- 1RTSP视频流显示(海康威视)
- 2新视频直播传输协议SRT使用简介_srt wob
- 3关于本地服务器怎么让外网访问到_服务器本地能上网需要异地访问服务器
- 4每日刷题总结——双指针_1229 - 寻找重复数
- 5Co. - VMware - vSphere
- 6Linux 中 Netcat 工具的使用_linux netcat
- 7win11浏览器显示“你尚未连接,代理服务器可能有问题,或地址不正确”_为什么微软浏览器显示尚未连接是什么原因
- 8【Linux】配置ssh免密登录_linux ssh authenticity
- 9Linux:使用ntpdate命令同步更新系统时间_ntpd 更新时间
- 10IPv6地址是免费的吗?用了IPV6是不是就不需要内网穿透了_ipv6还需要内网穿透吗
vue+flask实现视频目标检测yolov5_flask yolo 视频流
赞
踩
开始做这个之前,了解一些vue的基础,然后对flask完全不知道。所以特别感谢很多博主的文章。
主要参考的是这篇文章:在WEB端部署YOLOv5目标检测(Flask+VUE),博主在GitHub上详细的代码给我一个很好的参考,他采用的是前后端分离开发的方式。
一.前端搭建
参考视频:vue+elementUI管理平台系列
参考博客:Flask + Vue 搭建简易系统步骤总结
vue-cli2.9.6+ElementUI搭建。(首先要安装node)
1.搭建脚手架:npm install -g vue-cli@2.9.6
2.创建一个基于webpack模板的项目vue init webpack 自定义项目名
3.运行项目npm run dev
二.后端搭建
主要是yolov5环境的一个搭建。
参考博客:(1)使用conda创建python的虚拟环境,介绍了如何安装与删除虚拟环境
(2)【小白CV】手把手教你用YOLOv5训练自己的数据集(从Windows环境配置到模型部署),我的配置就是根据这个来的。
1.首先是虚拟环境的配置(最好是在虚拟环境中搭建,血与泪的教训),conda create -n torch107 python=3.7
2.激活虚拟环境activate torch107
3.安装pytorch,首先已经安装anaconda3,yolov5需要pytorch1.6以上,pip3 install torch==1.8.1+cu102 torchvision==0.9.1+cu102 torchaudio===0.8.1 -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html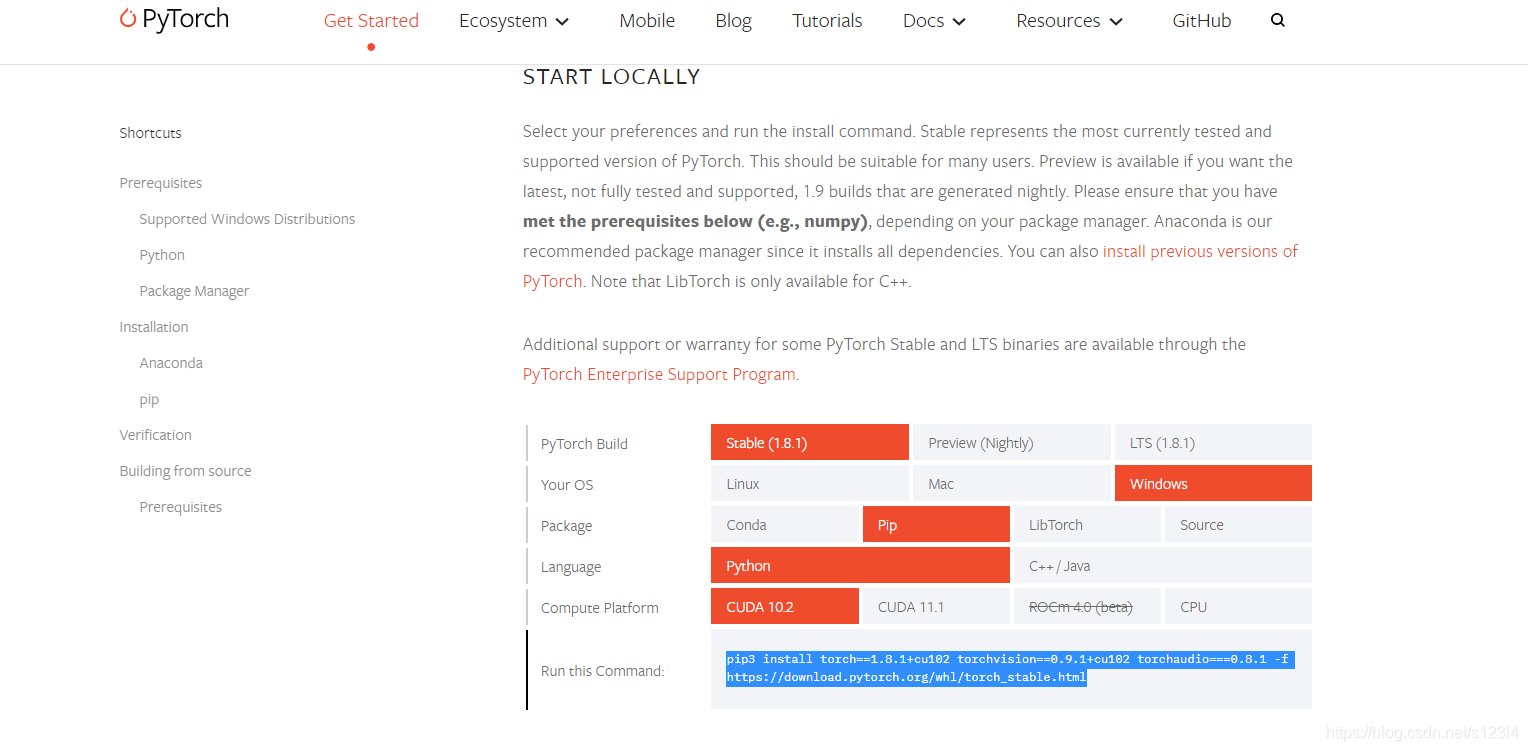
4.下载源码和安装环境依赖
源码指路:https://github.com/Sharpiless/Yolov5-Flask-VUE
安装依赖库:pip install -r requirements.txt,txt文件内容如下:
# pip install -r requirements.txt # base ---------------------------------------- matplotlib>=3.2.2 numpy>=1.18.5 opencv-python>=4.1.2 Pillow PyYAML>=5.3.1 scipy>=1.4.1 torch>=1.7.0 torchvision>=0.8.1 tqdm>=4.41.0 # logging ------------------------------------- tensorboard>=2.4.1 # wandb # plotting ------------------------------------ seaborn>=0.11.0 pandas # export -------------------------------------- # coremltools>=4.1 # onnx>=1.9.0 # scikit-learn==0.19.2 # for coreml quantization # extras -------------------------------------- # Cython # for pycocotools https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi/issues/172 pycocotools>=2.0 # COCO mAP thop # FLOPS computation
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
三.yolov5检测视频
参考视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1FK411K78w?t=1536,时间25:36以后
我的代码:
检测代码Detect.py:
import torch import numpy as np from models.experimental import attempt_load from utils.general import non_max_suppression, scale_coords, letterbox from utils.torch_utils import select_device import cv2 from random import randint class VideoCamera(object): def __init__(self): # 通过opencv获取实时视频流 self.img_size = 640 self.threshold = 0.4 self.max_frame = 160 self.video = cv2.VideoCapture("E:/videodata/1.mp4") #换成自己的视频文件 self.weights = 'weights/final.pt' #yolov5权重文件 self.device = '0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu' self.device = select_device(self.device) model = attempt_load(self.weights, map_location=self.device) model.to(self.device).eval() model.half() # torch.save(model, 'test.pt') self.m = model self.names = model.module.names if hasattr( model, 'module') else model.names self.colors = [ (randint(0, 255), randint(0, 255), randint(0, 255)) for _ in self.names ] def __del__(self): self.video.release() def get_frame(self): ret, frame = self.video.read() #读视频 im0, img = self.preprocess(frame) #转到处理函数 pred = self.m(img, augment=False)[0] #输入到模型 pred = pred.float() pred = non_max_suppression(pred, self.threshold, 0.3) pred_boxes = [] image_info = {} count = 0 for det in pred: if det is not None and len(det): det[:, :4] = scale_coords( img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im0.shape).round() for *x, conf, cls_id in det: lbl = self.names[int(cls_id)] x1, y1 = int(x[0]), int(x[1]) x2, y2 = int(x[2]), int(x[3]) pred_boxes.append( (x1, y1, x2, y2, lbl, conf)) count += 1 key = '{}-{:02}'.format(lbl, count) image_info[key] = ['{}×{}'.format( x2 - x1, y2 - y1), np.round(float(conf), 3)] frame = self.plot_bboxes(frame, pred_boxes) # 因为opencv读取的图片并非jpeg格式,因此要用motion JPEG模式需要先将图片转码成jpg格式图片 ret, jpeg = cv2.imencode('.jpg', frame) return jpeg.tobytes() def preprocess(self, img): img0 = img.copy() img = letterbox(img, new_shape=self.img_size)[0] img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) img = np.ascontiguousarray(img) img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(self.device) img = img.half() # 半精度 img /= 255.0 # 图像归一化 if img.ndimension() == 3: img = img.unsqueeze(0) return img0, img def plot_bboxes(self, image, bboxes, line_thickness=None): tl = line_thickness or round( 0.002 * (image.shape[0] + image.shape[1]) / 2) + 1 # line/font thickness for (x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_id, conf) in bboxes: color = self.colors[self.names.index(cls_id)] c1, c2 = (x1, y1), (x2, y2) cv2.rectangle(image, c1, c2, color, thickness=tl, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA) tf = max(tl - 1, 1) # font thickness t_size = cv2.getTextSize( cls_id, 0, fontScale=tl / 3, thickness=tf)[0] c2 = c1[0] + t_size[0], c1[1] - t_size[1] - 3 cv2.rectangle(image, c1, c2, color, -1, cv2.LINE_AA) # filled cv2.putText(image, '{}-{:.2f} '.format(cls_id, conf), (c1[0], c1[1] - 2), 0, tl / 3, [225, 255, 255], thickness=tf, lineType=cv2.LINE_AA) return image
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
app.py代码:
from flask import * import cv2 import logging as rel_log from datetime import timedelta from flask_cors import CORS from Detect import VideoCamera app = Flask(__name__) cors = CORS(app, resources={r"/getMsg": {"origins": "*"}}) #解决跨域问题,vue请求数据时能用上 @app.route('/') def index(): return render_template('index.html') #template文件夹下的index.html def gen(camera): while True: frame = camera.get_frame() # 使用generator函数输出视频流, 每次请求输出的content类型是image/jpeg yield (b'--frame\r\n' b'Content-Type: image/jpeg\r\n\r\n' + frame + b'\r\n\r\n') @app.route('/video_feed') # 这个地址返回视频流响应 def video_feed(): return Response(gen(VideoCamera()), mimetype='multipart/x-mixed-replace; boundary=frame') if __name__ == "__main__": app.run(host='127.0.0.1', port=5000, debug=True)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
index.html:
<html> <head> <title>视频检测</title> <style> div{ margin: 0 auto; text-align: center; width: 1200px; height: 800px; } img{ width: 100%; height: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div> <h1>linjie</h1> <img src="{{ url_for('video_feed') }}"> </div> </body> </html>
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
运行后端python app.py
输入http://localhost:5000/,得到一个用flask实现的网页端目标检测。至于如何将这个视频与vue写的前端结合起来,还请大家给点意见,我是直接通过:response = { 'image_url': 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/video_feed' },但总觉得哪里不妥。。。



