printf("堆为空,无法删除元素。\n");
- return -1;
- }
-
- int maxValue = heap->array[0];
-
- // 将最后一个元素移到堆顶
- heap->array[0] = heap->array[heap->size - 1];
- heap->size--;
-
- int currentIndex = 0;
- int leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
- int rightChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 2;
-
- // 自上而下调整堆结构
- while (1) {
- int maxIndex = currentIndex;
-
- // 与左子节点比较
- if (leftChildIndex < heap->size && heap->array[leftChildIndex] > heap->array[maxIndex]) {
- maxIndex = leftChildIndex;
- }
-
- // 与右子节点比较
- if (rightChildIndex < heap->size && heap->array[rightChildIndex] > heap->array[maxIndex]) {
- maxIndex = rightChildIndex;
- }
-
- // 如果当前节点已经是最大值,则堆已调整完毕
- if (maxIndex == currentIndex) {
- break;
- }
-
- // 否则,交换当前节点与最大子节点的位置
- swap(&heap->array[currentIndex], &heap->array[maxIndex]);
- currentIndex = maxIndex;
- leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;
- rightChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 2;
- }
-
- return maxValue;
- }
-
- // 打印堆元素
- void printHeap(Heap* heap) {
- printf("堆元素:");
- for (int i = 0; i < heap->size; i++) {
- printf("%d ", heap->array[i]);
- }
- printf("\n");
- }
-
- // 释放堆内存
- void destroyHeap(Heap* heap) {
- free(heap->array);
- free(heap);
- }
-
- int main() {
- Heap* heap = createHeap(10);
-
- insert(heap, 5);
- insert(heap, 8);
- insert(heap, 2);
- insert(heap, 10);
- insert(heap, 3);
-
- printHeap(heap);
-
- int max = deleteMax(heap);
- printf("删除的最大元素:%d\n", max);
-
- printHeap(heap);
-
- destroyHeap(heap);
-
- return 0;
- }



