- 1物流机器人独角兽公司24届项目管培生(合肥 广州)热招中!
- 2java技术--子查询和连接查询比较_子查询和连表查询的区别
- 3如何保证消息的顺序性
- 4mac安装linux虚拟机_mac安装虚拟机linux系统需要设置安全隔离吗
- 5用手势识别来测试视力?试试用百度AI来实现想法_oc 视力测试开发
- 6鸿蒙NEXT_鸿蒙next csdn
- 7数据库-表连接的几种方式
- 8小编辑的自我成长 | 出版、出版业与出版学概述_其中提到“所谓记载物件者,或定期出版或不定期出版”。
- 9openmv与stm32通讯实现控制舵机跟随颜色块转动[hal库]_openmv与是stm32二维自由度舵机(2)_openmv舵机不动怎么回事
- 10图像相似度比较算法总结_图片相似度算法
数据开放最全sql面试合集(leetcode)_leetcode sql
赞
踩

关注公众号“大数据领航员"领取PDF版本和大数据面经
https://leetcode-cn.com/problemset/database/
题目都是leetcode 上了可以点击题目会有相应的链接
由于个人比较喜欢用开窗函数,所以都优先用了开窗 ,当然这些并不一定都是最优解,答案仅供参考
每道题后面都应相应的难度等级,如果没时间做的话 可以在leetcode 按出题频率刷题
我是安顺序刷的题,后续还会继续更新
祝大家面试取得好的成绩
175. 组合两个表
难度简单
SQL架构
表1: Person
+-------------+---------+
| 列名 | 类型 |
+-------------+---------+
| PersonId | int |
| FirstName | varchar |
| LastName | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
PersonId 是上表主键
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表2: Address
+-------------+---------+
| 列名 | 类型 |
+-------------+---------+
| AddressId | int |
| PersonId | int |
| City | varchar |
| State | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
AddressId 是上表主键
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
编写一个 SQL 查询,满足条件:无论 person 是否有地址信息,都需要基于上述两表提供 person 的以下信息:
FirstName, LastName, City, State
select FirstName,LastName,City,State
from Person p
left join Address a
on a.PersonId = p.PersonId
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
176. 第二高的薪水
难度简单
SQL架构
编写一个 SQL 查询,获取 Employee 表中第二高的薪水(Salary) 。
+----+--------+
| Id | Salary |
+----+--------+
| 1 | 100 |
| 2 | 200 |
| 3 | 300 |
+----+--------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
例如上述 Employee 表,SQL查询应该返回 200 作为第二高的薪水。如果不存在第二高的薪水,那么查询应返回 null。
+---------------------+
| SecondHighestSalary |
+---------------------+
| 200 |
+---------------------+
SELECT
IFNULL(
(SELECT DISTINCT Salary
FROM Employee
ORDER BY Salary DESC
LIMIT 1 OFFSET 1),
NULL) AS SecondHighestSalary
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
177. 第N高的薪水
难度中等
编写一个 SQL 查询,获取 Employee 表中第 n 高的薪水(Salary)。
+----+--------+
| Id | Salary |
+----+--------+
| 1 | 100 |
| 2 | 200 |
| 3 | 300 |
+----+--------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
例如上述 Employee 表,n = 2 时,应返回第二高的薪水 200。如果不存在第 n 高的薪水,那么查询应返回 null。
+------------------------+ | getNthHighestSalary(2) | +------------------------+ | 200 | +------------------------+ CREATE FUNCTION getNthHighestSalary(N INT) RETURNS INT BEGIN RETURN ( SELECT IFNULL( (select salary from( select salary, rank() over(order by salary desc) rk from Employee group by salary )t1 where rk=N),NULL) SecondHighestSalary ); END
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
178. 分数排名
难度中等
SQL架构
编写一个 SQL 查询来实现分数排名。
如果两个分数相同,则两个分数排名(Rank)相同。请注意,平分后的下一个名次应该是下一个连续的整数值。换句话说,名次之间不应该有“间隔”。
+----+-------+
| Id | Score |
+----+-------+
| 1 | 3.50 |
| 2 | 3.65 |
| 3 | 4.00 |
| 4 | 3.85 |
| 5 | 4.00 |
| 6 | 3.65 |
+----+-------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
例如,根据上述给定的 Scores 表,你的查询应该返回(按分数从高到低排列):
+-------+------+
| Score | Rank |
+-------+------+
| 4.00 | 1 |
| 4.00 | 1 |
| 3.85 | 2 |
| 3.65 | 3 |
| 3.65 | 3 |
| 3.50 | 4 |
+-------+------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
**重要提示:**对于 MySQL 解决方案,如果要转义用作列名的保留字,可以在关键字之前和之后使用撇号。例如 Rank
select Score,
dense_rank() over(order by Score desc) `rank`
from Scores
- 1
- 2
- 3
180. 连续出现的数字
难度中等
SQL架构
编写一个 SQL 查询,查找所有至少连续出现三次的数字。
+----+-----+
| Id | Num |
+----+-----+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 1 |
| 6 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 |
+----+-----+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
例如,给定上面的 Logs 表, 1 是唯一连续出现至少三次的数字。
+-----------------+
| ConsecutiveNums |
+-----------------+
| 1 |
+-----------------+
select distinct Num ConsecutiveNums
from
(
select
Num,
lead(Num,1,null) over(order by id) n2,
lead(Num,2,null) over(order by id) n3
from Logs
)t1
where Num = n2 and Num = n3
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
181. 超过经理收入的员工
难度简单
SQL架构
Employee 表包含所有员工,他们的经理也属于员工。每个员工都有一个 Id,此外还有一列对应员工的经理的 Id。
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| Id | Name | Salary | ManagerId |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 3 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 4 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | NULL |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | NULL |
+----+-------+--------+-----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
给定 Employee 表,编写一个 SQL 查询,该查询可以获取收入超过他们经理的员工的姓名。在上面的表格中,Joe 是唯一一个收入超过他的经理的员工。
+----------+
| Employee |
+----------+
| Joe |
+----------+
select a.Name Employee
from Employee a
join Employee b
on a.ManagerId = b.id
where a.Salary>b.Salary
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
182. 查找重复的电子邮箱
难度简单
SQL架构
编写一个 SQL 查询,查找 Person 表中所有重复的电子邮箱。
示例:
+----+---------+
| Id | Email |
+----+---------+
| 1 | a@b.com |
| 2 | c@d.com |
| 3 | a@b.com |
+----+---------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
根据以上输入,你的查询应返回以下结果:
+---------+
| Email |
+---------+
| a@b.com |
+---------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
**说明:**所有电子邮箱都是小写字母。
select Email
from Person
group by Email
having count(*)>1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
183. 从不订购的客户
难度简单
SQL架构
某网站包含两个表,Customers 表和 Orders 表。编写一个 SQL 查询,找出所有从不订购任何东西的客户。
Customers 表:
+----+-------+
| Id | Name |
+----+-------+
| 1 | Joe |
| 2 | Henry |
| 3 | Sam |
| 4 | Max |
+----+-------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Orders 表:
+----+------------+
| Id | CustomerId |
+----+------------+
| 1 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 |
+----+------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
例如给定上述表格,你的查询应返回:
+-----------+
| Customers |
+-----------+
| Henry |
| Max |
+-----------+
select c.Name Customers
from Customers c left join Orders o
on c.id = o.CustomerId
where o.id is null
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
184. 部门工资最高的员工
难度中等
SQL架构
Employee 表包含所有员工信息,每个员工有其对应的 Id, salary 和 department Id。
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| Id | Name | Salary | DepartmentId |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 1 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 2 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | 2 |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | 1 |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Department 表包含公司所有部门的信息。
+----+----------+
| Id | Name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | IT |
| 2 | Sales |
+----+----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
编写一个 SQL 查询,找出每个部门工资最高的员工。例如,根据上述给定的表格,Max 在 IT 部门有最高工资,Henry 在 Sales 部门有最高工资。
+------------+----------+--------+
| Department | Employee | Salary |
+------------+----------+--------+
| IT | Max | 90000 |
| Sales | Henry | 80000 |
+------------+----------+--------+
select Department,Employee,Salary
from (
select d.Name Department,e.Name Employee, e.Salary,
rank() over(partition by d.id order by Salary desc) rk
from Employee e join Department d
on e.DepartmentId=d.id
)tmp
where rk = 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
185. 部门工资前三高的所有员工
难度困难
SQL架构
Employee 表包含所有员工信息,每个员工有其对应的工号 Id,姓名 Name,工资 Salary 和部门编号 DepartmentId 。
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| Id | Name | Salary | DepartmentId |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
| 1 | Joe | 85000 | 1 |
| 2 | Henry | 80000 | 2 |
| 3 | Sam | 60000 | 2 |
| 4 | Max | 90000 | 1 |
| 5 | Janet | 69000 | 1 |
| 6 | Randy | 85000 | 1 |
| 7 | Will | 70000 | 1 |
+----+-------+--------+--------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Department 表包含公司所有部门的信息。
+----+----------+
| Id | Name |
+----+----------+
| 1 | IT |
| 2 | Sales |
+----+----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
编写一个 SQL 查询,找出每个部门获得前三高工资的所有员工。例如,根据上述给定的表,查询结果应返回:
+------------+----------+--------+
| Department | Employee | Salary |
+------------+----------+--------+
| IT | Max | 90000 |
| IT | Randy | 85000 |
| IT | Joe | 85000 |
| IT | Will | 70000 |
| Sales | Henry | 80000 |
| Sales | Sam | 60000 |
+------------+----------+--------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
解释:
IT 部门中,Max 获得了最高的工资,Randy 和 Joe 都拿到了第二高的工资,Will 的工资排第三。销售部门(Sales)只有两名员工,Henry 的工资最高,Sam 的工资排第二。
select Department,Employee,Salary
from (
select d.Name Department,e.Name Employee, e.Salary,
dense_rank() over(partition by d.id order by Salary desc) rk
from Employee e join Department d
on e.DepartmentId=d.id
)tmp
where rk <=3
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
196. 删除重复的电子邮箱
难度简单
编写一个 SQL 查询,来删除 Person 表中所有重复的电子邮箱,重复的邮箱里只保留 Id最小 的那个。
+----+------------------+
| Id | Email |
+----+------------------+
| 1 | john@example.com |
| 2 | bob@example.com |
| 3 | john@example.com |
+----+------------------+
Id 是这个表的主键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
例如,在运行你的查询语句之后,上面的 Person 表应返回以下几行:
+----+------------------+
| Id | Email |
+----+------------------+
| 1 | john@example.com |
| 2 | bob@example.com |
+----+------------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
提示:
- 执行 SQL 之后,输出是整个 Person 表。
- 使用 delete 语句。
DELETE p1 FROM Person p1,
Person p2
WHERE
p1.Email = p2.Email AND p1.Id > p2.Id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
注意是删除 ,不是查询
197. 上升的温度
难度简单
SQL架构
给定一个 Weather 表,编写一个 SQL 查询,来查找与之前(昨天的)日期相比温度更高的所有日期的 Id。
+---------+------------------+------------------+
| Id(INT) | RecordDate(DATE) | Temperature(INT) |
+---------+------------------+------------------+
| 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 |
| 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 |
| 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 |
| 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 |
+---------+------------------+------------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
例如,根据上述给定的 Weather 表格,返回如下 Id:
+----+ | Id | +----+ | 2 | | 4 | +----+ select Id from ( select Id,RecordDate,Temperature, lag(RecordDate,1,9999-99-99) over (order by RecordDate) yd, lag(Temperature,1,999) over(order by RecordDate ) yt from Weather )tmp where Temperature >yt and datediff(RecordDate,yd)=1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
262. 行程和用户
难度困难
SQL架构
Trips 表中存所有出租车的行程信息。每段行程有唯一键 Id,Client_Id 和 Driver_Id 是 Users 表中 Users_Id 的外键。Status 是枚举类型,枚举成员为 (‘completed’, ‘cancelled_by_driver’, ‘cancelled_by_client’)。
+----+-----------+-----------+---------+--------------------+----------+
| Id | Client_Id | Driver_Id | City_Id | Status |Request_at|
+----+-----------+-----------+---------+--------------------+----------+
| 1 | 1 | 10 | 1 | completed |2013-10-01|
| 2 | 2 | 11 | 1 | cancelled_by_driver|2013-10-01|
| 3 | 3 | 12 | 6 | completed |2013-10-01|
| 4 | 4 | 13 | 6 | cancelled_by_client|2013-10-01|
| 5 | 1 | 10 | 1 | completed |2013-10-02|
| 6 | 2 | 11 | 6 | completed |2013-10-02|
| 7 | 3 | 12 | 6 | completed |2013-10-02|
| 8 | 2 | 12 | 12 | completed |2013-10-03|
| 9 | 3 | 10 | 12 | completed |2013-10-03|
| 10 | 4 | 13 | 12 | cancelled_by_driver|2013-10-03|
+----+-----------+-----------+---------+--------------------+----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
Users 表存所有用户。每个用户有唯一键 Users_Id。Banned 表示这个用户是否被禁止,Role 则是一个表示(‘client’, ‘driver’, ‘partner’)的枚举类型。
+----------+--------+--------+
| Users_Id | Banned | Role |
+----------+--------+--------+
| 1 | No | client |
| 2 | Yes | client |
| 3 | No | client |
| 4 | No | client |
| 10 | No | driver |
| 11 | No | driver |
| 12 | No | driver |
| 13 | No | driver |
+----------+--------+--------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
写一段 SQL 语句查出 2013年10月1日 至 2013年10月3日 期间非禁止用户的取消率。基于上表,你的 SQL 语句应返回如下结果,取消率(Cancellation Rate)保留两位小数。
取消率的计算方式如下:(被司机或乘客取消的非禁止用户生成的订单数量) / (非禁止用户生成的订单总数)
+------------+-------------------+ | Day | Cancellation Rate | +------------+-------------------+ | 2013-10-01 | 0.33 | | 2013-10-02 | 0.00 | | 2013-10-03 | 0.50 | +------------+-------------------+ SELECT T.request_at AS `Day`, ROUND( SUM( IF(T.STATUS = 'completed',0,1) ) / COUNT(T.STATUS), 2 ) AS `Cancellation Rate` FROM trips AS T WHERE T.Client_Id NOT IN ( SELECT users_id FROM users WHERE banned = 'Yes' ) AND T.Driver_Id NOT IN ( SELECT users_id FROM users WHERE banned = 'Yes' ) AND T.request_at BETWEEN '2013-10-01' AND '2013-10-03' GROUP BY T.request_at
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
511. 游戏玩法分析 I
难度简单
SQL架构
活动表 Activity:
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| player_id | int |
| device_id | int |
| event_date | date |
| games_played | int |
+--------------+---------+
表的主键是 (player_id, event_date)。
这张表展示了一些游戏玩家在游戏平台上的行为活动。
每行数据记录了一名玩家在退出平台之前,当天使用同一台设备登录平台后打开的游戏的数目(可能是 0 个)。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
写一条 SQL 查询语句获取每位玩家 第一次登陆平台的日期。
查询结果的格式如下所示:
Activity 表: +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | player_id | device_id | event_date | games_played | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | 1 | 2 | 2016-03-01 | 5 | | 1 | 2 | 2016-05-02 | 6 | | 2 | 3 | 2017-06-25 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | 2016-03-02 | 0 | | 3 | 4 | 2018-07-03 | 5 | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ Result 表: +-----------+-------------+ | player_id | first_login | +-----------+-------------+ | 1 | 2016-03-01 | | 2 | 2017-06-25 | | 3 | 2016-03-02 | +-----------+-------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
select player_id ,event_date first_login
from (
select player_id ,event_date,
rank() over(partition by player_id order by event_date) rk
from Activity
) tmp
where rk = 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2.最优 (选最小日期)
select player_id ,min(event_date) first_login
from Activity
group by player_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
512. 游戏玩法分析 II
难度简单
SQL架构
Table: Activity
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| player_id | int |
| device_id | int |
| event_date | date |
| games_played | int |
+--------------+---------+
(player_id, event_date) 是这个表的两个主键
这个表显示的是某些游戏玩家的游戏活动情况
每一行是在某天使用某个设备登出之前登录并玩多个游戏(可能为0)的玩家的记录
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
请编写一个 SQL 查询,描述每一个玩家首次登陆的设备名称
查询结果格式在以下示例中:
Activity table: +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | player_id | device_id | event_date | games_played | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | 1 | 2 | 2016-03-01 | 5 | | 1 | 2 | 2016-05-02 | 6 | | 2 | 3 | 2017-06-25 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | 2016-03-02 | 0 | | 3 | 4 | 2018-07-03 | 5 | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ Result table: +-----------+-----------+ | player_id | device_id | +-----------+-----------+ | 1 | 2 | | 2 | 3 | | 3 | 1 | +-----------+-----------+ select player_id ,device_id from ( select player_id ,event_date,device_id, rank() over(partition by player_id order by event_date) rk from Activity ) tmp where rk = 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
534. 游戏玩法分析 III
难度中等20收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
Table: Activity
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| player_id | int |
| device_id | int |
| event_date | date |
| games_played | int |
+--------------+---------+
(player_id,event_date)是此表的主键。
这张表显示了某些游戏的玩家的活动情况。
每一行是一个玩家的记录,他在某一天使用某个设备注销之前登录并玩了很多游戏(可能是 0 )。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
编写一个 SQL 查询,同时报告每组玩家和日期,以及玩家到目前为止玩了多少游戏。也就是说,在此日期之前玩家所玩的游戏总数。详细情况请查看示例。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Activity table: +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | player_id | device_id | event_date | games_played | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | 1 | 2 | 2016-03-01 | 5 | | 1 | 2 | 2016-05-02 | 6 | | 1 | 3 | 2017-06-25 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | 2016-03-02 | 0 | | 3 | 4 | 2018-07-03 | 5 | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ Result table: +-----------+------------+---------------------+ | player_id | event_date | games_played_so_far | +-----------+------------+---------------------+ | 1 | 2016-03-01 | 5 | | 1 | 2016-05-02 | 11 | | 1 | 2017-06-25 | 12 | | 3 | 2016-03-02 | 0 | | 3 | 2018-07-03 | 5 | +-----------+------------+---------------------+ 对于 ID 为 1 的玩家,2016-05-02 共玩了 5+6=11 个游戏,2017-06-25 共玩了 5+6+1=12 个游戏。 对于 ID 为 3 的玩家,2018-07-03 共玩了 0+5=5 个游戏。 请注意,对于每个玩家,我们只关心玩家的登录日期。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
开窗
select player_id,event_date ,
sum(games_played) over(partition by player_id order by event_date )games_played_so_far
from Activity
- 1
- 2
- 3
自连接
select
a1.player_id,
a1.event_date,
sum(a2.games_played) games_played_so_far
from Activity a1,Activity a2
where a1.player_id=a2.player_id and
a1.event_date>=a2.event_date
group by 1,2;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
550. 游戏玩法分析 IV
难度中等17收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
Table: Activity
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| player_id | int |
| device_id | int |
| event_date | date |
| games_played | int |
+--------------+---------+
(player_id,event_date)是此表的主键。
这张表显示了某些游戏的玩家的活动情况。
每一行是一个玩家的记录,他在某一天使用某个设备注销之前登录并玩了很多游戏(可能是 0)。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
编写一个 SQL 查询,报告在首次登录的第二天再次登录的玩家的分数,四舍五入到小数点后两位。换句话说,您需要计算从首次登录日期开始至少连续两天登录的玩家的数量,然后除以玩家总数。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Activity table: +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | player_id | device_id | event_date | games_played | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | 1 | 2 | 2016-03-01 | 5 | | 1 | 2 | 2016-03-02 | 6 | | 2 | 3 | 2017-06-25 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | 2016-03-02 | 0 | | 3 | 4 | 2018-07-03 | 5 | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ Result table: +-----------+ | fraction | +-----------+ | 0.33 | +-----------+ 只有 ID 为 1 的玩家在第一天登录后才重新登录,所以答案是 1/3 = 0.33 select round(avg(a.event_date is not null), 2) fraction from (select player_id, min(event_date) as login from activity group by player_id) p left join activity a on p.player_id=a.player_id and datediff(a.event_date, p.login)=1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
这个avg用的妙
is not null判断后,有eventdate值的返回1,null的返回0,avg相当于求和后(即符合条件的id个数)除以总id数即所求比例
569. 员工薪水中位数
难度困难
SQL架构
Employee 表包含所有员工。Employee 表有三列:员工Id,公司名和薪水。
+-----+------------+--------+ |Id | Company | Salary | +-----+------------+--------+ |1 | A | 2341 | |2 | A | 341 | |3 | A | 15 | |4 | A | 15314 | |5 | A | 451 | |6 | A | 513 | |7 | B | 15 | |8 | B | 13 | |9 | B | 1154 | |10 | B | 1345 | |11 | B | 1221 | |12 | B | 234 | |13 | C | 2345 | |14 | C | 2645 | |15 | C | 2645 | |16 | C | 2652 | |17 | C | 65 | +-----+------------+--------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
请编写SQL查询来查找每个公司的薪水中位数。挑战点:你是否可以在不使用任何内置的SQL函数的情况下解决此问题。
+-----+------------+--------+ |Id | Company | Salary | +-----+------------+--------+ |5 | A | 451 | |6 | A | 513 | |12 | B | 234 | |9 | B | 1154 | |14 | C | 2645 | +-----+------------+--------+ select Id,Company,Salary from ( select Id,Company,Salary, ROW_NUMBER() over(partition by Company order by Salary) rk, count(*) over(partition by Company) cnt from Employee )t1 where rk IN (FLOOR((cnt + 1)/2), FLOOR((cnt + 2)/2))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
中位数:
+1向下取整 +2 向下取整数
570. 至少有5名直接下属的经理
难度中等
SQL架构
Employee 表包含所有员工和他们的经理。每个员工都有一个 Id,并且还有一列是经理的 Id。
+------+----------+-----------+----------+
|Id |Name |Department |ManagerId |
+------+----------+-----------+----------+
|101 |John |A |null |
|102 |Dan |A |101 |
|103 |James |A |101 |
|104 |Amy |A |101 |
|105 |Anne |A |101 |
|106 |Ron |B |101 |
+------+----------+-----------+----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
给定 Employee 表,请编写一个SQL查询来查找至少有5名直接下属的经理。对于上表,您的SQL查询应该返回:
+-------+
| Name |
+-------+
| John |
+-------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
**注意:**没有人是自己的下属。
select Name
from Employee
where Id in (
select ManagerId
from Employee
group by ManagerId
having count(*)>=5
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
571. 给定数字的频率查询中位数
难度困难
SQL架构
Numbers 表保存数字的值及其频率。
+----------+-------------+
| Number | Frequency |
+----------+-------------|
| 0 | 7 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 1 |
+----------+-------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
在此表中,数字为 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3,所以中位数是 (0 + 0) / 2 = 0。
+--------+
| median |
+--------|
| 0.0000 |
+--------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
请编写一个查询来查找所有数字的中位数并将结果命名为 median 。
select avg(cast(number as float)) median from ( select Number, Frequency, sum(Frequency) over(order by Number) - Frequency prev_sum, sum(Frequency) over(order by Number) curr_sum from Numbers ) t1, ( select sum(Frequency) total_sum from Numbers ) t2 where t1.prev_sum <= (cast(t2.total_sum as float) / 2) and t1.curr_sum >= (cast(t2.total_sum as float) / 2)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
如果 n1.Number 为中位数,n1.Number(包含本身)前累计的数字应大于等于总数/2 同时n1.Number(不包含本身)前累计数字应小于等于总数/2
例如:0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3 共12个数
中位数0(包含本身)前累计的数字 7 >=6 0(不包含本身)前累计数字 0 <=6例如:0,0,0,3,3,3 共6个数
中位数0(包含本身)前累计的数字 3 >=3 0(不包含本身)前累计数字 0 <=3 中位数3(包含本身)前累计的数字 6 >=3 3(不包含本身)前累计数字 3 <=3
SELECT
AVG(Number)median
FROM
(SELECT n1.Number FROM Numbers n1 JOIN Numbers n2 ON n1.Number>=n2.Number
GROUP BY
n1.Number
HAVING
SUM(n2.Frequency)>=(SELECT SUM(Frequency) FROM Numbers)/2
AND
SUM(n2.Frequency)-AVG(n1.Frequency)<=(SELECT SUM(Frequency) FROM Numbers)/2
)s
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
574. 当选者
难度中等
SQL架构
表: Candidate
+-----+---------+
| id | Name |
+-----+---------+
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
| 4 | D |
| 5 | E |
+-----+---------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
表: Vote
+-----+--------------+
| id | CandidateId |
+-----+--------------+
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 5 |
+-----+--------------+
id 是自动递增的主键,
CandidateId 是 Candidate 表中的 id.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
请编写 sql 语句来找到当选者的名字,上面的例子将返回当选者 B.
+------+
| Name |
+------+
| B |
+------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
用了order by 全局排序 不够好
select
Name
from Candidate c
left join Vote v
on c.id = v.CandidateId
group by Name
order by count(*) desc
limit 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
先过滤再 效率高很多
select Name
from Candidate
where id =
(
select CandidateId
from
(
select CandidateId,
count(*) over(partition by CandidateId ) cnt
from Vote
order by cnt desc
limit 1
)t1
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
$\textcolor{Red}{577.员工奖金} $577. 员工奖金
难度简单
SQL架构
选出所有 bonus < 1000 的员工的 name 及其 bonus。
Employee 表单
+-------+--------+-----------+--------+
| empId | name | supervisor| salary |
+-------+--------+-----------+--------+
| 1 | John | 3 | 1000 |
| 2 | Dan | 3 | 2000 |
| 3 | Brad | null | 4000 |
| 4 | Thomas | 3 | 4000 |
+-------+--------+-----------+--------+
empId 是这张表单的主关键字
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Bonus 表单
+-------+-------+
| empId | bonus |
+-------+-------+
| 2 | 500 |
| 4 | 2000 |
+-------+-------+
empId 是这张表单的主关键字
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
输出示例:
+-------+-------+
| name | bonus |
+-------+-------+
| John | null |
| Dan | 500 |
| Brad | null |
+-------+-------+
select name,bonus
from Employee e
left join Bonus b on e.empId=b.empId
where bonus<1000 or bonus is null
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
578. 查询回答率最高的问题
难度中等3收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
从 survey_log 表中获得回答率最高的问题,survey_log 表包含这些列**:id**, action, question_id, answer_id, q_num, timestamp。
id 表示用户 id;action 有以下几种值:“show”,“answer”,“skip”;当 action 值为 “answer” 时 answer_id 非空,而 action 值为 “show” 或者 “skip” 时 answer_id 为空;q_num 表示当前会话中问题的编号。
请编写 SQL 查询来找到具有最高回答率的问题。
示例:
输入: +------+-----------+--------------+------------+-----------+------------+ | id | action | question_id | answer_id | q_num | timestamp | +------+-----------+--------------+------------+-----------+------------+ | 5 | show | 285 | null | 1 | 123 | | 5 | answer | 285 | 124124 | 1 | 124 | | 5 | show | 369 | null | 2 | 125 | | 5 | skip | 369 | null | 2 | 126 | +------+-----------+--------------+------------+-----------+------------+ 输出: +-------------+ | survey_log | +-------------+ | 285 | +-------------+ 解释: 问题 285 的回答率为 1/1,而问题 369 回答率为 0/1,因此输出 285 。 select question_id survey_log from ( select question_id, sum(if(action = 'answer', 1, 0)) as AnswerCnt, sum(if(action = 'show', 1, 0)) as ShowCnt from survey_log group by question_id ) as tbl order by (AnswerCnt / ShowCnt) desc limit 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
直接不嵌套
select question_id survey_log
from survey_log
group by question_id
order by sum(if(action = 'answer', 1, 0)) / sum(if(action = 'show', 1, 0)) desc
limit 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
579. 查询员工的累计薪水
难度困难
SQL架构
Employee 表保存了一年内的薪水信息。
请你编写 SQL 语句,对于每个员工,查询他除最近一个月(即最大月)之外,剩下每个月的近三个月的累计薪水(不足三个月也要计算)。
结果请按 Id 升序,然后按 Month 降序显示。
**示例:**输入:
| Id | Month | Salary |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 20 |
| 2 | 1 | 20 |
| 1 | 2 | 30 |
| 2 | 2 | 30 |
| 3 | 2 | 40 |
| 1 | 3 | 40 |
| 3 | 3 | 60 |
| 1 | 4 | 60 |
| 3 | 4 | 70 |
输出:
| Id | Month | Salary |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 90 |
| 1 | 2 | 50 |
| 1 | 1 | 20 |
| 2 | 1 | 20 |
| 3 | 3 | 100 |
| 3 | 2 | 40 |
解释:
员工 ‘1’ 除去最近一个月(月份 ‘4’),有三个月的薪水记录:月份 ‘3’ 薪水为 40,月份 ‘2’ 薪水为 30,月份 ‘1’ 薪水为 20。
所以近 3 个月的薪水累计分别为 (40 + 30 + 20) = 90,(30 + 20) = 50 和 20。
| Id | Month | Salary |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 90 |
| 1 | 2 | 50 |
| 1 | 1 | 20 |
员工 ‘2’ 除去最近的一个月(月份 ‘2’)的话,只有月份 ‘1’ 这一个月的薪水记录。
| Id | Month | Salary |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 20 |
员工 ‘3’ 除去最近一个月(月份 ‘4’)后有两个月,分别为:月份 ‘4’ 薪水为 60 和 月份 ‘2’ 薪水为 40。所以各月的累计情况如下:
| Id | Month | Salary |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 3 | 100 |
| 3 | 2 | 40 |
select Id,Month,
sum(Salary) over(partition by Id order by Month ROWS BETWEEN 2 PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW) Salary
from
(
select Id,Month,Salary,
lead(Month,1,0) over(partition by Id order by Month) lm
from Employee
)t1
where lm != 0
order by Id,Month desc
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
580. 统计各专业学生人数
难度中等
SQL架构
一所大学有 2 个数据表,分别是 student 和 department ,这两个表保存着每个专业的学生数据和院系数据。
写一个查询语句,查询 department 表中每个专业的学生人数 (即使没有学生的专业也需列出)。
将你的查询结果按照学生人数降序排列。 如果有两个或两个以上专业有相同的学生数目,将这些部门按照部门名字的字典序从小到大排列。
student**** 表格如下:
| Column Name | Type |
|---|---|
| student_id | Integer |
| student_name | String |
| gender | Character |
| dept_id | Integer |
其中, student_id 是学生的学号, student_name 是学生的姓名, gender 是学生的性别, dept_id 是学生所属专业的专业编号。
department**** 表格如下:
| Column Name | Type |
|---|---|
| dept_id | Integer |
| dept_name | String |
dept_id 是专业编号, dept_name 是专业名字。
这里是一个示例输入:student**** 表格:
| student_id | student_name | gender | dept_id |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Jack | M | 1 |
| 2 | Jane | F | 1 |
| 3 | Mark | M | 2 |
department**** 表格:
| dept_id | dept_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Engineering |
| 2 | Science |
| 3 | Law |
示例输出为:
| dept_name | student_number |
|---|---|
| Engineering | 2 |
| Science | 1 |
| Law | 0 |
select dept_name ,count(student_id) student_number
from department d left join student s
on d.dept_id=s.dept_id
group by dept_name
order by student_number desc
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
584. 寻找用户推荐人
难度简单9收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
给定表 customer ,里面保存了所有客户信息和他们的推荐人。
+------+------+-----------+
| id | name | referee_id|
+------+------+-----------+
| 1 | Will | NULL |
| 2 | Jane | NULL |
| 3 | Alex | 2 |
| 4 | Bill | NULL |
| 5 | Zack | 1 |
| 6 | Mark | 2 |
+------+------+-----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
写一个查询语句,返回一个编号列表,列表中编号的推荐人的编号都 不是 2。
对于上面的示例数据,结果为:
+------+
| name |
+------+
| Will |
| Jane |
| Bill |
| Zack |
+------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
SELECT name FROM customer WHERE referee_id != 2 OR referee_id IS NULL;
MySQL 使用三值逻辑 —— TRUE, FALSE 和 UNKNOWN。任何与 NULL 值进行的比较都会与第三种值 UNKNOWN 做比较。这个“任何值”包括 NULL 本身!这就是为什么 MySQL 提供 IS NULL 和 IS NOT NULL 两种操作来对 NULL 特殊判断。
因此,在 WHERE 语句中我们需要做一个额外的条件判断 `referee_id IS NULL’。
585. 2016年的投资
难度中等14收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
写一个查询语句,将 2016 年 (TIV_2016) 所有成功投资的金额加起来,保留 2 位小数。
对于一个投保人,他在 2016 年成功投资的条件是:
- 他在 2015 年的投保额 (TIV_2015) 至少跟一个其他投保人在 2015 年的投保额相同。
- 他所在的城市必须与其他投保人都不同(也就是说维度和经度不能跟其他任何一个投保人完全相同)。
输入格式:表 insurance 格式如下:
| Column Name | Type |
|---|---|
| PID | INTEGER(11) |
| TIV_2015 | NUMERIC(15,2) |
| TIV_2016 | NUMERIC(15,2) |
| LAT | NUMERIC(5,2) |
| LON | NUMERIC(5,2) |
PID 字段是投保人的投保编号, TIV_2015 是该投保人在2015年的总投保金额, TIV_2016 是该投保人在2016年的投保金额, LAT 是投保人所在城市的维度, LON 是投保人所在城市的经度。
样例输入
| PID | TIV_2015 | TIV_2016 | LAT | LON |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 10 |
| 2 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| 3 | 10 | 30 | 20 | 20 |
| 4 | 10 | 40 | 40 | 40 |
样例输出
| TIV_2016 |
|---|
| 45.00 |
解释
就如最后一个投保人,第一个投保人同时满足两个条件: 1. 他在 2015 年的投保金额 TIV_2015 为 '10' ,与第三个和第四个投保人在 2015 年的投保金额相同。 2. 他所在城市的经纬度是独一无二的。 第二个投保人两个条件都不满足。他在 2015 年的投资 TIV_2015 与其他任何投保人都不相同。 且他所在城市的经纬度与第三个投保人相同。基于同样的原因,第三个投保人投资失败。 所以返回的结果是第一个投保人和最后一个投保人的 TIV_2016 之和,结果是 45 。 select sum(TIV_2016) TIV_2016 from ( select PID,TIV_2016,cnt, count(*) over(partition by loc ) lcnt from ( select PID,TIV_2016, count(TIV_2015) over(partition by TIV_2015 ) cnt, concat_ws(",",LAT,LON) loc from insurance )t1 )t2 where lcnt=1 and cnt!=1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
注意去重顺序 不要先对TIV_2015去重 不然 local去重时会丢失数据
优化 窗口
SELECT
ROUND(SUM(TIV_2016), 2) as TIV_2016
FROM(
SELECT
*,
count(*) over(partition by TIV_2015) as cnt_1,
count(*) over(partition by LAT, LON) as cnt_2
FROM
insurance
) a
WHERE a.cnt_1 > 1 AND a.cnt_2 < 2
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
586. 订单最多的客户
难度简单
SQL架构
在表 orders 中找到订单数最多客户对应的 customer_number 。
数据保证订单数最多的顾客恰好只有一位。
表 orders**** 定义如下:
| Column | Type |
|---|---|
| order_number (PK) | int |
| customer_number | int |
| order_date | date |
| required_date | date |
| shipped_date | date |
| status | char(15) |
| comment | char(200) |
样例输入
| order_number | customer_number | order_date | required_date | shipped_date | status | comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2017-04-09 | 2017-04-13 | 2017-04-12 | Closed | |
| 2 | 2 | 2017-04-15 | 2017-04-20 | 2017-04-18 | Closed | |
| 3 | 3 | 2017-04-16 | 2017-04-25 | 2017-04-20 | Closed | |
| 4 | 3 | 2017-04-18 | 2017-04-28 | 2017-04-25 | Closed |
样例输出
| customer_number |
|---|
| 3 |
解释
customer_number 为 '3' 的顾客有两个订单,比顾客 '1' 或者 '2' 都要多,因为他们只有一个订单
所以结果是该顾客的 customer_number ,也就是 3 。
- 1
- 2
进阶: 如果有多位顾客订单数并列最多,你能找到他们所有的 customer_number 吗?
select customer_number
from orders
group by customer_number
order by count(*) desc
limit 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
如果 数据量很大 order by 不太好
595. 大的国家
难度简单
SQL架构
这里有张 World 表
+-----------------+------------+------------+--------------+---------------+
| name | continent | area | population | gdp |
+-----------------+------------+------------+--------------+---------------+
| Afghanistan | Asia | 652230 | 25500100 | 20343000 |
| Albania | Europe | 28748 | 2831741 | 12960000 |
| Algeria | Africa | 2381741 | 37100000 | 188681000 |
| Andorra | Europe | 468 | 78115 | 3712000 |
| Angola | Africa | 1246700 | 20609294 | 100990000 |
+-----------------+------------+------------+--------------+---------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
如果一个国家的面积超过300万平方公里,或者人口超过2500万,那么这个国家就是大国家。
编写一个SQL查询,输出表中所有大国家的名称、人口和面积。
例如,根据上表,我们应该输出:
+--------------+-------------+--------------+
| name | population | area |
+--------------+-------------+--------------+
| Afghanistan | 25500100 | 652230 |
| Algeria | 37100000 | 2381741 |
+--------------+-------------+--------------+
select name ,population,area
from World
where area >3000000 or population >25000000
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
596. 超过5名学生的课
难度简单
SQL架构
有一个courses 表 ,有: student (学生) 和 class (课程)。
请列出所有超过或等于5名学生的课。
例如,表:
+---------+------------+
| student | class |
+---------+------------+
| A | Math |
| B | English |
| C | Math |
| D | Biology |
| E | Math |
| F | Computer |
| G | Math |
| H | Math |
| I | Math |
+---------+------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
应该输出:
+---------+
| class |
+---------+
| Math |
+---------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
**Note:**学生在每个课中不应被重复计算。
select class
from courses
group by class
having count(distinct student)>=5
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
一个学生可能多次选课。。记得distinct
597. 好友申请 I :总体通过率
难度简单21收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
在 Facebook 或者 Twitter 这样的社交应用中,人们经常会发好友申请也会收到其他人的好友申请。现在给如下两个表:
表: friend_request
| sender_id | send_to_id | request_date |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 2016_06-01 |
| 1 | 3 | 2016_06-01 |
| 1 | 4 | 2016_06-01 |
| 2 | 3 | 2016_06-02 |
| 3 | 4 | 2016-06-09 |
表: request_accepted
| requester_id | accepter_id | accept_date |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 2016_06-03 |
| 1 | 3 | 2016-06-08 |
| 2 | 3 | 2016-06-08 |
| 3 | 4 | 2016-06-09 |
| 3 | 4 | 2016-06-10 |
写一个查询语句,求出好友申请的通过率,用 2 位小数表示。通过率由接受好友申请的数目除以申请总数。
对于上面的样例数据,你的查询语句应该返回如下结果。
| accept_rate |
|---|
| 0.80 |
注意:
通过的好友申请不一定都在表 friend_request 中。在这种情况下,你只需要统计总的被通过的申请数(不管它们在不在原来的申请中),并将它除以申请总数,得到通过率一个好友申请发送者有可能会给接受者发几条好友申请,也有可能一个好友申请会被通过好几次。这种情况下,重复的好友申请只统计一次。如果一个好友申请都没有,通过率为 0.00 。
解释: 总共有 5 个申请,其中 4 个是不重复且被通过的好友申请,所以成功率是 0.80 。
进阶:
你能写一个查询语句得到每个月的通过率吗?你能求出每一天的累计通过率吗?
select
round(
ifnull(
(select count(*) from (select distinct requester_id, accepter_id from request_accepted) as A)
/
(select count(*) from (select distinct sender_id, send_to_id from friend_request) as B),
0)
, 2) as accept_rate;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
601. 体育馆的人流量
难度困难113收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
X 市建了一个新的体育馆,每日人流量信息被记录在这三列信息中:序号 (id)、日期 (visit_date)、 人流量 (people)。
请编写一个查询语句,找出人流量的高峰期。高峰期时,至少连续三行记录中的人流量不少于100。
例如,表 stadium:
+------+------------+-----------+
| id | visit_date | people |
+------+------------+-----------+
| 1 | 2017-01-01 | 10 |
| 2 | 2017-01-02 | 109 |
| 3 | 2017-01-03 | 150 |
| 4 | 2017-01-04 | 99 |
| 5 | 2017-01-05 | 145 |
| 6 | 2017-01-06 | 1455 |
| 7 | 2017-01-07 | 199 |
| 8 | 2017-01-08 | 188 |
+------+------------+-----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
对于上面的示例数据,输出为:
+------+------------+-----------+
| id | visit_date | people |
+------+------------+-----------+
| 5 | 2017-01-05 | 145 |
| 6 | 2017-01-06 | 1455 |
| 7 | 2017-01-07 | 199 |
| 8 | 2017-01-08 | 188 |
+------+------------+-----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
**提示:**每天只有一行记录,日期随着 id 的增加而增加。
3表相连(244 ms)
select distinct t1.*
from stadium t1, stadium t2, stadium t3
where t1.people >= 100 and t2.people >= 100 and t3.people >= 100
and
(
(t1.id - t2.id = 1 and t1.id - t3.id = 2 and t2.id - t3.id =1) -- t1, t2, t3
or
(t2.id - t1.id = 1 and t2.id - t3.id = 2 and t1.id - t3.id =1) -- t2, t1, t3
or
(t3.id - t2.id = 1 and t2.id - t1.id =1 and t3.id - t1.id = 2) -- t3, t2, t1
)
order by t1.id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
窗口函数(272 ms)
select id,visit_date,people from
(
select id
,lead(people,1) over(order by id) ld
,lead(people,2) over(order by id) ld2
,visit_date
,lag(people,1) over(order by id) lg
,lag(people,2) over(order by id) lg2
,people
from stadium
) a
where (a.ld>=100 and a.lg>=100 and a.people>=100)
or (a.ld>=100 and a.ld2>=100 and a.people>=100)
or (a.lg>=100 and a.lg2>=100 and a.people>=100)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
602. 好友申请 II :谁有最多的好友
难度中等
SQL架构
在 Facebook 或者 Twitter 这样的社交应用中,人们经常会发好友申请也会收到其他人的好友申请。
表 request_accepted 存储了所有好友申请通过的数据记录,其中, requester_id 和 accepter_id 都是用户的编号。
| requester_id | accepter_id | accept_date |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 2016_06-03 |
| 1 | 3 | 2016-06-08 |
| 2 | 3 | 2016-06-08 |
| 3 | 4 | 2016-06-09 |
写一个查询语句,求出谁拥有最多的好友和他拥有的好友数目。对于上面的样例数据,结果为:
| id | num |
|---|---|
| 3 | 3 |
注意:
- 保证拥有最多好友数目的只有 1 个人。
- 好友申请只会被接受一次,所以不会有 requester_id 和 accepter_id 值都相同的重复记录。
解释:
编号为 ‘3’ 的人是编号为 ‘1’,‘2’ 和 ‘4’ 的好友,所以他总共有 3 个好友,比其他人都多。
进阶:
在真实世界里,可能会有多个人拥有好友数相同且最多,你能找到所有这些人吗?
select rid as `id`,count(aid) as `num`
from
(
select R1.requester_id as rid,R1.accepter_id as aid
from request_accepted as R1
UNION all
select R2.accepter_id as rid,R2.requester_id as aid
from request_accepted as R2
) as A
group by rid
order by num desc
limit 0,1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
603. 连续空余座位
难度简单
SQL架构
几个朋友来到电影院的售票处,准备预约连续空余座位。
你能利用表 cinema ,帮他们写一个查询语句,获取所有空余座位,并将它们按照 seat_id 排序后返回吗?
| seat_id | free |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 5 | 1 |
对于如上样例,你的查询语句应该返回如下结果。
| seat_id |
|---|
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
注意:
- seat_id 字段是一个自增的整数,free 字段是布尔类型(‘1’ 表示空余, ‘0’ 表示已被占据)。
- 连续空余座位的定义是大于等于 2 个连续空余的座位。
select seat_id
from (
select seat_id,
lag(seat_id,1,-99) over(order by seat_id) ls,
lead(seat_id,1,-99) over(order by seat_id) rs
from cinema
where free=1
)t1
where seat_id-ls = 1 or rs-seat_id =1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
607. 销售员
难度简单
SQL架构
描述
给定 3 个表: salesperson, company, orders。输出所有表 salesperson 中,没有向公司 ‘RED’ 销售任何东西的销售员。
**示例:**输入
表: salesperson
+----------+------+--------+-----------------+-----------+
| sales_id | name | salary | commission_rate | hire_date |
+----------+------+--------+-----------------+-----------+
| 1 | John | 100000 | 6 | 4/1/2006 |
| 2 | Amy | 120000 | 5 | 5/1/2010 |
| 3 | Mark | 65000 | 12 | 12/25/2008|
| 4 | Pam | 25000 | 25 | 1/1/2005 |
| 5 | Alex | 50000 | 10 | 2/3/2007 |
+----------+------+--------+-----------------+-----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
表 salesperson 存储了所有销售员的信息。每个销售员都有一个销售员编号 sales_id 和他的名字 name 。
表: company
+---------+--------+------------+
| com_id | name | city |
+---------+--------+------------+
| 1 | RED | Boston |
| 2 | ORANGE | New York |
| 3 | YELLOW | Boston |
| 4 | GREEN | Austin |
+---------+--------+------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表 company 存储了所有公司的信息。每个公司都有一个公司编号 com_id 和它的名字 name 。
表: orders
+----------+------------+---------+----------+--------+
| order_id | order_date | com_id | sales_id | amount |
+----------+------------+---------+----------+--------+
| 1 | 1/1/2014 | 3 | 4 | 100000 |
| 2 | 2/1/2014 | 4 | 5 | 5000 |
| 3 | 3/1/2014 | 1 | 1 | 50000 |
| 4 | 4/1/2014 | 1 | 4 | 25000 |
+----------+----------+---------+----------+--------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表 orders 存储了所有的销售数据,包括销售员编号 sales_id 和公司编号 com_id 。
输出
+------+
| name |
+------+
| Amy |
| Mark |
| Alex |
+------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
解释
根据表 orders 中的订单 ‘3’ 和 ‘4’ ,容易看出只有 ‘John’ 和 ‘Pam’ 两个销售员曾经向公司 ‘RED’ 销售过。
所以我们需要输出表 salesperson 中所有其他人的名字。\
select name
from salesperson
where sales_id not in
(
select sales_id
from orders
where com_id =
(
select com_id
from company
where name ='RED'
)
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
608. 树节点
难度中等
SQL架构
给定一个表 tree,id 是树节点的编号, p_id 是它父节点的 id 。
+----+------+
| id | p_id |
+----+------+
| 1 | null |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 |
+----+------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
树中每个节点属于以下三种类型之一:
- 叶子:如果这个节点没有任何孩子节点。
- 根:如果这个节点是整棵树的根,即没有父节点。
- 内部节点:如果这个节点既不是叶子节点也不是根节点。
写一个查询语句,输出所有节点的编号和节点的类型,并将结果按照节点编号排序。上面样例的结果为:
+----+------+
| id | Type |
+----+------+
| 1 | Root |
| 2 | Inner|
| 3 | Leaf |
| 4 | Leaf |
| 5 | Leaf |
+----+------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
解释
- 节点 ‘1’ 是根节点,因为它的父节点是 NULL ,同时它有孩子节点 ‘2’ 和 ‘3’ 。
- 节点 ‘2’ 是内部节点,因为它有父节点 ‘1’ ,也有孩子节点 ‘4’ 和 ‘5’ 。
- 节点 ‘3’, ‘4’ 和 ‘5’ 都是叶子节点,因为它们都有父节点同时没有孩子节点。
- 样例中树的形态如下:
1 / \ 2 3 / \ 4 5
注意
如果树中只有一个节点,你只需要输出它的根属性。
select id,
(case when p_id is null then "Root"
when id not in (select ifnull(p_id,0) from tree) then "Leaf"
else "Inner" end) Type
from tree
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
610. 判断三角形
难度简单
SQL架构
一个小学生 Tim 的作业是判断三条线段是否能形成一个三角形。
然而,这个作业非常繁重,因为有几百组线段需要判断。
假设表 triangle 保存了所有三条线段的三元组 x, y, z ,你能帮 Tim 写一个查询语句,来判断每个三元组是否可以组成一个三角形吗?
| x | y | z |
|---|---|---|
| 13 | 15 | 30 |
| 10 | 20 | 15 |
对于如上样例数据,你的查询语句应该返回如下结果:
| x | y | z | triangle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 15 | 30 | No |
| 10 | 20 | 15 | Yes |
select x,y,z,
if(x+y>z && x+z>y && y+z>x,'Yes','No') triangle
from triangle
- 1
- 2
- 3
612. 平面上的最近距离
难度中等
SQL架构
表 point_2d 保存了所有点(多于 2 个点)的坐标 (x,y) ,这些点在平面上两两不重合。
写一个查询语句找到两点之间的最近距离,保留 2 位小数。
| x | y |
|---|---|
| -1 | -1 |
| 0 | 0 |
| -1 | -2 |
最近距离在点 (-1,-1) 和(-1,2) 之间,距离为 1.00 。所以输出应该为:
| shortest |
|---|
| 1.00 |
**注意:**任意点之间的最远距离小于 10000 。
SELECT
ROUND(SQRT(MIN((POW(p1.x - p2.x, 2) + POW(p1.y - p2.y, 2)))), 2) AS shortest
FROM
point_2d p1
JOIN
point_2d p2 ON p1.x != p2.x OR p1.y != p2.y
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
优化 :减少重复计算
SELECT
ROUND(SQRT(MIN((POW(p1.x - p2.x, 2) + POW(p1.y - p2.y, 2)))),2) AS shortest
FROM
point_2d p1
JOIN
point_2d p2 ON (p1.x <= p2.x AND p1.y < p2.y)
OR (p1.x <= p2.x AND p1.y > p2.y)
OR (p1.x < p2.x AND p1.y = p2.y)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
613. 直线上的最近距离
难度简单
SQL架构
表 point 保存了一些点在 x 轴上的坐标,这些坐标都是整数。
写一个查询语句,找到这些点中最近两个点之间的距离。
| x |
|---|
| -1 |
| 0 |
| 2 |
最近距离显然是 ‘1’ ,是点 ‘-1’ 和 ‘0’ 之间的距离。所以输出应该如下:
| shortest |
|---|
| 1 |
**注意:**每个点都与其他点坐标不同,表 table 不会有重复坐标出现。
**进阶:**如果这些点在 x 轴上从左到右都有一个编号,输出结果时需要输出最近点对的编号呢?
开窗方法 178m
select min(l-x) shortest
from(
select x,lead(x,1,null) over(order by x) l
from point
)t1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
join方法 268m
SELECT
MIN(ABS(p1.x - p2.x)) AS shortest
FROM
point p1
JOIN
point p2 ON p1.x != p2.x
;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
614. 二级关注者
难度中等
SQL架构
在 facebook 中,表 follow 会有 2 个字段: followee, follower ,分别表示被关注者和关注者。
请写一个 sql 查询语句,对每一个关注者,查询关注他的关注者的数目。
比方说:
+-------------+------------+
| followee | follower |
+-------------+------------+
| A | B |
| B | C |
| B | D |
| D | E |
+-------------+------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
应该输出:
+-------------+------------+
| follower | num |
+-------------+------------+
| B | 2 |
| D | 1 |
+-------------+------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
解释:
B 和 D 都在在 follower 字段中出现,作为被关注者,B 被 C 和 D 关注,D 被 E 关注。A 不在 follower 字段内,所以A不在输出列表中。
注意:
- 被关注者永远不会被他 / 她自己关注。
- 将结果按照字典序返回。
select followee follower,count(distinct follower) num
from follow
where followee in (
select follower
from follow
group by follower
)
group by followee
order by follower
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
这里出现了重复关注 ,需要去重
615. 平均工资:部门与公司比较
难度困难
SQL架构
给如下两个表,写一个查询语句,求出在每一个工资发放日,每个部门的平均工资与公司的平均工资的比较结果 (高 / 低 / 相同)。
表: salary
| id | employee_id | amount | pay_date |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 9000 | 2017-03-31 |
| 2 | 2 | 6000 | 2017-03-31 |
| 3 | 3 | 10000 | 2017-03-31 |
| 4 | 1 | 7000 | 2017-02-28 |
| 5 | 2 | 6000 | 2017-02-28 |
| 6 | 3 | 8000 | 2017-02-28 |
employee_id 字段是表 employee 中 employee_id 字段的外键。
| employee_id | department_id |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 |
对于如上样例数据,结果为:
| pay_month | department_id | comparison |
|---|---|---|
| 2017-03 | 1 | higher |
| 2017-03 | 2 | lower |
| 2017-02 | 1 | same |
| 2017-02 | 2 | same |
解释
在三月,公司的平均工资是 (9000+6000+10000)/3 = 8333.33…
由于部门 ‘1’ 里只有一个 employee_id 为 ‘1’ 的员工,所以部门 ‘1’ 的平均工资就是此人的工资 9000 。因为 9000 > 8333.33 ,所以比较结果是 ‘higher’。
第二个部门的平均工资为 employee_id 为 ‘2’ 和 ‘3’ 两个人的平均工资,为 (6000+10000)/2=8000 。因为 8000 < 8333.33 ,所以比较结果是 ‘lower’ 。
在二月用同样的公式求平均工资并比较,比较结果为 ‘same’ ,因为部门 ‘1’ 和部门 ‘2’ 的平均工资与公司的平均工资相同,都是 7000 。
select pay_month, department_id, (case when avgs>ts then 'higher' when avgs<ts then 'lower' else 'same' end) as comparison from ( select date_format(pay_date,'%Y-%m')pay_month, department_id, avg(amount) over(partition by date_format(pay_date,'%Y-%m') )ts, avg(amount) over(partition by date_format(pay_date,'%Y-%m'),department_id) avgs from salary s left join employee e on s.employee_id = e.employee_id )t1 group by pay_month, department_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
也可以用if
IF(avgs>ts,‘higher’,IF(avgs=ts,‘same’,‘lower’)) AS comparison
618. 学生地理信息报告
难度困难
SQL架构
一所美国大学有来自亚洲、欧洲和美洲的学生,他们的地理信息存放在如下 student 表中。
| name | continent |
|---|---|
| Jack | America |
| Pascal | Europe |
| Xi | Asia |
| Jane | America |
写一个查询语句实现对大洲(continent)列的 透视表 操作,使得每个学生按照姓名的字母顺序依次排列在对应的大洲下面。输出的标题应依次为美洲(America)、亚洲(Asia)和欧洲(Europe)。数据保证来自美洲的学生不少于来自亚洲或者欧洲的学生。
对于样例输入,它的对应输出是:
| America | Asia | Europe |
|---|---|---|
| Jack | Xi | Pascal |
| Jane |
**进阶:**如果不能确定哪个大洲的学生数最多,你可以写出一个查询去生成上述学生报告吗?
开窗
select
max(if(continent='America',name,null)) America,
max(if(continent='Asia',name,null)) Asia,
max(if(continent='Europe',name,null)) Europe
from
(select *, row_number() over(partition by continent order by name) rk
from student) t
group by rk
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
变量
SELECT America, Asia, Europe FROM (SELECT @as:=0, @am:=0, @eu:=0) t, (SELECT @as:=@as + 1 AS asid, name AS Asia FROM student WHERE continent = 'Asia' ORDER BY Asia) AS t1 RIGHT JOIN (SELECT @am:=@am + 1 AS amid, name AS America FROM student WHERE continent = 'America' ORDER BY America) AS t2 ON asid = amid LEFT JOIN (SELECT @eu:=@eu + 1 AS euid, name AS Europe FROM student WHERE continent = 'Europe' ORDER BY Europe) AS t3 ON amid = euid
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
官方给出的。。同下方开窗
select America,Asia,Europe
from(
select row_number() over(order by name) as rn,name as America from student
where continent='America'
) a
left join(
select row_number() over(order by name) as rn,name as Asia from student
where continent='Asia'
) b on a.rn=b.rn
left join(
select row_number() over(order by name) as rn,name as Europe from student
where continent='Europe'
) c on a.rn=c.rn
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
619. 只出现一次的最大数字
难度简单
SQL架构
表 my_numbers 的 num 字段包含很多数字,其中包括很多重复的数字。
你能写一个 SQL 查询语句,找到只出现过一次的数字中,最大的一个数字吗?
+---+
|num|
+---+
| 8 |
| 8 |
| 3 |
| 3 |
| 1 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
| 6 |
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
对于上面给出的样例数据,你的查询语句应该返回如下结果:
+---+
|num|
+---+
| 6 |
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
注意:
如果没有只出现一次的数字,输出 null 。
SELECT
MAX(num) AS num
FROM
(SELECT
num
FROM
my_numbers
GROUP BY num
HAVING COUNT(num) = 1) t1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
620. 有趣的电影
难度简单86收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
某城市开了一家新的电影院,吸引了很多人过来看电影。该电影院特别注意用户体验,专门有个 LED显示板做电影推荐,上面公布着影评和相关电影描述。
作为该电影院的信息部主管,您需要编写一个 SQL查询,找出所有影片描述为非boring (不无聊) 的并且 id 为奇数 的影片,结果请按等级 rating 排列。
例如,下表 cinema:
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+
| id | movie | description | rating |
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+
| 1 | War | great 3D | 8.9 |
| 2 | Science | fiction | 8.5 |
| 3 | irish | boring | 6.2 |
| 4 | Ice song | Fantacy | 8.6 |
| 5 | House card| Interesting| 9.1 |
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
对于上面的例子,则正确的输出是为:
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+
| id | movie | description | rating |
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+
| 5 | House card| Interesting| 9.1 |
| 1 | War | great 3D | 8.9 |
+---------+-----------+--------------+-----------+
select id,movie,description,rating
from cinema
where id%2=1 and description !='boring'
order by rating desc,id,movie,description
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
626. 换座位
难度中等
SQL架构
小美是一所中学的信息科技老师,她有一张 seat 座位表,平时用来储存学生名字和与他们相对应的座位 id。
其中纵列的 id 是连续递增的
小美想改变相邻俩学生的座位。
你能不能帮她写一个 SQL query 来输出小美想要的结果呢?
示例:
+---------+---------+
| id | student |
+---------+---------+
| 1 | Abbot |
| 2 | Doris |
| 3 | Emerson |
| 4 | Green |
| 5 | Jeames |
+---------+---------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
假如数据输入的是上表,则输出结果如下:
+---------+---------+
| id | student |
+---------+---------+
| 1 | Doris |
| 2 | Abbot |
| 3 | Green |
| 4 | Emerson |
| 5 | Jeames |
+---------+---------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
注意:
如果学生人数是奇数,则不需要改变最后一个同学的座位。
开窗
select id,
(case when id%2=0 then f
when id%2=1 && b is not null then b
else student end) student
from(
select id,student,
lag(student,1,null) over(order by id) f,
lead(student,1,null) over(order by id) b
from seat
)t1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
非嵌套
select
if(id%2=0,
id-1,
if(id=(select count(distinct id) from seat),
id,
id+1))
as id,student
from seat
order by id;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
用异或
select b.id,a.student from
seat as a,seat as b,(select count(*) as cnt from seat) as c
where b.id=1^(a.id-1)+1
-- where a.id=1^(b.id-1)+1; 也可以这样写,更容易理解
|| (c.cnt%2 && b.id=c.cnt && a.id=c.cnt);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
627. 交换工资
难度简单
SQL架构
给定一个 salary 表,如下所示,有 m = 男性 和 f = 女性 的值。交换所有的 f 和 m 值(例如,将所有 f 值更改为 m,反之亦然)。要求只使用一个更新(Update)语句,并且没有中间的临时表。
注意,您必只能写一个 Update 语句,请不要编写任何 Select 语句。
例如:
| id | name | sex | salary |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | m | 2500 |
| 2 | B | f | 1500 |
| 3 | C | m | 5500 |
| 4 | D | f | 500 |
运行你所编写的更新语句之后,将会得到以下表:
| id | name | sex | salary |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | f | 2500 |
| 2 | B | m | 1500 |
| 3 | C | f | 5500 |
| 4 | D | m | 500 |
UPDATE salary
SET
sex = CASE sex
WHEN 'm' THEN 'f'
ELSE 'm'
END;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Update 和set的使用
1045. 买下所有产品的客户
难度中等
SQL架构
Customer 表:
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| customer_id | int |
| product_key | int |
+-------------+---------+
product_key 是 Customer 表的外键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Product 表:
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| product_key | int |
+-------------+---------+
product_key 是这张表的主键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
写一条 SQL 查询语句,从 Customer 表中查询购买了 Product 表中所有产品的客户的 id。
示例:
Customer 表: +-------------+-------------+ | customer_id | product_key | +-------------+-------------+ | 1 | 5 | | 2 | 6 | | 3 | 5 | | 3 | 6 | | 1 | 6 | +-------------+-------------+ Product 表: +-------------+ | product_key | +-------------+ | 5 | | 6 | +-------------+ Result 表: +-------------+ | customer_id | +-------------+ | 1 | | 3 | +-------------+ 购买了所有产品(5 和 6)的客户的 id 是 1 和 3 。 select customer_id from Customer group by customer_id having count(distinct product_key)=( select count(*) cnt from Product)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
1050. 合作过至少三次的演员和导演
难度简单
SQL架构
ActorDirector 表:
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| actor_id | int |
| director_id | int |
| timestamp | int |
+-------------+---------+
timestamp 是这张表的主键.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
写一条SQL查询语句获取合作过至少三次的演员和导演的 id 对 (actor_id, director_id)
示例:
ActorDirector 表: +-------------+-------------+-------------+ | actor_id | director_id | timestamp | +-------------+-------------+-------------+ | 1 | 1 | 0 | | 1 | 1 | 1 | | 1 | 1 | 2 | | 1 | 2 | 3 | | 1 | 2 | 4 | | 2 | 1 | 5 | | 2 | 1 | 6 | +-------------+-------------+-------------+ Result 表: +-------------+-------------+ | actor_id | director_id | +-------------+-------------+ | 1 | 1 | +-------------+-------------+ 唯一的 id 对是 (1, 1),他们恰好合作了 3 次。 select actor_id,director_id from ActorDirector group by actor_id,director_id having count(*)>=3
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
1068. 产品销售分析 I
难度简单
SQL架构
销售表 Sales:
+-------------+-------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+-------+
| sale_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| year | int |
| quantity | int |
| price | int |
+-------------+-------+
(sale_id, year) 是销售表 Sales 的主键.
product_id 是产品表 Product 的外键.
注意: price 表示每单位价格
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
产品表 Product:
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
+--------------+---------+
product_id 是表的主键.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
写一条SQL 查询语句获取产品表 Product 中所有的 产品名称 product name 以及 该产品在 Sales 表中相对应的 上市年份 year 和 价格 price。
示例:
Sales 表: +---------+------------+------+----------+-------+ | sale_id | product_id | year | quantity | price | +---------+------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | 100 | 2008 | 10 | 5000 | | 2 | 100 | 2009 | 12 | 5000 | | 7 | 200 | 2011 | 15 | 9000 | +---------+------------+------+----------+-------+ Product 表: +------------+--------------+ | product_id | product_name | +------------+--------------+ | 100 | Nokia | | 200 | Apple | | 300 | Samsung | +------------+--------------+ Result 表: +--------------+-------+-------+ | product_name | year | price | +--------------+-------+-------+ | Nokia | 2008 | 5000 | | Nokia | 2009 | 5000 | | Apple | 2011 | 9000 | +--------------+-------+-------+ select product_name,year,price from Sales s left join Product p on s.product_id = p.product_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
1069. 产品销售分析 II
难度简单
SQL架构
销售表:Sales
+-------------+-------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+-------+
| sale_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| year | int |
| quantity | int |
| price | int |
+-------------+-------+
sale_id 是这个表的主键。
product_id 是 Product 表的外键。
请注意价格是每单位的。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
产品表:Product
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
+--------------+---------+
product_id 是这个表的主键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
编写一个 SQL 查询,按产品 id product_id 来统计每个产品的销售总量。
查询结果格式如下面例子所示:
Sales 表: +---------+------------+------+----------+-------+ | sale_id | product_id | year | quantity | price | +---------+------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | 100 | 2008 | 10 | 5000 | | 2 | 100 | 2009 | 12 | 5000 | | 7 | 200 | 2011 | 15 | 9000 | +---------+------------+------+----------+-------+ Product 表: +------------+--------------+ | product_id | product_name | +------------+--------------+ | 100 | Nokia | | 200 | Apple | | 300 | Samsung | +------------+--------------+ Result 表: +--------------+----------------+ | product_id | total_quantity | +--------------+----------------+ | 100 | 22 | | 200 | 15 | +--------------+----------------+ select s.product_id,sum(quantity) total_quantity from Sales s left join Product p on s.product_id = p.product_id group by s.product_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
1070. 产品销售分析 III
难度中等
SQL架构
销售表 Sales:
+-------------+-------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+-------+
| sale_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| year | int |
| quantity | int |
| price | int |
+-------------+-------+
sale_id 是此表的主键。
product_id 是产品表的外键。
请注意,价格是按每单位计的。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
产品表 Product:
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
+--------------+---------+
product_id 是此表的主键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
编写一个 SQL 查询,选出每个销售产品的 第一年 的 产品 id、年份、数量 和 价格。
查询结果格式如下:
Sales table: +---------+------------+------+----------+-------+ | sale_id | product_id | year | quantity | price | +---------+------------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | 100 | 2008 | 10 | 5000 | | 2 | 100 | 2009 | 12 | 5000 | | 7 | 200 | 2011 | 15 | 9000 | +---------+------------+------+----------+-------+ Product table: +------------+--------------+ | product_id | product_name | +------------+--------------+ | 100 | Nokia | | 200 | Apple | | 300 | Samsung | +------------+--------------+ Result table: +------------+------------+----------+-------+ | product_id | first_year | quantity | price | +------------+------------+----------+-------+ | 100 | 2008 | 10 | 5000 | | 200 | 2011 | 15 | 9000 | +------------+------------+----------+-------+ select product_id,year first_year,quantity,price from ( select s.product_id,year,quantity,price, rank() over(partition by product_id order by year) rk from Sales s left join Product p on s.product_id = p.product_id )t1 where rk = 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
1075. 项目员工 I
难度简单
SQL架构
项目表 Project:
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| project_id | int |
| employee_id | int |
+-------------+---------+
主键为 (project_id, employee_id)。
employee_id 是员工表 Employee 表的外键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
员工表 Employee:
+------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+------------------+---------+
| employee_id | int |
| name | varchar |
| experience_years | int |
+------------------+---------+
主键是 employee_id。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
请写一个 SQL 语句,查询每一个项目中员工的 平均 工作年限,精确到小数点后两位。
查询结果的格式如下:
Project 表: +-------------+-------------+ | project_id | employee_id | +-------------+-------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 1 | 2 | | 1 | 3 | | 2 | 1 | | 2 | 4 | +-------------+-------------+ Employee 表: +-------------+--------+------------------+ | employee_id | name | experience_years | +-------------+--------+------------------+ | 1 | Khaled | 3 | | 2 | Ali | 2 | | 3 | John | 1 | | 4 | Doe | 2 | +-------------+--------+------------------+ Result 表: +-------------+---------------+ | project_id | average_years | +-------------+---------------+ | 1 | 2.00 | | 2 | 2.50 | +-------------+---------------+ 第一个项目中,员工的平均工作年限是 (3 + 2 + 1) / 3 = 2.00;第二个项目中,员工的平均工作年限是 (3 + 2) / 2 = 2.50 select project_id,round(avg(experience_years),2) average_years from Project p join Employee e on p.employee_id=e.employee_id group by project_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
1076. 项目员工II
难度简单
SQL架构
Table: Project
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| project_id | int |
| employee_id | int |
+-------------+---------+
主键为 (project_id, employee_id)。
employee_id 是员工表 Employee 表的外键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Table: Employee
+------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+------------------+---------+
| employee_id | int |
| name | varchar |
| experience_years | int |
+------------------+---------+
主键是 employee_id。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
编写一个SQL查询,报告所有雇员最多的项目。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Project table: +-------------+-------------+ | project_id | employee_id | +-------------+-------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 1 | 2 | | 1 | 3 | | 2 | 1 | | 2 | 4 | +-------------+-------------+ Employee table: +-------------+--------+------------------+ | employee_id | name | experience_years | +-------------+--------+------------------+ | 1 | Khaled | 3 | | 2 | Ali | 2 | | 3 | John | 1 | | 4 | Doe | 2 | +-------------+--------+------------------+ Result table: +-------------+ | project_id | +-------------+ | 1 | +-------------+ 第一个项目有3名员工,第二个项目有2名员工。 select project_id from Project group by project_id having count(*) = (select count(*) `num` from Project group by project_id order by count(*) desc limit 1);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
开窗
select project_id from
(select project_id,rank()over(order by count(employee_id) desc) ranking from Project group by project_id) temp where ranking=1
- 1
- 2
1077. 项目员工 III
难度中等
SQL架构
项目表 Project:
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| project_id | int |
| employee_id | int |
+-------------+---------+
(project_id, employee_id) 是这个表的主键
employee_id 是员工表 Employee 的外键
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
员工表 Employee:
+------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+------------------+---------+
| employee_id | int |
| name | varchar |
| experience_years | int |
+------------------+---------+
employee_id 是这个表的主键
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
写 一个 SQL 查询语句,报告在每一个项目中经验最丰富的雇员是谁。如果出现经验年数相同的情况,请报告所有具有最大经验年数的员工。
查询结果格式在以下示例中:
Project 表: +-------------+-------------+ | project_id | employee_id | +-------------+-------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 1 | 2 | | 1 | 3 | | 2 | 1 | | 2 | 4 | +-------------+-------------+ Employee 表: +-------------+--------+------------------+ | employee_id | name | experience_years | +-------------+--------+------------------+ | 1 | Khaled | 3 | | 2 | Ali | 2 | | 3 | John | 3 | | 4 | Doe | 2 | +-------------+--------+------------------+ Result 表: +-------------+---------------+ | project_id | employee_id | +-------------+---------------+ | 1 | 1 | | 1 | 3 | | 2 | 1 | +-------------+---------------+ employee_id 为 1 和 3 的员工在 project_id 为 1 的项目中拥有最丰富的经验。在 project_id 为 2 的项目中,employee_id 为 1 的员工拥有最丰富的经验。 select project_id ,employee_id from( select project_id,e.employee_id, rank()over(partition by project_id order by experience_years desc) rk from Project p join Employee e on p.employee_id=e.employee_id )t1 where rk=1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
1082. 销售分析 I
难度简单22
SQL架构
产品表:Product
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
| unit_price | int |
+--------------+---------+
product_id 是这个表的主键.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
销售表:Sales
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| seller_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| buyer_id | int |
| sale_date | date |
| quantity | int |
| price | int |
+------ ------+---------+
这个表没有主键,它可以有重复的行.
product_id 是 Product 表的外键.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
编写一个 SQL 查询,查询总销售额最高的销售者,如果有并列的,就都展示出来。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Product 表: +------------+--------------+------------+ | product_id | product_name | unit_price | +------------+--------------+------------+ | 1 | S8 | 1000 | | 2 | G4 | 800 | | 3 | iPhone | 1400 | +------------+--------------+------------+ Sales 表: +-----------+------------+----------+------------+----------+-------+ | seller_id | product_id | buyer_id | sale_date | quantity | price | +-----------+------------+----------+------------+----------+-------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2019-01-21 | 2 | 2000 | | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2019-02-17 | 1 | 800 | | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2019-06-02 | 1 | 800 | | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2019-05-13 | 2 | 2800 | +-----------+------------+----------+------------+----------+-------+ Result 表: +-------------+ | seller_id | +-------------+ | 1 | | 3 | +-------------+ Id 为 1 和 3 的销售者,销售总金额都为最高的 2800。 select seller_id from ( select seller_id ,sum(price) tp,rank() over(order by sum(price) desc) rk from Sales group by seller_id )t1 where rk =1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
1083. 销售分析 II
难度简单13
SQL架构
Table: Product
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
| unit_price | int |
+--------------+---------+
product_id 是这张表的主键
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Table: Sales
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| seller_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| buyer_id | int |
| sale_date | date |
| quantity | int |
| price | int |
+------ ------+---------+
这个表没有主键,它可以有重复的行.
product_id 是 Product 表的外键.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
编写一个 SQL 查询,查询购买了 S8 手机却没有购买 iPhone 的买家。注意这里 S8 和 iPhone 是 Product 表中的产品。
查询结果格式如下图表示:
Product table: +------------+--------------+------------+ | product_id | product_name | unit_price | +------------+--------------+------------+ | 1 | S8 | 1000 | | 2 | G4 | 800 | | 3 | iPhone | 1400 | +------------+--------------+------------+ Sales table: +-----------+------------+----------+------------+----------+-------+ | seller_id | product_id | buyer_id | sale_date | quantity | price | +-----------+------------+----------+------------+----------+-------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2019-01-21 | 2 | 2000 | | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2019-02-17 | 1 | 800 | | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2019-06-02 | 1 | 800 | | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2019-05-13 | 2 | 2800 | +-----------+------------+----------+------------+----------+-------+ Result table: +-------------+ | buyer_id | +-------------+ | 1 | +-------------+ id 为 1 的买家购买了一部 S8,但是却没有购买 iPhone,而 id 为 3 的买家却同时购买了这 2 部手机。 select t.buyer_id from( select s.buyer_id, p.product_name from sales s inner join product p on s.product_id=p.product_id and (p.product_name='S8' or p.product_name='iPhone') group by s.buyer_id having count(distinct p.product_name) = 1 ) t where t.product_name='S8'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
效率低
select s.buyer_id
from sales as s left join product as p
on s.product_id=p.product_id
group by buyer_id
having sum(p.product_name='S8')>0 and sum(p.product_name='iPhone')=0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
1084. 销售分析III
难度简单13
SQL架构
Table: Product
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
| unit_price | int |
+--------------+---------+
product_id 是这个表的主键
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Table: Sales
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| seller_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| buyer_id | int |
| sale_date | date |
| quantity | int |
| price | int |
+------ ------+---------+
这个表没有主键,它可以有重复的行.
product_id 是 Product 表的外键.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
编写一个SQL查询,报告2019年春季才售出的产品。即仅在2019-01-01至2019-03-31(含)之间出售的商品。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Product table: +------------+--------------+------------+ | product_id | product_name | unit_price | +------------+--------------+------------+ | 1 | S8 | 1000 | | 2 | G4 | 800 | | 3 | iPhone | 1400 | +------------+--------------+------------+ Sales table: +-----------+------------+----------+------------+----------+-------+ | seller_id | product_id | buyer_id | sale_date | quantity | price | +-----------+------------+----------+------------+----------+-------+ | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2019-01-21 | 2 | 2000 | | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2019-02-17 | 1 | 800 | | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2019-06-02 | 1 | 800 | | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2019-05-13 | 2 | 2800 | +-----------+------------+----------+------------+----------+-------+ Result table: +-------------+--------------+ | product_id | product_name | +-------------+--------------+ | 1 | S8 | +-------------+--------------+ id为1的产品仅在2019年春季销售,其他两个产品在之后销售。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
876ms
正常解法
select product_id, product_name
from product
where product_id not in (
select distinct product_id from sales
where sale_date > '2019-03-31' or sale_date < '2019-01-01')
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
867ms
sum = count
select product_id, product_name
from Sales join Product
using(product_id)
group by product_id
having sum(sale_date between "2019-01-01" and "2019-03-31") = count(sale_date)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
987ms
sum 为0 类似于第一种解法,计算了sum效率就低了
select p.product_id, p.product_name
from sales s, product p
where s.product_id = p.product_id
group by s.product_id
having sum(s.sale_date> '2019-03-31')=0 and sum(s.sale_date < '2019-01-01') = 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
上一解法sum换成max
859ms
select p.product_id, p.product_name
from sales s, product p
where s.product_id = p.product_id
group by s.product_id
having min(s.sale_date)>='2019-01-01' and max(s.sale_date) <= '2019-03-31'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
1097. 游戏玩法分析 V
难度困难
SQL架构
Activity 活动记录表
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| player_id | int |
| device_id | int |
| event_date | date |
| games_played | int |
+--------------+---------+
(player_id,event_date)是此表的主键
这张表显示了某些游戏的玩家的活动情况
每一行是一个玩家的记录,他在某一天使用某个设备注销之前登录并玩了很多游戏(可能是 0)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
我们将玩家的安装日期定义为该玩家的第一个登录日。
我们还将某个日期 X 的第 1 天留存时间定义为安装日期为 X 的玩家的数量,他们在 X 之后的一天重新登录,除以安装日期为 X 的玩家的数量,四舍五入到小数点后两位。
编写一个 SQL 查询,报告每个安装日期、当天安装游戏的玩家数量和第一天的留存时间。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Activity 表: +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | player_id | device_id | event_date | games_played | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ | 1 | 2 | 2016-03-01 | 5 | | 1 | 2 | 2016-03-02 | 6 | | 2 | 3 | 2017-06-25 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | 2016-03-01 | 0 | | 3 | 4 | 2016-07-03 | 5 | +-----------+-----------+------------+--------------+ Result 表: +------------+----------+----------------+ | install_dt | installs | Day1_retention | +------------+----------+----------------+ | 2016-03-01 | 2 | 0.50 | | 2017-06-25 | 1 | 0.00 | +------------+----------+----------------+ 玩家 1 和 3 在 2016-03-01 安装了游戏,但只有玩家 1 在 2016-03-02 重新登录,所以 2016-03-01 的第一天留存时间是 1/2=0.50 玩家 2 在 2017-06-25 安装了游戏,但在 2017-06-26 没有重新登录,因此 2017-06-25 的第一天留存时间为 0/1=0.00 select install_dt,count(distinct player_id)installs, round(sum(if(datediff(event_date,install_dt)=1,1,0))/count(distinct player_id),2) Day1_retention from ( select *,min(event_date) over(partition by player_id) install_dt from Activity )t1 group by install_dt
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
1098. 小众书籍
难度中等
SQL架构
书籍表 Books:
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+----------------+---------+
| book_id | int |
| name | varchar |
| available_from | date |
+----------------+---------+
book_id 是这个表的主键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
订单表 Orders:
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+----------------+---------+
| order_id | int |
| book_id | int |
| quantity | int |
| dispatch_date | date |
+----------------+---------+
order_id 是这个表的主键。
book_id 是 Books 表的外键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
你需要写一段 SQL 命令,筛选出过去一年中订单总量 少于10本 的 书籍 。
注意:不考虑 上架(available from)距今 不满一个月 的书籍。并且 假设今天是****2019-06-23 。
Write an SQL query that reports the books that have sold less than 10 copies in the last year, excluding books that have been available for less than 1 month from today. Assume today is 2019-06-23.
下面是样例输出结果:
Books 表: +---------+--------------------+----------------+ | book_id | name | available_from | +---------+--------------------+----------------+ | 1 | "Kalila And Demna" | 2010-01-01 | | 2 | "28 Letters" | 2012-05-12 | | 3 | "The Hobbit" | 2019-06-10 | | 4 | "13 Reasons Why" | 2019-06-01 | | 5 | "The Hunger Games" | 2008-09-21 | +---------+--------------------+----------------+ Orders 表: +----------+---------+----------+---------------+ | order_id | book_id | quantity | dispatch_date | +----------+---------+----------+---------------+ | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2018-07-26 | | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2018-11-05 | | 3 | 3 | 8 | 2019-06-11 | | 4 | 4 | 6 | 2019-06-05 | | 5 | 4 | 5 | 2019-06-20 | | 6 | 5 | 9 | 2009-02-02 | | 7 | 5 | 8 | 2010-04-13 | +----------+---------+----------+---------------+ Result 表: +-----------+--------------------+ | book_id | name | +-----------+--------------------+ | 1 | "Kalila And Demna" | | 2 | "28 Letters" | | 5 | "The Hunger Games" | +-----------+--------------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
这题中英文 都有歧义,看结果进行分析
SELECT a.book_id, a.name
FROM books a LEFT JOIN orders b ON a.book_id=b.book_id
AND dispatch_date BETWEEN DATE_ADD('2019-06-23', INTERVAL -1 YEAR) AND '2019-06-23'
WHERE a.available_from <= DATE_ADD('2019-06-23',INTERVAL -1 MONTH)
GROUP BY a.book_id, a.name
HAVING SUM(IFNULL(b.quantity,0)) < 10
ORDER BY a.book_id;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
此题有坑,首先订单近一年,再者quantity为null,还有近一月出版,sum不是订单是本数
还有就是date_add这个函数在hive里和mysql语法上有点小区别
1107. 每日新用户统计
难度中等
SQL架构
Traffic 表:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| activity | enum |
| activity_date | date |
+---------------+---------+
该表没有主键,它可能有重复的行。
activity 列是 ENUM 类型,可能取 ('login', 'logout', 'jobs', 'groups', 'homepage') 几个值之一。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
编写一个 SQL 查询,以查询从今天起最多 90 天内,每个日期该日期首次登录的用户数。假设今天是 2019-06-30.
查询结果格式如下例所示:
Traffic 表: +---------+----------+---------------+ | user_id | activity | activity_date | +---------+----------+---------------+ | 1 | login | 2019-05-01 | | 1 | homepage | 2019-05-01 | | 1 | logout | 2019-05-01 | | 2 | login | 2019-06-21 | | 2 | logout | 2019-06-21 | | 3 | login | 2019-01-01 | | 3 | jobs | 2019-01-01 | | 3 | logout | 2019-01-01 | | 4 | login | 2019-06-21 | | 4 | groups | 2019-06-21 | | 4 | logout | 2019-06-21 | | 5 | login | 2019-03-01 | | 5 | logout | 2019-03-01 | | 5 | login | 2019-06-21 | | 5 | logout | 2019-06-21 | +---------+----------+---------------+ Result 表: +------------+-------------+ | login_date | user_count | +------------+-------------+ | 2019-05-01 | 1 | | 2019-06-21 | 2 | +------------+-------------+ 请注意,我们只关心用户数非零的日期. ID 为 5 的用户第一次登陆于 2019-03-01,因此他不算在 2019-06-21 的的统计内。 select login_date,count(*) user_count from( select user_id,min(activity_date) login_date from Traffic where activity = 'login' group by user_id having login_date>= DATE_ADD('2019-06-30',INTERVAL -90 DAY) )t1 group by login_date
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
1112. 每位学生的最高成绩
难度中等
SQL架构
表:Enrollments
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| student_id | int |
| course_id | int |
| grade | int |
+---------------+---------+
(student_id, course_id) 是该表的主键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
编写一个 SQL 查询,查询每位学生获得的最高成绩和它所对应的科目,若科目成绩并列,取 course_id 最小的一门。查询结果需按 student_id 增序进行排序。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Enrollments 表: +------------+-------------------+ | student_id | course_id | grade | +------------+-----------+-------+ | 2 | 2 | 95 | | 2 | 3 | 95 | | 1 | 1 | 90 | | 1 | 2 | 99 | | 3 | 1 | 80 | | 3 | 2 | 75 | | 3 | 3 | 82 | +------------+-----------+-------+ Result 表: +------------+-------------------+ | student_id | course_id | grade | +------------+-----------+-------+ | 1 | 2 | 99 | | 2 | 2 | 95 | | 3 | 3 | 82 | +------------+-----------+-------+ select student_id,course_id ,grade from ( select student_id,course_id ,grade, rank()over(partition by student_id order by grade desc,course_id) rK from Enrollments )t1 where rk =1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
1113. 报告的记录
难度简单
SQL架构
动作表:Actions
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| post_id | int |
| action_date | date |
| action | enum |
| extra | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
此表没有主键,所以可能会有重复的行。
action 字段是 ENUM 类型的,包含:('view', 'like', 'reaction', 'comment', 'report', 'share')
extra 字段是可选的信息(可能为 null),其中的信息例如有:1.报告理由(a reason for report) 2.反应类型(a type of reaction)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
编写一条SQL,查询每种 报告理由(report reason)在昨天的报告数量。假设今天是 2019-07-05。
查询及结果的格式示例:
Actions table: +---------+---------+-------------+--------+--------+ | user_id | post_id | action_date | action | extra | +---------+---------+-------------+--------+--------+ | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | view | null | | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | like | null | | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | share | null | | 2 | 4 | 2019-07-04 | view | null | | 2 | 4 | 2019-07-04 | report | spam | | 3 | 4 | 2019-07-04 | view | null | | 3 | 4 | 2019-07-04 | report | spam | | 4 | 3 | 2019-07-02 | view | null | | 4 | 3 | 2019-07-02 | report | spam | | 5 | 2 | 2019-07-04 | view | null | | 5 | 2 | 2019-07-04 | report | racism | | 5 | 5 | 2019-07-04 | view | null | | 5 | 5 | 2019-07-04 | report | racism | +---------+---------+-------------+--------+--------+ Result table: +---------------+--------------+ | report_reason | report_count | +---------------+--------------+ | spam | 1 | | racism | 2 | +---------------+--------------+ 注意,我们只关心报告数量非零的结果。 SELECT extra AS report_reason, COUNT(distinct post_id) AS report_count FROM Actions WHERE `action` = 'report' AND action_date = date_add('2019-07-05',Interval -1 day) GROUP BY extra;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
1132. 报告的记录 II
难度中等
SQL架构
动作表: Actions
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| post_id | int |
| action_date | date |
| action | enum |
| extra | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
这张表没有主键,并有可能存在重复的行。
action 列的类型是 ENUM,可能的值为 ('view', 'like', 'reaction', 'comment', 'report', 'share')。
extra 列拥有一些可选信息,例如:报告理由(a reason for report)或反应类型(a type of reaction)等。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
移除表: Removals
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| post_id | int |
| remove_date | date |
+---------------+---------+
这张表的主键是 post_id。
这张表的每一行表示一个被移除的帖子,原因可能是由于被举报或被管理员审查。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
编写一段 SQL 来查找:在被报告为垃圾广告的帖子中,被移除的帖子的每日平均占比,四舍五入到小数点后 2 位。
查询结果的格式如下:
Actions table: +---------+---------+-------------+--------+--------+ | user_id | post_id | action_date | action | extra | +---------+---------+-------------+--------+--------+ | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | view | null | | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | like | null | | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-01 | share | null | | 2 | 2 | 2019-07-04 | view | null | | 2 | 2 | 2019-07-04 | report | spam | | 3 | 4 | 2019-07-04 | view | null | | 3 | 4 | 2019-07-04 | report | spam | | 4 | 3 | 2019-07-02 | view | null | | 4 | 3 | 2019-07-02 | report | spam | | 5 | 2 | 2019-07-03 | view | null | | 5 | 2 | 2019-07-03 | report | racism | | 5 | 5 | 2019-07-03 | view | null | | 5 | 5 | 2019-07-03 | report | racism | +---------+---------+-------------+--------+--------+ Removals table: +---------+-------------+ | post_id | remove_date | +---------+-------------+ | 2 | 2019-07-20 | | 3 | 2019-07-18 | +---------+-------------+ Result table: +-----------------------+ | average_daily_percent | +-----------------------+ | 75.00 | +-----------------------+ 2019-07-04 的垃圾广告移除率是 50%,因为有两张帖子被报告为垃圾广告,但只有一个得到移除。 2019-07-02 的垃圾广告移除率是 100%,因为有一张帖子被举报为垃圾广告并得到移除。 其余几天没有收到垃圾广告的举报,因此平均值为:(50 + 100) / 2 = 75% 注意,输出仅需要一个平均值即可,我们并不关注移除操作的日期。 SELECT ROUND(AVG(proportion) * 100, 2) AS average_daily_percent FROM ( SELECT actions.action_date, COUNT(DISTINCT removals.post_id)/COUNT(DISTINCT actions.post_id) AS proportion FROM actions LEFT JOIN removals ON actions.post_id = removals.post_id WHERE extra = 'spam' GROUP BY actions.action_date ) a
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
要理解spam的含义
1126. 查询活跃业务
难度中等
SQL架构
事件表:Events
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| business_id | int |
| event_type | varchar |
| occurences | int |
+---------------+---------+
此表的主键是 (business_id, event_type)。
表中的每一行记录了某种类型的事件在某些业务中多次发生的信息。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
写一段 SQL 来查询所有活跃的业务。
如果一个业务的某个事件类型的发生次数大于此事件类型在所有业务中的平均发生次数,并且该业务至少有两个这样的事件类型,那么该业务就可被看做是活跃业务。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Events table: +-------------+------------+------------+ | business_id | event_type | occurences | +-------------+------------+------------+ | 1 | reviews | 7 | | 3 | reviews | 3 | | 1 | ads | 11 | | 2 | ads | 7 | | 3 | ads | 6 | | 1 | page views | 3 | | 2 | page views | 12 | +-------------+------------+------------+ 结果表 +-------------+ | business_id | +-------------+ | 1 | +-------------+ 'reviews'、 'ads' 和 'page views' 的总平均发生次数分别是 (7+3)/2=5, (11+7+6)/3=8, (3+12)/2=7.5。 id 为 1 的业务有 7 个 'reviews' 事件(大于 5)和 11 个 'ads' 事件(大于 8),所以它是活跃业务。 select business_id from ( select business_id,occurences, avg(occurences) over(partition by event_type) avo from Events )t1 where occurences > avo group by business_id having count(*)>=2
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
1127. 用户购买平台
难度困难
SQL架构
支出表: Spending
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| spend_date | date |
| platform | enum |
| amount | int |
+-------------+---------+
这张表记录了用户在一个在线购物网站的支出历史,该在线购物平台同时拥有桌面端('desktop')和手机端('mobile')的应用程序。
这张表的主键是 (user_id, spend_date, platform)。
平台列 platform 是一种 ENUM ,类型为('desktop', 'mobile')。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
写一段 SQL 来查找每天 仅 使用手机端用户、仅 使用桌面端用户和 同时 使用桌面端和手机端的用户人数和总支出金额。
查询结果格式如下例所示:
Spending table: +---------+------------+----------+--------+ | user_id | spend_date | platform | amount | +---------+------------+----------+--------+ | 1 | 2019-07-01 | mobile | 100 | | 1 | 2019-07-01 | desktop | 100 | | 2 | 2019-07-01 | mobile | 100 | | 2 | 2019-07-02 | mobile | 100 | | 3 | 2019-07-01 | desktop | 100 | | 3 | 2019-07-02 | desktop | 100 | +---------+------------+----------+--------+ Result table: +------------+----------+--------------+-------------+ | spend_date | platform | total_amount | total_users | +------------+----------+--------------+-------------+ | 2019-07-01 | desktop | 100 | 1 | | 2019-07-01 | mobile | 100 | 1 | | 2019-07-01 | both | 200 | 1 | | 2019-07-02 | desktop | 100 | 1 | | 2019-07-02 | mobile | 100 | 1 | | 2019-07-02 | both | 0 | 0 | +------------+----------+--------------+-------------+ 在 2019-07-01, 用户1 同时 使用桌面端和手机端购买, 用户2 仅 使用了手机端购买,而用户3 仅 使用了桌面端购买。 在 2019-07-02, 用户2 仅 使用了手机端购买, 用户3 仅 使用了桌面端购买,且没有用户 同时 使用桌面端和手机端购买。 select spend_date, platform, ifnull(sum(total_am),0) total_amount, ifnull(sum(total_u),0) total_users from ( select p.spend_date, p.platform, t.total_am, t.total_u from ( select distinct spend_date, "desktop" platform from Spending union select distinct spend_date, "mobile" platform from Spending union select distinct spend_date, "both" platform from Spending ) p left join ( select spend_date, if(count(distinct platform)=1, platform, 'both') plat, sum(amount) total_am, count(distinct user_id) total_u from Spending group by spend_date, user_id ) t on p.platform = t.plat and p.spend_date = t.spend_date ) temp group by spend_date, platform
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
必须保证 desktop mobile both的顺序 ,所以 先列出三个字段
1141. 查询近30天活跃用户数
难度简单
SQL架构
活动记录表:Activity
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| session_id | int |
| activity_date | date |
| activity_type | enum |
+---------------+---------+
该表是用户在社交网站的活动记录。
该表没有主键,可能包含重复数据。
activity_type 字段为以下四种值 ('open_session', 'end_session', 'scroll_down', 'send_message')。
每个 session_id 只属于一个用户。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
请写SQL查询出截至 2019-07-27(包含2019-07-27),近 30天的每日活跃用户数(当天只要有一条活动记录,即为活跃用户)。
查询结果示例如下:
Activity table: +---------+------------+---------------+---------------+ | user_id | session_id | activity_date | activity_type | +---------+------------+---------------+---------------+ | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | open_session | | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | scroll_down | | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | end_session | | 2 | 4 | 2019-07-20 | open_session | | 2 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | send_message | | 2 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | end_session | | 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | open_session | | 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | send_message | | 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | end_session | | 4 | 3 | 2019-06-25 | open_session | | 4 | 3 | 2019-06-25 | end_session | +---------+------------+---------------+---------------+ Result table: +------------+--------------+ | day | active_users | +------------+--------------+ | 2019-07-20 | 2 | | 2019-07-21 | 2 | +------------+--------------+ 非活跃用户的记录不需要展示。 select activity_date day,count(distinct user_id) active_users from Activity where activity_date > date_add('2019-07-27',INTERVAL -1 MONTH) group by activity_date
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
1142. 过去30天的用户活动 II
难度简单7收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
Table: Activity
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| session_id | int |
| activity_date | date |
| activity_type | enum |
+---------------+---------+
该表没有主键,它可能有重复的行。
activity_type列是一种类型的ENUM(“ open_session”,“ end_session”,“ scroll_down”,“ send_message”)。
该表显示了社交媒体网站的用户活动。
请注意,每个会话完全属于一个用户。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
编写SQL查询以查找截至2019年7月27日(含)的30天内每个用户的平均会话数,四舍五入到小数点后两位。我们只统计那些会话期间用户至少进行一项活动的有效会话。
查询结果格式如下例所示:
Activity table: +---------+------------+---------------+---------------+ | user_id | session_id | activity_date | activity_type | +---------+------------+---------------+---------------+ | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | open_session | | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | scroll_down | | 1 | 1 | 2019-07-20 | end_session | | 2 | 4 | 2019-07-20 | open_session | | 2 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | send_message | | 2 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | end_session | | 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | open_session | | 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | send_message | | 3 | 2 | 2019-07-21 | end_session | | 3 | 5 | 2019-07-21 | open_session | | 3 | 5 | 2019-07-21 | scroll_down | | 3 | 5 | 2019-07-21 | end_session | | 4 | 3 | 2019-06-25 | open_session | | 4 | 3 | 2019-06-25 | end_session | +---------+------------+---------------+---------------+ Result table: +---------------------------+ | average_sessions_per_user | +---------------------------+ | 1.33 | +---------------------------+ User 1 和 2 在过去30天内各自进行了1次会话,而用户3进行了2次会话,因此平均值为(1 +1 + 2)/ 3 = 1.33。 SELECT IFNULL(ROUND(COUNT(DISTINCT session_id) / COUNT(DISTINCT user_id), 2), 0) AS average_sessions_per_user from Activity where activity_date > date_add('2019-07-27',INTERVAL -1 MONTH)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
1个session id 代表一次会话
1148. 文章浏览 I
难度简单3收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
Views 表:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| article_id | int |
| author_id | int |
| viewer_id | int |
| view_date | date |
+---------------+---------+
此表无主键,因此可能会存在重复行。
此表的每一行都表示某人在某天浏览了某位作者的某篇文章。
请注意,同一人的 author_id 和 viewer_id 是相同的。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
请编写一条 SQL 查询以找出所有浏览过自己文章的作者,结果按照 id 升序排列。
查询结果的格式如下所示:
Views 表: +------------+-----------+-----------+------------+ | article_id | author_id | viewer_id | view_date | +------------+-----------+-----------+------------+ | 1 | 3 | 5 | 2019-08-01 | | 1 | 3 | 6 | 2019-08-02 | | 2 | 7 | 7 | 2019-08-01 | | 2 | 7 | 6 | 2019-08-02 | | 4 | 7 | 1 | 2019-07-22 | | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | +------------+-----------+-----------+------------+ 结果表: +------+ | id | +------+ | 4 | | 7 | +------+ select distinct author_id id from Views where author_id= viewer_id order by id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
1149. 文章浏览 II
难度中等4收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
Table: Views
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| article_id | int |
| author_id | int |
| viewer_id | int |
| view_date | date |
+---------------+---------+
此表无主键,因此可能会存在重复行。此表的每一行都表示某人在某天浏览了某位作者的某篇文章。 请注意,同一人的 author_id 和 viewer_id 是相同的。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
编写一条 SQL 查询来找出在同一天阅读至少两篇文章的人,结果按照 id 升序排序。
查询结果的格式如下:
Views table: +------------+-----------+-----------+------------+ | article_id | author_id | viewer_id | view_date | +------------+-----------+-----------+------------+ | 1 | 3 | 5 | 2019-08-01 | | 3 | 4 | 5 | 2019-08-01 | | 1 | 3 | 6 | 2019-08-02 | | 2 | 7 | 7 | 2019-08-01 | | 2 | 7 | 6 | 2019-08-02 | | 4 | 7 | 1 | 2019-07-22 | | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | | 3 | 4 | 4 | 2019-07-21 | +------------+-----------+-----------+------------+ Result table: +------+ | id | +------+ | 5 | | 6 | +------+ SELECT DISTINCT viewer_id AS id FROM Views GROUP BY view_date, viewer_id HAVING COUNT(DISTINCT article_id) >= 2 ORDER BY viewer_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
1158. 市场分析 I
难度中等
SQL架构
Table: Users
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+----------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| join_date | date |
| favorite_brand | varchar |
+----------------+---------+
此表主键是 user_id,表中描述了购物网站的用户信息,用户可以在此网站上进行商品买卖。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Table: Orders
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| order_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| item_id | int |
| buyer_id | int |
| seller_id | int |
+---------------+---------+
此表主键是 order_id,外键是 item_id 和(buyer_id,seller_id)。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Table: Item
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| item_id | int |
| item_brand | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
此表主键是 item_id。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
请写出一条SQL语句以查询每个用户的注册日期和在 2019 年作为买家的订单总数。
查询结果格式如下:
Users table: +---------+------------+----------------+ | user_id | join_date | favorite_brand | +---------+------------+----------------+ | 1 | 2018-01-01 | Lenovo | | 2 | 2018-02-09 | Samsung | | 3 | 2018-01-19 | LG | | 4 | 2018-05-21 | HP | +---------+------------+----------------+ Orders table: +----------+------------+---------+----------+-----------+ | order_id | order_date | item_id | buyer_id | seller_id | +----------+------------+---------+----------+-----------+ | 1 | 2019-08-01 | 4 | 1 | 2 | | 2 | 2018-08-02 | 2 | 1 | 3 | | 3 | 2019-08-03 | 3 | 2 | 3 | | 4 | 2018-08-04 | 1 | 4 | 2 | | 5 | 2018-08-04 | 1 | 3 | 4 | | 6 | 2019-08-05 | 2 | 2 | 4 | +----------+------------+---------+----------+-----------+ Items table: +---------+------------+ | item_id | item_brand | +---------+------------+ | 1 | Samsung | | 2 | Lenovo | | 3 | LG | | 4 | HP | +---------+------------+ Result table: +-----------+------------+----------------+ | buyer_id | join_date | orders_in_2019 | +-----------+------------+----------------+ | 1 | 2018-01-01 | 1 | | 2 | 2018-02-09 | 2 | | 3 | 2018-01-19 | 0 | | 4 | 2018-05-21 | 0 | +-----------+------------+----------------+ select user_id buyer_id,join_date, ifnull(cnt,0)orders_in_2019 from Users u left join (select buyer_id,count(*) cnt from Orders where year(order_date) = 2019 group by buyer_id )t1 on u.user_id =t1.buyer_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
1159. 市场分析 II
难度困难
SQL架构
表: Users
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+----------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| join_date | date |
| favorite_brand | varchar |
+----------------+---------+
user_id 是该表的主键
表中包含一位在线购物网站用户的个人信息,用户可以在该网站出售和购买商品。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
表: Orders
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| order_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| item_id | int |
| buyer_id | int |
| seller_id | int |
+---------------+---------+
order_id 是该表的主键
item_id 是 Items 表的外键
buyer_id 和 seller_id 是 Users 表的外键
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
表: Items
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| item_id | int |
| item_brand | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
item_id 是该表的主键
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
写一个 SQL 查询确定每一个用户按日期顺序卖出的第二件商品的品牌是否是他们最喜爱的品牌。如果一个用户卖出少于两件商品,查询的结果是 no 。
题目保证没有一个用户在一天中卖出超过一件商品
下面是查询结果格式的例子:
Users table: +---------+------------+----------------+ | user_id | join_date | favorite_brand | +---------+------------+----------------+ | 1 | 2019-01-01 | Lenovo | | 2 | 2019-02-09 | Samsung | | 3 | 2019-01-19 | LG | | 4 | 2019-05-21 | HP | +---------+------------+----------------+ Orders table: +----------+------------+---------+----------+-----------+ | order_id | order_date | item_id | buyer_id | seller_id | +----------+------------+---------+----------+-----------+ | 1 | 2019-08-01 | 4 | 1 | 2 | | 2 | 2019-08-02 | 2 | 1 | 3 | | 3 | 2019-08-03 | 3 | 2 | 3 | | 4 | 2019-08-04 | 1 | 4 | 2 | | 5 | 2019-08-04 | 1 | 3 | 4 | | 6 | 2019-08-05 | 2 | 2 | 4 | +----------+------------+---------+----------+-----------+ Items table: +---------+------------+ | item_id | item_brand | +---------+------------+ | 1 | Samsung | | 2 | Lenovo | | 3 | LG | | 4 | HP | +---------+------------+ Result table: +-----------+--------------------+ | seller_id | 2nd_item_fav_brand | +-----------+--------------------+ | 1 | no | | 2 | yes | | 3 | yes | | 4 | no | +-----------+--------------------+ id 为 1 的用户的查询结果是 no,因为他什么也没有卖出 id为 2 和 3 的用户的查询结果是 yes,因为他们卖出的第二件商品的品牌是他们自己最喜爱的品牌 id为 4 的用户的查询结果是 no,因为他卖出的第二件商品的品牌不是他最喜爱的品牌 select user_id seller_id, if(item_brand=favorite_brand,'yes','no') 2nd_item_fav_brand from Users u left join ( select i.item_id,seller_id,item_brand from Items i join ( select seller_id,item_id,rank() over(partition by seller_id order by order_date ) rk from Orders )t1 on i.item_id = t1.item_id where rk =2 )t2 on u.user_id = t2.seller_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
1164. 指定日期的产品价格
难度中等
SQL架构
产品数据表: Products
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| new_price | int |
| change_date | date |
+---------------+---------+
这张表的主键是 (product_id, change_date)。
这张表的每一行分别记录了 某产品 在某个日期 更改后 的新价格。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
写一段 SQL来查找在 2019-08-16 时全部产品的价格,假设所有产品在修改前的价格都是 10。
查询结果格式如下例所示:
Products table: +------------+-----------+-------------+ | product_id | new_price | change_date | +------------+-----------+-------------+ | 1 | 20 | 2019-08-14 | | 2 | 50 | 2019-08-14 | | 1 | 30 | 2019-08-15 | | 1 | 35 | 2019-08-16 | | 2 | 65 | 2019-08-17 | | 3 | 20 | 2019-08-18 | +------------+-----------+-------------+ Result table: +------------+-------+ | product_id | price | +------------+-------+ | 2 | 50 | | 1 | 35 | | 3 | 10 | +------------+-------+ select distinct p.product_id,ifnull(t1.new_price,10) price from Products p left join ( select product_id,new_price from ( select product_id,new_price,change_date,Max(change_date) over(partition by product_id ) md from Products where change_date<='2019-08-16' )tmp where change_date = md )t1 on p. product_id = t1.product_id order by price desc
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
1173. 即时食物配送 I
难度简单
SQL架构
配送表: Delivery
+-----------------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-----------------------------+---------+
| delivery_id | int |
| customer_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| customer_pref_delivery_date | date |
+-----------------------------+---------+
delivery_id 是表的主键。
该表保存着顾客的食物配送信息,顾客在某个日期下了订单,并指定了一个期望的配送日期(和下单日期相同或者在那之后)。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
如果顾客期望的配送日期和下单日期相同,则该订单称为 「即时订单」,否则称为「计划订单」。
写一条 SQL 查询语句获取即时订单所占的百分比, 保留两位小数。
查询结果如下所示:
Delivery 表: +-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------------------+ | delivery_id | customer_id | order_date | customer_pref_delivery_date | +-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------------------+ | 1 | 1 | 2019-08-01 | 2019-08-02 | | 2 | 5 | 2019-08-02 | 2019-08-02 | | 3 | 1 | 2019-08-11 | 2019-08-11 | | 4 | 3 | 2019-08-24 | 2019-08-26 | | 5 | 4 | 2019-08-21 | 2019-08-22 | | 6 | 2 | 2019-08-11 | 2019-08-13 | +-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------------------+ Result 表: +----------------------+ | immediate_percentage | +----------------------+ | 33.33 | +----------------------+ 2 和 3 号订单为即时订单,其他的为计划订单。 select round(sum(if(order_date=customer_pref_delivery_date,1,0))/count(*)*100,2) immediate_percentage from Delivery
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
1174. 即时食物配送 II
难度中等
SQL架构
配送表: Delivery
+-----------------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-----------------------------+---------+
| delivery_id | int |
| customer_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| customer_pref_delivery_date | date |
+-----------------------------+---------+
delivery_id 是表的主键。
该表保存着顾客的食物配送信息,顾客在某个日期下了订单,并指定了一个期望的配送日期(和下单日期相同或者在那之后)。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
如果顾客期望的配送日期和下单日期相同,则该订单称为 「即时订单」,否则称为「计划订单」。
「首次订单」是顾客最早创建的订单。我们保证一个顾客只会有一个「首次订单」。
写一条 SQL 查询语句获取即时订单在所有用户的首次订单中的比例。保留两位小数。
查询结果如下所示:
Delivery 表: +-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------------------+ | delivery_id | customer_id | order_date | customer_pref_delivery_date | +-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------------------+ | 1 | 1 | 2019-08-01 | 2019-08-02 | | 2 | 2 | 2019-08-02 | 2019-08-02 | | 3 | 1 | 2019-08-11 | 2019-08-12 | | 4 | 3 | 2019-08-24 | 2019-08-24 | | 5 | 3 | 2019-08-21 | 2019-08-22 | | 6 | 2 | 2019-08-11 | 2019-08-13 | | 7 | 4 | 2019-08-09 | 2019-08-09 | +-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------------------+ Result 表: +----------------------+ | immediate_percentage | +----------------------+ | 50.00 | +----------------------+ 1 号顾客的 1 号订单是首次订单,并且是计划订单。 2 号顾客的 2 号订单是首次订单,并且是即时订单。 3 号顾客的 5 号订单是首次订单,并且是计划订单。 4 号顾客的 7 号订单是首次订单,并且是即时订单。 因此,一半顾客的首次订单是即时的。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
开窗
select round(sum(if(order_date = fo && fo=d,1,0))/count(distinct customer_id)*100,2) immediate_percentage
from
(
select customer_id,order_date,min(order_date)over ( partition by customer_id) fo,
if(order_date=customer_pref_delivery_date,order_date ,null) d
from Delivery
)t1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
另一种思路
select round (
sum(order_date = customer_pref_delivery_date) * 100 /
count(*),
2
) as immediate_percentage
from Delivery
where (customer_id, order_date) in (
select customer_id, min(order_date)
from delivery
group by customer_id
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
1179. 重新格式化部门表
难度
SQL架构
部门表 Department:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| revenue | int |
| month | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
(id, month) 是表的联合主键。
这个表格有关于每个部门每月收入的信息。
月份(month)可以取下列值 ["Jan","Feb","Mar","Apr","May","Jun","Jul","Aug","Sep","Oct","Nov","Dec"]。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
编写一个 SQL 查询来重新格式化表,使得新的表中有一个部门 id 列和一些对应 每个月 的收入(revenue)列。
查询结果格式如下面的示例所示:
Department 表: +------+---------+-------+ | id | revenue | month | +------+---------+-------+ | 1 | 8000 | Jan | | 2 | 9000 | Jan | | 3 | 10000 | Feb | | 1 | 7000 | Feb | | 1 | 6000 | Mar | +------+---------+-------+ 查询得到的结果表: +------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----+-------------+ | id | Jan_Revenue | Feb_Revenue | Mar_Revenue | ... | Dec_Revenue | +------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----+-------------+ | 1 | 8000 | 7000 | 6000 | ... | null | | 2 | 9000 | null | null | ... | null | | 3 | null | 10000 | null | ... | null | +------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----+-------------+ 注意,结果表有 13 列 (1个部门 id 列 + 12个月份的收入列)。 SELECT id, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Jan' THEN revenue END) Jan_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Feb' THEN revenue END) Feb_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Mar' THEN revenue END) Mar_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Apr' THEN revenue END) Apr_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'May' THEN revenue END) May_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Jun' THEN revenue END) Jun_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Jul' THEN revenue END) Jul_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Aug' THEN revenue END) Aug_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Sep' THEN revenue END) Sep_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Oct' THEN revenue END) Oct_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Nov' THEN revenue END) Nov_Revenue, SUM(CASE `month` WHEN 'Dec' THEN revenue END) Dec_Revenue FROM Department GROUP BY id; 1193. 每月交易 I SQL架构 Table: Transactions +---------------+---------+ | Column Name | Type | +---------------+---------+ | id | int | | country | varchar | | state | enum | | amount | int | | trans_date | date | +---------------+---------+ id 是这个表的主键。 该表包含有关传入事务的信息。 state 列类型为 “[”批准“,”拒绝“] 之一。 编写一个 sql 查询来查找每个月和每个国家/地区的事务数及其总金额、已批准的事务数及其总金额。 查询结果格式如下所示: Transactions table: +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+ | id | country | state | amount | trans_date | +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+ | 121 | US | approved | 1000 | 2018-12-18 | | 122 | US | declined | 2000 | 2018-12-19 | | 123 | US | approved | 2000 | 2019-01-01 | | 124 | DE | approved | 2000 | 2019-01-07 | +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+ Result table: +----------+---------+-------------+----------------+--------------------+-----------------------+ | month | country | trans_count | approved_count | trans_total_amount | approved_total_amount | +----------+---------+-------------+----------------+--------------------+-----------------------+ | 2018-12 | US | 2 | 1 | 3000 | 1000 | | 2019-01 | US | 1 | 1 | 2000 | 2000 | | 2019-01 | DE | 1 | 1 | 2000 | 2000 | +----------+---------+-------------+----------------+--------------------+-----------------------+ SELECT DATE_FORMAT(trans_date, '%Y-%m') AS month, country, COUNT(*) AS trans_count, COUNT(IF(state = 'approved', 1, NULL)) AS approved_count, SUM(amount) AS trans_total_amount, SUM(IF(state = 'approved', amount, 0)) AS approved_total_amount FROM Transactions GROUP BY month, country
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
1193. 每月交易 I
难度中等
SQL架构
Table: Transactions
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| country | varchar |
| state | enum |
| amount | int |
| trans_date | date |
+---------------+---------+
id 是这个表的主键。
该表包含有关传入事务的信息。
state 列类型为 “[”批准“,”拒绝“] 之一。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
编写一个 sql 查询来查找每个月和每个国家/地区的事务数及其总金额、已批准的事务数及其总金额。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Transactions table: +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+ | id | country | state | amount | trans_date | +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+ | 121 | US | approved | 1000 | 2018-12-18 | | 122 | US | declined | 2000 | 2018-12-19 | | 123 | US | approved | 2000 | 2019-01-01 | | 124 | DE | approved | 2000 | 2019-01-07 | +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+ Result table: +----------+---------+-------------+----------------+--------------------+-----------------------+ | month | country | trans_count | approved_count | trans_total_amount | approved_total_amount | +----------+---------+-------------+----------------+--------------------+-----------------------+ | 2018-12 | US | 2 | 1 | 3000 | 1000 | | 2019-01 | US | 1 | 1 | 2000 | 2000 | | 2019-01 | DE | 1 | 1 | 2000 | 2000 | +----------+---------+-------------+----------------+--------------------+-----------------------+ SELECT DATE_FORMAT(trans_date, '%Y-%m') AS month, country, COUNT(*) AS trans_count, COUNT(IF(state = 'approved', 1, NULL)) AS approved_count, SUM(amount) AS trans_total_amount, SUM(IF(state = 'approved', amount, 0)) AS approved_total_amount FROM Transactions GROUP BY month, country
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
1205. 每月交易II
难度中等
SQL架构
Transactions 记录表
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+----------------+---------+
| id | int |
| country | varchar |
| state | enum |
| amount | int |
| trans_date | date |
+----------------+---------+
id 是这个表的主键。
该表包含有关传入事务的信息。
状态列是类型为 [approved(已批准)、declined(已拒绝)] 的枚举。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
Chargebacks 表
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+----------------+---------+
| trans_id | int |
| charge_date | date |
+----------------+---------+
退单包含有关放置在事务表中的某些事务的传入退单的基本信息。
trans_id 是 transactions 表的 id 列的外键。
每项退单都对应于之前进行的交易,即使未经批准。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
编写一个 SQL 查询,以查找每个月和每个国家/地区的已批准交易的数量及其总金额、退单的数量及其总金额。
注意:在您的查询中,给定月份和国家,忽略所有为零的行。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Transactions 表: +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+ | id | country | state | amount | trans_date | +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+ | 101 | US | approved | 1000 | 2019-05-18 | | 102 | US | declined | 2000 | 2019-05-19 | | 103 | US | approved | 3000 | 2019-06-10 | | 104 | US | declined | 4000 | 2019-06-13 | | 105 | US | approved | 5000 | 2019-06-15 | +------+---------+----------+--------+------------+ Chargebacks 表: +------------+------------+ | trans_id | trans_date | +------------+------------+ | 102 | 2019-05-29 | | 101 | 2019-06-30 | | 105 | 2019-09-18 | +------------+------------+ Result 表: +----------+---------+----------------+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------+ | month | country | approved_count | approved_amount | chargeback_count | chargeback_amount | +----------+---------+----------------+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------+ | 2019-05 | US | 1 | 1000 | 1 | 2000 | | 2019-06 | US | 2 | 8000 | 1 | 1000 | | 2019-09 | US | 0 | 0 | 1 | 5000 | +----------+---------+----------------+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------+ select date_format(trans_date, '%Y-%m') month, country, sum(state = 'approved') approved_count, sum(if(state = 'approved', amount, 0)) approved_amount, sum(state = 'chargeback') chargeback_count, sum(if(state = 'chargeback', amount, 0)) chargeback_amount from ( select * from transactions union all select id, country, 'chargeback' state, amount, c.trans_date from chargebacks c left join transactions t on c.trans_id = t.id ) tmp group by month, country having approved_amount or chargeback_amount
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
1194. 锦标赛优胜者
难度困难
SQL架构
Players 玩家表
+-------------+-------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+-------+
| player_id | int |
| group_id | int |
+-------------+-------+
玩家 ID 是此表的主键。
此表的每一行表示每个玩家的组。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Matches 赛事表
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| match_id | int |
| first_player | int |
| second_player | int |
| first_score | int |
| second_score | int |
+---------------+---------+
match_id 是此表的主键。
每一行是一场比赛的记录,第一名和第二名球员包含每场比赛的球员 ID。
第一个玩家和第二个玩家的分数分别包含第一个玩家和第二个玩家的分数。
你可以假设,在每一场比赛中,球员都属于同一组。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
每组的获胜者是在组内得分最高的选手。如果平局,player_id 最小 的选手获胜。
编写一个 SQL 查询来查找每组中的获胜者。
查询结果格式如下所示
Players 表: +-----------+------------+ | player_id | group_id | +-----------+------------+ | 15 | 1 | | 25 | 1 | | 30 | 1 | | 45 | 1 | | 10 | 2 | | 35 | 2 | | 50 | 2 | | 20 | 3 | | 40 | 3 | +-----------+------------+ Matches 表: +------------+--------------+---------------+-------------+--------------+ | match_id | first_player | second_player | first_score | second_score | +------------+--------------+---------------+-------------+--------------+ | 1 | 15 | 45 | 3 | 0 | | 2 | 30 | 25 | 1 | 2 | | 3 | 30 | 15 | 2 | 0 | | 4 | 40 | 20 | 5 | 2 | | 5 | 35 | 50 | 1 | 1 | +------------+--------------+---------------+-------------+--------------+ Result 表: +-----------+------------+ | group_id | player_id | +-----------+------------+ | 1 | 15 | | 2 | 35 | | 3 | 40 | +-----------+------------+
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
union all
SELECT group_id, player_id FROM ( SELECT group_id, player_id, SUM(score) AS score FROM ( -- 每个用户总的 first_score SELECT Players.group_id, Players.player_id, SUM(Matches.first_score) AS score FROM Players JOIN Matches ON Players.player_id = Matches.first_player GROUP BY Players.player_id UNION ALL -- 每个用户总的 second_score SELECT Players.group_id, Players.player_id, SUM(Matches.second_score) AS score FROM Players JOIN Matches ON Players.player_id = Matches.second_player GROUP BY Players.player_id ) s GROUP BY player_id ORDER BY score DESC, player_id ) result GROUP BY group_id select group_id, player_id from ( select players.*, sum(if(player_id = first_player, first_score, second_score)) score from players join matches on player_id = first_player or player_id = second_player group by player_id order by score desc, player_id ) tmp group by group_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
1204. 最后一个能进入电梯的人
难度中等
SQL架构
表: Queue
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| person_id | int |
| person_name | varchar |
| weight | int |
| turn | int |
+-------------+---------+
person_id 是这个表的主键。
该表展示了所有等待电梯的人的信息。
表中 person_id 和 turn 列将包含从 1 到 n 的所有数字,其中 n 是表中的行数。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
电梯最大载重量为 1000。
写一条 SQL 查询语句查找最后一个能进入电梯且不超过重量限制的 person_name 。题目确保队列中第一位的人可以进入电梯 。
查询结果如下所示 :
Queue 表 +-----------+-------------------+--------+------+ | person_id | person_name | weight | turn | +-----------+-------------------+--------+------+ | 5 | George Washington | 250 | 1 | | 3 | John Adams | 350 | 2 | | 6 | Thomas Jefferson | 400 | 3 | | 2 | Will Johnliams | 200 | 4 | | 4 | Thomas Jefferson | 175 | 5 | | 1 | James Elephant | 500 | 6 | +-----------+-------------------+--------+------+ Result 表 +-------------------+ | person_name | +-------------------+ | Thomas Jefferson | +-------------------+ 为了简化,Queue 表按 turn 列由小到大排序。 上例中 George Washington(id 5), John Adams(id 3) 和 Thomas Jefferson(id 6) 将可以进入电梯,因为他们的体重和为 250 + 350 + 400 = 1000。 Thomas Jefferson(id 6) 是最后一个体重合适并进入电梯的人。 select person_name from( select person_name ,sum(weight) over(order by turn) t from Queue )t1 where t<=1000 order by t desc limit 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
1211. 查询结果的质量和占比
难度简单
SQL架构
查询表 Queries:
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| query_name | varchar |
| result | varchar |
| position | int |
| rating | int |
+-------------+---------+
此表没有主键,并可能有重复的行。
此表包含了一些从数据库中收集的查询信息。
“位置”(position)列的值为 1 到 500 。
“评分”(rating)列的值为 1 到 5 。评分小于 3 的查询被定义为质量很差的查询。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
将查询结果的质量 quality 定义为:
各查询结果的评分与其位置之间比率的平均值。
将劣质查询百分比 poor_query_percentage 为:
评分小于 3 的查询结果占全部查询结果的百分比。
编写一组 SQL 来查找每次查询的名称(query_name)、质量(quality) 和 劣质查询百分比(poor_query_percentage)。
质量(quality) 和劣质查询百分比(poor_query_percentage) 都应四舍五入到小数点后两位。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Queries table: +------------+-------------------+----------+--------+ | query_name | result | position | rating | +------------+-------------------+----------+--------+ | Dog | Golden Retriever | 1 | 5 | | Dog | German Shepherd | 2 | 5 | | Dog | Mule | 200 | 1 | | Cat | Shirazi | 5 | 2 | | Cat | Siamese | 3 | 3 | | Cat | Sphynx | 7 | 4 | +------------+-------------------+----------+--------+ Result table: +------------+---------+-----------------------+ | query_name | quality | poor_query_percentage | +------------+---------+-----------------------+ | Dog | 2.50 | 33.33 | | Cat | 0.66 | 33.33 | +------------+---------+-----------------------+ Dog 查询结果的质量为 ((5 / 1) + (5 / 2) + (1 / 200)) / 3 = 2.50 Dog 查询结果的劣质查询百分比为 (1 / 3) * 100 = 33.33 Cat 查询结果的质量为 ((2 / 5) + (3 / 3) + (4 / 7)) / 3 = 0.66 Cat 查询结果的劣质查询百分比为 (1 / 3) * 100 = 33.33 select query_name, round(avg(rating/position),2) quality, round(sum(if(rating<3,1,0))/count(*)*100,2) poor_query_percentage from Queries group by query_name
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
1212. 查询球队积分
难度中等
SQL架构
Table: Teams
+---------------+----------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+----------+
| team_id | int |
| team_name | varchar |
+---------------+----------+
此表的主键是 team_id,表中的每一行都代表一支独立足球队。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Table: Matches
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| match_id | int |
| host_team | int |
| guest_team | int |
| host_goals | int |
| guest_goals | int |
+---------------+---------+
此表的主键是 match_id,表中的每一行都代表一场已结束的比赛,比赛的主客队分别由它们自己的 id 表示,他们的进球由 host_goals 和 guest_goals 分别表示。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
积分规则如下:
- 赢一场得三分;
- 平一场得一分;
- 输一场不得分。
写出一条SQL语句以查询每个队的 team_id,team_name 和 num_points。结果根据 num_points 降序排序,如果有两队积分相同,那么这两队按 team_id 升序排序。
查询结果格式如下:
Teams table: +-----------+--------------+ | team_id | team_name | +-----------+--------------+ | 10 | Leetcode FC | | 20 | NewYork FC | | 30 | Atlanta FC | | 40 | Chicago FC | | 50 | Toronto FC | +-----------+--------------+ Matches table: +------------+--------------+---------------+-------------+--------------+ | match_id | host_team | guest_team | host_goals | guest_goals | +------------+--------------+---------------+-------------+--------------+ | 1 | 10 | 20 | 3 | 0 | | 2 | 30 | 10 | 2 | 2 | | 3 | 10 | 50 | 5 | 1 | | 4 | 20 | 30 | 1 | 0 | | 5 | 50 | 30 | 1 | 0 | +------------+--------------+---------------+-------------+--------------+ Result table: +------------+--------------+---------------+ | team_id | team_name | num_points | +------------+--------------+---------------+ | 10 | Leetcode FC | 7 | | 20 | NewYork FC | 3 | | 50 | Toronto FC | 3 | | 30 | Atlanta FC | 1 | | 40 | Chicago FC | 0 | +------------+--------------+---------------+ select team_id , team_name ,sum( if(team_id = host_team && host_goals>guest_goals ,3,0)+ if(team_id = host_team && host_goals=guest_goals,1,0)+ if(team_id = guest_team && host_goals=guest_goals,1,0)+ if(team_id = guest_team && host_goals<guest_goals ,3,0) )num_points from Teams t left join Matches m on t.team_id =m.host_team or t.team_id =m.guest_team group by team_id ,team_name order by num_points desc,team_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
1225. 报告系统状态的连续日期
难度困难
SQL架构
Table: Failed
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| fail_date | date |
+--------------+---------+
该表主键为 fail_date。
该表包含失败任务的天数.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Table: Succeeded
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| success_date | date |
+--------------+---------+
该表主键为 success_date。
该表包含成功任务的天数.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
系统 每天 运行一个任务。每个任务都独立于先前的任务。任务的状态可以是失败或是成功。
编写一个 SQL 查询 2019-01-01 到 2019-12-31 期间任务连续同状态 period_state 的起止日期(start_date 和 end_date)。即如果任务失败了,就是失败状态的起止日期,如果任务成功了,就是成功状态的起止日期。
最后结果按照起始日期 start_date 排序
查询结果样例如下所示:
Failed table: +-------------------+ | fail_date | +-------------------+ | 2018-12-28 | | 2018-12-29 | | 2019-01-04 | | 2019-01-05 | +-------------------+ Succeeded table: +-------------------+ | success_date | +-------------------+ | 2018-12-30 | | 2018-12-31 | | 2019-01-01 | | 2019-01-02 | | 2019-01-03 | | 2019-01-06 | +-------------------+ Result table: +--------------+--------------+--------------+ | period_state | start_date | end_date | +--------------+--------------+--------------+ | succeeded | 2019-01-01 | 2019-01-03 | | failed | 2019-01-04 | 2019-01-05 | | succeeded | 2019-01-06 | 2019-01-06 | +--------------+--------------+--------------+ 结果忽略了 2018 年的记录,因为我们只关心从 2019-01-01 到 2019-12-31 的记录 从 2019-01-01 到 2019-01-03 所有任务成功,系统状态为 "succeeded"。 从 2019-01-04 到 2019-01-05 所有任务失败,系统状态为 "failed"。 从 2019-01-06 到 2019-01-06 所有任务成功,系统状态为 "succeeded"。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
开窗函数
select type period_state, min(date) start_date, max(date) as end_date
from
(
select type, date, subdate(date,row_number()over(partition by type order by date)) as diff
from
(
select 'failed' as type, fail_date as date from Failed
where fail_date between '2019-01-01' and '2019-12-31'
union all
select 'succeeded' as type, success_date as date from Succeeded
where success_date between '2019-01-01' and '2019-12-31'
) a
)b
group by type,diff
order by start_date
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
1241. 每个帖子的评论数
难度简单
SQL架构
表 Submissions 结构如下:
+---------------+----------+
| 列名 | 类型 |
+---------------+----------+
| sub_id | int |
| parent_id | int |
+---------------+----------+
上表没有主键, 所以可能会出现重复的行。
每行可以是一个帖子或对该帖子的评论。
如果是帖子的话,parent_id 就是 null。
对于评论来说,parent_id 就是表中对应帖子的 sub_id。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
编写 SQL 语句以查找每个帖子的评论数。
结果表应包含帖子的 post_id 和对应的评论数 number_of_comments 并且按 post_id 升序排列。
Submissions 可能包含重复的评论。您应该计算每个帖子的唯一评论数。
Submissions 可能包含重复的帖子。您应该将它们视为一个帖子。
查询结果格式如下例所示:
Submissions table: +---------+------------+ | sub_id | parent_id | +---------+------------+ | 1 | Null | | 2 | Null | | 1 | Null | | 12 | Null | | 3 | 1 | | 5 | 2 | | 3 | 1 | | 4 | 1 | | 9 | 1 | | 10 | 2 | | 6 | 7 | +---------+------------+ 结果表: +---------+--------------------+ | post_id | number_of_comments | +---------+--------------------+ | 1 | 3 | | 2 | 2 | | 12 | 0 | +---------+--------------------+ 表中 ID 为 1 的帖子有 ID 为 3、4 和 9 的三个评论。表中 ID 为 3 的评论重复出现了,所以我们只对它进行了一次计数。 表中 ID 为 2 的帖子有 ID 为 5 和 10 的两个评论。 ID 为 12 的帖子在表中没有评论。 表中 ID 为 6 的评论是对 ID 为 7 的已删除帖子的评论,因此我们将其忽略。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
后join
select s.sub_id post_id,ifnull(number_of_comments,0) number_of_comments
from Submissions s
left join (
select parent_id ,count(distinct sub_id) number_of_comments
from Submissions
group by parent_id
) t1
on s.sub_id = t1.parent_id
where s.parent_id is null
group by post_id,number_of_comments
order by sub_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
先join
SELECT post_id, COUNT(sub_id) AS number_of_comments
FROM (
SELECT DISTINCT post.sub_id AS post_id, sub.sub_id AS sub_id
FROM Submissions post
LEFT JOIN Submissions sub
ON post.sub_id = sub.parent_id
WHERE post.parent_id is null
) T
GROUP BY post_id
ORDER BY post_id ASC
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
1251. 平均售价
难度简单
SQL架构
Table: Prices
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| start_date | date |
| end_date | date |
| price | int |
+---------------+---------+
(product_id,start_date,end_date) 是 Prices 表的主键。
Prices 表的每一行表示的是某个产品在一段时期内的价格。
每个产品的对应时间段是不会重叠的,这也意味着同一个产品的价格时段不会出现交叉。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Table: UnitsSold
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| purchase_date | date |
| units | int |
+---------------+---------+
UnitsSold 表没有主键,它可能包含重复项。
UnitsSold 表的每一行表示的是每种产品的出售日期,单位和产品 id。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
编写SQL查询以查找每种产品的平均售价。average_price 应该四舍五入到小数点后两位。查询结果格式如下例所示:
Prices table: +------------+------------+------------+--------+ | product_id | start_date | end_date | price | +------------+------------+------------+--------+ | 1 | 2019-02-17 | 2019-02-28 | 5 | | 1 | 2019-03-01 | 2019-03-22 | 20 | | 2 | 2019-02-01 | 2019-02-20 | 15 | | 2 | 2019-02-21 | 2019-03-31 | 30 | +------------+------------+------------+--------+ UnitsSold table: +------------+---------------+-------+ | product_id | purchase_date | units | +------------+---------------+-------+ | 1 | 2019-02-25 | 100 | | 1 | 2019-03-01 | 15 | | 2 | 2019-02-10 | 200 | | 2 | 2019-03-22 | 30 | +------------+---------------+-------+ Result table: +------------+---------------+ | product_id | average_price | +------------+---------------+ | 1 | 6.96 | | 2 | 16.96 | +------------+---------------+ 平均售价 = 产品总价 / 销售的产品数量。 产品 1 的平均售价 = ((100 * 5)+(15 * 20) )/ 115 = 6.96 产品 2 的平均售价 = ((200 * 15)+(30 * 30) )/ 230 = 16.96 SELECT product_id, Round(SUM(sales) / SUM(units), 2) AS average_price FROM ( SELECT Prices.product_id AS product_id, Prices.price * UnitsSold.units AS sales, UnitsSold.units AS units FROM Prices JOIN UnitsSold ON Prices.product_id = UnitsSold.product_id WHERE UnitsSold.purchase_date BETWEEN Prices.start_date AND Prices.end_date ) T GROUP BY product_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
2表关联的时候直接把日期做过滤
1264. 页面推荐
难度中等
SQL架构
朋友关系列表: Friendship
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user1_id | int |
| user2_id | int |
+---------------+---------+
这张表的主键是 (user1_id, user2_id)。
这张表的每一行代表着 user1_id 和 user2_id 之间存在着朋友关系。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
喜欢列表: Likes
+-------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| page_id | int |
+-------------+---------+
这张表的主键是 (user_id, page_id)。
这张表的每一行代表着 user_id 喜欢 page_id。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
写一段 SQL 向user_id = 1 的用户,推荐其朋友们喜欢的页面。不要推荐该用户已经喜欢的页面。
你返回的结果中不应当包含重复项。
返回结果的格式如下例所示:
Friendship table: +----------+----------+ | user1_id | user2_id | +----------+----------+ | 1 | 2 | | 1 | 3 | | 1 | 4 | | 2 | 3 | | 2 | 4 | | 2 | 5 | | 6 | 1 | +----------+----------+ Likes table: +---------+---------+ | user_id | page_id | +---------+---------+ | 1 | 88 | | 2 | 23 | | 3 | 24 | | 4 | 56 | | 5 | 11 | | 6 | 33 | | 2 | 77 | | 3 | 77 | | 6 | 88 | +---------+---------+ Result table: +------------------+ | recommended_page | +------------------+ | 23 | | 24 | | 56 | | 33 | | 77 | +------------------+ 用户1 同 用户2, 3, 4, 6 是朋友关系。 推荐页面为: 页面23 来自于 用户2, 页面24 来自于 用户3, 页面56 来自于 用户3 以及 页面33 来自于 用户6。 页面77 同时被 用户2 和 用户3 推荐。 页面88 没有被推荐,因为 用户1 已经喜欢了它。 select distinct page_id recommended_page from Likes where user_id in( select if(user1_id=1,user2_id,user1_id) user_id from Friendship where user1_id =1 or user2_id =1 ) and page_id not in (select page_id from Likes where user_id=1)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
1270. 向公司CEO汇报工作的所有人
难度中等
SQL架构
员工表:Employees
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| employee_id | int |
| employee_name | varchar |
| manager_id | int |
+---------------+---------+
employee_id 是这个表的主键。
这个表中每一行中,employee_id 表示职工的 ID,employee_name 表示职工的名字,manager_id 表示该职工汇报工作的直线经理。
这个公司 CEO 是 employee_id = 1 的人。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
用 SQL 查询出所有直接或间接向公司 CEO 汇报工作的职工的 employee_id 。
由于公司规模较小,经理之间的间接关系不超过 3 个经理。
可以以任何顺序返回的结果,不需要去重。
查询结果示例如下:
Employees table: +-------------+---------------+------------+ | employee_id | employee_name | manager_id | +-------------+---------------+------------+ | 1 | Boss | 1 | | 3 | Alice | 3 | | 2 | Bob | 1 | | 4 | Daniel | 2 | | 7 | Luis | 4 | | 8 | Jhon | 3 | | 9 | Angela | 8 | | 77 | Robert | 1 | +-------------+---------------+------------+ Result table: +-------------+ | employee_id | +-------------+ | 2 | | 77 | | 4 | | 7 | +-------------+ 公司 CEO 的 employee_id 是 1. employee_id 是 2 和 77 的职员直接汇报给公司 CEO。 employee_id 是 4 的职员间接汇报给公司 CEO 4 --> 2 --> 1 。 employee_id 是 7 的职员间接汇报给公司 CEO 7 --> 4 --> 2 --> 1 。 employee_id 是 3, 8 ,9 的职员不会直接或间接的汇报给公司 CEO。 select employee_id from ( select a.employee_id from Employees a left join Employees b on a.manager_id = b.employee_id left join Employees c on b.manager_id = c.employee_id where a.manager_id=1 or b.manager_id=1 or c.manager_id=1 )t1 where employee_id!=1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
1280. 学生们参加各科测试的次数
难度简单
SQL架构
学生表: Students
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| student_id | int |
| student_name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
主键为 student_id(学生ID),该表内的每一行都记录有学校一名学生的信息。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
科目表: Subjects
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| subject_name | varchar |
+--------------+---------+
主键为 subject_name(科目名称),每一行记录学校的一门科目名称。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
考试表: Examinations
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| student_id | int |
| subject_name | varchar |
+--------------+---------+
这张表压根没有主键,可能会有重复行。
学生表里的一个学生修读科目表里的每一门科目,而这张考试表的每一行记录就表示学生表里的某个学生参加了一次科目表里某门科目的测试。
SELECT a.student_id, a.student_name, b.subject_name, COUNT(e.subject_name) AS attended_exams
FROM Students a CROSS JOIN Subjects b
LEFT JOIN Examinations e ON a.student_id = e.student_id AND b.subject_name = e.subject_name
GROUP BY a.student_id, b.subject_name
ORDER BY a.student_id, b.subject_name
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
CROSS JOIN Mysql中没有full outer join hive中可以用
1285. 找到连续区间的开始和结束数字
难度中等
SQL架构
表:Logs
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| log_id | int |
+---------------+---------+
id 是上表的主键。
上表的每一行包含日志表中的一个 ID。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
后来一些 ID 从 Logs 表中删除。编写一个 SQL 查询得到 Logs 表中的连续区间的开始数字和结束数字。
将查询表按照 start_id 排序。
查询结果格式如下面的例子:
Logs 表: +------------+ | log_id | +------------+ | 1 | | 2 | | 3 | | 7 | | 8 | | 10 | +------------+ 结果表: +------------+--------------+ | start_id | end_id | +------------+--------------+ | 1 | 3 | | 7 | 8 | | 10 | 10 | +------------+--------------+ 结果表应包含 Logs 表中的所有区间。 从 1 到 3 在表中。 从 4 到 6 不在表中。 从 7 到 8 在表中。 9 不在表中。 10 在表中。 SELECT MIN(log_id) start_id, MAX(log_id) end_id FROM (SELECT log_id, log_id - row_number() OVER(ORDER BY log_id) as diff FROM Logs) t GROUP BY diff
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
相似1225题
1294. 不同国家的天气类型
难度简单
SQL架构
国家表:Countries
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| country_id | int |
| country_name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
country_id 是这张表的主键。
该表的每行有 country_id 和 country_name 两列。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
天气表:Weather
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| country_id | int |
| weather_state | varchar |
| day | date |
+---------------+---------+
(country_id, day) 是该表的复合主键。
该表的每一行记录了某个国家某一天的天气情况。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
写一段 SQL 来找到表中每个国家在 2019 年 11 月的天气类型。
天气类型的定义如下:当 weather_state 的平均值小于或等于15返回 Cold,当 weather_state 的平均值大于或等于 25 返回 Hot,否则返回 Warm。
你可以以任意顺序返回你的查询结果。
查询结果格式如下所示:
Countries table: +------------+--------------+ | country_id | country_name | +------------+--------------+ | 2 | USA | | 3 | Australia | | 7 | Peru | | 5 | China | | 8 | Morocco | | 9 | Spain | +------------+--------------+ Weather table: +------------+---------------+------------+ | country_id | weather_state | day | +------------+---------------+------------+ | 2 | 15 | 2019-11-01 | | 2 | 12 | 2019-10-28 | | 2 | 12 | 2019-10-27 | | 3 | -2 | 2019-11-10 | | 3 | 0 | 2019-11-11 | | 3 | 3 | 2019-11-12 | | 5 | 16 | 2019-11-07 | | 5 | 18 | 2019-11-09 | | 5 | 21 | 2019-11-23 | | 7 | 25 | 2019-11-28 | | 7 | 22 | 2019-12-01 | | 7 | 20 | 2019-12-02 | | 8 | 25 | 2019-11-05 | | 8 | 27 | 2019-11-15 | | 8 | 31 | 2019-11-25 | | 9 | 7 | 2019-10-23 | | 9 | 3 | 2019-12-23 | +------------+---------------+------------+ Result table: +--------------+--------------+ | country_name | weather_type | +--------------+--------------+ | USA | Cold | | Austraila | Cold | | Peru | Hot | | China | Warm | | Morocco | Hot | +--------------+--------------+ USA 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (15) / 1 = 15 所以天气类型为 Cold。 Australia 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (-2 + 0 + 3) / 3 = 0.333 所以天气类型为 Cold。 Peru 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (25) / 1 = 25 所以天气类型为 Hot。 China 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (16 + 18 + 21) / 3 = 18.333 所以天气类型为 Warm。 Morocco 11 月的平均 weather_state 为 (25 + 27 + 31) / 3 = 27.667 所以天气类型为 Hot。 我们并不知道 Spain 在 11 月的 weather_state 情况所以无需将他包含在结果中。 select country_name,( case when avg(weather_state)<=15 then 'Cold' when avg(weather_state)>=25 then 'Hot' else 'Warm' end ) weather_type from Countries c join Weather w on c.country_id = w.country_id where date_format(day,"%Y-%m")='2019-11' group by country_name
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
1303. 求团队人数
难度简单
SQL架构
员工表:Employee
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| employee_id | int |
| team_id | int |
+---------------+---------+
employee_id 字段是这张表的主键,表中的每一行都包含每个员工的 ID 和他们所属的团队。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
编写一个 SQL 查询,以求得每个员工所在团队的总人数。
查询结果中的顺序无特定要求。
查询结果格式示例如下:
Employee Table: +-------------+------------+ | employee_id | team_id | +-------------+------------+ | 1 | 8 | | 2 | 8 | | 3 | 8 | | 4 | 7 | | 5 | 9 | | 6 | 9 | +-------------+------------+ Result table: +-------------+------------+ | employee_id | team_size | +-------------+------------+ | 1 | 3 | | 2 | 3 | | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 1 | | 5 | 2 | | 6 | 2 | +-------------+------------+ ID 为 1、2、3 的员工是 team_id 为 8 的团队的成员, ID 为 4 的员工是 team_id 为 7 的团队的成员, ID 为 5、6 的员工是 team_id 为 9 的团队的成员。 select employee_id,count(*) over(partition by team_id) team_size from Employee
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
1308. 不同性别每日分数总计
难度中等
SQL架构
表: Scores
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| player_name | varchar |
| gender | varchar |
| day | date |
| score_points | int |
+---------------+---------+
(gender, day)是该表的主键
一场比赛是在女队和男队之间举行的
该表的每一行表示一个名叫 (player_name) 性别为 (gender) 的参赛者在某一天获得了 (score_points) 的分数
如果参赛者是女性,那么 gender 列为 'F',如果参赛者是男性,那么 gender 列为 'M'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
写一条SQL语句查询每种性别在每一天的总分,并按性别和日期对查询结果排序
下面是查询结果格式的例子:
Scores表: +-------------+--------+------------+--------------+ | player_name | gender | day | score_points | +-------------+--------+------------+--------------+ | Aron | F | 2020-01-01 | 17 | | Alice | F | 2020-01-07 | 23 | | Bajrang | M | 2020-01-07 | 7 | | Khali | M | 2019-12-25 | 11 | | Slaman | M | 2019-12-30 | 13 | | Joe | M | 2019-12-31 | 3 | | Jose | M | 2019-12-18 | 2 | | Priya | F | 2019-12-31 | 23 | | Priyanka | F | 2019-12-30 | 17 | +-------------+--------+------------+--------------+ 结果表: +--------+------------+-------+ | gender | day | total | +--------+------------+-------+ | F | 2019-12-30 | 17 | | F | 2019-12-31 | 40 | | F | 2020-01-01 | 57 | | F | 2020-01-07 | 80 | | M | 2019-12-18 | 2 | | M | 2019-12-25 | 13 | | M | 2019-12-30 | 26 | | M | 2019-12-31 | 29 | | M | 2020-01-07 | 36 | +--------+------------+-------+ 女性队伍: 第一天是 2019-12-30,Priyanka 获得 17 分,队伍的总分是 17 分 第二天是 2019-12-31, Priya 获得 23 分,队伍的总分是 40 分 第三天是 2020-01-01, Aron 获得 17 分,队伍的总分是 57 分 第四天是 2020-01-07, Alice 获得 23 分,队伍的总分是 80 分 男性队伍: 第一天是 2019-12-18, Jose 获得 2 分,队伍的总分是 2 分 第二天是 2019-12-25, Khali 获得 11 分,队伍的总分是 13 分 第三天是 2019-12-30, Slaman 获得 13 分,队伍的总分是 26 分 第四天是 2019-12-31, Joe 获得 3 分,队伍的总分是 29 分 第五天是 2020-01-07, Bajrang 获得 7 分,队伍的总分是 36 分 select gender , day ,sum( score_points) over(partition by gender order by day) total from Scores
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
1321. 餐馆营业额变化增长
难度中等
SQL架构
表: Customer
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| customer_id | int |
| name | varchar |
| visited_on | date |
| amount | int |
+---------------+---------+
(customer_id, visited_on) 是该表的主键
该表包含一家餐馆的顾客交易数据
visited_on 表示 (customer_id) 的顾客在 visited_on 那天访问了餐馆
amount 是一个顾客某一天的消费总额
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
你是餐馆的老板,现在你想分析一下可能的营业额变化增长(每天至少有一位顾客)
写一条 SQL 查询计算以 7 天(某日期 + 该日期前的 6 天)为一个时间段的顾客消费平均值
查询结果格式的例子如下:
- 查询结果按 visited_on 排序
- average_amount 要 保留两位小数,日期数据的格式为 (‘YYYY-MM-DD’)
Customer 表: +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+ | customer_id | name | visited_on | amount | +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+ | 1 | Jhon | 2019-01-01 | 100 | | 2 | Daniel | 2019-01-02 | 110 | | 3 | Jade | 2019-01-03 | 120 | | 4 | Khaled | 2019-01-04 | 130 | | 5 | Winston | 2019-01-05 | 110 | | 6 | Elvis | 2019-01-06 | 140 | | 7 | Anna | 2019-01-07 | 150 | | 8 | Maria | 2019-01-08 | 80 | | 9 | Jaze | 2019-01-09 | 110 | | 1 | Jhon | 2019-01-10 | 130 | | 3 | Jade | 2019-01-10 | 150 | +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+ 结果表: +--------------+--------------+----------------+ | visited_on | amount | average_amount | +--------------+--------------+----------------+ | 2019-01-07 | 860 | 122.86 | | 2019-01-08 | 840 | 120 | | 2019-01-09 | 840 | 120 | | 2019-01-10 | 1000 | 142.86 | +--------------+--------------+----------------+ 第一个七天消费平均值从 2019-01-01 到 2019-01-07 是 (100 + 110 + 120 + 130 + 110 + 140 + 150)/7 = 122.86 第二个七天消费平均值从 2019-01-02 到 2019-01-08 是 (110 + 120 + 130 + 110 + 140 + 150 + 80)/7 = 120 第三个七天消费平均值从 2019-01-03 到 2019-01-09 是 (120 + 130 + 110 + 140 + 150 + 80 + 110)/7 = 120 第四个七天消费平均值从 2019-01-04 到 2019-01-10 是 (130 + 110 + 140 + 150 + 80 + 110 + 130 + 150)/7 = 142.86 select visited_on,amount,round(amount/7,2) average_amount from ( select visited_on,ant,lag(visited_on,6,null) over(order by visited_on) lg, sum(ant) over(order by visited_on rows between 6 PRECEDING and current row) amount from( select visited_on ,sum(amount) ant from Customer group by visited_on )t1 )t2 where lg is not null
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
1322. 广告效果
难度简单8收藏分享切换为英文关注反馈
SQL架构
表: Ads
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| ad_id | int |
| user_id | int |
| action | enum |
+---------------+---------+
(ad_id, user_id) 是该表的主键
该表的每一行包含一条广告的 ID(ad_id),用户的 ID(user_id) 和用户对广告采取的行为 (action)
action 列是一个枚举类型 ('Clicked', 'Viewed', 'Ignored') 。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
一家公司正在运营这些广告并想计算每条广告的效果。
广告效果用点击通过率(Click-Through Rate:CTR)来衡量,公式如下:
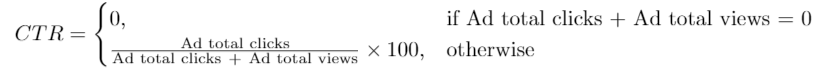
写一条SQL语句来查询每一条广告的 ctr ,
ctr 要保留两位小数。结果需要按 ctr降序、按 ad_id升序 进行排序。
查询结果示例如下:
Ads 表: +-------+---------+---------+ | ad_id | user_id | action | +-------+---------+---------+ | 1 | 1 | Clicked | | 2 | 2 | Clicked | | 3 | 3 | Viewed | | 5 | 5 | Ignored | | 1 | 7 | Ignored | | 2 | 7 | Viewed | | 3 | 5 | Clicked | | 1 | 4 | Viewed | | 2 | 11 | Viewed | | 1 | 2 | Clicked | +-------+---------+---------+ 结果表: +-------+-------+ | ad_id | ctr | +-------+-------+ | 1 | 66.67 | | 3 | 50.00 | | 2 | 33.33 | | 5 | 0.00 | +-------+-------+ 对于 ad_id = 1, ctr = (2/(2+1)) * 100 = 66.67 对于 ad_id = 2, ctr = (1/(1+2)) * 100 = 33.33 对于 ad_id = 3, ctr = (1/(1+1)) * 100 = 50.00 对于 ad_id = 5, ctr = 0.00, 注意 ad_id = 5 没有被点击 (Clicked) 或查看 (Viewed) 过 注意我们不关心 action 为 Ingnored 的广告 结果按 ctr(降序),ad_id(升序)排序
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
精简
SELECT ad_id,
ROUND(IFNULL(SUM(action = 'Clicked') /
(SUM(action = 'Clicked') + SUM(action = 'Viewed')) * 100, 0), 2) AS ctr
FROM Ads
GROUP BY ad_id
ORDER BY ctr DESC, ad_id ASC;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
笨方法
select a.ad_id,ifnull(ctr,0) ctr
from Ads a
left join (
select ad_id,round(sum(if(action='Clicked',1,0))/count(*)*100,2) ctr
from Ads
where action !='Ignored'
group by ad_id
)t1
on a.ad_id= t1.ad_id
group by ad_id,ctr
order by ctr desc,ad_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
1327. 列出指定时间段内所有的下单产品
难度简单
SQL架构
表: Products
+------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+------------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
| product_category | varchar |
+------------------+---------+
product_id 是该表主键。
该表包含该公司产品的数据。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
表: Orders
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| unit | int |
+---------------+---------+
该表无主键,可能包含重复行。
product_id 是表单 Products 的外键。
unit 是在日期 order_date 内下单产品的数目。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
写一个 SQL 语句,要求获取在 2020 年 2 月份下单的数量不少于 100 的产品的名字和数目。
返回结果表单的顺序无要求。
查询结果的格式如下:
Products 表: +-------------+-----------------------+------------------+ | product_id | product_name | product_category | +-------------+-----------------------+------------------+ | 1 | Leetcode Solutions | Book | | 2 | Jewels of Stringology | Book | | 3 | HP | Laptop | | 4 | Lenovo | Laptop | | 5 | Leetcode Kit | T-shirt | +-------------+-----------------------+------------------+ Orders 表: +--------------+--------------+----------+ | product_id | order_date | unit | +--------------+--------------+----------+ | 1 | 2020-02-05 | 60 | | 1 | 2020-02-10 | 70 | | 2 | 2020-01-18 | 30 | | 2 | 2020-02-11 | 80 | | 3 | 2020-02-17 | 2 | | 3 | 2020-02-24 | 3 | | 4 | 2020-03-01 | 20 | | 4 | 2020-03-04 | 30 | | 4 | 2020-03-04 | 60 | | 5 | 2020-02-25 | 50 | | 5 | 2020-02-27 | 50 | | 5 | 2020-03-01 | 50 | +--------------+--------------+----------+ Result 表: +--------------------+---------+ | product_name | unit | +--------------------+---------+ | Leetcode Solutions | 130 | | Leetcode Kit | 100 | +--------------------+---------+ 2020 年 2 月份下单 product_id = 1 的产品的数目总和为 (60 + 70) = 130 。 2020 年 2 月份下单 product_id = 2 的产品的数目总和为 80 。 2020 年 2 月份下单 product_id = 3 的产品的数目总和为 (2 + 3) = 5 。 2020 年 2 月份 product_id = 4 的产品并没有下单。 2020 年 2 月份下单 product_id = 5 的产品的数目总和为 (50 + 50) = 100 。 select product_name,sum(unit) unit from Orders o left join Products p on o.product_id=p.product_id where date_format(order_date,'%Y-%m')='2020-02' group by product_name having unit>=100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
1336. 每次访问的交易次数
难度困难
SQL架构
表: Visits
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| visit_date | date |
+---------------+---------+
(user_id, visit_date) 是该表的主键
该表的每行表示 user_id 在 visit_date 访问了银行
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表: Transactions
+------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+------------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| transaction_date | date |
| amount | int |
+------------------+---------+
该表没有主键,所以可能有重复行
该表的每一行表示 user_id 在 transaction_date 完成了一笔 amount 数额的交易
可以保证用户 (user) 在 transaction_date 访问了银行 (也就是说 Visits 表包含 (user_id, transaction_date) 行)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
银行想要得到银行客户在一次访问时的交易次数和相应的在一次访问时该交易次数的客户数量的图表
写一条 SQL 查询多少客户访问了银行但没有进行任何交易,多少客户访问了银行进行了一次交易等等
结果包含两列:
- transactions_count: 客户在一次访问中的交易次数
- visits_count: 在 transactions_count 交易次数下相应的一次访问时的客户数量
transactions_count的值从0到所有用户一次访问中的max(transactions_count)
按 transactions_count 排序
下面是查询结果格式的例子:
Visits 表: +---------+------------+ | user_id | visit_date | +---------+------------+ | 1 | 2020-01-01 | | 2 | 2020-01-02 | | 12 | 2020-01-01 | | 19 | 2020-01-03 | | 1 | 2020-01-02 | | 2 | 2020-01-03 | | 1 | 2020-01-04 | | 7 | 2020-01-11 | | 9 | 2020-01-25 | | 8 | 2020-01-28 | +---------+------------+ Transactions 表: +---------+------------------+--------+ | user_id | transaction_date | amount | +---------+------------------+--------+ | 1 | 2020-01-02 | 120 | | 2 | 2020-01-03 | 22 | | 7 | 2020-01-11 | 232 | | 1 | 2020-01-04 | 7 | | 9 | 2020-01-25 | 33 | | 9 | 2020-01-25 | 66 | | 8 | 2020-01-28 | 1 | | 9 | 2020-01-25 | 99 | +---------+------------------+--------+ 结果表: +--------------------+--------------+ | transactions_count | visits_count | +--------------------+--------------+ | 0 | 4 | | 1 | 5 | | 2 | 0 | | 3 | 1 | +--------------------+--------------+ * 对于 transactions_count = 0, visits 中 (1, "2020-01-01"), (2, "2020-01-02"), (12, "2020-01-01") 和 (19, "2020-01-03") 没有进行交易,所以 visits_count = 4 。 * 对于 transactions_count = 1, visits 中 (2, "2020-01-03"), (7, "2020-01-11"), (8, "2020-01-28"), (1, "2020-01-02") 和 (1, "2020-01-04") 进行了一次交易,所以 visits_count = 5 。 * 对于 transactions_count = 2, 没有客户访问银行进行了两次交易,所以 visits_count = 0 。 * 对于 transactions_count = 3, visits 中 (9, "2020-01-25") 进行了三次交易,所以 visits_count = 1 。 * 对于 transactions_count >= 4, 没有客户访问银行进行了超过3次交易,所以我们停止在 transactions_count = 3 。 如下是这个例子的图表: SELECT * FROM ( SELECT t5.rnb AS transactions_count, IFNULL(visits_count, 0) AS visits_count FROM ( SELECT 0 AS rnb UNION SELECT ROW_NUMBER() OVER () AS rnb FROM Transactions ) t5 LEFT JOIN ( SELECT cnt AS transactions_count ,COUNT(user_id) AS visits_count FROM ( SELECT t1.user_id, COUNT(t2.amount) AS cnt FROM Visits t1 LEFT JOIN Transactions t2 ON t1.user_id = t2.user_id AND t1.visit_date = t2.transaction_date GROUP BY user_id, visit_date ) t3 GROUP BY cnt ) t4 ON t5.rnb = t4.transactions_count ) t6 WHERE transactions_count <= ( SELECT COUNT(t2.amount) AS cnt FROM Visits t1 LEFT JOIN Transactions t2 ON t1.user_id = t2.user_id AND t1.visit_date = t2.transaction_date GROUP BY t1.user_id, visit_date ORDER BY cnt DESC LIMIT 1)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
难点 从0自增序列,2交易的人数为0
select pcnt transactions_count,count(*) visits_count
from (
select visit_date,
sum(if(amount is null,0,1)) over(partition by transaction_date ) pcnt,
count(*) over(partition by visit_date ) tcnt
from Visits v left join Transactions t
on v.user_id= t.user_id and v.visit_date=t.transaction_date
)t1
group by pcnt
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
这个得出结果是[0, 4], [1, 5], [3, 3] 少了[2,0] 还没想到什么好办法能把[2,0]加进去。。。
1341. 电影评分
难度中等
SQL架构
表:Movies
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| movie_id | int |
| title | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
movie_id 是这个表的主键。
title 是电影的名字。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表:Users
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
user_id 是表的主键。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
表:Movie_Rating
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| movie_id | int |
| user_id | int |
| rating | int |
| created_at | date |
+---------------+---------+
(movie_id, user_id) 是这个表的主键。
这个表包含用户在其评论中对电影的评分 rating 。
created_at 是用户的点评日期。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
请你编写一组 SQL 查询:
- 查找评论电影数量最多的用户名。
如果出现平局,返回字典序较小的用户名。
- 查找在
2020 年 2 月 平均评分最高
的电影名称。
如果出现平局,返回字典序较小的电影名称。
查询分两行返回,查询结果格式如下例所示:
Movies 表: +-------------+--------------+ | movie_id | title | +-------------+--------------+ | 1 | Avengers | | 2 | Frozen 2 | | 3 | Joker | +-------------+--------------+ Users 表: +-------------+--------------+ | user_id | name | +-------------+--------------+ | 1 | Daniel | | 2 | Monica | | 3 | Maria | | 4 | James | +-------------+--------------+ Movie_Rating 表: +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+ | movie_id | user_id | rating | created_at | +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+ | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2020-01-12 | | 1 | 2 | 4 | 2020-02-11 | | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2020-02-12 | | 1 | 4 | 1 | 2020-01-01 | | 2 | 1 | 5 | 2020-02-17 | | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2020-02-01 | | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2020-03-01 | | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2020-02-22 | | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2020-02-25 | +-------------+--------------+--------------+-------------+ Result 表: +--------------+ | results | +--------------+ | Daniel | | Frozen 2 | +--------------+ Daniel 和 Monica 都点评了 3 部电影("Avengers", "Frozen 2" 和 "Joker") 但是 Daniel 字典序比较小。 Frozen 2 和 Joker 在 2 月的评分都是 3.5,但是 Frozen 2 的字典序比较小。 select name results from ( select m.user_id ,u.name from Movie_Rating m left join Users u on m.user_id = u.user_id group by user_id order by count(*) desc,name limit 1 )t1 union ( select title results from Movie_Rating r left join Movies m on r.movie_id =m.movie_id where date_format(created_at,'%Y-%m')='2020-02' group by r.movie_id order by avg(rating) desc,title limit 1 )
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
1350. 院系无效的学生
难度简单
SQL架构
院系表: Departments
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
id 是该表的主键
该表包含一所大学每个院系的 id 信息
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
学生表: Students
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
| department_id | int |
+---------------+---------+
id 是该表的主键
该表包含一所大学每个学生的 id 和他/她就读的院系信息
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
写一条 SQL 语句以查询那些所在院系不存在的学生的 id 和姓名
可以以任何顺序返回结果
下面是返回结果格式的例子
Departments 表: +------+--------------------------+ | id | name | +------+--------------------------+ | 1 | Electrical Engineering | | 7 | Computer Engineering | | 13 | Bussiness Administration | +------+--------------------------+ Students 表: +------+----------+---------------+ | id | name | department_id | +------+----------+---------------+ | 23 | Alice | 1 | | 1 | Bob | 7 | | 5 | Jennifer | 13 | | 2 | John | 14 | | 4 | Jasmine | 77 | | 3 | Steve | 74 | | 6 | Luis | 1 | | 8 | Jonathan | 7 | | 7 | Daiana | 33 | | 11 | Madelynn | 1 | +------+----------+---------------+ 结果表: +------+----------+ | id | name | +------+----------+ | 2 | John | | 7 | Daiana | | 4 | Jasmine | | 3 | Steve | +------+----------+ John, Daiana, Steve 和 Jasmine 所在的院系分别是 14, 33, 74 和 77, 其中 14, 33, 74 和 77 并不存在于院系表 select id,name from Students where department_id not in ( select id from Departments )
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
1355. 活动参与者
难度中等
SQL架构
表: Friends
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
| activity | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
id 是朋友的 id 和该表的主键
name 是朋友的名字
activity 是朋友参加的活动的名字
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
表: Activities
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
id 是该表的主键
name 是活动的名字
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
写一条 SQL 查询那些既没有最多,也没有最少参与者的活动的名字
可以以任何顺序返回结果,Activities 表的每项活动的参与者都来自 Friends 表
下面是查询结果格式的例子:
Friends 表: +------+--------------+---------------+ | id | name | activity | +------+--------------+---------------+ | 1 | Jonathan D. | Eating | | 2 | Jade W. | Singing | | 3 | Victor J. | Singing | | 4 | Elvis Q. | Eating | | 5 | Daniel A. | Eating | | 6 | Bob B. | Horse Riding | +------+--------------+---------------+ Activities 表: +------+--------------+ | id | name | +------+--------------+ | 1 | Eating | | 2 | Singing | | 3 | Horse Riding | +------+--------------+ Result 表: +--------------+ | activity | +--------------+ | Singing | +--------------+ Eating 活动有三个人参加, 是最多人参加的活动 (Jonathan D. , Elvis Q. and Daniel A.) Horse Riding 活动有一个人参加, 是最少人参加的活动 (Bob B.) Singing 活动有两个人参加 (Victor J. and Jade W.) select activity from ( select activity, rank()over(order by cnt) rk1, rank()over(order by cnt desc) rk2 from ( select activity ,count(*) cnt from Friends group by activity )t1 )t2 where rk1 !=1 and rk2 != 1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
不需要关联 Activities表,因为 至少有一人参加
1364. 顾客的可信联系人数量
难度中等
SQL架构
顾客表:Customers
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| customer_id | int |
| customer_name | varchar |
| email | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
customer_id 是这张表的主键。
此表的每一行包含了某在线商店顾客的姓名和电子邮件。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
联系方式表:Contacts
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user_id | id |
| contact_name | varchar |
| contact_email | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
(user_id, contact_email) 是这张表的主键。
此表的每一行表示编号为 user_id 的顾客的某位联系人的姓名和电子邮件。
此表包含每位顾客的联系人信息,但顾客的联系人不一定存在于顾客表中。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
发票表:Invoices
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| invoice_id | int |
| price | int |
| user_id | int |
+--------------+---------+
invoice_id 是这张表的主键。
此表的每一行分别表示编号为 user_id 的顾客拥有有一张编号为 invoice_id、价格为 price 的发票。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
为每张发票 invoice_id 编写一个SQL查询以查找以下内容:
- customer_name:与发票相关的顾客名称。
- price:发票的价格。
- contacts_cnt:该顾客的联系人数量。
- trusted_contacts_cnt:可信联系人的数量:既是该顾客的联系人又是商店顾客的联系人数量(即:可信联系人的电子邮件存在于客户表中)。
将查询的结果按照 invoice_id 排序。
查询结果的格式如下例所示:
Customers table: +-------------+---------------+--------------------+ | customer_id | customer_name | email | +-------------+---------------+--------------------+ | 1 | Alice | alice@leetcode.com | | 2 | Bob | bob@leetcode.com | | 13 | John | john@leetcode.com | | 6 | Alex | alex@leetcode.com | +-------------+---------------+--------------------+ Contacts table: +-------------+--------------+--------------------+ | user_id | contact_name | contact_email | +-------------+--------------+--------------------+ | 1 | Bob | bob@leetcode.com | | 1 | John | john@leetcode.com | | 1 | Jal | jal@leetcode.com | | 2 | Omar | omar@leetcode.com | | 2 | Meir | meir@leetcode.com | | 6 | Alice | alice@leetcode.com | +-------------+--------------+--------------------+ Invoices table: +------------+-------+---------+ | invoice_id | price | user_id | +------------+-------+---------+ | 77 | 100 | 1 | | 88 | 200 | 1 | | 99 | 300 | 2 | | 66 | 400 | 2 | | 55 | 500 | 13 | | 44 | 60 | 6 | +------------+-------+---------+ Result table: +------------+---------------+-------+--------------+----------------------+ | invoice_id | customer_name | price | contacts_cnt | trusted_contacts_cnt | +------------+---------------+-------+--------------+----------------------+ | 44 | Alex | 60 | 1 | 1 | | 55 | John | 500 | 0 | 0 | | 66 | Bob | 400 | 2 | 0 | | 77 | Alice | 100 | 3 | 2 | | 88 | Alice | 200 | 3 | 2 | | 99 | Bob | 300 | 2 | 0 | +------------+---------------+-------+--------------+----------------------+ Alice 有三位联系人,其中两位(Bob 和 John)是可信联系人。 Bob 有两位联系人, 他们中的任何一位都不是可信联系人。 Alex 只有一位联系人(Alice),并是一位可信联系人。 John 没有任何联系人。 select invoice_id ,customer_name,price,ifnull(cnt,0) contacts_cnt,ifnull(bc,0) trusted_contacts_cnt from Invoices i left join ( select user_id ,count(*) cnt from Contacts group by user_id ) t1 on i.user_id=t1.user_id left join ( select user_id ,count(*) bc from Contacts where contact_name in ( select customer_name from Customers ) group by user_id )t2 on i.user_id = t2.user_id left join Customers c on i.user_id= c.customer_id order by invoice_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
就是麻烦点 各种join
1369. 获取最近第二次的活动
难度困难
SQL架构
表: UserActivity
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| username | varchar |
| activity | varchar |
| startDate | Date |
| endDate | Date |
+---------------+---------+
该表不包含主键
该表包含每个用户在一段时间内进行的活动的信息
名为 username 的用户在 startDate 到 endDate 日内有一次活动
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
写一条SQL查询展示每一位用户 最近第二次 的活动
如果用户仅有一次活动,返回该活动
一个用户不能同时进行超过一项活动,以 任意 顺序返回结果
下面是查询结果格式的例子:
UserActivity 表: +------------+--------------+-------------+-------------+ | username | activity | startDate | endDate | +------------+--------------+-------------+-------------+ | Alice | Travel | 2020-02-12 | 2020-02-20 | | Alice | Dancing | 2020-02-21 | 2020-02-23 | | Alice | Travel | 2020-02-24 | 2020-02-28 | | Bob | Travel | 2020-02-11 | 2020-02-18 | +------------+--------------+-------------+-------------+ Result 表: +------------+--------------+-------------+-------------+ | username | activity | startDate | endDate | +------------+--------------+-------------+-------------+ | Alice | Dancing | 2020-02-21 | 2020-02-23 | | Bob | Travel | 2020-02-11 | 2020-02-18 | +------------+--------------+-------------+-------------+ Alice 最近第二次的活动是从 2020-02-24 到 2020-02-28 的旅行, 在此之前的 2020-02-21 到 2020-02-23 她进行了舞蹈 Bob 只有一条记录,我们就取这条记录 select username, activity ,startDate,endDate from ( select username, activity ,startDate,endDate , rank()over(partition by username order by startDate desc) rk, lag( startDate ,1,null)over(partition by username order by startDate ) lg from UserActivity )t1 where rk=2 or (rk = 1 && lg is null)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
1378. 使用唯一标识码替换员工ID
难度简单
SQL架构
Employees 表:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
id 是这张表的主键。
这张表的每一行分别代表了某公司其中一位员工的名字和 ID 。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
EmployeeUNI 表:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| unique_id | int |
+---------------+---------+
(id, unique_id) 是这张表的主键。
这张表的每一行包含了该公司某位员工的 ID 和他的唯一标识码(unique ID)。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
写一段SQL查询来展示每位用户的 唯一标识码(unique ID );如果某位员工没有唯一标识码,使用 null 填充即可。
你可以以 任意 顺序返回结果表。
查询结果的格式如下例所示:
Employees table: +----+----------+ | id | name | +----+----------+ | 1 | Alice | | 7 | Bob | | 11 | Meir | | 90 | Winston | | 3 | Jonathan | +----+----------+ EmployeeUNI table: +----+-----------+ | id | unique_id | +----+-----------+ | 3 | 1 | | 11 | 2 | | 90 | 3 | +----+-----------+ EmployeeUNI table: +-----------+----------+ | unique_id | name | +-----------+----------+ | null | Alice | | null | Bob | | 2 | Meir | | 3 | Winston | | 1 | Jonathan | +-----------+----------+ Alice and Bob 没有唯一标识码, 因此我们使用 null 替代。 Meir 的唯一标识码是 2 。 Winston 的唯一标识码是 3 。 Jonathan 唯一标识码是 1 。 select unique_id,e.name from Employees e left join EmployeeUNI u on e.id = u.id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
1384. 按年度列出销售总额
难度困难
SQL架构
Product 表:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
product_id 是这张表的主键。
product_name 是产品的名称。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Sales 表:
+---------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| period_start | varchar |
| period_end | date |
| average_daily_sales | int |
+---------------------+---------+
product_id 是这张表的主键。
period_start 和 period_end 是该产品销售期的起始日期和结束日期,且这两个日期包含在销售期内。
average_daily_sales 列存储销售期内该产品的日平均销售额。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
编写一段SQL查询每个产品每年的总销售额,并包含 product_id, product_name 以及 report_year 等信息。
销售年份的日期介于 2018 年到 2020 年之间。你返回的结果需要按 product_id 和 report_year 排序。
查询结果格式如下例所示:
Product table: +------------+--------------+ | product_id | product_name | +------------+--------------+ | 1 | LC Phone | | 2 | LC T-Shirt | | 3 | LC Keychain | +------------+--------------+ Sales table: +------------+--------------+-------------+---------------------+ | product_id | period_start | period_end | average_daily_sales | +------------+--------------+-------------+---------------------+ | 1 | 2019-01-25 | 2019-02-28 | 100 | | 2 | 2018-12-01 | 2020-01-01 | 10 | | 3 | 2019-12-01 | 2020-01-31 | 1 | +------------+--------------+-------------+---------------------+ Result table: +------------+--------------+-------------+--------------+ | product_id | product_name | report_year | total_amount | +------------+--------------+-------------+--------------+ | 1 | LC Phone | 2019 | 3500 | | 2 | LC T-Shirt | 2018 | 310 | | 2 | LC T-Shirt | 2019 | 3650 | | 2 | LC T-Shirt | 2020 | 10 | | 3 | LC Keychain | 2019 | 31 | | 3 | LC Keychain | 2020 | 31 | +------------+--------------+-------------+--------------+ LC Phone 在 2019-01-25 至 2019-02-28 期间销售,该产品销售时间总计35天。销售总额 35*100 = 3500。 LC T-shirt 在 2018-12-01 至 2020-01-01 期间销售,该产品在2018年、2019年、2020年的销售时间分别是31天、365天、1天,2018年、2019年、2020年的销售总额分别是31*10=310、365*10=3650、1*10=10。 LC Keychain 在 2019-12-01 至 2020-01-31 期间销售,该产品在2019年、2020年的销售时间分别是:31天、31天,2019年、2020年的销售总额分别是31*1=31、31*1=31。 ( select Sales.product_id, product_name, '2018' as 'report_year', if(period_start<'2019-01-01', (datediff(if(period_end<'2019-01-01', period_end, date('2018-12-31')), if(period_start>='2018-01-01', period_start, date('2018-01-01')))+1)*average_daily_sales, 0) as total_amount from Sales join Product on Sales.product_id = Product.product_id having total_amount>0 ) union( select Sales.product_id, product_name, '2019' as 'report_year', if( period_start<'2020-01-01', (datediff(if(period_end<'2020-01-01', period_end, date('2019-12-31')), if(period_start>='2019-01-01', period_start, date('2019-01-01')))+1)*average_daily_sales , 0) as total_amount from Sales join Product on (Sales.product_id = Product.product_id ) having total_amount>0 ) union( select Sales.product_id, product_name, '2020' as 'report_year', (datediff(if(period_end<'2021-01-01', period_end, date('2020-12-31')), if(period_start>='2020-01-01', period_start, date('2020-01-01')))+1)*average_daily_sales as total_amount from Sales join Product on (Sales.product_id = Product.product_id) having total_amount>0 ) order by product_id, report_year
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
各个年份进行union,就是年份判断的时候麻烦些
1393. 股票的资本损益
难度中等
SQL架构
Stocks 表:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| stock_name | varchar |
| operation | enum |
| operation_day | int |
| price | int |
+---------------+---------+
(stock_name, day) 是这张表的主键
operation 列使用的是一种枚举类型,包括:('Sell','Buy')
此表的每一行代表了名为 stock_name 的某支股票在 operation_day 这一天的操作价格。
保证股票的每次'Sell'操作前,都有相应的'Buy'操作。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
编写一个SQL查询来报告每支股票的资本损益。
股票的资本损益是一次或多次买卖股票后的全部收益或损失。
以任意顺序返回结果即可。
SQL查询结果的格式如下例所示:
Stocks 表: +---------------+-----------+---------------+--------+ | stock_name | operation | operation_day | price | +---------------+-----------+---------------+--------+ | Leetcode | Buy | 1 | 1000 | | Corona Masks | Buy | 2 | 10 | | Leetcode | Sell | 5 | 9000 | | Handbags | Buy | 17 | 30000 | | Corona Masks | Sell | 3 | 1010 | | Corona Masks | Buy | 4 | 1000 | | Corona Masks | Sell | 5 | 500 | | Corona Masks | Buy | 6 | 1000 | | Handbags | Sell | 29 | 7000 | | Corona Masks | Sell | 10 | 10000 | +---------------+-----------+---------------+--------+ Result 表: +---------------+-------------------+ | stock_name | capital_gain_loss | +---------------+-------------------+ | Corona Masks | 9500 | | Leetcode | 8000 | | Handbags | -23000 | +---------------+-------------------+ Leetcode 股票在第一天以1000美元的价格买入,在第五天以9000美元的价格卖出。资本收益=9000-1000=8000美元。 Handbags 股票在第17天以30000美元的价格买入,在第29天以7000美元的价格卖出。资本损失=7000-30000=-23000美元。 Corona Masks 股票在第1天以10美元的价格买入,在第3天以1010美元的价格卖出。在第4天以1000美元的价格再次购买,在第5天以500美元的价格出售。最后,它在第6天以1000美元的价格被买走,在第10天以10000美元的价格被卖掉。资本损益是每次(’Buy'->'Sell')操作资本收益或损失的和=(1010-10)+(500-1000)+(10000-1000)=1000-500+9000=9500美元。 select stock_name,sell-buy capital_gain_loss from( select stock_name , sum(if(operation='Buy', price,0))over(partition by stock_name ) buy, sum(if(operation='Sell',price,0))over(partition by stock_name) sell from Stocks s )t1 group by stock_name,buy,sell
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
1398. 购买了产品A和产品B却没有购买产品C的顾客
难度中等
SQL架构
Customers 表:
+---------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------------+---------+
| customer_id | int |
| customer_name | varchar |
+---------------------+---------+
customer_id 是这张表的主键。
customer_name 是顾客的名称。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Orders 表:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| order_id | int |
| customer_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
order_id 是这张表的主键。
customer_id 是购买了名为 "product_name" 产品顾客的id。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
请你设计 SQL 查询来报告购买了产品 A 和产品 B 却没有购买产品 C 的顾客的 ID 和姓名( customer_id 和 customer_name ),我们将基于此结果为他们推荐产品 C 。您返回的查询结果需要按照 customer_id排序。
查询结果如下例所示。
Customers table: +-------------+---------------+ | customer_id | customer_name | +-------------+---------------+ | 1 | Daniel | | 2 | Diana | | 3 | Elizabeth | | 4 | Jhon | +-------------+---------------+ Orders table: +------------+--------------+---------------+ | order_id | customer_id | product_name | +------------+--------------+---------------+ | 10 | 1 | A | | 20 | 1 | B | | 30 | 1 | D | | 40 | 1 | C | | 50 | 2 | A | | 60 | 3 | A | | 70 | 3 | B | | 80 | 3 | D | | 90 | 4 | C | +------------+--------------+---------------+ Result table: +-------------+---------------+ | customer_id | customer_name | +-------------+---------------+ | 3 | Elizabeth | +-------------+---------------+ 只有 customer_id 为 3 的顾客购买了产品 A 和产品 B ,却没有购买产品 C 。 select o.customer_id, customer_name from Orders o left join Customers c on o.customer_id=c.customer_id group by customer_id having sum(product_name ='A')>=1 and sum(product_name='B')>=1 and sum(product_name='C')=0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
1407. 排名靠前的旅行者
难度简单
SQL架构
表单: Users
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
id 是该表单主键.
name 是用户名字.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表单: Rides
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| user_id | int |
| distance | int |
+---------------+---------+
id 是该表单主键.
user_id 是本次行程的用户的 id, 而该用户此次行程距离为 distance.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
写一段 SQL , 报告每个用户的旅行距离.
返回的结果表单, 以 travelled_distance 降序排列, 如果有两个或者更多的用户旅行了相同的距离, 那么再以 name 升序排列.
查询结果格式, 如下例所示.
Users 表单: +------+-----------+ | id | name | +------+-----------+ | 1 | Alice | | 2 | Bob | | 3 | Alex | | 4 | Donald | | 7 | Lee | | 13 | Jonathan | | 19 | Elvis | +------+-----------+ Rides 表单: +------+----------+----------+ | id | user_id | distance | +------+----------+----------+ | 1 | 1 | 120 | | 2 | 2 | 317 | | 3 | 3 | 222 | | 4 | 7 | 100 | | 5 | 13 | 312 | | 6 | 19 | 50 | | 7 | 7 | 120 | | 8 | 19 | 400 | | 9 | 7 | 230 | +------+----------+----------+ Result 表单: +----------+--------------------+ | name | travelled_distance | +----------+--------------------+ | Elvis | 450 | | Lee | 450 | | Bob | 317 | | Jonathan | 312 | | Alex | 222 | | Alice | 120 | | Donald | 0 | +----------+--------------------+ Elvis 和 Lee 旅行了 450 英里, Elvis 是排名靠前的旅行者, 因为他的名字在字母表上的排序比 Lee 更小. Bob, Jonathan, Alex 和 Alice 只有一次行程, 我们只按此次行程的全部距离对他们排序. Donald 没有任何行程, 他的旅行距离为 0. select name,sum(ifnull(distance,0)) travelled_distance from Users u left join Rides r on u.id = r.user_id group by name order by travelled_distance desc, name
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
1412. 查找成绩处于中游的学生
难度困难
SQL架构
表: Student
+---------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------------+---------+
| student_id | int |
| student_name | varchar |
+---------------------+---------+
student_id 是该表主键.
student_name 学生名字.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表: Exam
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| exam_id | int |
| student_id | int |
| score | int |
+---------------+---------+
(exam_id, student_id) 是该表主键.
学生 student_id 在测验 exam_id 中得分为 score.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
成绩处于中游的学生是指至少参加了一次测验, 且得分既不是最高分也不是最低分的学生。
写一个 SQL 语句,找出在所有测验中都处于中游的学生 (student_id, student_name)。
不要返回从来没有参加过测验的学生。返回结果表按照 student_id 排序。
查询结果格式如下。
Student 表: +-------------+---------------+ | student_id | student_name | +-------------+---------------+ | 1 | Daniel | | 2 | Jade | | 3 | Stella | | 4 | Jonathan | | 5 | Will | +-------------+---------------+ Exam 表: +------------+--------------+-----------+ | exam_id | student_id | score | +------------+--------------+-----------+ | 10 | 1 | 70 | | 10 | 2 | 80 | | 10 | 3 | 90 | | 20 | 1 | 80 | | 30 | 1 | 70 | | 30 | 3 | 80 | | 30 | 4 | 90 | | 40 | 1 | 60 | | 40 | 2 | 70 | | 40 | 4 | 80 | +------------+--------------+-----------+ Result 表: +-------------+---------------+ | student_id | student_name | +-------------+---------------+ | 2 | Jade | +-------------+---------------+ 对于测验 1: 学生 1 和 3 分别获得了最低分和最高分。 对于测验 2: 学生 1 既获得了最高分, 也获得了最低分。 对于测验 3 和 4: 学生 1 和 4 分别获得了最低分和最高分。 学生 2 和 5 没有在任一场测验中获得了最高分或者最低分。 因为学生 5 从来没有参加过任何测验, 所以他被排除于结果表。 由此, 我们仅仅返回学生 2 的信息。 select e.student_id,student_name from Exam e left join Student s on e.student_id=s.student_id where e.student_id not in( select student_id from( select student_id,rank() over(partition by exam_id order by score desc) rkmax, rank() over(partition by exam_id order by score ) rkmin from Exam )t1 where rkmax = 1 or rkmin =1 ) group by e.student_id,student_name order by e.student_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
1421. 净现值查询
难度中等
SQL架构
表: NPV
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| year | int |
| npv | int |
+---------------+---------+
(id, year) 是该表主键.
该表有每一笔存货的年份, id 和对应净现值的信息.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
表: Queries
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| year | int |
+---------------+---------+
(id, year) 是该表主键.
该表有每一次查询所对应存货的 id 和年份的信息.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
写一个 SQL, 找到 Queries 表中每一次查询的净现值.
结果表没有顺序要求.
查询结果的格式如下所示:
NPV 表: +------+--------+--------+ | id | year | npv | +------+--------+--------+ | 1 | 2018 | 100 | | 7 | 2020 | 30 | | 13 | 2019 | 40 | | 1 | 2019 | 113 | | 2 | 2008 | 121 | | 3 | 2009 | 12 | | 11 | 2020 | 99 | | 7 | 2019 | 0 | +------+--------+--------+ Queries 表: +------+--------+ | id | year | +------+--------+ | 1 | 2019 | | 2 | 2008 | | 3 | 2009 | | 7 | 2018 | | 7 | 2019 | | 7 | 2020 | | 13 | 2019 | +------+--------+ 结果表: +------+--------+--------+ | id | year | npv | +------+--------+--------+ | 1 | 2019 | 113 | | 2 | 2008 | 121 | | 3 | 2009 | 12 | | 7 | 2018 | 0 | | 7 | 2019 | 0 | | 7 | 2020 | 30 | | 13 | 2019 | 40 | +------+--------+--------+ (7, 2018)的净现值不在 NPV 表中, 我们把它看作是 0. 所有其它查询的净现值都能在 NPV 表中找到. select q.id,q.year,ifnull(npv,0) npv from Queries q left join NPV n on q.id = n.id and q.year = n.year
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
npv 净现值概念 了解下
1435. 制作会话柱状图
难度简单
SQL架构
表:Sessions
+---------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------------+---------+
| session_id | int |
| duration | int |
+---------------------+---------+
session_id 是该表主键
duration 是用户访问应用的时间, 以秒为单位
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
你想知道用户在你的 app 上的访问时长情况。因此决定统计访问时长区间分别为 “[0-5>”, “[5-10>”, “[10-15>” 和 “15 or more” (单位:分钟)的会话数量,并以此绘制柱状图。
写一个SQL查询来报告(访问时长区间,会话总数)。结果可用任何顺序呈现。
下方为查询的输出格式:
Sessions 表: +-------------+---------------+ | session_id | duration | +-------------+---------------+ | 1 | 30 | | 2 | 199 | | 3 | 299 | | 4 | 580 | | 5 | 1000 | +-------------+---------------+ Result 表: +--------------+--------------+ | bin | total | +--------------+--------------+ | [0-5> | 3 | | [5-10> | 1 | | [10-15> | 0 | | 15 or more | 1 | +--------------+--------------+ 对于 session_id 1,2 和 3 ,它们的访问时间大于等于 0 分钟且小于 5 分钟。 对于 session_id 4,它的访问时间大于等于 5 分钟且小于 10 分钟。 没有会话的访问时间大于等于 10 分钟且小于 15 分钟。 对于 session_id 5, 它的访问时间大于等于 15 分钟。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
Union
select '[0-5>' as bin, count(*) as total from Sessions where duration/60>=0 and duration/60<5
union
select '[5-10>' as bin, count(*) as total from Sessions where duration/60>=5 and duration/60<10
union
select '[10-15>' as bin, count(*) as total from Sessions where duration/60>=10 and duration/60<15
union
select '15 or more'as bin, count(*) as total from Sessions where duration/60>=15
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
还有很多其他解法
select a.bin, count(b.bin) as total from ( select '[0-5>' as bin union select '[5-10>' as bin union select '[10-15>' as bin union select '15 or more' as bin )a left join ( select case when duration < 300 then '[0-5>' when duration >= 300 and duration < 600 then '[5-10>' when duration >= 600 and duration < 900 then '[10-15>' else '15 or more' end bin from Sessions )b on a.bin = b.bin group by a.bin
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
1440. 计算布尔表达式的值
难度中等
SQL架构
表 Variables:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| name | varchar |
| value | int |
+---------------+---------+
name 是该表主键.
该表包含了存储的变量及其对应的值.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表 Expressions:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| left_operand | varchar |
| operator | enum |
| right_operand | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
(left_operand, operator, right_operand) 是该表主键.
该表包含了需要计算的布尔表达式.
operator 是枚举类型, 取值于('<', '>', '=')
left_operand 和 right_operand 的值保证存在于 Variables 表单中.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
写一个 SQL 查询, 以计算表 Expressions 中的布尔表达式.
返回的结果表没有顺序要求.
查询结果格式如下例所示.
Variables 表: +------+-------+ | name | value | +------+-------+ | x | 66 | | y | 77 | +------+-------+ Expressions 表: +--------------+----------+---------------+ | left_operand | operator | right_operand | +--------------+----------+---------------+ | x | > | y | | x | < | y | | x | = | y | | y | > | x | | y | < | x | | x | = | x | +--------------+----------+---------------+ Result 表: +--------------+----------+---------------+-------+ | left_operand | operator | right_operand | value | +--------------+----------+---------------+-------+ | x | > | y | false | | x | < | y | true | | x | = | y | false | | y | > | x | true | | y | < | x | false | | x | = | x | true | +--------------+----------+---------------+-------+ 如上所示, 你需要通过使用 Variables 表来找到 Expressions 表中的每一个布尔表达式的值. select e.left_operand,e.operator,e.right_operand, case e.operator when '>' then if(v1.value>v2.value,'true','false') when '<' then if(v1.value<v2.value,'true','false') else if(v1.value=v2.value,'true','false') end value from Expressions e left join Variables v1 on v1.name = e.left_operand left join Variables v2 on v2.name = e.right_operand
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
1445. 苹果和桔子
难度中等
SQL架构
表: Sales
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| sale_date | date |
| fruit | enum |
| sold_num | int |
+---------------+---------+
(sale_date,fruit) 是该表主键.
该表包含了每一天中"苹果" 和 "桔子"的销售情况.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
写一个 SQL 查询, 报告每一天 苹果 和 桔子 销售的数目的差异.
返回的结果表, 按照格式为 (‘YYYY-MM-DD’) 的 sale_date 排序.
查询结果表如下例所示:
Sales 表: +------------+------------+-------------+ | sale_date | fruit | sold_num | +------------+------------+-------------+ | 2020-05-01 | apples | 10 | | 2020-05-01 | oranges | 8 | | 2020-05-02 | apples | 15 | | 2020-05-02 | oranges | 15 | | 2020-05-03 | apples | 20 | | 2020-05-03 | oranges | 0 | | 2020-05-04 | apples | 15 | | 2020-05-04 | oranges | 16 | +------------+------------+-------------+ Result 表: +------------+--------------+ | sale_date | diff | +------------+--------------+ | 2020-05-01 | 2 | | 2020-05-02 | 0 | | 2020-05-03 | 20 | | 2020-05-04 | -1 | +------------+--------------+ 在 2020-05-01, 卖了 10 个苹果 和 8 个桔子 (差异为 10 - 8 = 2). 在 2020-05-02, 卖了 15 个苹果 和 15 个桔子 (差异为 15 - 15 = 0). 在 2020-05-03, 卖了 20 个苹果 和 0 个桔子 (差异为 20 - 0 = 20). 在 2020-05-04, 卖了 15 个苹果 和 16 个桔子 (差异为 15 - 16 = -1). select sale_date,sold_num-ld diff from ( select sale_date,sold_num , fruit ,lead(sold_num ,1,null) over(partition by sale_date ) ld from Sales )t1 where fruit='apples'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
1454. 活跃用户
难度中等
SQL架构
表 Accounts:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
id 是该表主键.
该表包含账户 id 和账户的用户名.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表 Logins:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| login_date | date |
+---------------+---------+
该表无主键, 可能包含重复项.
该表包含登录用户的账户 id 和登录日期. 用户也许一天内登录多次.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
写一个 SQL 查询, 找到活跃用户的 id 和 name.
活跃用户是指那些至少连续 5 天登录账户的用户.
返回的结果表按照 id 排序.
结果表格式如下例所示:
Accounts 表: +----+----------+ | id | name | +----+----------+ | 1 | Winston | | 7 | Jonathan | +----+----------+ Logins 表: +----+------------+ | id | login_date | +----+------------+ | 7 | 2020-05-30 | | 1 | 2020-05-30 | | 7 | 2020-05-31 | | 7 | 2020-06-01 | | 7 | 2020-06-02 | | 7 | 2020-06-02 | | 7 | 2020-06-03 | | 1 | 2020-06-07 | | 7 | 2020-06-10 | +----+------------+ Result 表: +----+----------+ | id | name | +----+----------+ | 7 | Jonathan | +----+----------+ id = 1 的用户 Winston 仅仅在不同的 2 天内登录了 2 次, 所以, Winston 不是活跃用户. id = 7 的用户 Jonathon 在不同的 6 天内登录了 7 次, , 6 天中有 5 天是连续的, 所以, Jonathan 是活跃用户.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
**后续问题:**如果活跃用户是那些至少连续 n 天登录账户的用户, 你能否写出通用的解决方案?
select t3.id,name from ( select distinct id from ( select id,login_date,lead(login_date,4,null) over(partition by id order by login_date) ld from ( select id,login_date from Logins group by id,login_date )t1 )t2 where datediff(ld,login_date)=4 )t3 left join Accounts a on t3.id = a.id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
注意用户当天重复登入
1459. 矩形面积
难度中等
SQL架构
表: Points
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| id | int |
| x_value | int |
| y_value | int |
+---------------+---------+
id 是该表主键.
每个点都表示为二维空间 (x_value, y_value).
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
写一个 SQL 语句, 报告由表中任意两点可以形成的所有可能的矩形.
结果表中的每一行包含三列 (p1, p2, area) 如下:
- p1 和 p2 是矩形两个对角的 id 且 p1 < p2.
- 矩形的面积由列 area 表示.
请按照面积大小降序排列,如果面积相同的话, 则按照 p1 和 p2 升序对结果表排序
Points 表: +----------+-------------+-------------+ | id | x_value | y_value | +----------+-------------+-------------+ | 1 | 2 | 8 | | 2 | 4 | 7 | | 3 | 2 | 10 | +----------+-------------+-------------+ Result 表: +----------+-------------+-------------+ | p1 | p2 | area | +----------+-------------+-------------+ | 2 | 3 | 6 | | 1 | 2 | 2 | +----------+-------------+-------------+ p1 应该小于 p2 并且面积大于 0. p1 = 1 且 p2 = 2 时, 面积等于 |2-4| * |8-7| = 2. p1 = 2 且 p2 = 3 时, 面积等于 |4-2| * |7-10| = 6. p1 = 1 且 p2 = 3 时, 是不可能为矩形的, 因为面积等于 0. select a.id P1,b.id P2,abs(a.x_value-b.x_value)*abs(a.y_value-b.y_value) as area from Points a,Points b where a.id<b.id and a.x_value != b.x_value and a.y_value != b.y_value order by area desc,P1 ,P2
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
1468. 计算税后工资
难度中等
SQL架构
Salaries 表:
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| company_id | int |
| employee_id | int |
| employee_name | varchar |
| salary | int |
+---------------+---------+
(company_id, employee_id) 是这个表的主键
这个表包括员工的company id, id, name 和 salary
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
写一条查询 SQL 来查找每个员工的税后工资
每个公司的税率计算依照以下规则
- 如果这个公司员工最高工资不到 1000 ,税率为 0%
- 如果这个公司员工最高工资在 1000 到 10000 之间,税率为 24%
- 如果这个公司员工最高工资大于 10000 ,税率为 49%
按任意顺序返回结果,税后工资结果取整
结果表格式如下例所示:
Salaries 表: +------------+-------------+---------------+--------+ | company_id | employee_id | employee_name | salary | +------------+-------------+---------------+--------+ | 1 | 1 | Tony | 2000 | | 1 | 2 | Pronub | 21300 | | 1 | 3 | Tyrrox | 10800 | | 2 | 1 | Pam | 300 | | 2 | 7 | Bassem | 450 | | 2 | 9 | Hermione | 700 | | 3 | 7 | Bocaben | 100 | | 3 | 2 | Ognjen | 2200 | | 3 | 13 | Nyancat | 3300 | | 3 | 15 | Morninngcat | 1866 | +------------+-------------+---------------+--------+ Result 表: +------------+-------------+---------------+--------+ | company_id | employee_id | employee_name | salary | +------------+-------------+---------------+--------+ | 1 | 1 | Tony | 1020 | | 1 | 2 | Pronub | 10863 | | 1 | 3 | Tyrrox | 5508 | | 2 | 1 | Pam | 300 | | 2 | 7 | Bassem | 450 | | 2 | 9 | Hermione | 700 | | 3 | 7 | Bocaben | 76 | | 3 | 2 | Ognjen | 1672 | | 3 | 13 | Nyancat | 2508 | | 3 | 15 | Morninngcat | 5911 | +------------+-------------+---------------+--------+ 对于公司 1 ,最高工资是 21300 ,其每个员工的税率为 49% 对于公司 2 ,最高工资是 700 ,其每个员工税率为 0% 对于公司 3 ,最高工资是 7777 ,其每个员工税率是 24% 税后工资计算 = 工资 - ( 税率 / 100)*工资 对于上述案例,Morninngcat 的税后工资 = 7777 - 7777 * ( 24 / 100) = 7777 - 1866.48 = 5910.52 ,取整为 5911 select company_id,employee_id , employee_name, round(case when maxsalary<1000 then salary when maxsalary<10000 then salary*(1-0.24) else salary*(1-0.49) end ,0)salary from( select *,max(salary) over(partition by company_id ) maxsalary from Salaries )t1
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
1479. 周内每天的销售情况
难度困难
SQL架构
表:Orders
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| order_id | int |
| customer_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| item_id | varchar |
| quantity | int |
+---------------+---------+
(order_id, item_id) 是该表主键
该表包含了订单信息
order_date 是id为 item_id 的商品被id为 customer_id 的消费者订购的日期.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
表:Items
+---------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------------+---------+
| item_id | varchar |
| item_name | varchar |
| item_category | varchar |
+---------------------+---------+
item_id 是该表主键
item_name 是商品的名字
item_category 是商品的类别
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
你是企业主,想要获得分类商品和周内每天的销售报告。
写一个SQL语句,报告 周内每天 每个商品类别下订购了多少单位。
返回结果表单 按商品类别排序 。
查询结果格式如下例所示:
Orders 表: +------------+--------------+-------------+--------------+-------------+ | order_id | customer_id | order_date | item_id | quantity | +------------+--------------+-------------+--------------+-------------+ | 1 | 1 | 2020-06-01 | 1 | 10 | | 2 | 1 | 2020-06-08 | 2 | 10 | | 3 | 2 | 2020-06-02 | 1 | 5 | | 4 | 3 | 2020-06-03 | 3 | 5 | | 5 | 4 | 2020-06-04 | 4 | 1 | | 6 | 4 | 2020-06-05 | 5 | 5 | | 7 | 5 | 2020-06-05 | 1 | 10 | | 8 | 5 | 2020-06-14 | 4 | 5 | | 9 | 5 | 2020-06-21 | 3 | 5 | +------------+--------------+-------------+--------------+-------------+ Items 表: +------------+----------------+---------------+ | item_id | item_name | item_category | +------------+----------------+---------------+ | 1 | LC Alg. Book | Book | | 2 | LC DB. Book | Book | | 3 | LC SmarthPhone | Phone | | 4 | LC Phone 2020 | Phone | | 5 | LC SmartGlass | Glasses | | 6 | LC T-Shirt XL | T-Shirt | +------------+----------------+---------------+ Result 表: +------------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+ | Category | Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday | Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday | +------------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+ | Book | 20 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | | Glasses | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | | Phone | 0 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 10 | | T-Shirt | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +------------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+-----------+ 在周一(2020-06-01, 2020-06-08),Book分类(ids: 1, 2)下,总共销售了20个单位(10 + 10) 在周二(2020-06-02),Book分类(ids: 1, 2)下,总共销售了5个单位 在周三(2020-06-03),Phone分类(ids: 3, 4)下,总共销售了5个单位 在周四(2020-06-04),Phone分类(ids: 3, 4)下,总共销售了1个单位 在周五(2020-06-05),Book分类(ids: 1, 2)下,总共销售了10个单位,Glasses分类(ids: 5)下,总共销售了5个单位 在周六, 没有商品销售 在周天(2020-06-14, 2020-06-21),Phone分类(ids: 3, 4)下,总共销售了10个单位(5 + 5) 没有销售 T-Shirt 类别的商品 select item_category as category, sum(case when num = 2 then quantity else 0 end) as Monday, sum(case when num = 3 then quantity else 0 end) as Tuesday, sum(case when num = 4 then quantity else 0 end) as Wednesday, sum(case when num = 5 then quantity else 0 end) as Thursday, sum(case when num = 6 then quantity else 0 end) as Friday, sum(case when num = 7 then quantity else 0 end) as Saturday, sum(case when num = 1 then quantity else 0 end) as Sunday from (select item_category, quantity,dayofweek(order_date) as num from items i left join orders o on i.item_id=o.item_id) t group by item_category order by item_category
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
1485. 按日期分组销售产品
难度简单
SQL架构
表 Activities:
+-------------+---------+
| 列名 | 类型 |
+-------------+---------+
| sell_date | date |
| product | varchar |
+-------------+---------+
此表没有主键,它可能包含重复项。
此表的每一行都包含产品名称和在市场上销售的日期。
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
编写一个 SQL 查询来查找每个日期、销售的不同产品的数量及其名称。每个日期的销售产品名称应按词典序排列。返回按 sell_date 排序的结果表。
查询结果格式如下例所示。
Activities 表: +------------+-------------+ | sell_date | product | +------------+-------------+ | 2020-05-30 | Headphone | | 2020-06-01 | Pencil | | 2020-06-02 | Mask | | 2020-05-30 | Basketball | | 2020-06-01 | Bible | | 2020-06-02 | Mask | | 2020-05-30 | T-Shirt | +------------+-------------+ Result 表: +------------+----------+------------------------------+ | sell_date | num_sold | products | +------------+----------+------------------------------+ | 2020-05-30 | 3 | Basketball,Headphone,T-shirt | | 2020-06-01 | 2 | Bible,Pencil | | 2020-06-02 | 1 | Mask | +------------+----------+------------------------------+ 对于2020-05-30,出售的物品是 (Headphone, Basketball, T-shirt),按词典序排列,并用逗号 ',' 分隔。 对于2020-06-01,出售的物品是 (Pencil, Bible),按词典序排列,并用逗号分隔。 对于2020-06-02,出售的物品是 (Mask),只需返回该物品名。 select sell_date, count(distinct product) num_sold, group_concat(distinct product order by product) products from Activities group by sell_date
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
行转列
1495. 上月播放的儿童适宜电影
难度简单
SQL架构
表: TVProgram
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| program_date | date |
| content_id | int |
| channel | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
(program_date, content_id) 是该表主键.
该表包含电视上的节目信息.
content_id 是电视一些频道上的节目的 id.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
表: Content
+------------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+------------------+---------+
| content_id | varchar |
| title | varchar |
| Kids_content | enum |
| content_type | varchar |
+------------------+---------+
content_id 是该表主键.
Kids_content 是枚举类型, 取值为('Y', 'N'), 其中:
'Y' 表示儿童适宜内容, 而'N'表示儿童不宜内容.
content_type 表示内容的类型, 比如电影, 电视剧等.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
写一个 SQL 语句, 报告在 2020 年 6 月份播放的儿童适宜电影的去重电影名.
返回的结果表单没有顺序要求.
查询结果的格式如下例所示.
TVProgram 表: +--------------------+--------------+-------------+ | program_date | content_id | channel | +--------------------+--------------+-------------+ | 2020-06-10 08:00 | 1 | LC-Channel | | 2020-05-11 12:00 | 2 | LC-Channel | | 2020-05-12 12:00 | 3 | LC-Channel | | 2020-05-13 14:00 | 4 | Disney Ch | | 2020-06-18 14:00 | 4 | Disney Ch | | 2020-07-15 16:00 | 5 | Disney Ch | +--------------------+--------------+-------------+ Content 表: +------------+----------------+---------------+---------------+ | content_id | title | Kids_content | content_type | +------------+----------------+---------------+---------------+ | 1 | Leetcode Movie | N | Movies | | 2 | Alg. for Kids | Y | Series | | 3 | Database Sols | N | Series | | 4 | Aladdin | Y | Movies | | 5 | Cinderella | Y | Movies | +------------+----------------+---------------+---------------+ Result 表: +--------------+ | title | +--------------+ | Aladdin | +--------------+ "Leetcode Movie" 是儿童不宜的电影. "Alg. for Kids" 不是电影. "Database Sols" 不是电影 "Alladin" 是电影, 儿童适宜, 并且在 2020 年 6 月份播放. "Cinderella" 不在 2020 年 6 月份播放. select distinct title from TVProgram t left join Content c on t.content_id = c.content_id where Kids_content ='Y' and date_format(program_date ,'%Y-%m')='2020-06' and content_type='Movies'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
LEFT()函数参见:https://www.begtut.com/sql/func-mysql-left.htmlREGEXP语法参见:https://www.cnblogs.com/timssd/p/5882742.htmlhttps://www.cnblogs.com/zhaopanpan/p/10133224.htmlDATE_FORMAT()函数参见:https://www.w3school.com.cn/sql/func_date_format.aspEXTRACT()函数参见:https://www.runoob.com/sql/func-extract.htmlDATEDIFF()函数参见:https://www.runoob.com/sql/func-datediff-mysql.htmlYEAR()函数参见:https://blog.csdn.net/moakun/article/details/82528829MONTH()函数参见:https://www.yiibai.com/mysql/month.html
1501. 可以放心投资的国家
难度中等
SQL架构
表 Person:
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+----------------+---------+
| id | int |
| name | varchar |
| phone_number | varchar |
+----------------+---------+
id 是该表主键.
该表每一行包含一个人的名字和电话号码.
电话号码的格式是:'xxx-yyyyyyy', 其中xxx是国家码(3个字符), yyyyyyy是电话号码(7个字符), x和y都表示数字. 同时, 国家码和电话号码都可以包含前导0.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
表 Country:
+----------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+----------------+---------+
| name | varchar |
| country_code | varchar |
+----------------+---------+
country_code是该表主键.
该表每一行包含国家名和国家码. country_code的格式是'xxx', x是数字.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
表 Calls:
+-------------+------+
| Column Name | Type |
+-------------+------+
| caller_id | int |
| callee_id | int |
| duration | int |
+-------------+------+
该表无主键, 可能包含重复行.
每一行包含呼叫方id, 被呼叫方id和以分钟为单位的通话时长. caller_id != callee_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
一家电信公司想要投资新的国家. 该公司想要投资的国家是: 该国的平均通话时长要严格地大于全球平均通话时长.
写一段 SQL, 找到所有该公司可以投资的国家.
返回的结果表没有顺序要求.
查询的结果格式如下例所示.
Person 表: +----+----------+--------------+ | id | name | phone_number | +----+----------+--------------+ | 3 | Jonathan | 051-1234567 | | 12 | Elvis | 051-7654321 | | 1 | Moncef | 212-1234567 | | 2 | Maroua | 212-6523651 | | 7 | Meir | 972-1234567 | | 9 | Rachel | 972-0011100 | +----+----------+--------------+ Country 表: +----------+--------------+ | name | country_code | +----------+--------------+ | Peru | 051 | | Israel | 972 | | Morocco | 212 | | Germany | 049 | | Ethiopia | 251 | +----------+--------------+ Calls 表: +-----------+-----------+----------+ | caller_id | callee_id | duration | +-----------+-----------+----------+ | 1 | 9 | 33 | | 2 | 9 | 4 | | 1 | 2 | 59 | | 3 | 12 | 102 | | 3 | 12 | 330 | | 12 | 3 | 5 | | 7 | 9 | 13 | | 7 | 1 | 3 | | 9 | 7 | 1 | | 1 | 7 | 7 | +-----------+-----------+----------+ Result 表: +----------+ | country | +----------+ | Peru | +----------+ 国家Peru的平均通话时长是 (102 + 102 + 330 + 330 + 5 + 5) / 6 = 145.666667 国家Israel的平均通话时长是 (33 + 4 + 13 + 13 + 3 + 1 + 1 + 7) / 8 = 9.37500 国家Morocco的平均通话时长是 (33 + 4 + 59 + 59 + 3 + 7) / 6 = 27.5000 全球平均通话时长 = (2 * (33 + 3 + 59 + 102 + 330 + 5 + 13 + 3 + 1 + 7)) / 20 = 55.70000 所以, Peru是唯一的平均通话时长大于全球平均通话时长的国家, 也是唯一的推荐投资的国家.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
笛卡尔积
select c2.name as country
from Calls c1,Person p,Country c2
where (p.id=c1.caller_id or p.id=c1.callee_id) and c2.country_code=left(p.phone_number,3)
group by c2.name
having avg(duration)>(select avg(duration) from Calls)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
思路更清晰
with people_country as ( select id, c.name country from Person p left join Country c on left(p.phone_number,3) = c.country_code ) select country from ( select country, avg(duration) avgtime from ( select caller_id id, duration from Calls union all select callee_id, duration from Calls ) t left join people_country using(id) group by country ) temp where avgtime > ( select avg(duration) avgtime from ( select caller_id, duration from Calls union all select callee_id, duration from Calls ) t )
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
1511. 消费者下单频率
难度简单
SQL架构
表: Customers
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| customer_id | int |
| name | varchar |
| country | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
customer_id 是该表主键.
该表包含公司消费者的信息.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
表: Product
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| description | varchar |
| price | int |
+---------------+---------+
product_id 是该表主键.
该表包含公司产品的信息.
price 是本产品的花销.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
表: Orders
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| order_id | int |
| customer_id | int |
| product_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| quantity | int |
+---------------+---------+
order_id 是该表主键.
该表包含消费者下单的信息.
customer_id 是买了数量为"quantity", id为"product_id"产品的消费者的 id.
Order_date 是订单发货的日期, 格式为('YYYY-MM-DD').
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
写一个 SQL 语句, 报告消费者的 id 和名字, 其中消费者在 2020 年 6 月和 7 月, 每月至少花费了$100.
结果表无顺序要求.
查询结果格式如下例所示.
Customers +--------------+-----------+-------------+ | customer_id | name | country | +--------------+-----------+-------------+ | 1 | Winston | USA | | 2 | Jonathan | Peru | | 3 | Moustafa | Egypt | +--------------+-----------+-------------+ Product +--------------+-------------+-------------+ | product_id | description | price | +--------------+-------------+-------------+ | 10 | LC Phone | 300 | | 20 | LC T-Shirt | 10 | | 30 | LC Book | 45 | | 40 | LC Keychain | 2 | +--------------+-------------+-------------+ Orders +--------------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----------+ | order_id | customer_id | product_id | order_date | quantity | +--------------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----------+ | 1 | 1 | 10 | 2020-06-10 | 1 | | 2 | 1 | 20 | 2020-07-01 | 1 | | 3 | 1 | 30 | 2020-07-08 | 2 | | 4 | 2 | 10 | 2020-06-15 | 2 | | 5 | 2 | 40 | 2020-07-01 | 10 | | 6 | 3 | 20 | 2020-06-24 | 2 | | 7 | 3 | 30 | 2020-06-25 | 2 | | 9 | 3 | 30 | 2020-05-08 | 3 | +--------------+-------------+-------------+-------------+-----------+ Result 表: +--------------+------------+ | customer_id | name | +--------------+------------+ | 1 | Winston | +--------------+------------+ Winston 在2020年6月花费了$300(300 * 1), 在7月花费了$100(10 * 1 + 45 * 2). Jonathan 在2020年6月花费了$600(300 * 2), 在7月花费了$20(2 * 10). Moustafa 在2020年6月花费了$110 (10 * 2 + 45 * 2), 在7月花费了$0. select customer_id,name from Customers where customer_id in (select customer_id from (select customer_id, month(order_date) as month , sum(quantity*price) as total from Orders o left join Product p on o.product_id = p.product_id where month(order_date) = 6 or month(order_date)=7 group by customer_id,month(order_date) ) as t1 where total >=100 group by customer_id having count(*)>=2 )
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
1517. Find Users With Valid E-Mails
难度简单
SQL架构
Table: Users
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| user_id | int |
| name | varchar |
| mail | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
user_id is the primary key for this table.
This table contains information of the users signed up in a website. Some e-mails are invalid.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Write an SQL query to find the users who have valid emails.
A valid e-mail has a prefix name and a domain where:
- The prefix name is a string that may contain letters (upper or lower case), digits, underscore ‘_’, period ‘.’ and/or dash ‘-’. The prefix name must start with a letter.
- The domain is ‘@leetcode.com’.
Return the result table in any order.
The query result format is in the following example.
Users +---------+-----------+-------------------------+ | user_id | name | mail | +---------+-----------+-------------------------+ | 1 | Winston | winston@leetcode.com | | 2 | Jonathan | jonathanisgreat | | 3 | Annabelle | bella-@leetcode.com | | 4 | Sally | sally.come@leetcode.com | | 5 | Marwan | quarz#2020@leetcode.com | | 6 | David | david69@gmail.com | | 7 | Shapiro | .shapo@leetcode.com | +---------+-----------+-------------------------+ Result table: +---------+-----------+-------------------------+ | user_id | name | mail | +---------+-----------+-------------------------+ | 1 | Winston | winston@leetcode.com | | 3 | Annabelle | bella-@leetcode.com | | 4 | Sally | sally.come@leetcode.com | +---------+-----------+-------------------------+ The mail of user 2 doesn't have a domain. The mail of user 5 has # sign which is not allowed. The mail of user 6 doesn't have leetcode domain. The mail of user 7 starts with a period.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
考察正则表达式的使用
SELECT *
FROM Users
WHERE mail REGEXP '^[a-zA-Z]+[\\w_\\.\\-]*@leetcode.com$'
ORDER BY user_id;
select * from Users
where mail regexp '^[a-zA-Z]+[a-zA-Z0-9_\\./\\-]{0,}@leetcode.com$'
order by user_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
坑点:1、前缀可能是一个字母,比如“J@leetcode.com”,所以匹配非首字母外的前缀字符数量要用{0,}或*,不能用+。2、题意要求:underscore ‘’, period ‘.’ and/or dash ‘-’,/没加单引号,不留神可能写漏/。3、后缀可能是“@leetcodeecom”,所以要对“.”加转义符号。4、后缀可能是“@LEETCODE.COM”,默认是不区分大小写匹配,所以要加上“BINARY”区分大小写。语法:1、https://www.cnblogs.com/timssd/p/5882742.html2、https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaopanpan/p/10133224.html3、"双反斜杠+w"表示字母、数字、下划线,相对"a-zA-Z0-9"的写法更简洁。
1527. Patients With a Condition
难度简单
SQL架构
Table: Patients
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| patient_id | int |
| patient_name | varchar |
| conditions | varchar |
+--------------+---------+
patient_id is the primary key for this table.
'conditions' contains 0 or more code separated by spaces.
This table contains information of the patients in the hospital.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Write an SQL query to report the patient_id, patient_name all conditions of patients who have Type I Diabetes. Type I Diabetes always starts with DIAB1 prefix
Return the result table in any order.
The query result format is in the following example.
Patients +------------+--------------+--------------+ | patient_id | patient_name | conditions | +------------+--------------+--------------+ | 1 | Daniel | YFEV COUGH | | 2 | Alice | | | 3 | Bob | DIAB100 MYOP | | 4 | George | ACNE DIAB100 | | 5 | Alain | DIAB201 | +------------+--------------+--------------+ Result table: +------------+--------------+--------------+ | patient_id | patient_name | conditions | +------------+--------------+--------------+ | 3 | Bob | DIAB100 MYOP | | 4 | George | ACNE DIAB100 | +------------+--------------+--------------+ Bob and George both have a condition that starts with DIAB1. select patient_id , patient_name ,conditions from Patients where conditions like '%DIAB1%'
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
1532. The Most Recent Three Orders
难度中等
SQL架构
Table: Customers
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| customer_id | int |
| name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
customer_id is the primary key for this table.
This table contains information about customers.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Table: Orders
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| order_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| customer_id | int |
| cost | int |
+---------------+---------+
order_id is the primary key for this table.
This table contains information about the orders made by customer_id.
Each customer has one order per day.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Write an SQL query to find the most recent 3 orders of each user. If a user ordered less than 3 orders return all of their orders.
Return the result table sorted by customer_name in ascending order and in case of a tie by the customer_id in ascending order. If there still a tie, order them by the order_date in descending order.
The query result format is in the following example:
Customers +-------------+-----------+ | customer_id | name | +-------------+-----------+ | 1 | Winston | | 2 | Jonathan | | 3 | Annabelle | | 4 | Marwan | | 5 | Khaled | +-------------+-----------+ Orders +----------+------------+-------------+------+ | order_id | order_date | customer_id | cost | +----------+------------+-------------+------+ | 1 | 2020-07-31 | 1 | 30 | | 2 | 2020-07-30 | 2 | 40 | | 3 | 2020-07-31 | 3 | 70 | | 4 | 2020-07-29 | 4 | 100 | | 5 | 2020-06-10 | 1 | 1010 | | 6 | 2020-08-01 | 2 | 102 | | 7 | 2020-08-01 | 3 | 111 | | 8 | 2020-08-03 | 1 | 99 | | 9 | 2020-08-07 | 2 | 32 | | 10 | 2020-07-15 | 1 | 2 | +----------+------------+-------------+------+ Result table: +---------------+-------------+----------+------------+ | customer_name | customer_id | order_id | order_date | +---------------+-------------+----------+------------+ | Annabelle | 3 | 7 | 2020-08-01 | | Annabelle | 3 | 3 | 2020-07-31 | | Jonathan | 2 | 9 | 2020-08-07 | | Jonathan | 2 | 6 | 2020-08-01 | | Jonathan | 2 | 2 | 2020-07-30 | | Marwan | 4 | 4 | 2020-07-29 | | Winston | 1 | 8 | 2020-08-03 | | Winston | 1 | 1 | 2020-07-31 | | Winston | 1 | 10 | 2020-07-15 | +---------------+-------------+----------+------------+ Winston has 4 orders, we discard the order of "2020-06-10" because it is the oldest order. Annabelle has only 2 orders, we return them. Jonathan has exactly 3 orders. Marwan ordered only one time. We sort the result table by customer_name in ascending order, by customer_id in ascending order and by order_date in descending order in case of a tie.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
**Follow-up:**Can you write a general solution for the most recent n orders?
select name customer_name ,customer_id,order_id,order_date
from (
select name ,o.customer_id,order_id,order_date ,rank()over(partition by o.customer_id order by order_date desc) rk
from Orders o left join Customers c
on o.customer_id=c.customer_id
)t1
where rk <=3
order by customer_name ,customer_id,order_date desc
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
1543. Fix Product Name Format
难度简单
SQL架构
Table: Sales
+--------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+--------------+---------+
| sale_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
| sale_date | date |
+--------------+---------+
sale_id is the primary key for this table.
Each row of this table contains the product name and the date it was sold.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Since table Sales was filled manually in the year 2000, product_name may contain leading and/or trailing white spaces, also they are case-insensitive.
Write an SQL query to report
- product_name in lowercase without leading or trailing white spaces.
- sale_date in the format (‘YYYY-MM’)
- total the number of times the product was sold in this month.
Return the result table ordered by product_name in ascending order, in case of a tie order it by sale_date in ascending order.
The query result format is in the following example.
Sales +------------+------------------+--------------+ | sale_id | product_name | sale_date | +------------+------------------+--------------+ | 1 | LCPHONE | 2000-01-16 | | 2 | LCPhone | 2000-01-17 | | 3 | LcPhOnE | 2000-02-18 | | 4 | LCKeyCHAiN | 2000-02-19 | | 5 | LCKeyChain | 2000-02-28 | | 6 | Matryoshka | 2000-03-31 | +------------+------------------+--------------+ Result table: +--------------+--------------+----------+ | product_name | sale_date | total | +--------------+--------------+----------+ | lcphone | 2000-01 | 2 | | lckeychain | 2000-02 | 2 | | lcphone | 2000-02 | 1 | | matryoshka | 2000-03 | 1 | +--------------+--------------+----------+ In January, 2 LcPhones were sold, please note that the product names are not case sensitive and may contain spaces. In Februery, 2 LCKeychains and 1 LCPhone were sold. In March, 1 matryoshka was sold. select trim(lower(product_name)) as product_name, date_format(sale_date,'%Y-%m') as sale_date, count(*) as total from Sales group by trim(lower(product_name)), date_format(sale_date,'%Y-%m') order by product_name asc, sale_date asc
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
注意大小写、空格
1549. The Most Recent Orders for Each Product
难度中等
SQL架构
Table: Customers
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| customer_id | int |
| name | varchar |
+---------------+---------+
customer_id is the primary key for this table.
This table contains information about the customers.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Table: Orders
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| order_id | int |
| order_date | date |
| customer_id | int |
| product_id | int |
+---------------+---------+
order_id is the primary key for this table.
This table contains information about the orders made by customer_id.
There will be no product ordered by the same user more than once in one day.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
Table: Products
+---------------+---------+
| Column Name | Type |
+---------------+---------+
| product_id | int |
| product_name | varchar |
| price | int |
+---------------+---------+
product_id is the primary key for this table.
This table contains information about the Products.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Write an SQL query to find the most recent order(s) of each product.
Return the result table sorted by product_name in ascending order and in case of a tie by the product_id in ascending order. If there still a tie, order them by the order_id in ascending order.
The query result format is in the following example:
Customers +-------------+-----------+ | customer_id | name | +-------------+-----------+ | 1 | Winston | | 2 | Jonathan | | 3 | Annabelle | | 4 | Marwan | | 5 | Khaled | +-------------+-----------+ Orders +----------+------------+-------------+------------+ | order_id | order_date | customer_id | product_id | +----------+------------+-------------+------------+ | 1 | 2020-07-31 | 1 | 1 | | 2 | 2020-07-30 | 2 | 2 | | 3 | 2020-08-29 | 3 | 3 | | 4 | 2020-07-29 | 4 | 1 | | 5 | 2020-06-10 | 1 | 2 | | 6 | 2020-08-01 | 2 | 1 | | 7 | 2020-08-01 | 3 | 1 | | 8 | 2020-08-03 | 1 | 2 | | 9 | 2020-08-07 | 2 | 3 | | 10 | 2020-07-15 | 1 | 2 | +----------+------------+-------------+------------+ Products +------------+--------------+-------+ | product_id | product_name | price | +------------+--------------+-------+ | 1 | keyboard | 120 | | 2 | mouse | 80 | | 3 | screen | 600 | | 4 | hard disk | 450 | +------------+--------------+-------+ Result table: +--------------+------------+----------+------------+ | product_name | product_id | order_id | order_date | +--------------+------------+----------+------------+ | keyboard | 1 | 6 | 2020-08-01 | | keyboard | 1 | 7 | 2020-08-01 | | mouse | 2 | 8 | 2020-08-03 | | screen | 3 | 3 | 2020-08-29 | +--------------+------------+----------+------------+ keyboard's most recent order is in 2020-08-01, it was ordered two times this day. mouse's most recent order is in 2020-08-03, it was ordered only once this day. screen's most recent order is in 2020-08-29, it was ordered only once this day. The hard disk was never ordered and we don't include it in the result table. select product_name,product_id,order_id,order_date from ( select product_name ,o.product_id ,order_id,order_date , rank() over(partition by o.product_id order by order_date desc) rk from Orders o left join Products p on o.product_id =p.product_id )t1 where rk =1 order by product_name,product_id,order_id
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60



