- 1pyhanlp 停用词与用户自定义词典
- 2python错题集(1)_在python中,以下语句错误的是()。出+b=b. b=ac. b/=b+1ib+=1
- 3一文读懂:MongoDB Atlas怎样在AWS和Google Cloud上进行私有端点配置?
- 4共享库报错“error while loading shared libraries: lib**.so.**”_error while loading shared libraries: libcjson.so.
- 5特征值和特征向量及其在机器学习中的应用
- 6假期练习——两个整数的几种运算_本题目要求读入2个整数a和b和+,-,* 中的一个符号,计算加减乘的值。输入格式:
- 7【matlab】matlab随机函数
- 8qml中ListModel使用方法
- 9miniUI改变行的背景色,设置行的颜色_addrowcls
- 10matlab快速入门(25):匿名函数+主函数子函数_matlab主函数和子函数的位置
长短期记忆网络LSTM识别验证码、车牌识别
赞
踩
长短期记忆网络LSTM、验证码识别、车牌识别
关于LSTM的介绍和认识,可以参考这篇文章
长短期记忆网络LSTM:https://blog.csdn.net/eagleuniversityeye/article/details/91345671
数据处理:
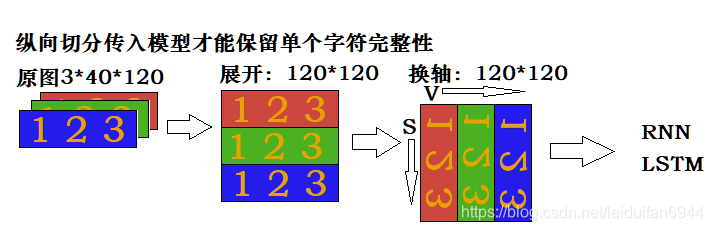
…entry原图 ———————— reshape展开 —————— permute换轴 ———————— 输入LSTM

当我们传入车牌时,会将车牌展开为 C H W 形状,然后转为(C*H) W 形状,如下图一样,依次将1、2、3、4……传入RNN模型进行识别,RNN的特点就是可以保留输入的序列信息,所以当第3次输入以后,模型输出的就是包含“川”字的信息,当第5次输入以后,模型输出会包含“川A”的信息,以此类推。但是普通RNN有个致命的缺点:只能解决短期依赖,就是如果序列过长,很难保留下靠前的输入。因此,一个变种的RNN——LSTM解决了这个问题,他在RNN里面加入3个门来决定对前面的信息应该保留和丢弃哪些信息,所以这里我们也是选用的LSTM网络模型。

从上图我们可以看出,只有1列1列的信息组合起来,才能在几次输入以后得到某个字符的完整信息(比如1、2、3次输入以后可以得到川字的完整信息),如果1行1行输入,很难保留单个字符的完整信息,而要将数据1列1列的切出来传入模型,又会有点麻烦,所以我们在将上图做一次变换,做permute换轴操作,得到如下图的形状。

现在将图片一行一行循环索引,就能很好的得到单个字符的信息了。
一、LSTM识别验证码——一个模型
使用LSTM结合Seq2Seq结构实现验证码识别
验证码样式如下图:

代码生成42000张验证码(train:40000, test:2000),验证码有清晰的,有低度模糊的,也有中度模糊的,位置也随机。
验证码和标签采用DataLoader加载,标签采用4*10的one-hot编码,网络输出每个图片也是4*10,训练20轮即达到了正确率100%,效果不错。
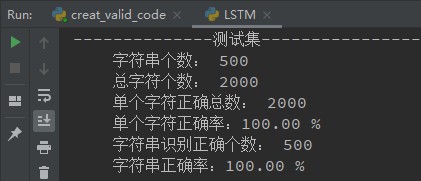
下面是模型部分代码,其他部分的代码就不贴了,损失函数MSELoss,优化器Adam。
import torch from torch import nn class Lstm(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.fc1 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(180, 128), nn.BatchNorm1d(128), nn.LeakyReLU(), ) self.lstm1 = nn.LSTM(128, 256, 2, batch_first=True) self.lstm2 = nn.LSTM(256, 128, 2, batch_first=True) self.fc2 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(128, 10), ) def forward(self, entry): # N C H W N * 3 * 60 * 120 entry = entry.reshape(-1, 3*60, 120) # N V S N * 180 * 120 entry = entry.permute(0, 2, 1) # N S V N * 120 * 180 entry = entry.reshape(-1, 180) # N V 120N * 180 fc1_out = self.fc1(entry) # N V 120N * 128 fc1_out = fc1_out.reshape(-1, 120, 128) # N S V N * 120 * 128 lstm1_out, _ = self.lstm1(fc1_out) # N S V N * 120 * 256网络会输出S次 lstm1_out = lstm1_out[:, -1, :] # N V N * 256只保留最后一次输出 lstm1_out = lstm1_out.reshape(-1, 1, 256) # N 1 V N * 1 * 256 # 下行代码:N 4 V 广播为N * 4 * 256,后面对每个256提取特征输出做损失,后面的优化使得每个V保留一个字符的特征 lstm1_out = lstm1_out.expand(lstm1_out.shape[0], 4, 256) lstm2_out, _ = self.lstm2(lstm1_out) # N 4 V N * 4 * 128 lstm2_out = lstm2_out.reshape(-1, 128) # 4N, V 4N * 128 fc2_out = self.fc2(lstm2_out) # 4N, V 4N * 10 fc2_out = fc2_out.reshape(-1, 4, 10) # N S V N * 4 * 10 return fc2_out
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
二、编码器和解码器分离
import torch from torch import nn class Encoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.fc = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(180, 128), nn.BatchNorm1d(128), nn.LeakyReLU(), ) self.lstm = nn.LSTM(128, 256, 2, batch_first=True) # V h num_layer def forward(self, x): # N C H W N 3 60 120 x = x.reshape(-1, 180, 120) # N V S N 180 120 x = x.permute(0, 2, 1) # N S V N 120 180 x = x.reshape(-1, 180) # N V 120N 180 fc_out = self.fc(x) # N V 120N 128 fc_out = fc_out.reshape(-1, 120, 128) # N S V N 120 128 lstm_out, _ = self.lstm(fc_out) # N S V N 120 256 lstm_out = lstm_out[:, -1, :] # N V N 256 lstm_out = lstm_out.reshape(-1, 1, 256) # N 1 V N 1 256 lstm_out = lstm_out.expand(lstm_out.shape[0], 4, 256) # N 4 256 return lstm_out class Decoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.lstm = nn.LSTM(256, 128, 2, batch_first=True) self.fc = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(128, 10), ) def forward(self, x): lstm_out, _ = self.lstm(x) # N S V N 4 128 lstm_out = lstm_out.reshape(-1, 128) # N V 4N 128 fc_out = self.fc(lstm_out) # N V 4N 10 fc_out = fc_out.reshape(-1, 4, 10) # N S V N 4 10 return fc_out class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.encoder = Encoder() self.decoder = Decoder() def forward(self, x): encoder = self.encoder(x) decoder = self.decoder(encoder) return decoder # 直接实例化Net()即可,优化也是直接优化Net()的权重即可 # self.net = Net().to(self.device) # self.opt = torch.optim.Adam(self.net.parameters())
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
可以修改LSTM参数以改变模型识别率,代价是计算量的增减。
三、车牌识别
车牌识别的原理和验证码识别相似,不过车牌识别最后将第一个汉字和后面6个字符分开输出单独做损失(当然也可以一起输出做损失),汉字为29个省及直辖市简称,相当于做29分类,字符为24个字母(车牌中没有字母I、O)+10个数字,相当于后6个字符做34分类

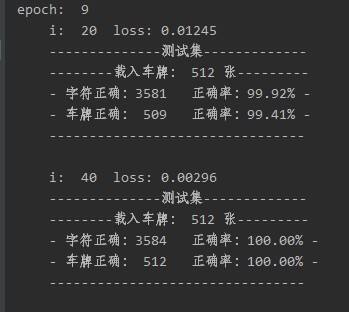
3.1训练效果
17万张车牌数据集进行训练,训练了8个epoch,第9个epoch在与训练集无重复的验证集上就达到了100%正确的精度。
(车牌是标准尺度、标准角度、标准光线,是用代码生成的数据集)如下所示

损失图(每个epoch保存17个数据,11个epoch得到的损失和正确率曲线图),蓝色:损失;橙色:当个字符识别正确率;绿色:车牌上7个字符都识别正确率

3.2 模型
输入为N C H W (N * 3 * 40 * 150)
输出为N V 和 N S V(N * 29, N * 6 * 34)
29为汉字29分类,6*34为6个(字符+数字34分类)
class Lstm(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.fc1 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(120, 256), nn.BatchNorm1d(256), nn.LeakyReLU(), ) self.lstm1 = nn.LSTM(256, 512, 2, batch_first=True) self.lstm2 = nn.LSTM(512, 256, 2, batch_first=True) self.fc_pai1 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(256, 29) ) self.fc_pai6 = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(256, 34) ) def forward(self, entry): # N C H W N * 3 * 40 * 150 entry = entry.reshape(-1, 3*40, 150) # N V S N * 120 * 150 entry = entry.permute(0, 2, 1) # N S V N * 150 * 120 entry = entry.reshape(-1, 120) # N V 150N * 120 fc1_out = self.fc1(entry) # N V 150N * 256 fc1_out = fc1_out.reshape(-1, 150, 256) # N S V N * 150 * 256 lstm1_out, _ = self.lstm1(fc1_out) # N S V N * 150 * 512网络会输出S次 lstm1_out = lstm1_out[:, -1, :] # N V N * 512只保留最后一次输出 lstm1_out = lstm1_out.reshape(-1, 1, 512) # N 1 V N * 1 * 512 # 下行代码:N 7 V 广播为N * 7 * 512,后面对每个256提取特征输出做损失,后面的优化使得每个 # V保留一个字符的特征 lstm1_out = lstm1_out.expand(lstm1_out.shape[0], 7, 512) lstm2_out, _ = self.lstm2(lstm1_out) # N 7 V N * 7 * 256 pai1 = lstm2_out[:, 0, :] # 切出第一位,汉字 pai6 = lstm2_out[:, 1:, :] # 切出后6位字符 pai1_out = self.fc_pai1(pai1) # N, V N * 29 pai6 = pai6.reshape(-1, 256) # 6N, V 6N * 256 pai6_out = self.fc_pai6(pai6) # 6N, V 6N * 34 pai6_out = pai6_out.reshape(-1, 6, 34) # N S V N * 6 * 34 return pai1_out, pai6_out
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
print('The End !')
- 1



