这几天又在玩树莓派,先是搞了个物联网,又在尝试在树莓派上搞一些简单的神经网络,这次搞得是mlp识别mnist手写数字识别
训练代码在电脑上,cpu就能训练,很快的:
- 1 import torch
- 2 import torch.nn as nn
- 3 import torch.optim as optim
- 4 from torchvision import datasets, transforms
- 5
- 6 # 设置随机种子
- 7 torch.manual_seed(42)
- 8
- 9 # 定义MLP模型
- 10 class MLP(nn.Module):
- 11 def __init__(self):
- 12 super(MLP, self).__init__()
- 13 self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784, 256)
- 14 self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
- 15 self.fc3 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
- 16
- 17 def forward(self, x):
- 18 x = x.view(-1, 784)
- 19 x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
- 20 x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
- 21 x = self.fc3(x)
- 22 return x
- 23
- 24 # 加载MNIST数据集
- 25 transform = transforms.Compose([
- 26 transforms.ToTensor(),
- 27 # transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
- 28 ])
- 29
- 30 train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
- 31 test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, download=True, transform=transform)
- 32
- 33 train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
- 34 test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=64, shuffle=False)
- 35
- 36 # 创建模型实例
- 37 model = MLP()
- 38
- 39 # 定义损失函数和优化器
- 40 criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
- 41 optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.5)
- 42
- 43 # 训练模型
- 44 def train(model, train_loader, optimizer, criterion, epochs):
- 45 model.train()
- 46 for epoch in range(1, epochs + 1):
- 47 for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
- 48 optimizer.zero_grad()
- 49 output = model(data)
- 50 loss = criterion(output, target)
- 51 loss.backward()
- 52 optimizer.step()
- 53
- 54 if batch_idx % 100 == 0:
- 55 print('Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
- 56 epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
- 57 100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
- 58
- 59 # 训练模型
- 60 train(model, train_loader, optimizer, criterion, epochs=5)
- 61
- 62 # 保存模型为NumPy格式
- 63 numpy_model = {}
- 64 numpy_model['fc1.weight'] = model.fc1.weight.detach().numpy()
- 65 numpy_model['fc1.bias'] = model.fc1.bias.detach().numpy()
- 66 numpy_model['fc2.weight'] = model.fc2.weight.detach().numpy()
- 67 numpy_model['fc2.bias'] = model.fc2.bias.detach().numpy()
- 68 numpy_model['fc3.weight'] = model.fc3.weight.detach().numpy()
- 69 numpy_model['fc3.bias'] = model.fc3.bias.detach().numpy()
- 70
- 71 # 保存为NumPy格式的数据
- 72 import numpy as np
- 73 np.savez('mnist_model.npz', **numpy_model)
然后需要自己倒出一些图片在dataset里:我保存在了mnist_pi文件夹下,“_”后面的是标签,主要是在pc端导出保存到树莓派下
树莓派推理端的代码,需要numpy手动重新搭建网络,然后加载那些保存的矩阵参数,做矩阵乘法和加法
- 1 import numpy as np
- 2 import os
- 3 from PIL import Image
- 4
- 5 # 加载模型
- 6 model_data = np.load('mnist_model.npz')
- 7 weights1 = model_data['fc1.weight']
- 8 biases1 = model_data['fc1.bias']
- 9 weights2 = model_data['fc2.weight']
- 10 biases2 = model_data['fc2.bias']
- 11 weights3 = model_data['fc3.weight']
- 12 biases3 = model_data['fc3.bias']
- 13
- 14 # 进行推理
- 15 def predict(image, weights1, biases1,weights2, biases2,weights3, biases3):
- 16 image = image.flatten()/255 # 将输入图像展平并进行归一化
- 17 output = np.dot(weights1, image) + biases1
- 18 output = np.dot(weights2, output) + biases2
- 19 output = np.dot(weights3, output) + biases3
- 20 predicted_class = np.argmax(output)
- 21 return predicted_class
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26 folder_path = './mnist_pi' # 替换为图片所在的文件夹路径
- 27 def infer_images_in_folder(folder_path):
- 28 for file_name in os.listdir(folder_path):
- 29 file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, file_name)
- 30 if os.path.isfile(file_path) and file_name.endswith(('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png')):
- 31 image = Image.open(file_path)
- 32 label = file_name.split(".")[0].split("_")[1]
- 33 image = np.array(image)
- 34 print("file_path:",file_path,"img size:",image.shape,"label:",label)
- 35 predicted_class = predict(image, weights1, biases1,weights2, biases2,weights3, biases3)
- 36 print('Predicted class:', predicted_class)
- 37
- 38 infer_images_in_folder(folder_path)
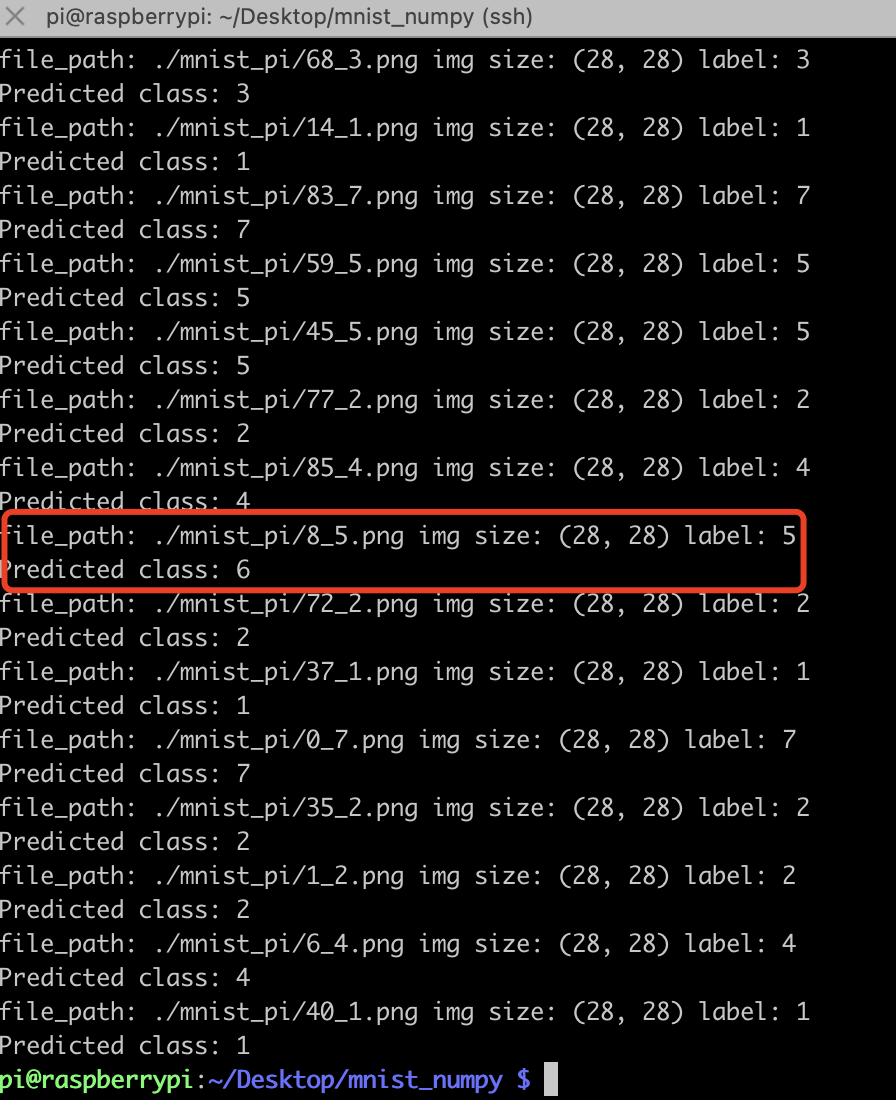
结果:
效果还不错:
这次内容就到这里了,下次争取做一个卷积的神经网络在树莓派上推理,然后争取做一个目标检测的模型在树莓派上



