热门标签
热门文章
- 1C语言——简单的飞机小游戏_c语言飞机小游戏代码
- 2电力线路故障检测:机器学习应用于电力系统维护和故障预测_机器学习与水电机组故障检修的结合
- 3Java springbot项目qq机器人AI生成原神角色语音发送到QQ群,简单易懂,无需写python代码_spring bot机器人
- 4【论文笔记】BioGPT: generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining
- 5吴恩达2022机器学习专项课程(一) 4.5 线性回归的梯度下降
- 6CUDA、HIP、OpenCL和oneAPI编程模型总结及比较_cuda hip
- 7基于大数据技术的共享单车数据分析系统设计与实现任务书_基于hadoop的公共自行车数据分析设计与实现
- 8在 Amazon Timestream 上通过时序数据机器学习进行预测分析
- 9bootstrap + django的简单后台管理系统_bootstrap django
- 10标注工具—labelme, label-studio
当前位置: article > 正文
yolov5检测视频流的原理、detect.py解读
作者:IT小白 | 2024-04-05 18:41:24
赞
踩
yolov5检测视频
前言
yolov5可以检测视频,实验室为该实验配备了一个工业相机,并想使用该相机进行实时检测,为了能使用该相机,今天去看了下yolov5的源代码。记录下自己的体会。
一、先从readme开始
detect.pyruns inference on a variety of sources, downloading models automatically from the latest YOLOv5 release and saving results toruns/detect.
$ python detect.py --source 0 # webcam
file.jpg # image
file.mp4 # video
path/ # directory
path/*.jpg # glob
'https://youtu.be/NUsoVlDFqZg' # YouTube video
'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4' # RTSP, RTMP, HTTP stream
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
上面的语句是yolov5的readme文件的教程。传送门
可以看出,调用摄像头使用的是–source 参数,到detect.py去查看该参数是如何使用的。
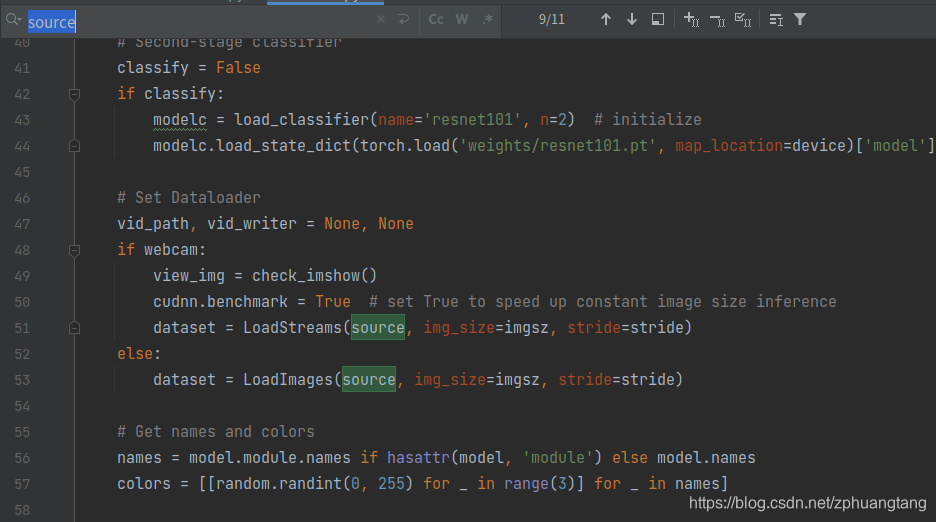
很明显是调用的是LoadStream()函数。
二、查看LoadStream()具体实现
class LoadStreams: # multiple IP or RTSP cameras def __init__(self, sources='streams.txt', img_size=640, stride=32): self.mode = 'stream' self.img_size = img_size self.stride = stride # 如果参数为源的列表,则读取为一个列表 if os.path.isfile(sources): with open(sources, 'r') as f: sources = [x.strip() for x in f.read().strip().splitlines() if len(x.strip())] else: sources = [sources] n = len(sources) self.imgs = [None] * n self.sources = [clean_str(x) for x in sources] # clean source names for later # 遍历列表 for i, s in enumerate(sources): # Start the thread to read frames from the video stream print(f'{i + 1}/{n}: {s}... ', end='') url = eval(s) if s.isnumeric() else s if 'youtube.com/' in url or 'youtu.be/' in url: # if source is YouTube video check_requirements(('pafy', 'youtube_dl')) import pafy url = pafy.new(url).getbest(preftype="mp4").url # 使用opencv读取帧 cap = cv2.VideoCapture(url) assert cap.isOpened(), f'Failed to open {s}' # 帧的宽高 w = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH)) h = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT)) self.fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS) % 100 _, self.imgs[i] = cap.read() # guarantee first frame # 使用多线程读取视频帧 thread = Thread(target=self.update, args=([i, cap]), daemon=True) print(f' success ({w}x{h} at {self.fps:.2f} FPS).') thread.start() print('') # newline # check for common shapes s = np.stack([letterbox(x, self.img_size, stride=self.stride)[0].shape for x in self.imgs], 0) # shapes self.rect = np.unique(s, axis=0).shape[0] == 1 # rect inference if all shapes equal if not self.rect: print('WARNING: Different stream shapes detected. For optimal performance supply similarly-shaped streams.') def update(self, index, cap): # Read next stream frame in a daemon thread n = 0 # 只要cap没有关闭,就是一直读取视频的帧 while cap.isOpened(): n += 1 # _, self.imgs[index] = cap.read() # 从视频文件或捕获设备抓取下一帧。 cap.grab() if n == 4: # read every 4th frame # cap.retrieve() 解码并安返回抓取的视频帧 success, im = cap.retrieve() self.imgs[index] = im if success else self.imgs[index] * 0 n = 0 time.sleep(1 / self.fps) # wait time # 作为可迭代对象,必须实现下面两个方法 def __iter__(self): self.count = -1 return self def __next__(self): self.count += 1 # 复制图片列表 img0 = self.imgs.copy() # 按q退出 if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord('q'): # q to quit cv2.destroyAllWindows() raise StopIteration # Letterbox img = [letterbox(x, self.img_size, auto=self.rect, stride=self.stride)[0] for x in img0] # Stack img = np.stack(img, 0) # Convert img = img[:, :, :, ::-1].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2) # BGR to RGB, to bsx3x416x416 img = np.ascontiguousarray(img) return self.sources, img, img0, None def __len__(self): return 0 # 1E12 frames = 32 streams at 30 FPS for 30 years
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
总结
对视频处理,工业相机需要使用第三方工具包来调用。
声明:本文内容由网友自发贡献,不代表【wpsshop博客】立场,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有侵权的内容,请联系我们。转载请注明出处:https://www.wpsshop.cn/w/IT小白/article/detail/367366
推荐阅读
相关标签



