- 1Redis 那些故障转移、高可用方案
- 2解读一下最近Midjourney开放的中国版_midjourney国内版和国外区别
- 3Java_单元测试、反射
- 4requests 代理设置问题解决方案_requests.post不走代理
- 5ChatGLM2-6B下载/部署/微调_chatglm下载
- 6排序算法--冒泡排序
- 7【EMQX】EMQX中webhook配置数据源 https以及http配置内容 规则引擎转发webhook_webhook emqx
- 8【kubernetes常用命令记录】_查看节点标签
- 9面试官给我挖坑:单台服务器并发TCP连接数到底可以有多少 ?_单台负载机 能发起多少并发
- 10(深度学习)PyCharm 连接配置服务器_pycharm连接服务器
使用窗函数方法设计FIR滤波器与MATLAB代码分析_ideal_lp
赞
踩
一,写在前面的话.
学习了以下链接,然后写出了MATLAB代码,在本文末,大家可以随便下载代码,进行尝试,我代码调试正常,可使用。
1. 如果你是初学者,建议你看一下这个链接https://blog.csdn.net/zhoufan900428/article/details/8969470
自学什么是窗函数,什么是滤波器,为啥要用窗函数,怎么计算一些值,怎么根据这些值选择窗函数。
2. 如果你明白了上述内容,但还不能单独写代码进行分析,推荐你看这个链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/xhslovecx/p/10196851.html
自学怎么计算,然后选好窗函数,就设计,写公式。在那文章末尾他给了MATLAB采用FIR I型设计20Hz以下的低通滤波器的代码。
3. 如果你明白了以上内容,那么就请看下去吧:
(代码都上传到下面了,随便用,但如果你要发表的话,请改一改,因为我的论文已经入库了,你要是直接抄,老师可能从查重率上把你毙了,改个参数名啥的可以,写论文很少发代码的)
二,简单介绍
我们知道IIR(无限脉冲响应)数字滤波器的设计方法是利用模拟滤波器成熟的理论及设计图表进行的,因而保留了一些典型模拟滤波器优良的幅度特性,但设计中只考虑到了幅度特性,没考虑到相位特性,所设计的滤波器相位特性一般是非线性的。而FIR(有限脉冲响应)滤波器在保证幅度特性满足技术要求的同时,比较容易做到有严格的线性相位特性。
FIR滤波器分为四种:LP(低通滤波器),HP(高通滤波器),BP(带通滤波器),BS(带阻滤波器)。

它们的公式我就不写了,但是需要知道。还要知道什么是线性相位FIR滤波器幅度特性和零点分布特点。
我们熟知的窗函数有:三角窗,矩形窗,汉明窗,汉宁窗,布莱克曼窗,

我们若是分析特性,则需要知道什么是主瓣,旁瓣,若是选择窗函数,则需要计算窗长度N,然后选择合适的阻带衰减(dB),阻带衰减不能比窗长度小。
然后写代码的时候,要手写时域表达式(这个叫写窗)。我把它们的公式写在下面:大家可以直接复制粘贴。
我直接贴了四个窗函数MATLAB的代码,请大家先参悟一下,再看加上滤波器的代码。
第一个是矩形窗:
第二个是汉宁窗
第三个是汉明窗
第四个是布莱克曼窗
希望大家结合公式与窗函数特性加上代码,参悟一下。
好了现在我们开始设计FIR滤波器,至于书面的计算过程我就不写了,又不懂得请参考本文“写在前面的话”的第一个链接的内容。
第一个例子,用汉明窗设计一个低通滤波器,Wp=0.2π, Ws=0.4π, Ap=0.25dB, As=50dB
- %%%%%Write by Han%%%%%这是实时脚本文件%%%%%
- close all;
- clc
- Wp=0.2*pi;
- Ws=0.4*pi;
- tr_width=Ws-Wp; %Transition zone width
- N=ceil(6.6*pi/tr_width)+1 %Filter length
- n=0:1:N-1;
- Wc=(Ws+Wp)/2; %Cutoff frequency of ideal low-pass filter
- hd = ideal_lp(Wc,N); %Unit impulse response of an ideal low-pass filter
- w_ham=0.54-0.46*cos(2*pi*n/(14+eps)); % Writing a haming window
- h=hd.*w_ham; %Truncated to the actual unit impulse response
- [db,mag,pha,w]=freqz_m4(h,[1]); %Calculate the amplitude response of the actual filter
- delta_w=2*pi/1000;
- Ap=-(min(db(1:1:Wp/delta_w+1))) %Actual passband ripple
- As=-round(max(db(Ws/delta_w+1:1:501))) %Actual stop band ripple
- subplot(221)
- stem(n,hd) %Matchstick figure
- title('Ideal unit impulse response: hd(n)')
- subplot(222)
- stem(n,w_ham)
- title('Hamming window: w(n)')
- subplot(223)
- stem(n,h)
- title('Actual unit impulse response: h(n)')
- subplot(224)
- plot(w/pi,db)
- title('Amplitude response: (dB)')
- axis([0,1,-100,10])
- %2 Custom functions used by this program
- % One is the "freqz_m4.m"
- % Another is the "ideal_lp.m"

我在这用了两个自定义函数,所以大家还需要新建两个.m文件,一个是“freqz_m4.m”文件名与函数名需要保持一致。
- function[db,mag,pha,w]=freqz_m4(b,a)
- [H,w]=freqz(b,a,1000,'whole');
- H=(H(1:1:501));
- w=(w(1:1:501));
- mag=abs(H);
- db=20*log10((mag+eps)/max(mag));
- pha=angle(H);
- end
另一个是“ideal_lp.m”
- function hd=ideal_lp(Wc,N)
- alpha= (N-1)/2;
- n=0:1:N-1;
- m=n-alpha+eps;
- hd=sin (Wc*m)./(pi*m);
- end
注意要把这三个文件保存在一个英文命名的文件夹中,不然MATLAB可能会出现.m文件打不开,或者找不到路径的问题。这个问题可参考(https://blog.csdn.net/Smile_h_ahaha/article/details/92477206)进行修正。代码是没问题的。
然后生成了以下图像:

第二个,我们设计个使用汉宁窗的高通滤波器,设计参数是:Wp=0.6 π,Ws=0.4 π,,Ap=0.25dB,As=40dB
- %%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Write by Han %%%%%%%%%这是实时脚本文件%%%%%%%%%%%%
- Wp=0.6*pi; Ws=0.4*pi;
- tr_width=Wp-Ws; %Transition zone width
- N=ceil (6.2*pi/tr_width) +1 %Filter length
- n=0:1:N-1;
- Wc= (Ws+Wp) /2; %The cut-off frequency of the ideal high-pass filter
- hd=ideal_hp2(Wc,N); %Unit impulse response of an ideal high-pass filter
- w_han=0.5*(1-cos(2*pi/14*n)); % Writing Hanning window
- h=hd.*w_han; %Truncated to the actual unit impulse response
- [db,mag,pha,w]=freqz_m4 (h,[1]); %Calculate the amplitude response of the actual filter
- delta_w=2*pi/1000;
- Ap=-(min(db(Wp/delta_w+1:1:500))) %Actual passband ripple
- As=-round(max(db(1:1:Wp/delta_w+1))) %Actual stop band ripple
- subplot(221)
- stem(n,hd) %Matchstick figure
- title('Ideal unit impulse response: hd(n)')
- subplot(222)
- stem(n,w_han)
- title('Hanning: w(n)')
- subplot(223)
- stem(n,h)
- title('Actual unit impulse response: h(n)')
- subplot(224)
- plot(w/pi,db)
- title('FIR digital high-pass filter amplitude response: (dB)')
- axis([0,1,-100,10])

这也用到两个自定义函数,
- %%%%%%%%%%%%% ideal_hp2.m %%%%%%%%%%%%%
- function hd=ideal_hp2(Wc,N)
- alpha= (N-1)/2;
- n=0:1:N-1;
- m=n-alpha+eps;
- hd=(sin (pi*m)-sin(Wc*m))./(pi*m);
- %%%%%%%%%%%请再新建一个.m文件放以下部分%%%%%
- function[db,mag,pha,w]=freqz_m4(b,a)
- [H,w]=freqz(b,a,1000,'whole');
- H=(H(1:1:501));
- w=(w(1:1:501));
- mag=abs(H);
- db=20*log10((mag+eps)/max(mag));
- pha=angle(H);
- end

第三个,我们用汉宁窗设计一个bandstop(带阻) FIR滤波器,设计参数是:
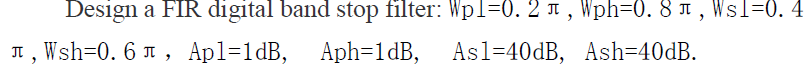
- %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Write by Han %%%%%%%%%%这是实时脚本文件%%%%%%%%%%%%
- Wpl=0.2*pi; Wph=0.8*pi; Wsl=0.4*pi; Wsh=0.6*pi;
- tr_width=min((Wsl-Wpl),(Wph-Wsh));
- N=ceil (6.2*pi/tr_width)
- n=0:1:N-1;
- Wcl= (Wsl+Wpl) /2; %Lower cutoff frequency of ideal band stop filter
- Wch= (Wsh+Wph) /2; %Upper cutoff frequency of ideal band stop filter
- hd=ideal_bs(Wcl,Wch,N); %Unit impulse response of an ideal band stop filter
- w_hann= 0.5*(1-cos(2*pi/14*n)); %Hanning window
- h=hd.*w_hann; %Truncated to the actual unit impulse response
- [db,mag,pha,w]=freqz_m4 (h,[1]); %Calculate the amplitude response of the actual filter
- delta_w=2*pi/1000;
- Ap=-(min(db(1:1:Wpl/delta_w+1))) %Actual passband ripple
- As=-round(max(db(Wsl/delta_w+1:1:Wsh/delta_w+1))) %Actual stop band ripple
- subplot(221)
- stem(n,hd) %Matchstick figure
- title('Ideal: hd(n)')
- subplot(222)
- stem(n,w_hann)
- title('hanning w(n)')
- subplot(223)
- stem(n,h)
- title('Real h(n)')
- subplot(224)
- plot(w/pi,db)
- title('FIRHanning window digital band rejection filter amplitude response(dB)')
- axis([0,1,-100,10])
- %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% ideal_bs.m %%%%%%%%新建一个.m文件%%%%%%%%%%%%
-
- function hd=ideal_bs(Wcl,Wch,N)
- alpha= (N-1) /2; n=0:1:N-1;
- m=n-alpha+eps;
- hd=(sin (Wcl*m) + sin(pi*m)-sin(Wch*m) ) ./(pi*m);
- end
- %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%freqz_m4.m%%%%%%新建一个.m文件%%%%%%%%%%%
- function[db,mag,pha,w]=freqz_m4(b,a)
- [H,w]=freqz(b,a,1000,'whole');
- H=(H(1:1:501));
- w=(w(1:1:501));
- mag=abs(H);
- db=20*log10((mag+eps)/max(mag));
- pha=angle(H);
- end


其他的大家能参悟到这,其他的估计也就触类旁通了吧,学海无涯,兴趣作舟,祝大家好运!


