- 1添加作者_投稿后,你要临时加“作者”?别逗了……
- 2利用LSTM+CNN+glove词向量预训练模型进行微博评论情感分析(二分类)_glove lstm 情感分类
- 3鸿蒙Harmony应用开发—ArkTS声明式开发(容器组件:Grid)_arkts grid
- 4安装pyrender和OSMesa(非常详细)从零基础入门到精通,看完这一篇就够了
- 5国内外各ChatGPT类语言大模型API价格汇总, 对比,ChatGPT/Gmini/PaLM/Clude/Ernie/ChatGLM/千问/混元/星火/Minimax/百川
- 6three-sum(3个数的和)_three sum
- 7神经网络:GRU基础学习
- 8NLP自然语言处理的基本语言任务介绍_nlp基础任务
- 9前端学习笔记____基础篇HTML&CSS_前端学习时,一个盒子上边时ul加li,下边是img,为社么给ul加padding-bottom没有效
- 10Pygame —— 一个好玩的游戏 Python 库_pygame库
Keras中那些学习率衰减策略_keras学习率策略
赞
踩
神经网路的训练绕不开的调参,调参中学习率至为重要。下面聊聊Keras中提供的学习率策略。
从optimizer的SGD说起
最常见的就是SGD和Adam。这里以SGD为例,看看在模型训练过程中,学习率是如何改变的。
参考官方文档,SGD的定义如下:
tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(
learning_rate=0.01, momentum=0.0, nesterov=False, name='SGD', **kwargs
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
梯度下降算法中,一般情况下权重
θ
t
\theta_{t}
θt的更新方法如下式,其中
g
t
g_{t}
gt表示求得的梯度。
θ
t
=
θ
t
−
1
−
l
e
a
r
n
i
n
g
_
r
a
t
e
∗
g
t
\theta_{t}=\theta_{t-1}- learning\_rate * g_{t}
θt=θt−1−learning_rate∗gt
当考虑momentum优化方法时,更新方式变为如下:
v
t
=
m
o
m
e
n
t
u
m
∗
v
t
−
1
−
l
e
a
r
n
i
n
g
r
a
t
e
∗
g
t
v_{t}= momentum * v_{t-1}- learning rate * g_{t}
vt=momentum∗vt−1−learningrate∗gt
θ
t
=
θ
t
−
1
+
v
t
\theta_{t}=\theta_{t-1}+v_{t}
θt=θt−1+vt
(1)自定义 time-Based Learning Rate Schedule(基于时间的学习率计划)
具体计算如下:
LearningRate = LearningRate * 1/(1 + decay * epoch)
- 1
在上述的SGD定义中,**kwargs中有decay这个参数,默认值为0时,学习率不会衰减。
当初始learning_rate=0.1,decay=0.001时,
Epoch Learning Rate
1 0.1
2 0.0999000999
3 0.0997006985
4 0.09940249103
5 0.09900646517
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
from tf.keras.optimizers import SGD
#...
# Compile model
epochs = 50
learning_rate = 0.1
decay_rate = learning_rate / epochs
momentum = 0.8
sgd = SGD(lr=learning_rate, momentum=momentum, decay=decay_rate, nesterov=False)
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=sgd, metrics=['accuracy'])
# Fit the model
model.fit(X, Y, validation_split=0.33, epochs=epochs, batch_size=28, verbose=2)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
(2) 四种Keras提供的学习率衰减策略
四种衰减策略分别是ExponentialDecay(指数衰减), PiecewiseConstantDecay(分段常数衰减) , PolynomialDecay(多项式衰减)
InverseTimeDecay(逆时间衰减)。
直接使用方法:
假如当拟合Keras模型时,每100000步衰减一次,基数为0.96
lr_schedule = keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay(
initial_learning_rate=1e-2,
decay_steps=10000,
decay_rate=0.96)
optimizer = keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=lr_schedule)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
a.指数衰减
定义:
tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.ExponentialDecay(
initial_learning_rate, decay_steps, decay_rate, staircase=False, name=None
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
具体的计算实现:
def decayed_learning_rate(step):
return initial_learning_rate * decay_rate ^ (step / decay_steps)
- 1
- 2
由此我们可以知道,随着训练step的增加,学习率不断地被更新。
这里的一个step指的是一个batch。
b.分段常数衰减
例如:对于前100001步,学习率为1.0,对于接下来的10000步,学习率为0.5,对于任何其他步骤,学习率为0.1
step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
boundaries = [100000, 110000]
values = [1.0, 0.5, 0.1]
learning_rate_fn = keras.optimizers.schedules.PiecewiseConstantDecay(
boundaries, values)
# Later, whenever we perform an optimization step, we pass in the step.
learning_rate = learning_rate_fn(step)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
c.多项式衰减
给定一个初始学习率和一个结束学习率,优化过程中使用指定多项式形式从初始学习率降到一个结束学习率,比如用2次、3次多项式。
计算过程如下:
def decayed_learning_rate(step):
step = min(step, decay_steps)
return ((initial_learning_rate - end_learning_rate) *
(1 - step / decay_steps) ^ (power)
) + end_learning_rate
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
比如:拟合一个模型,在10000步中从0.1衰减到0.01,使用开根式( power=0.5):
starter_learning_rate = 0.1
end_learning_rate = 0.01
decay_steps = 10000
learning_rate_fn = tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.PolynomialDecay(
starter_learning_rate,
decay_steps,
end_learning_rate,
power=0.5)
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(
learning_rate=learning_rate_fn),
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(data, labels, epochs=5)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
d.逆时间衰减
def decayed_learning_rate(step):
return initial_learning_rate / (1 + decay_rate * step / decay_step)
- 1
- 2
以0.5衰减率,decay_step=1拟合模型:
initial_learning_rate = 0.1
decay_steps = 1.0
decay_rate = 0.5
learning_rate_fn = keras.optimizers.schedules.InverseTimeDecay(
initial_learning_rate, decay_steps, decay_rate)
model.compile(optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(
learning_rate=learning_rate_fn),
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
2. 使用callbacks来实现动态、自定义学习率衰减策略
由于optimizer无法访问 validation metrics,因此使用这些调度对象无法实现动态学习率调度(例如,在验证集中loss不再改善时降低学习率)。然而,callbacks可以访问所有指标,包括 validation metrics。因此,您可以通过使用一个callback来修改优化器上的当前学习率来实现动态修改学习率。实际上,这甚至是内置的ReduceLROnPlateau回调。
当我们使用calllback定义的学习率衰减策略时,optimizer中的学习率衰减策略就会被忽视。
(1)自定义 time-Based Learning Rate Schedule
tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(
schedule, verbose=0
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
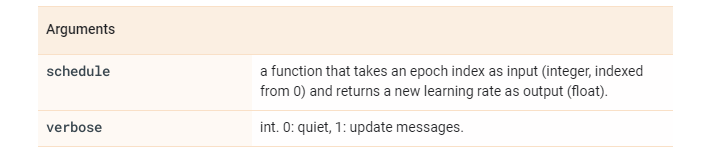
例如:前10个epochs学习率保持不变,后面学习率呈指数衰减
# This function keeps the learning rate at 0.001 for the first ten epochs
# and decreases it exponentially after that.
def scheduler(epoch):
if epoch < 10:
return 0.001
else:
return 0.001 * tf.math.exp(0.1 * (10 - epoch))
callback = tf.keras.callbacks.LearningRateScheduler(scheduler)
model.fit(data, labels, epochs=100, callbacks=[callback],
validation_data=(val_data, val_labels))
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
(2)Drop-Based Learning Rate Schedule
LearningRateScheduler的callback允许我们定义一个函数来调用epoch number 作为参数并返回随机梯度下降中使用的学习速率。可以定义一个半衰减的学习策略,如下计算公式,DropRate=0.5, floor(Epoch / EpochDrop)计算什么时候更新学习率,当EpochDrop=10时表示每经过10epochs,学习率变为原来的一半。
LearningRate = InitialLearningRate * DropRate^floor(Epoch / EpochDrop)
- 1
具体实现和使用:
# Drop-Based Learning Rate Decay import math from tf.keras.optimizers import SGD from tf.keras.callbacks import LearningRateScheduler # learning rate schedule def step_decay(epoch): initial_lrate = 0.1 drop = 0.5 epochs_drop = 10.0 lrate = initial_lrate * math.pow(drop, math.floor((1+epoch)/epochs_drop)) return lrate # ... # Compile model sgd = SGD(lr=0.0, momentum=0.9) model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=sgd, metrics=['accuracy']) # learning schedule callback lrate = LearningRateScheduler(step_decay) callbacks_list = [lrate] # Fit the model model.fit(X, Y, validation_split=0.33, epochs=50, batch_size=28, callbacks=callbacks_list, verbose=2)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
(3)使用ReduceLROnPlateau动态修改学习率
当验证集上的loss几乎不在改变时,修改学习率为原来的2-10倍通常能获得更好的结果。使用ReduceLROnPlateau就能做到。
其定义如下:
tf.keras.callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='val_loss', factor=0.1, patience=10, verbose=0, mode='auto',
min_delta=0.0001, cooldown=0, min_lr=0, **kwargs
)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
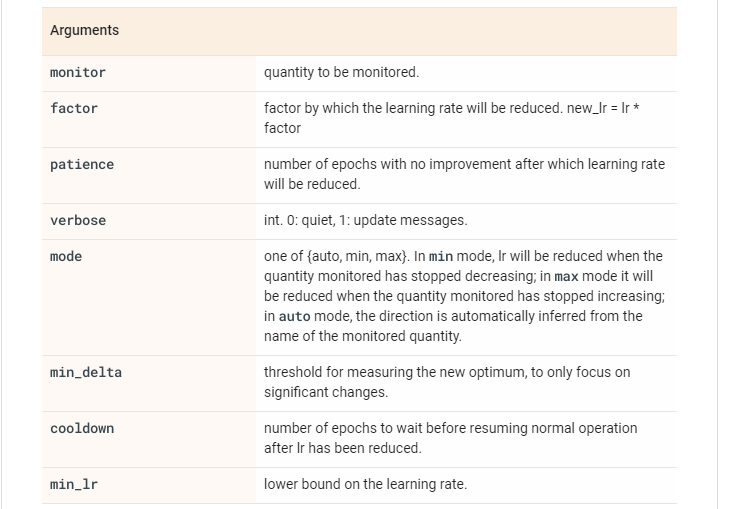
例如当训练集连续5个epochs的改变小于min_delta(默认为0.0001)时,修改学习率为原来的五分之一(new_lr = lr * factor)。
reduce_lr = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.2,
patience=5, min_lr=0.001)
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, callbacks=[reduce_lr])
- 1
- 2
- 3
Using Learning Rate Schedules for Deep Learning Models in Python with Keras
Keras官方文档



